VCE Biology Unit 1 Chapter 1 Jacaranda Nature of Biology
4.5(2)Studied by 24 people
Card Sorting
1/35
Last updated 12:32 AM on 11/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
1
New cards
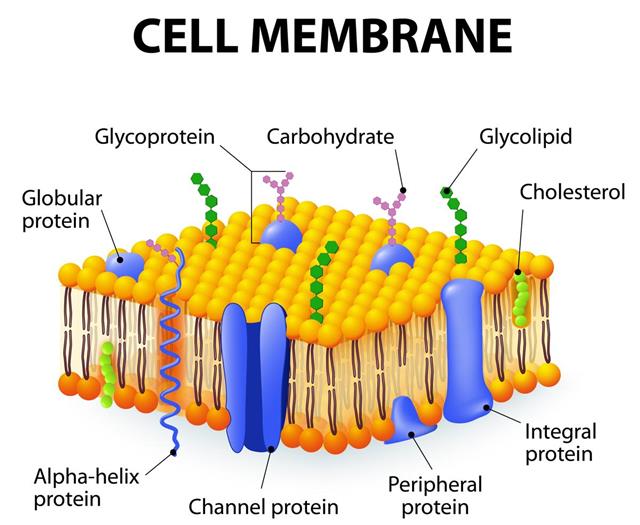
plasma membrane
Forms boundary between cell and extracellular environment and regulates movement of substances in and out of the cell.
2
New cards
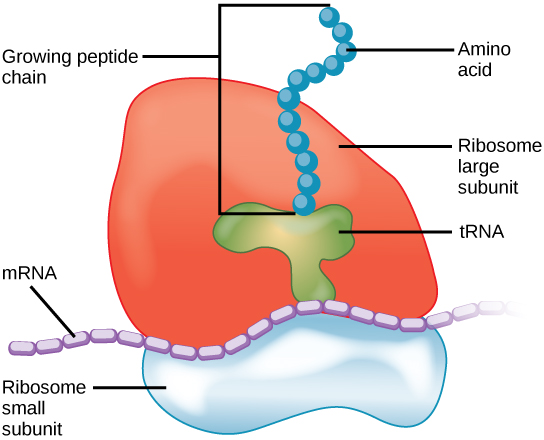
ribosomes
Makes polypeptides (proteins). Located free in the cytoplasm or bound to the rough endoplasmic reticulum
3
New cards
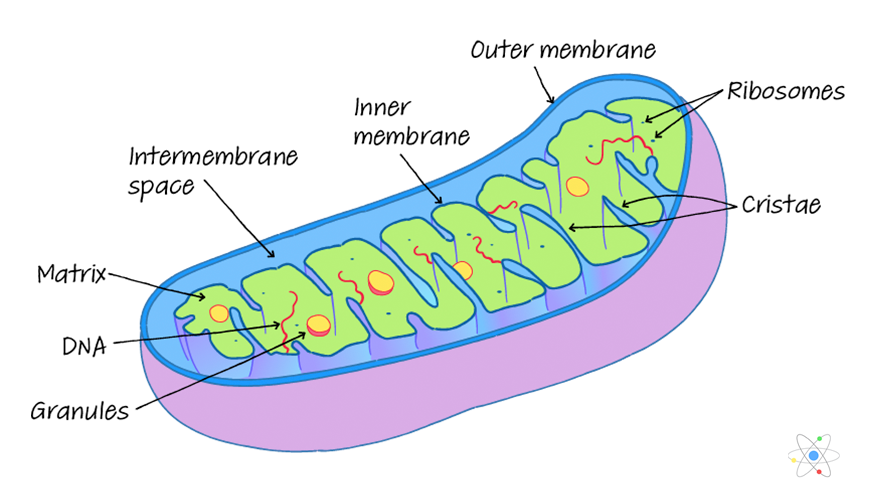
mitochondria
Site of cellular respiration (production of ATP). Located in the cytoplasm
4
New cards
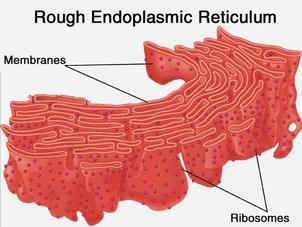
rough endoplasmic reticulum
Synthesis, folding and modification of proteins. Transport of proteins through the cell.
5
New cards
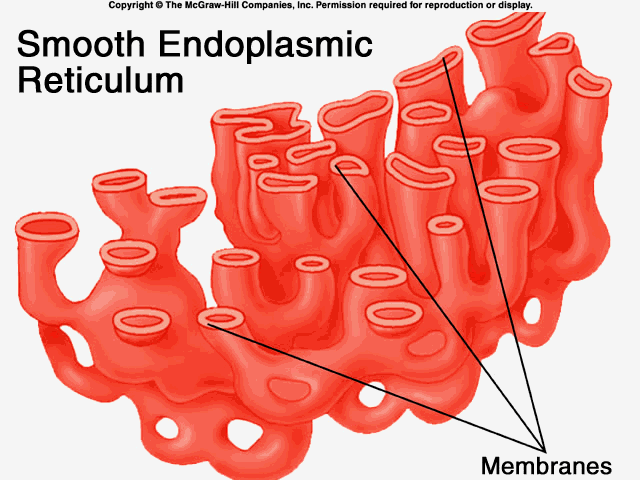
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Synthesis of lipids (oils, phospholipids, steroids). transport of these materials through the cell. Detoxification of drugs and poisons.
