Biological Membranes
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What are the roles of cell membranes?
partially permeable barriers
isolates cell contents from external environment
form vesicles
site for attachment (of enzymes)
regulating the transport of materials into or out the cell
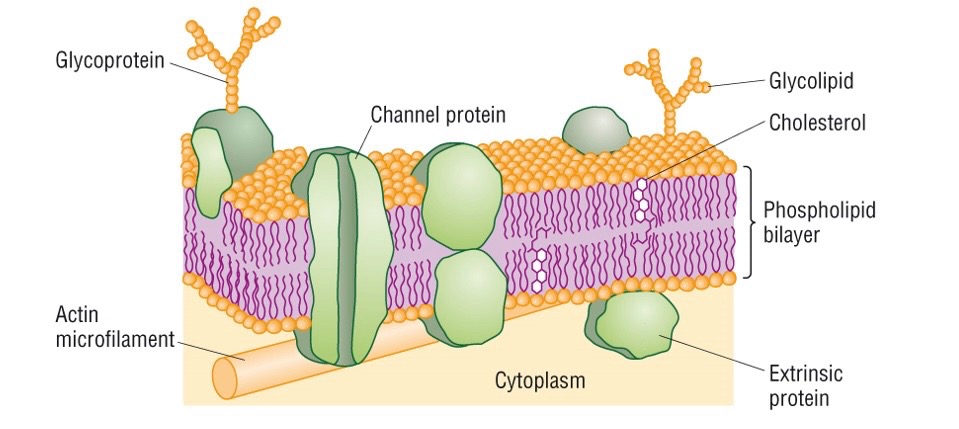
What is the structure of plasma membrane? (7-10nm)
formed of a bilayer of phospholipids with hydrophillic heads facing out the bilayer and hydrophobic tails facing into the bilayer
contains different types of proteins within
has cholestrol which regulates fluidity in the membrane
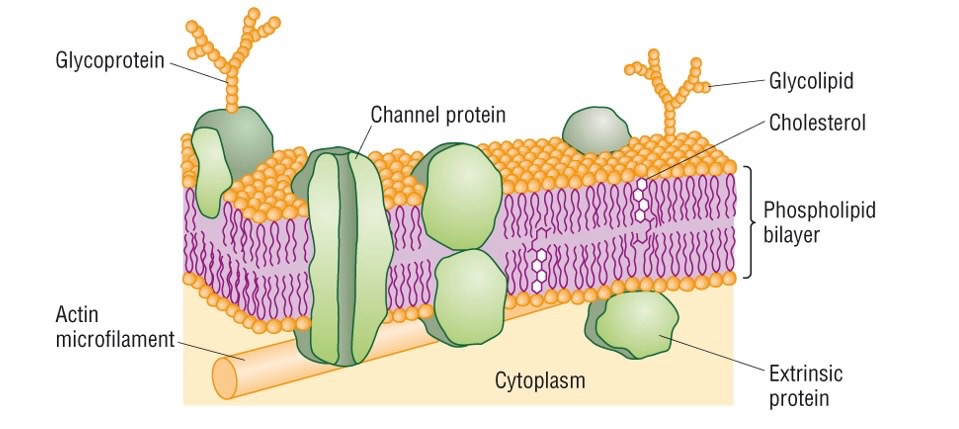
What is the fluid mosaic model?
fluid: phospholipids in bilayer can move freely within the membrane
mosaic: different proteins scattered randomly in the bilayer (patchwork effect)
What is permeable through the plasma membrane?
