Human Geography Exam 1 prep
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
What is human geography?
studies how humans interact with and shape the Earth's surface through culture, politics, economics, and population patterns.
What is physical geography?
Physical geography examines natural systems such as landforms, water, climate, and ecosystems, providing the environmental context for human activity.
What are the five themes of geography?
The five themes are location, place, region, movement, and human-environment interaction — frameworks used to analyze spatial patterns and human impact.
What is absolute vs. relative location?
Absolute location uses latitude and longitude to pinpoint exact positions, while relative location describes a place’s situation compared to other locations.
What is place in geography?
Place describes the human and physical characteristics that give a location meaning and identity, such as culture, architecture, or climate.
What is space in human geography?
Space refers to the abstract dimension in which objects, people, and processes exist and interact, emphasizing patterns and distributions.
What is scale in geography?
Scale refers to the level of analysis — local, regional, national, or global — showing how processes and patterns vary across levels.
What is distance decay?
the intensity of interaction between two places decreases as distance increases.
What is time-space compression?
Time-space compression refers to how technology and globalization reduce the perceived distance between places, speeding up interaction.
What is cultural landscape?
the visible imprint of human activity on the environment, including buildings, roads, agriculture, and monuments.
What is spatial diffusion?
Spatial diffusion is the process by which a feature, idea, or innovation spreads from its origin to other places over time.
What are the four types of diffusion?
Relocation (through movement), contagious (rapid person-to-person spread), hierarchical (through levels of power or cities), and stimulus (partial adoption and change)
What is GIS (Geographic Information Systems)?
GIS is a computer-based tool for capturing, analyzing, and visualizing spatial data to reveal patterns and relationships.
What is remote sensing?
collecting data about Earth’s surface from satellites or aircraft without direct contact, useful for mapping and monitoring change.
What is GPS?
GPS (Global Positioning System) uses satellites to determine precise locations anywhere on Earth.
What is population density?
Population density measures how many people live per unit of area, showing how population is distributed.
What is arithmetic density?
total population divided by total land area, providing a general measure of population pressure.
What is physiological density?
Physiological density compares population to arable (farmable) land, showing food-producing pressure.
What is agricultural density?
measures the number of farmers per unit of arable land, indicating agricultural efficiency.
What is natural increase rate (NIR)?
NIR is the percentage by which a population grows in a year, found by subtracting the death rate from the birth rate.
What is doubling time?
the number of years required for a population to double at its current growth rate.
What is total fertility rate (TFR)?
TFR is the average number of children a woman is expected to have during her lifetime.
What is infant mortality rate (IMR)?
IMR measures the number of deaths of infants under one year old per 1,000 live births.
What is life expectancy?
Life expectancy is the average number of years a newborn is expected to live under current conditions.
What is the dependency ratio?
compares dependents (young and old) to the working-age population, affecting economic pressure.
What is brain drain?
Brain drain is the emigration of highly skilled individuals from developing countries to wealthier nations.
What are remittances?
Remittances are money migrants send back to family in their home countries, often sustaining local economies
What is step migration?
Step migration involves movement in stages toward a final destination, such as village → town → city.
What is counterurbanization?
when people move from urban to rural areas, often for lifestyle or affordability reasons
What is a cultural hearth?
A cultural hearth is a geographic origin of cultural traits or innovations, such as Mesopotamia or the Nile Valley.
What is acculturation?
Acculturation occurs when cultures exchange traits while maintaining distinct identities.
What is assimilation?
happens when a minority group gradually adopts the customs of the dominant culture.
What is syncretism?
Syncretism is the blending of cultural or religious traits from different traditions into new forms.
What is cultural convergence?
Cultural convergence occurs when different cultures become more alike through globalization and communication.
What is cultural divergence?
Cultural divergence happens when cultural groups become increasingly distinct, often resisting outside influence.
What is the difference between universalizing and ethnic religions?
Universalizing religions (like Islam or Christianity) seek global appeal, while ethnic religions (like Hinduism) are tied to specific groups or regions.
What is political geography?
Political geography studies spatial organization of political processes, including boundaries, states, and power distribution.
What is a state vs. nation?
A state is a political entity with sovereignty; a nation is a group sharing cultural identity. A nation-state combines both.
What are supranational organizations?
These are entities where multiple countries cooperate for shared goals, like the EU or UN.
What are the types of political boundaries?
Boundaries can be geometric (lines), physical (rivers, mountains), cultural (language), or superimposed (colonial legacy)
What is centripetal vs. centrifugal force?
Centripetal forces unify a state (shared language), while centrifugal forces divide it (ethnic conflict).
What is counterurbanization?
Counterurbanization is the migration from cities back to rural areas, often for quality of life reasons.
What is the rank-size rule?
The rank-size rule states that the nth largest city is 1/n the size of the largest city, common in developed nations.
