biology final
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
A cell cycle checkpoint for S phase would likely inhibit progression through the cell cycle if _____.
there is DNA damage
The nucleus of an atom contains ____.
protons and neutrons
A cell cycle checkpoint at which phase would ensure sufficient nutrients for cell division were available?
G1 or G2
Which cell feature is absent in bacterial cells?
nucleus
Nuclear envelopes reform during _____.
telophase
Cell shape is reinforced by ____.
cytoskeletal filaments
Eukaryotic cells have their DNA enclosed in the _____.
nucleus
Which cellular component is common to all cells?
cytoplasm
The negative subatomic particle is the ____.
electron
The spindle apparatus appears during _____.
prophase
Chromosomes are unduplicated during which phase of cell cycle?
G1
An example of a biofilm is ____.
oral bacteria living on teeth
In which phase of mitosis do chromosomes arrive at opposite sides of the cell?
telophase
Abnormal cell division that does not pose a threat to surrounding tissues is termed _____.
benign
A parent cell with 12 chromosomes will produce daughter cells with _____ chromosomes by mitosis.
12
Chromosomes are aligned at the middle of the cell during _
metaphase
The positively charged ion, potassium, and the negatively charged ion, fluoride, will form what kind of bond?
ionic
Nucleotides are monomers of ____.
nucleic acids
Which of the following is the proper sequence for mitosis? I. metaphase II. telophase III. prophase IV. anaphase
III, I, IV, II
Which event occurs during interphase?
the cell doubles its cytoplasmic contents
Ribosomes are ____.
involved in protein synthesis
Which of the following treatment methods are not currently being utilized in cancer treatment?
immunotherapy
____ are long whip like cellular structures that act like propellers to move a cell through fluid environments.
flagella
_____ is the stage of the cell cycle during which a cell performs its normal metabolic processes.
G1
The organelle that pinches off portions of its membrane to form a vesicle used for storage or transport is the ____.
golgi body
The spread of cancer cells from one site to others in the body is known as _____.
metastasis
The positive subatomic particle is the ____.
proton
Which bond is weakest?
hydrogen
The bond in table salt (Na+Cl-) is ____.
ionic
Which of the following occurs in prophase?
the nuclear envelope breaks down
Blood pressure is lowest when ventricles are _____; this is known as _____.
fully relaxed; diastolic pressure
Large polymers are formed from smaller subunits by which type of reaction?
condensation
Diffusion of water from a hypertonic solution to a hypotonic solution across a semi-permeable membrane ____.
will occur until both solutions are isotonic
Breathing is under _____ control.
voluntary and involuntary
The driving force for blood circulation is ____.
contraction of the ventricles
The second law of thermodynamics states that ____.
energy disperses spontaneously
Fermentation reactions occur in the ____.
cytoplasm
ADH____.
increases water reabsorption
Osmosis is an example of ____.
passive transport
Substances that enter a reaction are termed __.
reactants
Our primary source of energy is obtained from ____.
carbohydrates
The primary role of bile salts during digestion is ____.
to coat fat droplets and separate them into small droplets
Pulmonary veins carry ____.
oxygen-rich blood back to the heart
The longest segment of the gut is the____.
small intestine
Wilting of a plant (shriveling of the cells) occurs ____.
if the plant is placed in a hypertonic solution
In alcoholic fermentation, the final product is ____.
ethanol
A(n) ____ is a protein monomer.
amino acid
Nucleotides are monomers of ____.
nucleic acids
The sodium–potassium pump is an example of ___.
active transport
What happens in an electron transport chain?
Electron movement transfers energy to enzymes that create ATP.
Over working the heart by having too much blood volume, making it more difficult to push blood forward in the system is which of the following conditions?
hypertension
The main enzyme produced in the saliva acts on ____.
carbohydrates
The ____ contain(s) oxygen-poor blood.
pulmonary arteries
An individual who does not produce bile has the most trouble digesting ____.
fats
The energy in chemical bonds is what type of energy?
potential
During inhalation, the diaphragm moves _____ and the intercostal muscles move the rib cage _____.
downward; outward
ATP contains ____.
phosphate
Cellular respiration that requires oxygen is called ____.
aerobic respiration
Energy is defined as ____.
the capacity to do work
The three main categories of energy-producing foods are ____.
fats, carbohydrates, and proteins
Meiosis in a diploid organism typically produces _____.
four haploid cells
An allele is ____ if its effect masks that of a ____ allele paired with it.
dominant; recessive
During a human pregnancy, implantation occurs at which stage?
blastocyst
Paired homologous chromosomes are found at the center of the cell during _____ of meiosis.
metaphase I
Frameshift mutations may involve _____.
the insertion of one to several base pairs
How many nucleotides comprise one codon?