6
New cards
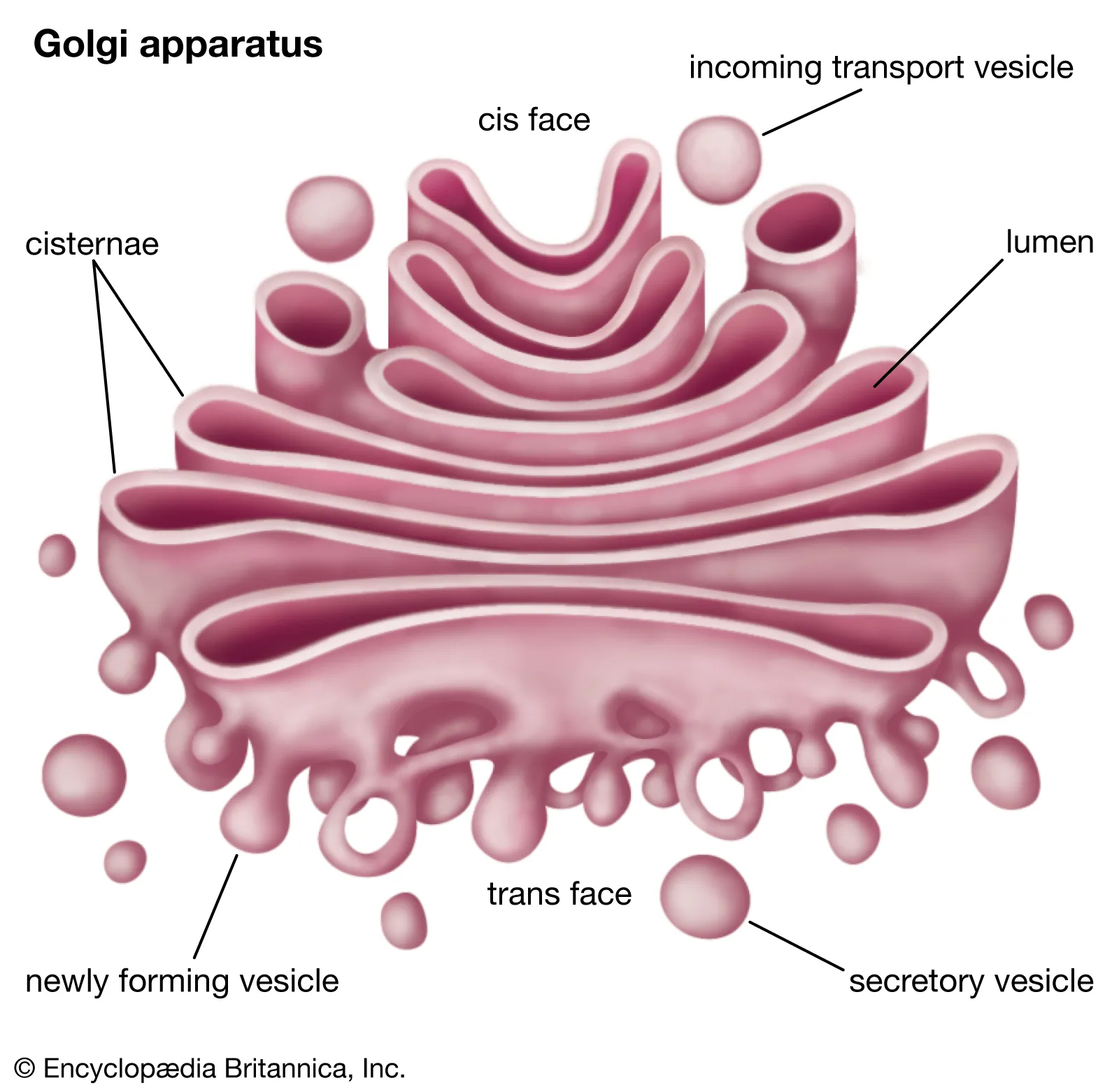
golgi apparatus
Changes proteins and lipids receives from endoplasmic reticulum. Sorts, packages and stores proteins and lipids. Transports these in vesicles through the cell
7
New cards
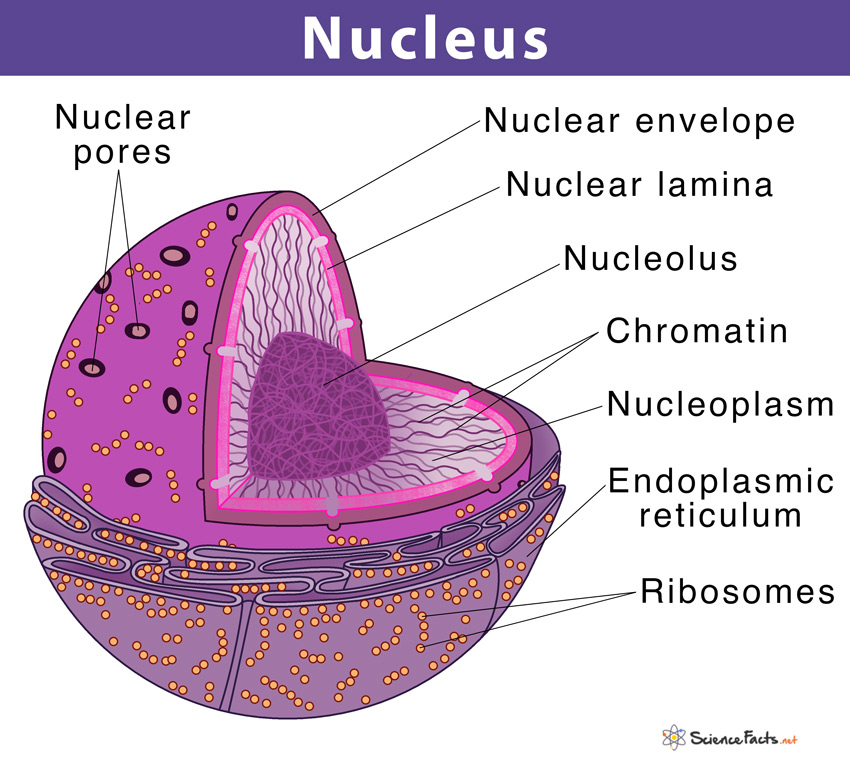
nucleus
Contains most of the cell’s genetic material (DNA) which regulates all the activities of the cell
8
New cards
nucleolus
Makes rRNA (ribosomal RNA). Assembles ribosomal subunits
9
New cards

centrioles
Involved in organising microtubule assembly (spindle formation) in plants
10
New cards