What is a primate city?
dominates a country’s economy and culture, being more than twice the size of the next largest city.
What is a megacity?
has over 10 million inhabitants
What are the indicators of development?
GDP per capita, literacy rates, life expectancy, and access to healthcare.
What is the Human Development Index (HDI)?
The HDI combines income, education, and life expectancy to measure a country’s overall development.
What is the dependency theory
Dependency theory argues that global inequality results from historical exploitation where core nations benefit from the periphery’s resources.
What is globalization’s economic impact?
Globalization increases trade and technology flow but can widen inequalities between and within nations.
What is sustainable development
meets present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet theirs.
What is environmental determinism vs. possibilism?
Environmental determinism claims environment shapes culture, while possibilism argues humans adapt and modify their surroundings creatively.
What is cultural ecology?
studies how human cultures adapt to and modify their environments for survival.
What is the gravity model in geography?
predicts spatial interaction based on population size and distance — larger and closer places interact more.
Who was Karl Marx and how did his ideas relate to population and development?
argued that poverty and hunger are results of unequal resource distribution under capitalism, not overpopulation. He believed that social change and fair resource sharing would eliminate scarcity.
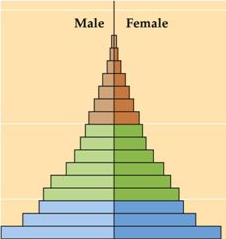
Rapid Population Growth
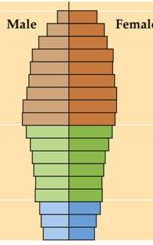
Negative growth
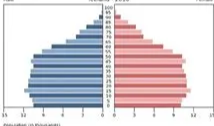
Slow growth
What is dependency ratio and why does it matter?
The dependency ratio measures the proportion of dependents (young and old) to the working-age population. High ratios strain economic productivity and social systems.
What is the epidemiologic transition?
It describes how disease patterns change with development: from infectious and communicable diseases dominating in early stages to chronic, degenerative diseases in advanced stages.
What is Alfred Weber’s “agglomeration” concept?
businesses clustering together to share resources, labor, and infrastructure. This concentration lowers costs and stimulates innovation.
Carrying Capacity
maximum population size an environment can sustain based on available resources. When exceeded, it leads to resource depletion and population decline.
What is spatial analysis in geography?
how and why phenomena are distributed in space. It helps geographers identify patterns, relationships, and causes of geographic variation.
What is spatial diffusion?
the process by which an innovation or idea spreads from one place to another. It can be contagious, hierarchical, or relocation-based.
What is distance decay?
the decline in interaction and influence between two places as distance increases. Modern technology reduces this effect.
What is a gravity model in geography?
The gravity model predicts interaction between places based on their size and distance. Larger and closer places have stronger connections, much like gravitational attraction.
What is the concept of “ecumene”?
portion of Earth’s surface permanently inhabited by humans. It expands as technology and agriculture improve.
What is agricultural density?
y measures the number of farmers per unit of arable land. Lower densities suggest higher agricultural efficiency.
What is a population doubling time?
the number of years it takes for a population to double in size, assuming a constant rate of growth. It’s inversely related to the rate of natural increase.
What is the rate of natural increase (RNI)?
measures population growth based only on births and deaths, excluding migration. It’s calculated by subtracting the crude death rate from the crude birth rate.
What is demographic momentum?
occurs when a population continues to grow despite declining fertility, due to a large base of young people entering reproductive age.
What is the fertility transition?
refers to the shift from high to low birth rates as societies industrialize, urbanize, and improve education and healthcare.
What is sustainability in population geography?
meeting present needs without compromising future generations’ ability to meet theirs. It involves balancing population, resources, and environmental health.
What is Modernization Theory?
all countries move through similar stages of economic growth, from traditional to industrial societies. It emphasizes internal change—like technology, education, and cultural modernization—as the key to development.
What is Dependency Theory?
underdevelopment results from unequal economic relationships between rich and poor nations. Peripheral countries are kept dependent on core nations through trade, investment, and resource extraction.
How does Wallerstein’s World-Systems Theory connect to Dependency Theory?
Both emphasize global inequality, but Wallerstein’s model divides the world into core, semi-periphery, and periphery states within a capitalist system. It shows how core nations exploit the periphery through economic dominance and labor control.
What is Structuralism in development studies?
Structuralism holds that global economic structures inherently favor developed nations. It calls for state intervention, diversification, and regional cooperation to reduce dependence on industrialized economies.
What is the difference between GDP and GNP?
GDP (Gross Domestic Product) measures all goods and services produced within a country, while GNP (Gross National Product) includes income earned by nationals abroad and excludes foreign income earned domestically.
What does the Human Development Index (HDI) measure?