non-polar molecules diffuse rapidly across bilayer if theyre small enough eg O2
lipid soluble molecules
large charged polar molecules hardly permeate the bilayer eg glucose, NaCl

Explain why phospholipids form a bilayer in the membranes (3)
has a polar phosphate head which is hydrophillic and faces the aqueous solutions
has non-polar fatty acid tails which are hydrophobic and face away from the aqueous environment
creates a barrier between the aqueous environment and the cell
What are the functions of glycoproteins
act as antigens for cell recognition
act as receptor sites; allowing hormones to bind
act as recognition sites
form H bonds with H2O to stabilise membrane structure
act as enzymes
form protein channels and carrier proteins

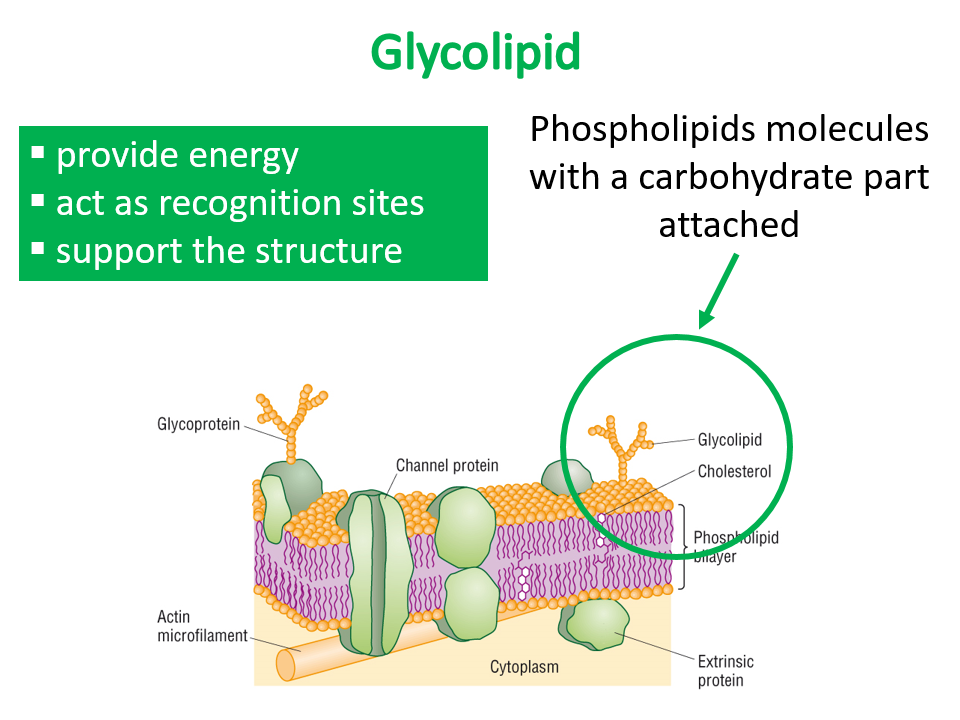
What are the functions of glycolipids
provide energy
support the structure
act as recognition sites
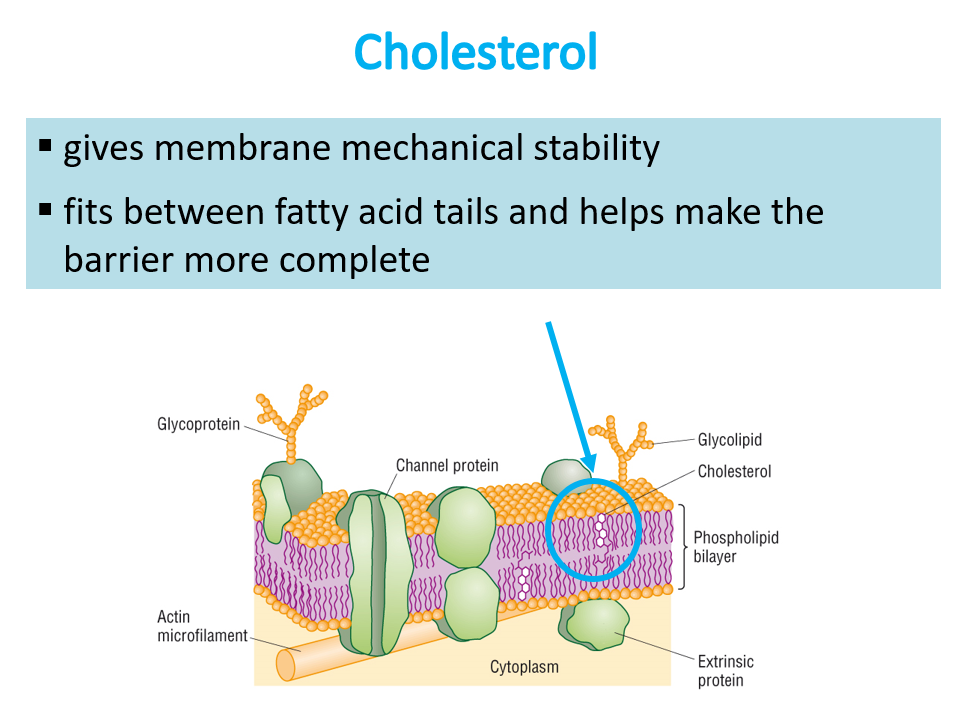
What are the functions of cholestrol
regulates fluidity
gives membrane mechanical stability
fits between fatty acid tails to help make the barrier more complete
What are the mechanisms of cell signalling
receptor acts as an ion channel
receptor activates a glycoprotein
receptor acts as an enzyme
What is cytokines (signal molecule)
small proteins; peptides; glycoproteins
secreted by specific cells of the immune system and glial cells
carry signals locally between cells + have an effect on other cells
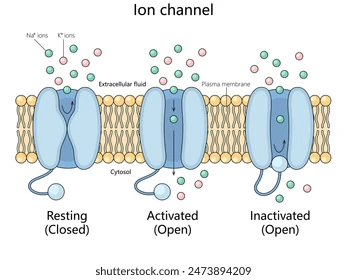
Explain the ion channel process
in the plasma membrane the G-protein is acting as an ion channel
the signal (may be ligand) attaches to the receptor - they are complementary / specific to each other
the channel opens and this allows the ions to enter the cell
this brings about a response
What is a ligand
a signal molecule which is specific and binds to a receptor
Explain how cell surface membrane contribute to cell signalling process (4)
signal molecule released by exocytosis
glycoproteins act as receptors
a signal molecule which is specific binds to a receptor, complimentary
this attachment causes a change on the cell surface
surface membrane allows entry of some signal molecules
What are the functions of channel proteins
form a hydrophillic channel through membrane which ions can pass through by diffusion (down conc gradient)
each channel formed by a protein will only allow a specific ion/molecule to pass through
channel can change shape
act as PORES
What are the functions of carrier proteins
shaped so that a specific molecule can fit onto them at membrane surface
when specific molecule fits, the protein changes shape to allow the molecule through the other side of the membrane