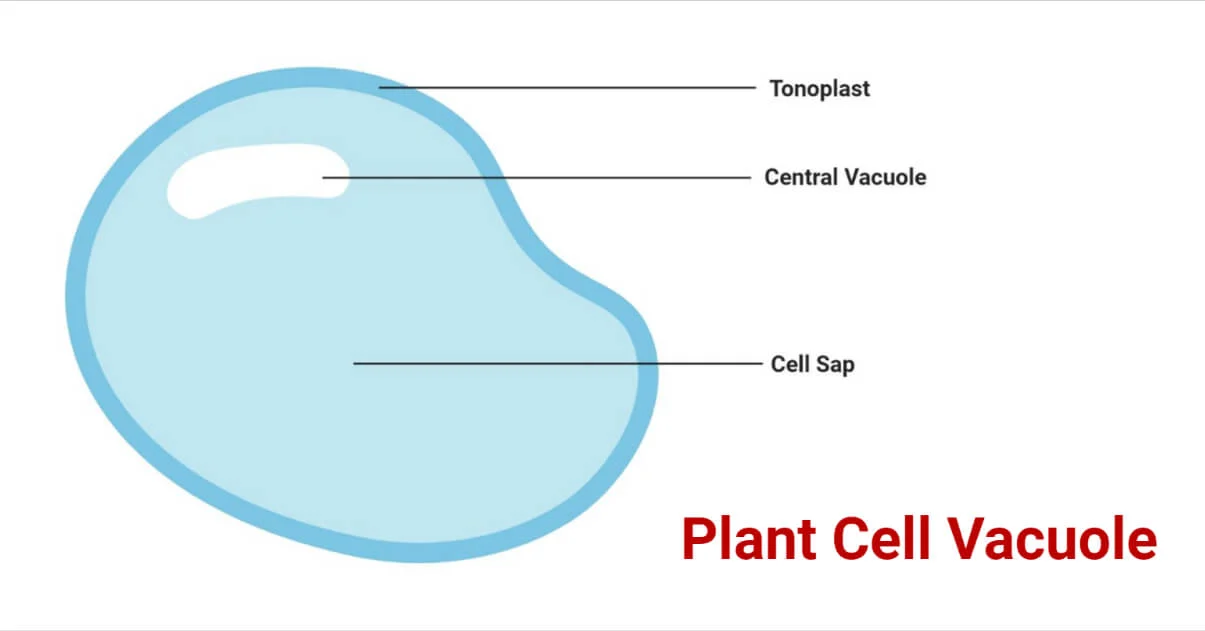
vacuoles
Provides plant cell volume and stores inorganic ions and metabolic waste
11
New cards
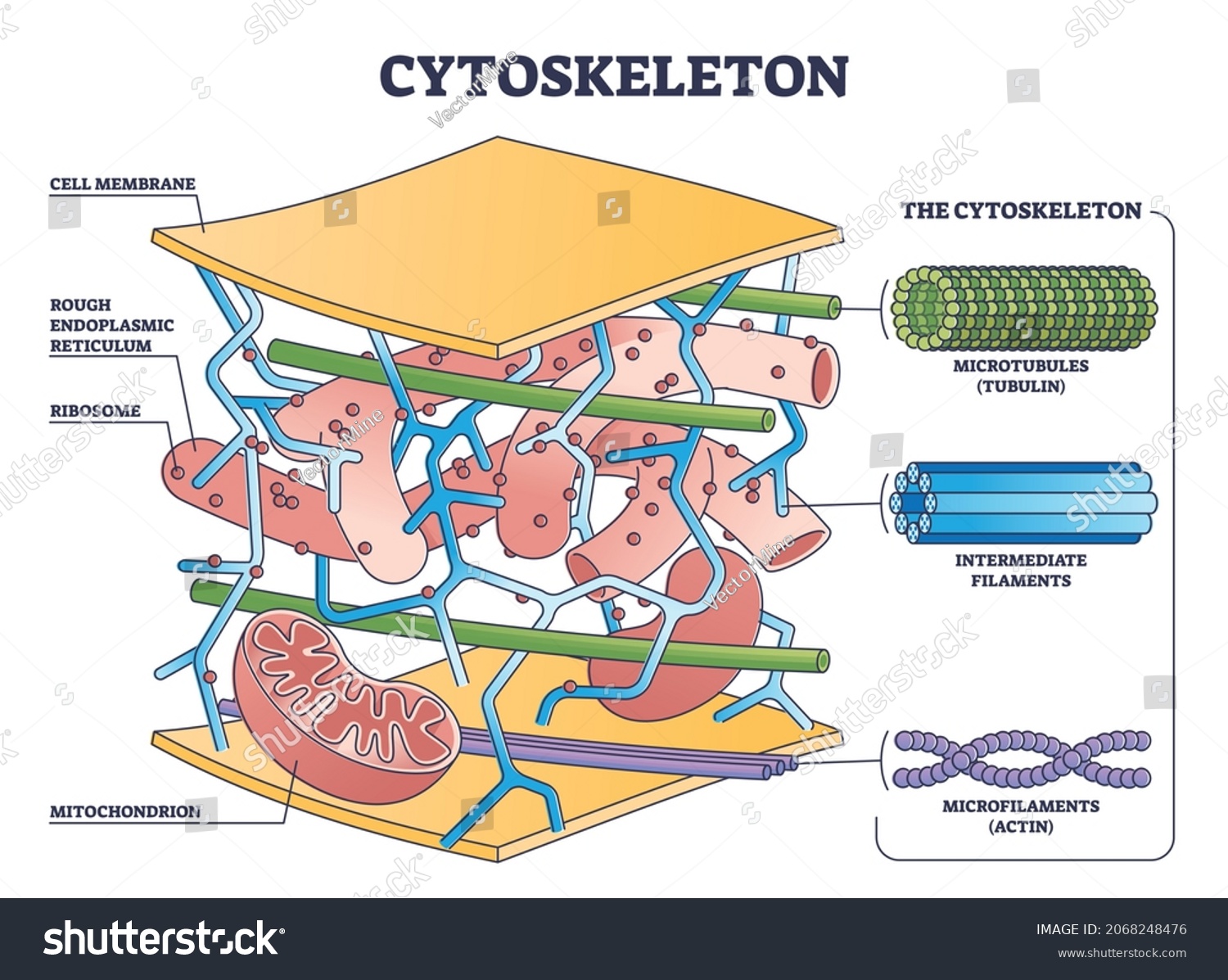
cytoskeleton
Adds shape and mechanical support and regulates cellular activities
12
New cards
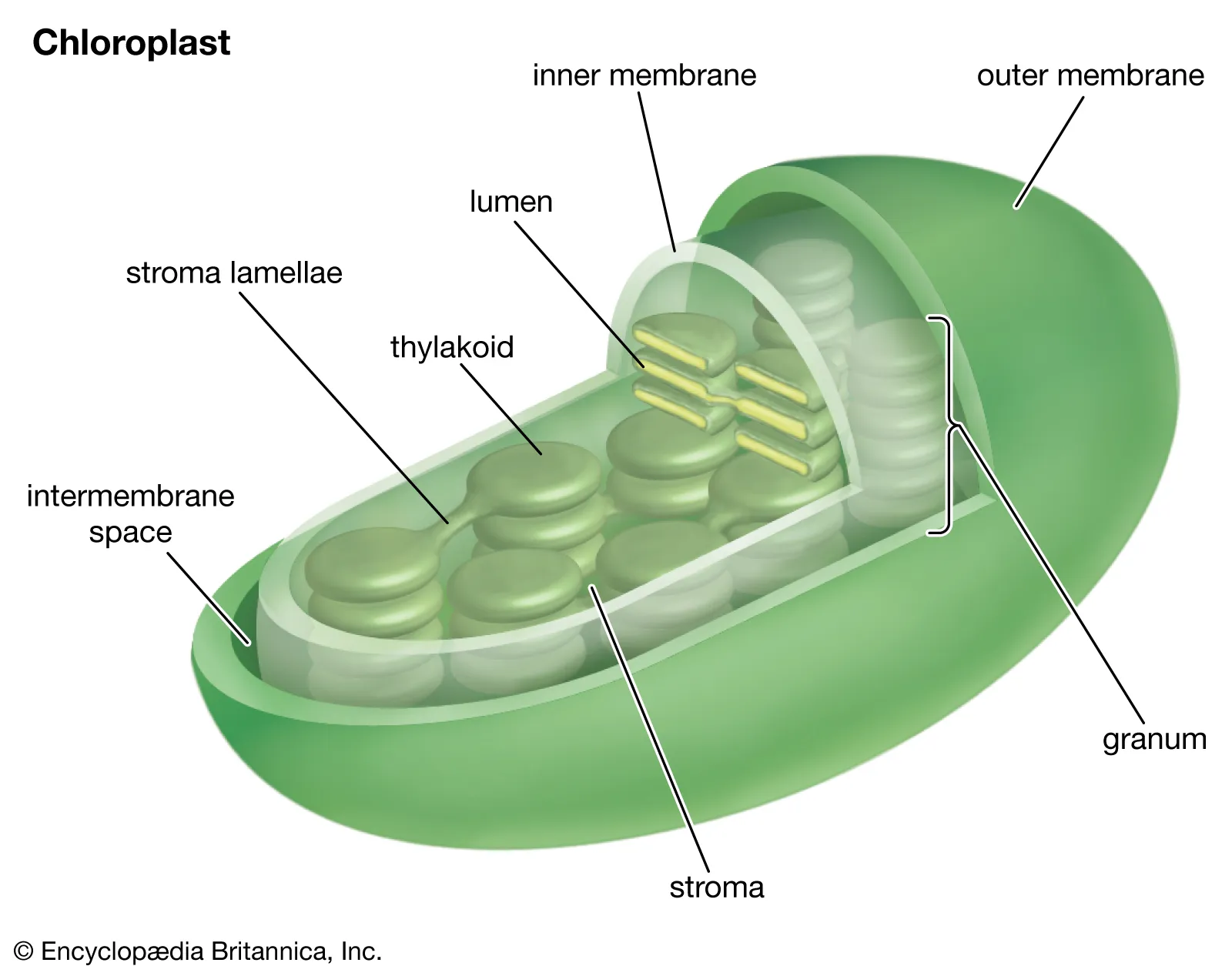
chloroplasts
Site of photosynthesis with specialised plastids containing the green pigment chlorophyll
13
New cards
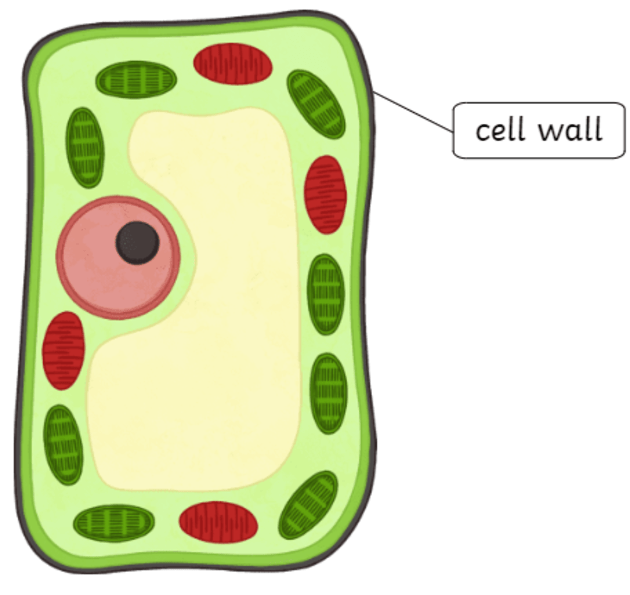
cell wall
Protects and maintains the cell shape and prevents too much water uptake. outside the plasma membrane of a plant cell
14
New cards