3
DNA molecules contain protein-coding sequences called _____.
genes
Human female gametes form ____.
before birth
In the human male, sperm are produced in the ____.
seminiferous tubules
Which effect is not controlled by a hormone feedback pathway?
temperature induced sterility in males
When two alleles of the same gene are identical, the individual carrying those alleles is said to be ____.
homozygous
Which structure is responsible for keeping the fetus from slipping out of the uterus prematurely?
cervix
The first cell of a new individual is the ____.
zygote
Which membrane is referenced in the expression my water broke?amnion
amnionFertilization in humans occurs in the ____.
Fertilization in humans occurs in the ____.
oviductAn individual’s ____ determines its observable ____
An individual’s ____ determines its observable ____
genotype; phenotype17. FSH and LH regulate ____.
FSH and LH regulate ____.
the production of sex hormones and gametes
Observable traits are known in genetics as ____.
phenotypes
In meiosis, _____ are separated during anaphase I, and _____ are separated during anaphase II.
homologous chromosomes; sister chromatids
Which part of a cell's machinery reads the mRNA strand during translation?
ribosome
A gene that produces multiple effects is called a(n) ____
pleiotropic gene
What is an anticodon?
the region of the tRNA that base-pairs with the mRNA
What is the function of the prostate secretions?
to protect sperm from vaginal acidity
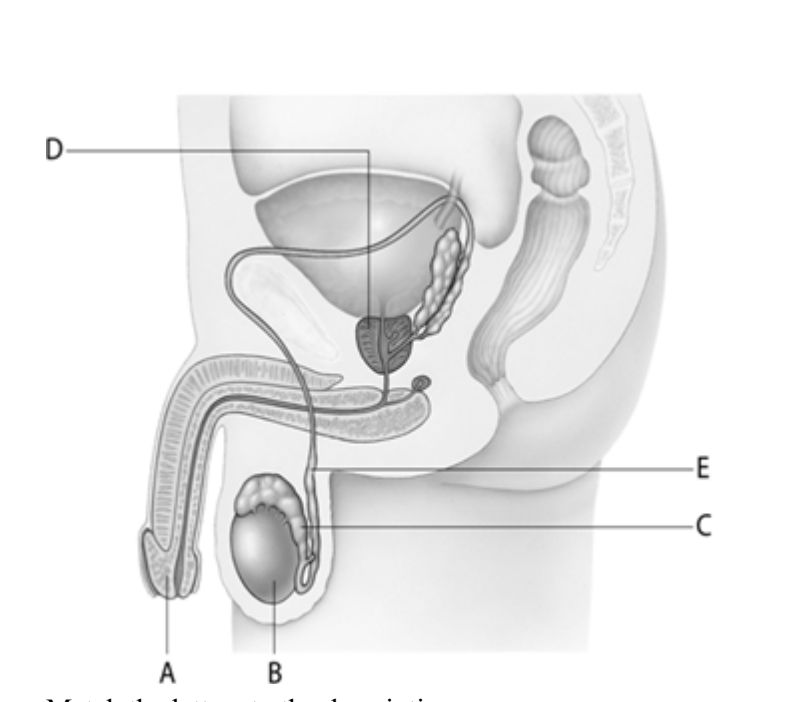
The organ at letter _____is the male counterpart to the female ovary.