act as PUMPS
What are passive processes
simple diffusion
facilitated diffusion
osmosis
the purpose of diffusion is to reach an equilibrium
What happens to the membrane at higher temperatures
phospholipids have more KE so move more freely
proteins in membrane denatured
this causes gaps in the plasma membrane
membrane become more fluid as structure is damaged
What is the role of intrinsic proteins
span the entire membrane
involved in transport by acting as carriers or channels for ions
What is the role of extrinsic proteins
on the surface of the plasma membrane
involved in cell recognition, structural support by interacting with the cytoskeleton
What is cell signalling
the communication between cells
to trigger a response / cause a change in another cell
Define simple diffusion
the net movement of molecules from an area of high conc to low conc
where non-polar, small molecules pass directly through the phospholipid bilayer
eg O2 entering RBCs
Define facilitated diffusion
the net movement of molecules from an area of high conc to low conc
where large, polar molecules pass through the cell surface membrane with the aid of a channel/carrier protein
eg glucose, amino acids, Ca2+ entering nerve cell
How does a protein channel act in faciliited diffusion
ions and smaller molecules pass through
protein channel acts like a pore in the membrane
can often be opened and closed to change the flow
How does a carrier protein act in facilitated diffusion
larger molecules are transported and attach to the protein
protein changes shape to transfer the molecule across the membrane
What factors increase the rate of diffusion
higher concentration gradient
increased temperature (more KE)
greater SA
thinner membrane (short diffusion pathway)
What are the adaptations of alveoli to maximise gas exchange
thin membrane → short diffusion pathway
large surface area → increases rate of diffusion
large capillary network → good ventilation & maintains conc gradient
moist → gases like O2 dissolve in water before diffusing across membranes
Explain the differences + similarities between simple and facilitated diffusion
both passive processes
both move substances down the conc gradient (high-low)
simple diffusion transports small non-polar molecules eg O2 directly through the phospholipid bilayer
facilitated diffusion involves the use of channel/carrier protein to transport larger polar molecules eg glucose and ions across the surface membrane
Formula for rate of diffusion
SA X Concentration difference / distance
Define osmosis
The net movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from an area which is more dilute to an area that is less dilute (more concentrated)