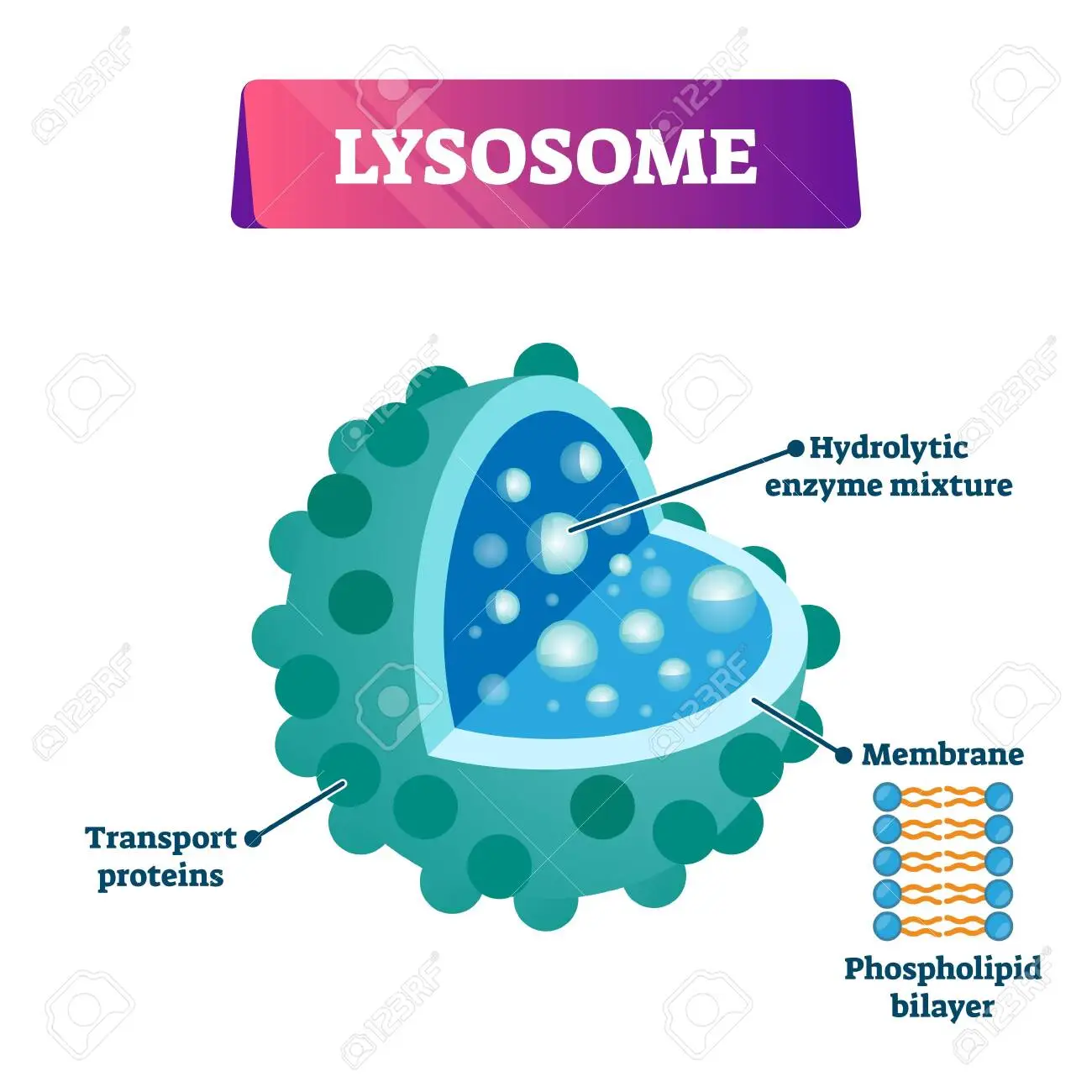
lysosomes
Intracellular digestion of macromolecules. recycles cellular components (autophagy)
15
New cards
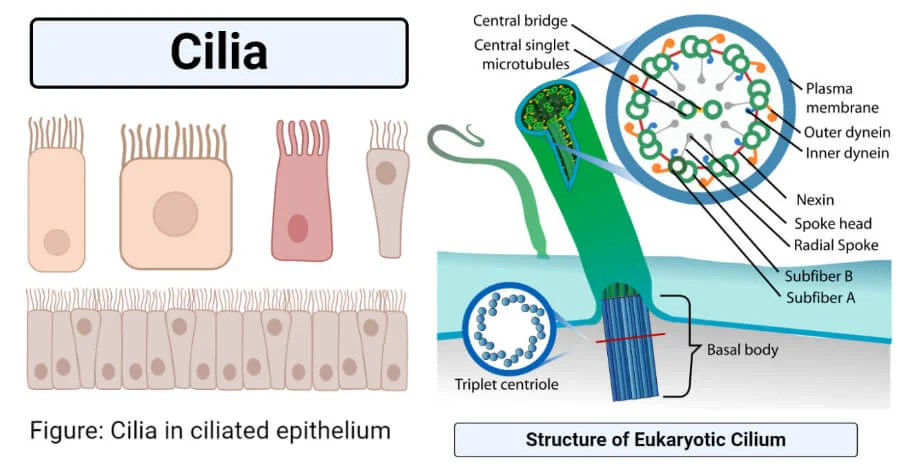
cilia
Protects animal cells and helps the cell move substances across
16
New cards
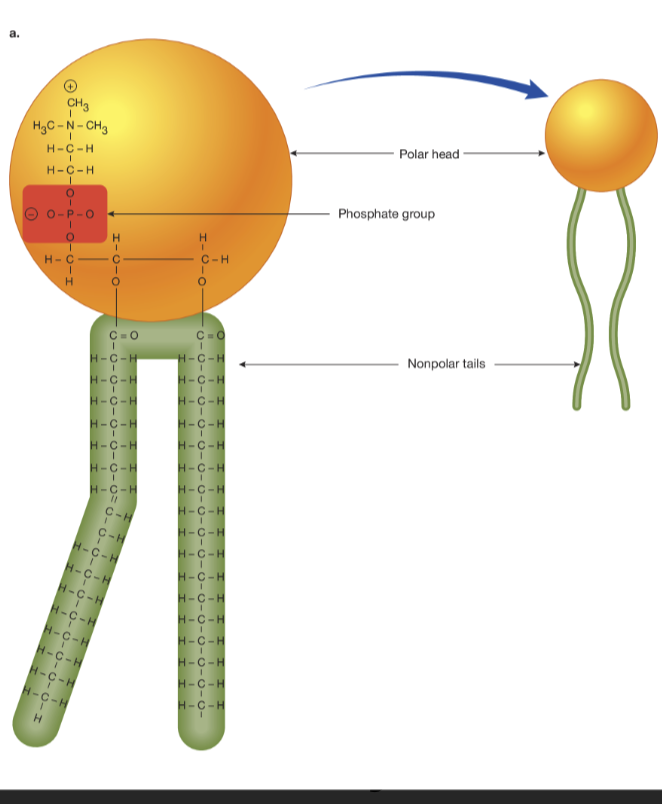
phospholipids
Comprised of a hydrophilic phosphate head and a hydrophobic lipid tail
17
New cards
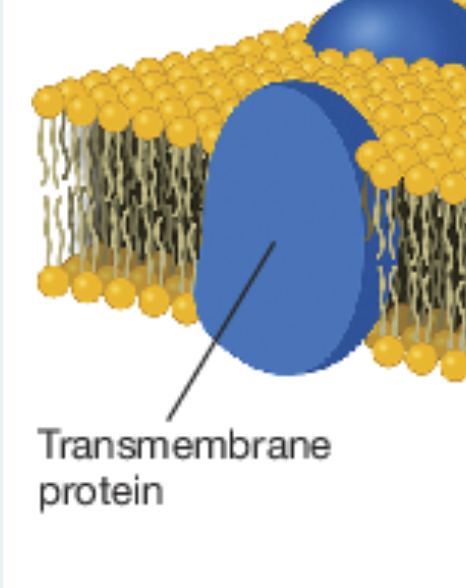
integral proteins
Vital components of the plasma membrane that are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer
18
New cards