B
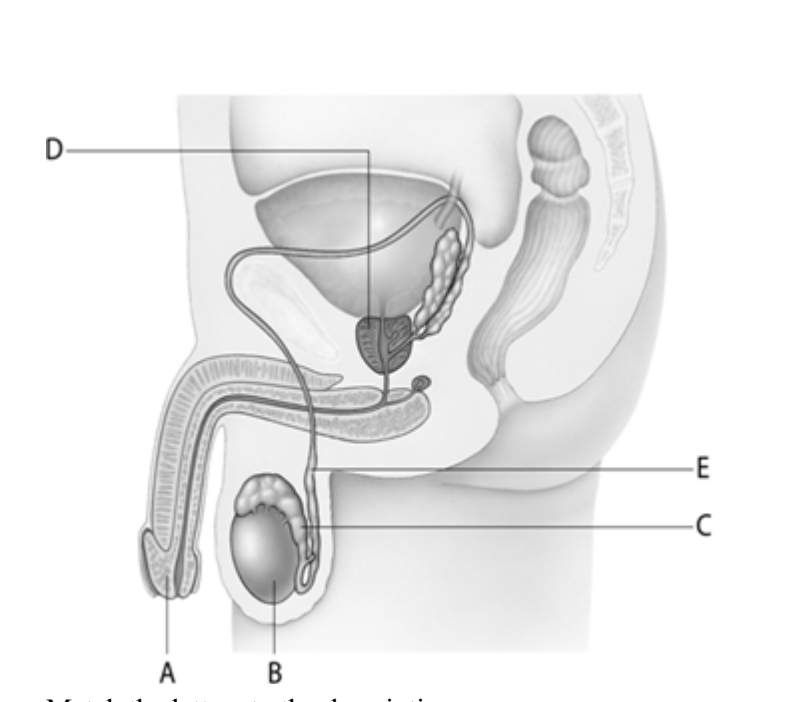
Sperm are stored to allow for maturation in the structure at letter ____.
C
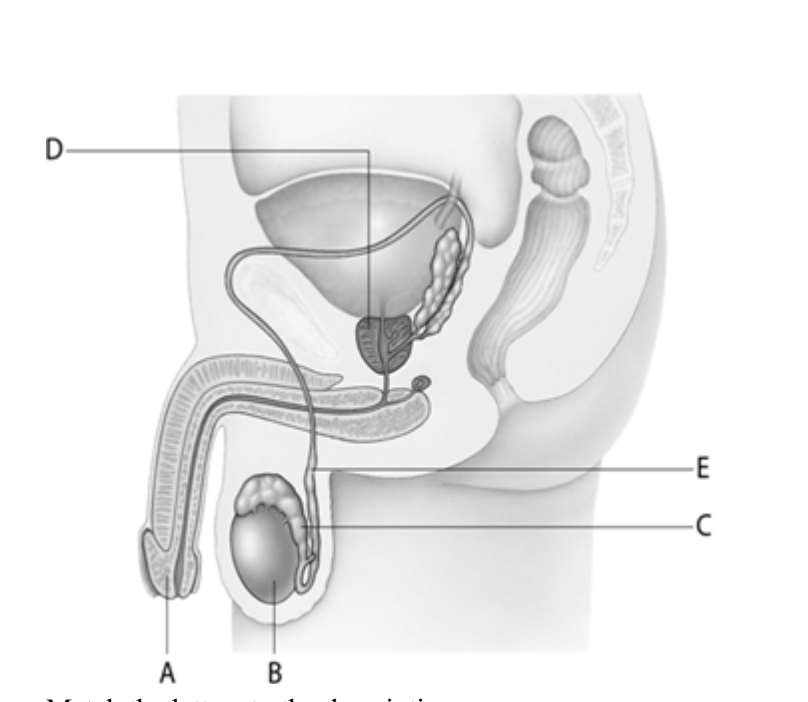
The vas deferens are represented by letter ____.
