Electrode potentials
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is a half-cell?
contains the chemical species present in a redox half-equation
How can a volatile cell be made?
connecting together 2 different half cells, which then allows electrons to flow
What occurs at the negative electrode? Is it typically on the left or right?
oxidation
more reactive metal
left
What occurs at the positive electrode? Is it typically on the left or right?
reduction (+ve charge attracts electrons)
less reactive metal
right
How do you determine which half-cell will be the positive or negative pole?
the more positive Eo - positive pole
What does a vertical line represent? (metal/metal ion)
the phase boundary between the aqueous solution and the metal
e.g Zn2+(aq) | Zn(s)
What does a double vertical line represent?
junction between 2 solutions (the salt bridge)
e.g Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq) || Cu2+(aq) | Cu(s)
What does the equilibrium in a half-cell look like?
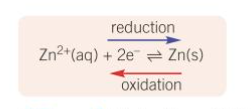
What does a metal/metal ion half-cell contain?
metal rod dipped into a solution of its aqueous metal ion
What does an ion/ion half-cell contain?
ions of the same element in different oxidation states
What is an example of an ion/ion half-cell?
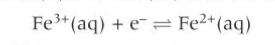
What is used to transport ions in an ion/ion half cell?
inert metal electrode made out of platinum
What is the standard electrode potential? (Eo)
the e.m.f. (of a half-cell) compared with / connected
to a (standard) hydrogen half-cell / (standard)
hydrogen electrode
Temperature of 298 K / 25°C
AND (solution) concentrations of 1 mol dm−3
AND pressure of 100kPa OR 105 Pa OR 1 bar
What are the standard conditions?
solution concentration of 1 mol dm-3
temperature of 298K
pressure of 100kPa
What does a standard hydrogen electrode look like?
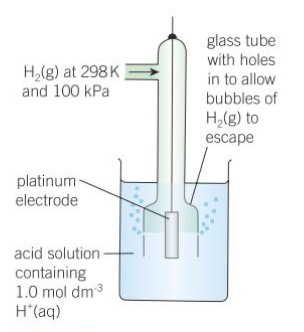
How do you measure a standard electrode potential?
half-cell is connected to a standard hydrogen electrode
electrodes are connected by a wire - allows flow of electrons
solutions connected with a salt bridge - allows flow of IONS
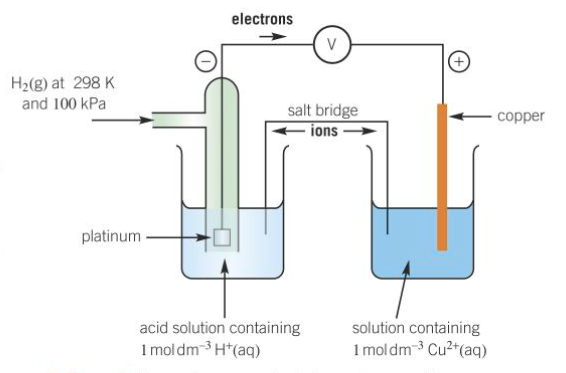
What is an example of a salt bridge?
filter paper soaked in KNO3 (aq)
What does it mean if there’s a more negative Eo value?
greater tendency to lose electrons - undergo oxidation
generally, the greater the reactivity of the metal
What does it mean if there’s a more positive Eo value?
the greater the tendency to gain electrons - undergo reduction
generally, greater reactivity of non-metal
The best oxidising agents have what kind of Eo value?
more positive - them themselves are reduced
The best reducing agents have what kind of Eo value?
more negative
they are oxidised themselves
How do you work out the standard cell potential?
Ecell = Eo(positive electrode) - Eo(negative electrode)
The more positive E value means the equilibrium is shifted where?
to the right
Reduction - Right
The less positive E value means the equilibrium is shifted to where?
the left
oxidation - left