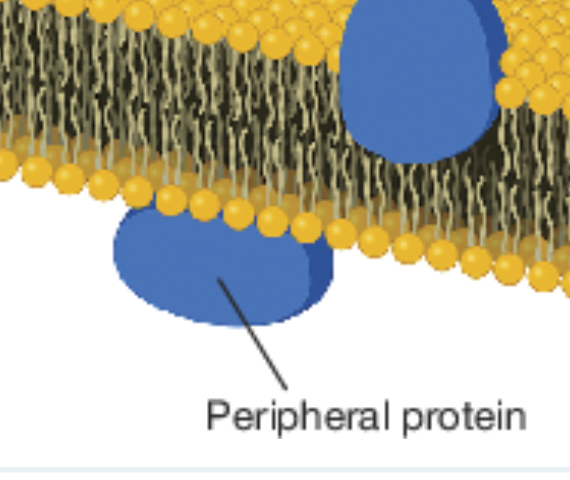
peripheral protein
Anchored to the outside of the plasma membrane through lipid bonding or interactions with integral proteins
19
New cards
cholesterol
Sterol compound that aids the composition of cell membranes, puts space between fatty acids and ensures flexibility in extreme temperatures
20
New cards
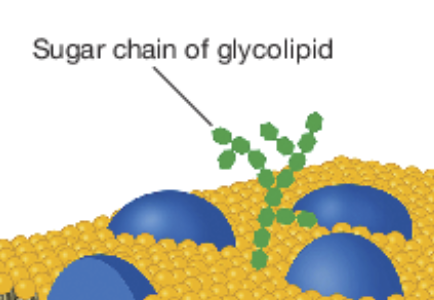
glycolipids
Small chains of carbohydrates attached to phospholipids and proteins that aid in cell recognition
21
New cards
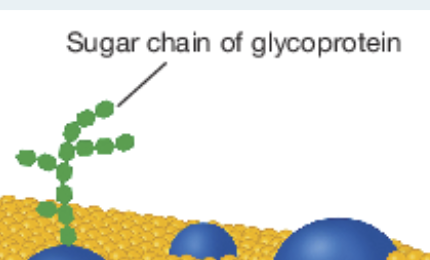
glycoproteins