What is water potential
the pressure exerted on water molecules as they collide with a membrane or container
measure of tendency of water molecules to diffuse from one place to another
What is the pattern between water potential and solution concentration
pure water: 0kPa
dilute solution: ~ -10kpa
concentrated solution: ~ -500 kPa
The more concentrated, the lower the water potential
Define iso ,hypo & hypertonic solutions
isotonic: a solution which has equal concentration to the cell
hypotonic: a solution which has lower concentration than the cell
hypertonic: a solution which has a higher concentration than the cell
What is the effect of a hypertonic solution on an animal cell
water potential is lower outside the cell, so water moves out of the cell
cell shrivels
CRENATION
What is the effect of an isotonic solution on animal & plant cells
water potential inside and outside the cell are equal
no net movement of water
equilibrium reached
What is the effect of a hypotonic solution on an animal cell
water potential is higher outside the cell, so water moves into the cell
cell bursts
LYSIS
What is the effect of a hypertonic solution on a plant cell
water potential is lower outside the cell, so water moves out the cell
cytoplasm pulls away from the cell wall
cell is PLASMOLYSED
What is the equation for water potential
water potential = solute potential + pressure potential
Define active transport
movement of molecules from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration which requires energy in the form of ATP
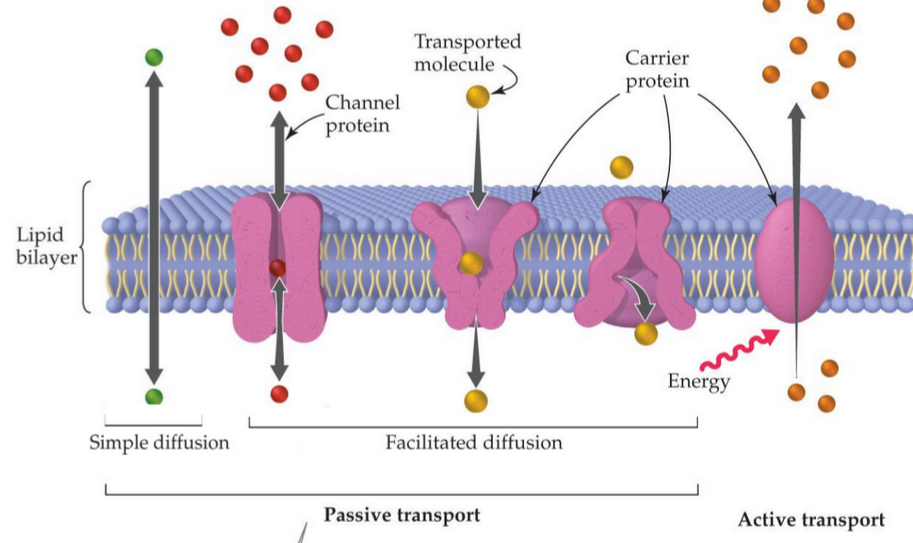
What is the active transport mechanism using carrier protein pumps
solute molecule is recognised by carrier protein and grabs it
protein rotates in the membrane and releases it inside the cell by using energy
protein rotates back again using energy
Why does active transport require energy in the form of ATP
ATP is hydrolysed into ADP and a phosphate
phosphate binds to the carrier protein which changes its shape
phosphate is released and original shape is restored
What are the functions of the protein pumps (carriers)
carries specific molecules one way across the membrane
uses energy in the form of ATP to carry molecules across membrane
carries molecules against conc gradient
carries molecules at a faster rate than by diffusion
What is exocytosis
when a substance is released from the plasma membrane
along microtubules
in a vesicle which fuses with plasma membrane
What is endocytosis
cells engulfing materials into the cell to allow larger molecules to enter (vesicle formed at membrane)
phagocytosis; cells engulf solid particles
pinocytosis: cells take in liquids & small molecules