E
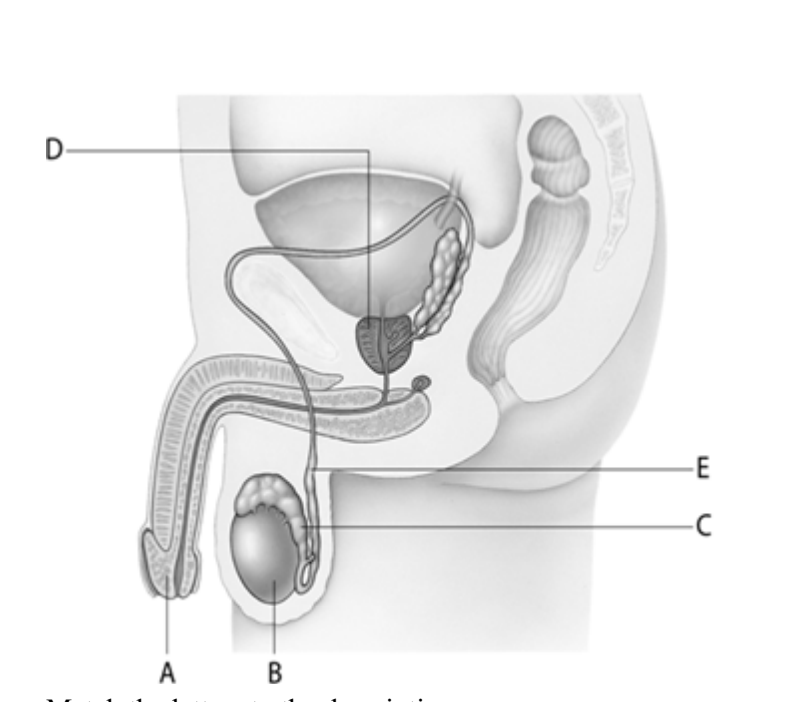
The organ at letter ____ is a structure that contributes fluid to the semen mixture during ejaculation.
D
Mammals nourish their embryos by means of a(n) ____.
placenta
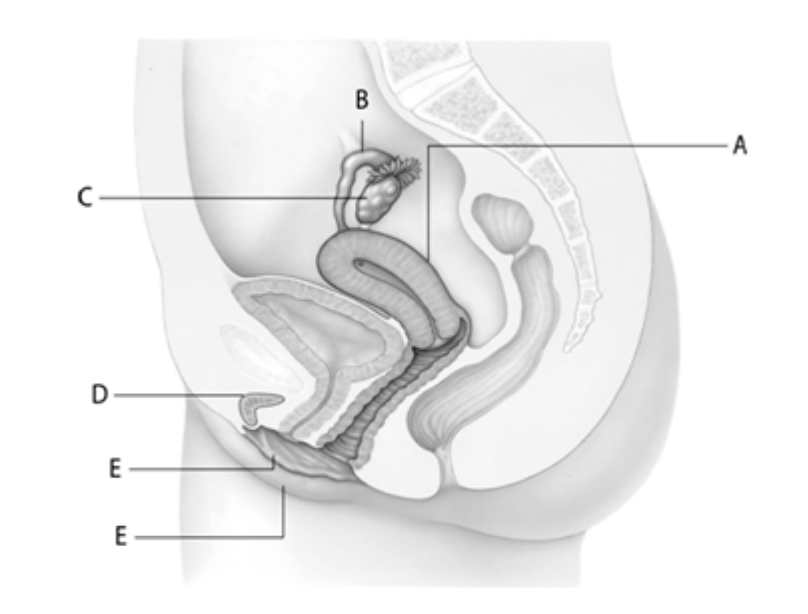
The organ that produces eggs and sex hormones is at letter ____.
C
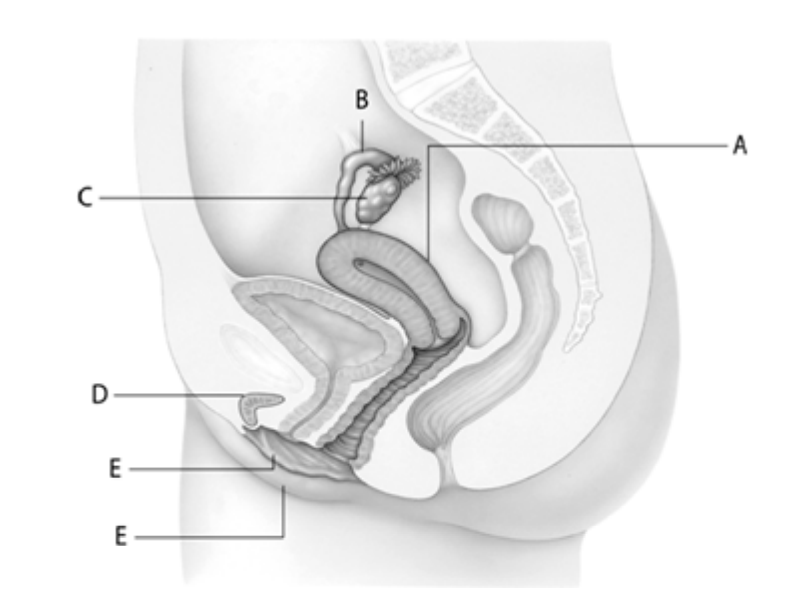
Which letter indicates the oviduct?