Combination formed when a carbohydrate group attaches to the exposed part of an integral protein
22
New cards
passive transport
Movement from an area of a high concentration to a low concentration
23
New cards
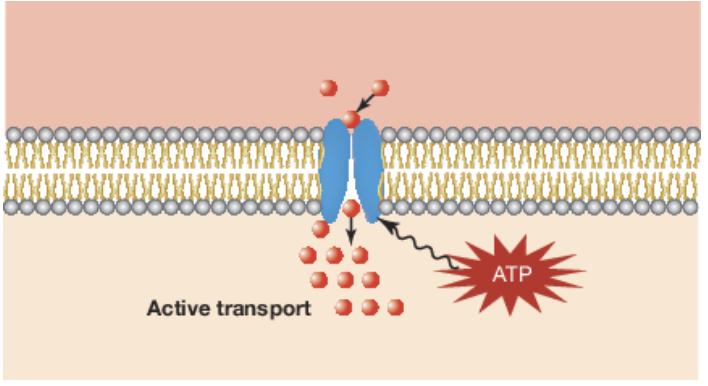
active transport
Movement from a low concentration to a high concentration with ATP (energy)
24
New cards
facilitated diffusion
When channel or carrier proteins assist particles in diffusion without the use of ATP
25
New cards
simple diffusion
Net movement of a substance from an area of a high concentration to a low concentration
26
New cards
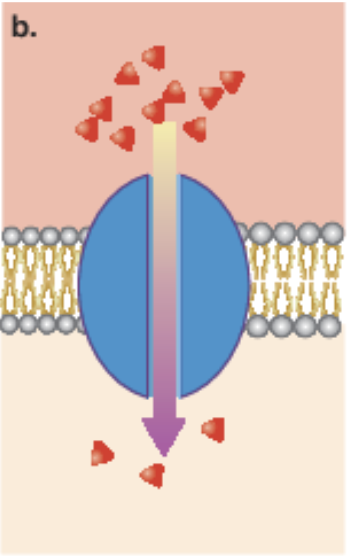
