AP Bio Chapter 12-14 Genetics
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
ok
read DNA notes (from chapter 3)
telomerase
lengthens strands and makes sure there is no kinks
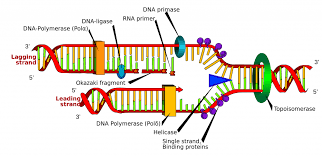
DNA fork
where DNA splits
DNA polymerase
there are 3 of them
makes sure everything is correct at the end
RNA primase
preps DNA strand to make a new strand
has 5 to 10 nucleotides
topoisomerase
untwists DNA and makes it stay untwisted
46
how many chromosomes in each cell
bonded molecules names
dimer- 2 molecules together
oligomer- a few molecules bonded
polymer- many molecules together
helicase
protein that breaks the hydrogen bonds between DNA strands
acts as an enzyme
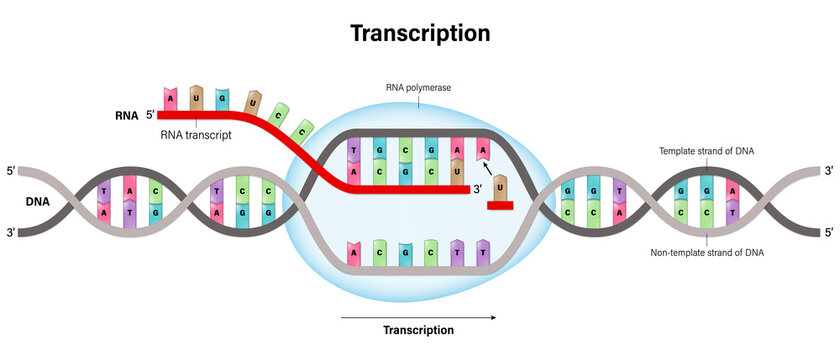
rna
DNA replication
reads 3 prime to 5 prime
prime ends
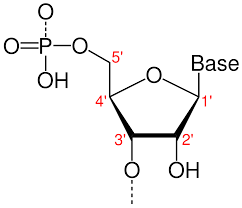
5 prime and 3 prime ends of a nucleotide
phosphate group attached to the 5th carbon
nitrogen base is attached to the first carbon
nucleotides bond with one right side up and the other upside down
5 prime is lagging (has fragments for new DNA called Okazaki fragments)
3 prime is leading (hooks to 3 prime first and is a continuously new strand)
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
molecule with a double-helix that carries the genetic information of a cell
bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine
Monomer
the smallest unit of larger molecules called polymers
Messenger Rna
Nucleic acid
macromolecule that contains the DNA of a cell and the instructions for the functioning of the cell
monomer: nucleotides
bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, uracil
Nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids; has sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base
Phosphodiester linkage
covalent chemical bond that holds together the polynucleotide chains, with a phosphate group linking two pentose sugars of neighboring nucleotides
Polymer
chain of monomers that are linked by covalent bonds; polymerization is the process of polymer formation from monomers by condensation
Polynucleotide
long chain of nucleotides
Purine
type of nitrogen base in DNA and RNA; adenine and guanine are purines
Pyrimidine
type of nitrogen base in DNA and RNA; cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
single-stranded, often internally base paired, molecule that is involved in protein synthesis
bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
RNA that makes sure there is proper alignment of the mRNA and the ribosomes during protein synthesis and starts the formation of the peptide linkage
Transcription
process through messenger RNA forms on a template of DNA
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
RNA that carries activated amino acids to where protein synthesis is occurring on the ribosome
Translation
process through which RNA directs the formation of protein
polymer
made up of monomers
joined together through dehydration synthesis
genetic drift
the change in frequency of an existing gene variant in the population due to random chance. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation. It could also cause initially rare alleles to become much more frequent, and even fixed.
pedigree
shows relationships between family members and indicates which individuals have certain genetic pathogenic variants, traits, and diseases within a family as well as vital status. A pedigree can be used to determine disease inheritance patterns within a family.
translocation
occurs when a chromosome breaks and the (typically two) fragmented pieces re-attach to different chromosomes.
Hardy Weinburg
genetic variation in a population will remain constant from one generation to the next in the absense og disturbing factors. These factors disturb the population:
prey disappearing
significant change in habitat (climate change, humans develop)
genetic mutation/new species introduced
conditions must be met in a population for the genetic variation to remain constant:
large population
the population must be isolated from other populations, no immigration/emigration
no mutations
random mating
no natural selection (every gen can survive to the next)
p + q= 1
p² + 2pq +q² = 1
p = frequency of the dominant allele in the population
q = frequency of the recessive allele in the population
p² = percentage of homozygous dominant individuals
q²= percentage of homozygous recessive individuals
2pq = percentage of heterozygous individuals
Population Genetics
the study of genetic variation within and among populations and the evolutionary factors that explain this variation
nondisjunction
is the failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division. This can lead to abnormal chromosome numbers in daughter cells
occurs during anaphase one or two
inversion
occurs when a segment breaks off and reattaches within the same chromosome, but in reverse orientation. DNA may or may not be lost in the process.