B
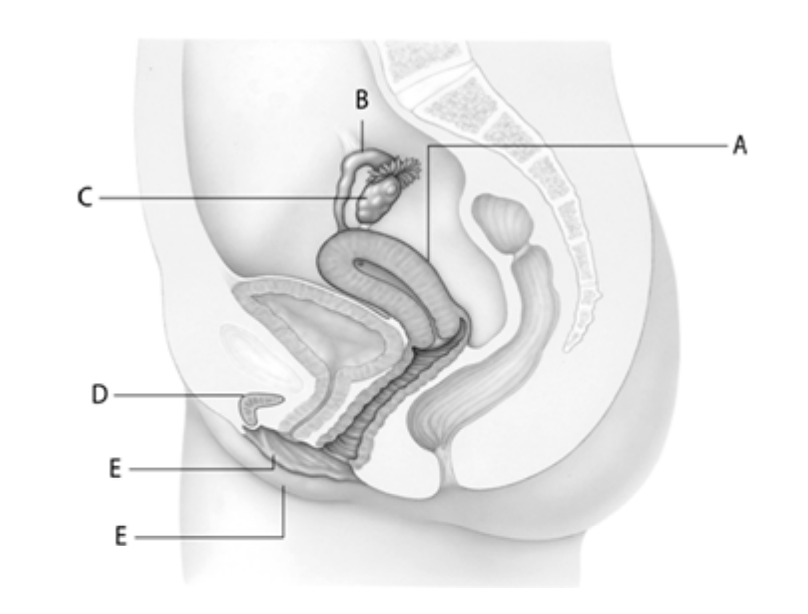
Which letter indicates female tissue that contains a large nerve bundle?
D
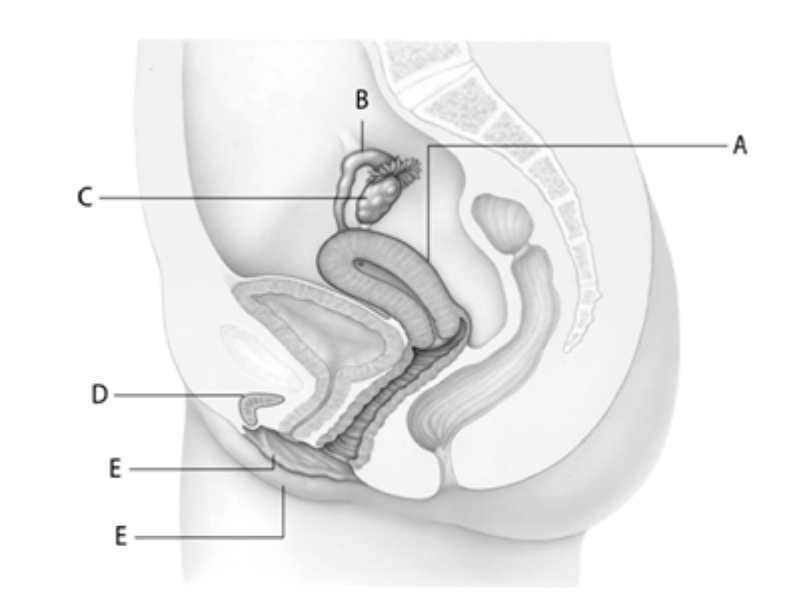
The organ at letter ____ is lined with endometrium.
A
____ is the degree of adaptation to a specific environment.
fitness
Morphological divergence ____.
is the change in body form to something different than that of a common ancestor
Passive immunization ____. a. involves exposure to antigens
involves receiving antibodies from another individual
Which immune cells provide "memory" that can be used as defense for many years?
B-cells
Biogeography is the study of the ____.
patterns in the geographical distribution of species
____ selection occurs when individuals choose mates with a particular desirable trait.
sexual
Individuals with adaptive traits tend to survive longer and produce more offspring, leading to ___ of the species.
evolution
What is the best definition of a population?
a group of interbreeding individuals of the same species in a given area