channel protein
Form narrow passageways for small ions to travel through
27
New cards
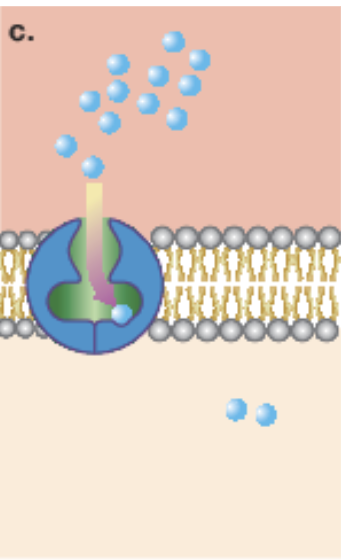
carrier protein
Bind to specific molecules on one side and change shape to release it on the other side
28
New cards
osmosis
The movement of water down the concentration gradient
29
New cards
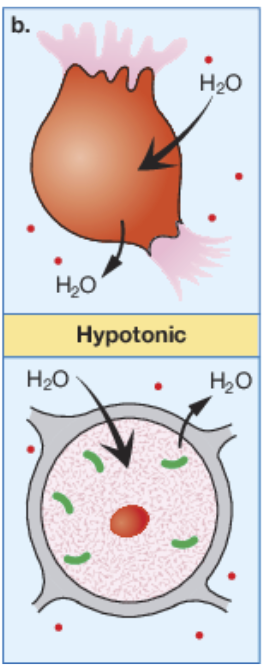
hypotonic
When the solute concentration is lower outside than inside
30
New cards
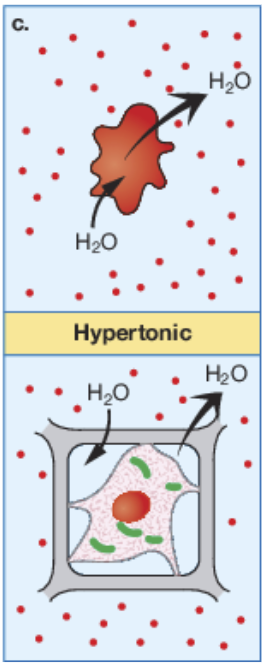
hypertonic
When the solute concentration is higher outside of the cell
31
New cards