karyotypes
an individual's complete set of chromosomes.
crossing over
a cellular process that happens during meiosis when chromosomes of the same type are lined up. When two chromosomes — one from the mother and one from the father — line up, parts of the chromosome can be switched. The two chromosomes contain the same genes, but may have different forms of the genes
autosomal
equal trait among female and males
sex linked
more males with trait is result
traits are traits controlled by genes located on sex chromosomes. In humans, these traits are often associated with the X chromosome and can be passed from one generation to the next through the sex chromosomes.
cis
dominant and recessive trait on the same chromosome
trans
dominant and recessive trait on difference chromosomes
lethal mutations
genetic alterations that cause severe abnormalities, often resulting in the death of the organism.
proofreading
when the DNA is checked to make sure it is right. the enzymes can backtrack
repairs mismatches
primase is almost always right so repair is very rare
homologous
describes descent from a common evolutionary origin: two genes are homologous if they derive from the same ancestral gene.
analogous
genes that have identical or similar function but don't share a common ancestor and are therefore unrelated as opposed to homologous genes.
vestigial
the retention, during the process of evolution, of genetically determined structures or attributes that have lost some or all of the ancestral function in a given species
ex: wisdom teeth
SSBS
stabilize the strands and prevent the old strands from coming together after they have been separated by the helicase; single stranded binding protein; preps the area on the original strand for DNA polymerase
nucleotides want to hook together like magnets
Alleles
a variant form of a gene, which can result in different traits or characteristics in an organism. ______ are located on corresponding positions on homologous chromosomes.
Punnet Squares
a square diagram that is used to predict the genotypes of a particular cross or breeding experiment.
Dna polymerase 1
removes the primer and identifies where the nucleotides need to hook up
incomplete dominance
a form of Gene interaction in which both alleles of a gene at a locus are partially expressed, often resulting in an intermediate or different phenotype. It is also known as partial dominance. For eg., in roses, the allele for red colour is dominant over the allele for white colour.
complete dominance
the effect of one allele in a heterozygous genotype completely masks the effect of the other. The allele that masks are considered dominant to the other allele, and the masked allele is considered recessive.
codominance
a type of inheritance in which two versions (alleles) of the same gene are expressed separately to yield different traits in an individual
law of segregation
states that each individual has two alleles for each gene, and these alleles separate during the formation of gametes.
law of independent assortment
states that alleles of different genes segregate independently of one another during gamete formation.
Dna polymerase 3
attaches nucleotides.
responsible for synthesizing the leading and lagging strands during DNA replication in prokaryotes.
ligase
will make sure nucleotides are joined together (because they are not originally fully connected)
phosphodiester bond
A phosphodiester bond is a chemical bond that links nucleotides in DNA and RNA strands. It connects the phosphate group of one nucleotide to the hydroxyl group on the sugar of another nucleotide.
semicontinuous
the leading strand is continuous but the lagging strand is discontinuous
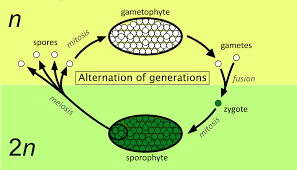
alternation of generations in plants
sporophyte- produces spores (on a fern, a sori)
spore undergoes mitosis and produces a gameophyte (haploid that makes gametes)
gametes come together to make a zygote
asexual reproduction (spore) sexual reproduction (gamete)
triglyceride
neutral fats
composed of two types of building blocks: 3 fatty acids and a glycerol
glycerol- makes the backbone, 3 fatty acids make the chains coming off of the backbone
E shape
glycerol remains the same for all neutral fats but the 3 fatty acids can differ (gives the fats their individual characteristics)
oxidation process
Chemical reaction in which a substance loses electrons, resulting in an increase in its oxidation state. It involves the addition of oxygen or the removal of hydrogen, and often produces heat and light.
breaks down glucose to make ATP
ATP production from carbs
energy that was trapped in the bonds of ATP is released during oxidation process
carbs ingested are converted to glycogen or fat and stored (eat too many carbs—→ gain weight)
genotype
genes you have
phenotype
how the genes are expressed or presented
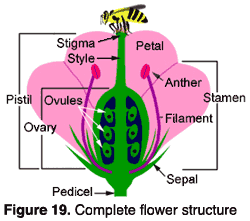
flower parts
ripe ovary= fruit
alternation of gen if no fruit
onion is in a bulb
tulips grow faster in bulbs than seeds
petals= protect
sperm lands in stigma = fertilized ovules = zygote = seed develops at the bottom
anther= pollen, spore
hardy weinburg steps
solve for q² (dominant/total)
find q (square root)
solve for p (1-q= p)
solve for heterozygous (2pq)
nucleotide parts
sugar, (5 carbon) nitrogen base, phosphate group
replication fork
when DNA strands split to make a fork