Combined indicators of life expectancy, education, and income to assess overall human well-being. It offers a more holistic measure of development than GDP alone.
What is the Gini Coefficient used for?
measures income inequality within a country, ranging from 0 (perfect equality) to 1 (perfect inequality). A high Gini value indicates a wide gap between rich and poor.
What is the goal of sustainable development?
aims to balance economic growth with environmental protection and social equity. It ensures that progress today does not deplete the resources or opportunities of future generations.
Robinson map projection
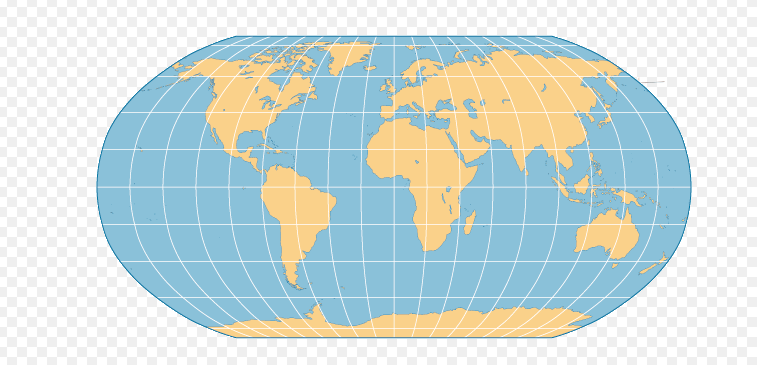
Mercator projection
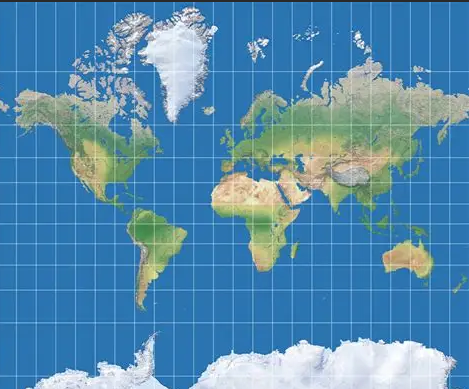
Gall Peters Projection
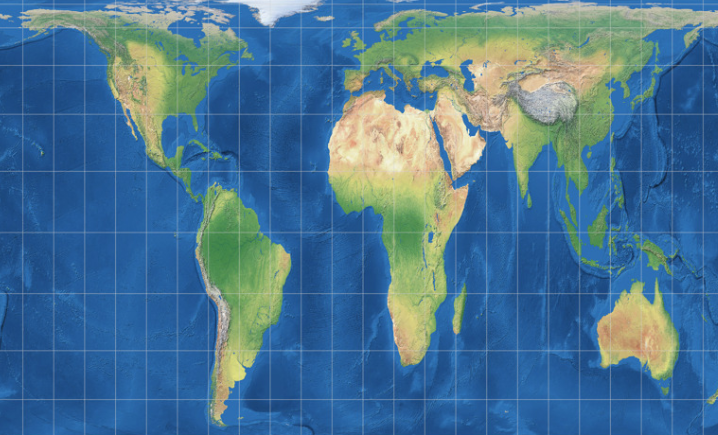
Goodes projeciton
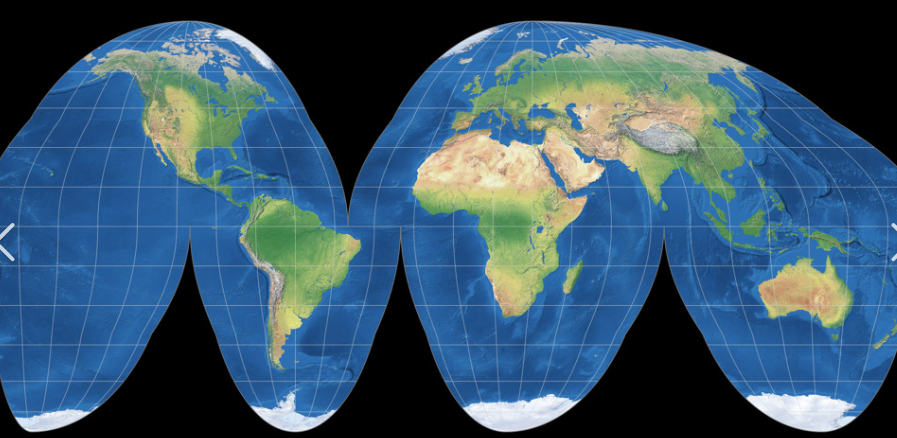
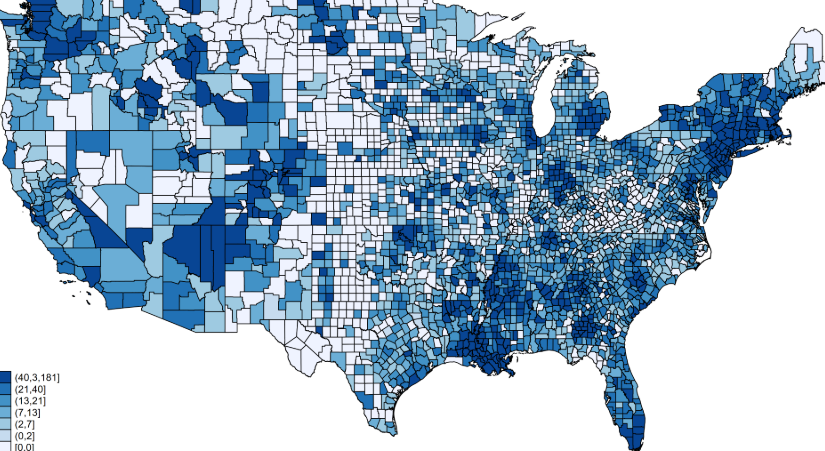
choropleth map
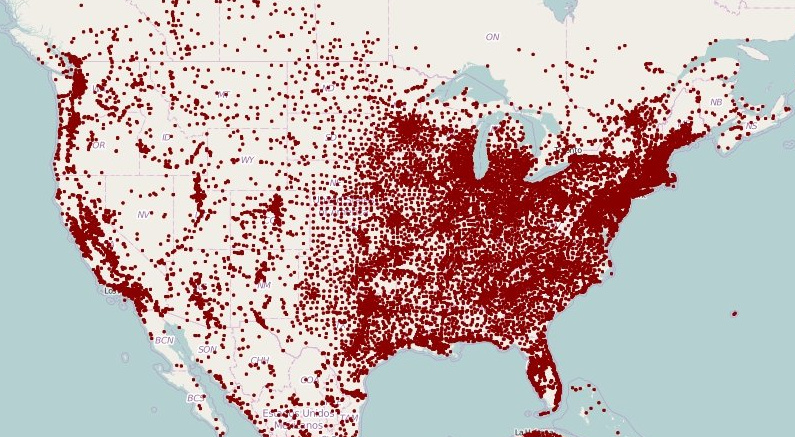
Dot density map
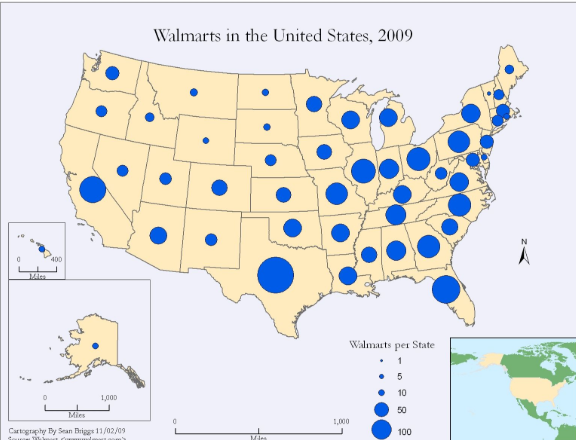
proportional symbol map
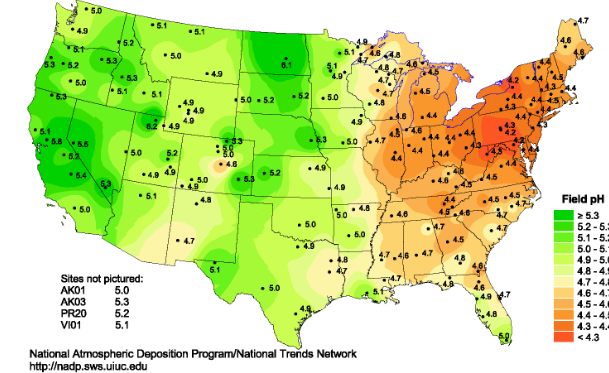
Isopleth
cartogram
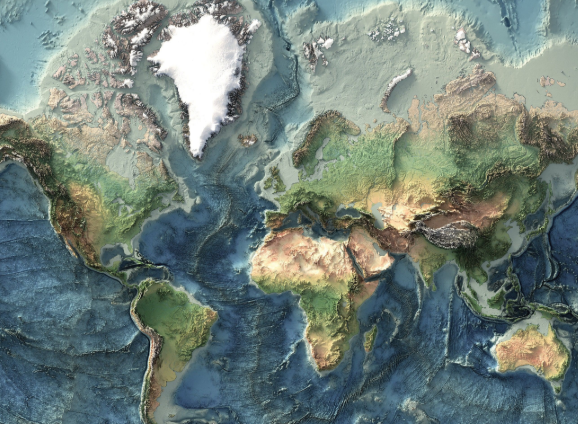
topographic map

flow map
Reference map