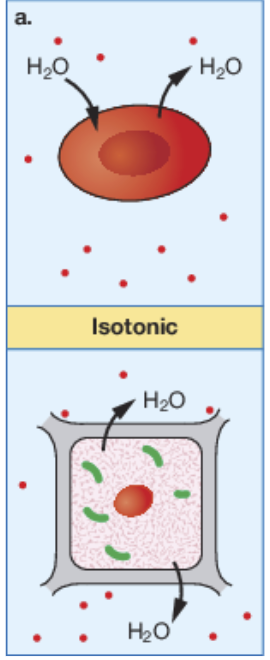
isotonic
When the solute concentration is equal throughout the cell
32
New cards
pumps
Special transport proteins that use energy to move small polar molecules against the concentration gradient
33
New cards
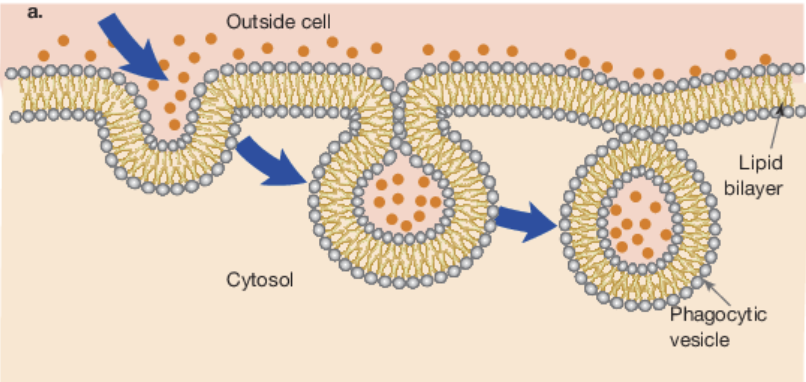
endocytosis
Bulk transport of material into a cell
34
New cards
phagocytosis
Bulk transport of solid materials into the cell
35
New cards
pinocytosis
Form of endocytosis that involves materials in a solution
36
New cards
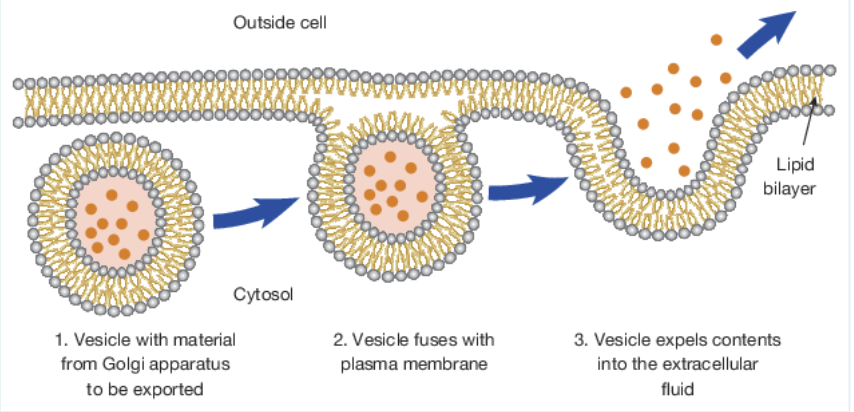
exocytosis
Bulk transport of materials out of the cell