PSY202 Stress and Health
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/34
Earn XP
Last updated 7:46 AM on 3/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
1
New cards
What is Stress?
Tension, discomfort and produce physical symptoms.
2
New cards
What is a Stressor?
Threatening or demanding situations that cause tension and discomfort.
3
New cards
What are __Catastrophes?__
* Very-large-scale disasters or horrible events; impact an entire community
* Despite the stress, catastrophes increase social awareness and cement people’s interpersonal bonds
* Despite the stress, catastrophes increase social awareness and cement people’s interpersonal bonds
4
New cards
What are the Approaches to Stress?
* Stressors as Stimuli
* Stress as a Transaction
* Stress as a Response
* Stress as a Transaction
* Stress as a Response
5
New cards
Stressors as Stimuli.
* Focuses on identifying types of stressful events, situations that cause more stress, and people who are more vulnerable to stress
* Catastrophes
* Catastrophes
6
New cards
Stress as a Transaction.
* How people cope with stressors
* Cognitive Appraisal Theory
* Primary and Secondary Appraisals
* Cognitive Appraisal Theory
* Primary and Secondary Appraisals
7
New cards
What is the __Cognitive Appraisal Theory?__
Looks at the critical factor for determining why we react to stressful events.
8
New cards
What is a __Primary Appraisal__?
If the stressor can be handled, then a person will not be stressed.
9
New cards
What is a __Secondary Appraisal__?
* If the stressor is a *threat*, then the person __will__ be stressed
* If the stressor is a *challenge*, then the person __will not__ be stressed
* If the stressor is a *challenge*, then the person __will not__ be stressed
10
New cards
Stress as a Response.
* Psychological and physiological reactions to stress
* Physiological Measures and Psychological assessments which is how we react and cope with stress
* Lab-Included or Real-World stressors
* Physiological Measures and Psychological assessments which is how we react and cope with stress
* Lab-Included or Real-World stressors
11
New cards
How is Stress Measured?
* Significant Life Events (SRRS)
* Daily Hassles (Hassles Scale)
* Daily Hassles (Hassles Scale)
12
New cards
What is the __Social Readjustment Rating Scale (SRRS)?__
* A list of 43 events ranked to “life-changing units (LCU)”; things that readjust the lives of people
* The **lower** the number on the list, the less stressful; the **higher** the number, the more readjustment was needed for an event
* The **lower** the number on the list, the less stressful; the **higher** the number, the more readjustment was needed for an event
13
New cards
What does the scoring on the SRRS state?
*
14
New cards
What is the __Hassles Scale__?
* Minor annoyances or nuisances that strain our ability to cope
* The scale is the cumulative load of hassles may be more responsible for stress than major events; the number and severity is significant
* People who face more hassles, face lots more major life events
* Living in Big Cities (personal space)
* The scale is the cumulative load of hassles may be more responsible for stress than major events; the number and severity is significant
* People who face more hassles, face lots more major life events
* Living in Big Cities (personal space)
15
New cards
What does Living in Big Cities contribute to stress?
* Exposure to *potential stressors*
* Overcrowding VS Personal Space
* Invades personal space, and causes stress and discomfort; anxiety
* Tension state that affects mental health; a sense of insecurity
* Overcrowding VS Personal Space
* Invades personal space, and causes stress and discomfort; anxiety
* Tension state that affects mental health; a sense of insecurity
16
New cards
How do we Adapt to Stress?
* General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)
* Three stages of psychological reactions to stress
* Three stages of psychological reactions to stress
17
New cards
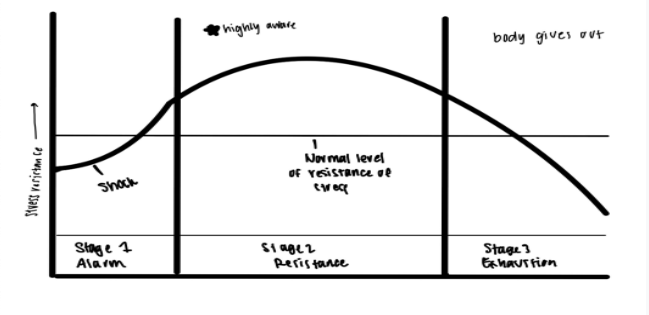
What is __General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)__?
* The reactions are general (all humans respond in a similar pattern) and nonspecific (we all react specifically, even animals)
* Three stages: 1. Alarm, 2. Resistance, and 3. Exhaustion
* Three stages: 1. Alarm, 2. Resistance, and 3. Exhaustion
18
New cards
What happens in the __Alarm__ Stage?
* Stress hormones are released; physical symptoms of anxiety; “fight or flight” response
* State of __Shock__
* Loss in muscle control and blood pressure and body temperature drops; lasts a short period of time and then __Counter Shock__ hits which will bring you back to Normal resistance state
* State of __Shock__
* Loss in muscle control and blood pressure and body temperature drops; lasts a short period of time and then __Counter Shock__ hits which will bring you back to Normal resistance state
19
New cards
What happens in the __Resistance__ Stage?
* Adapt and find ways to cope with the stressor; resources are limited
* Constantly high
* Constantly high
20
New cards
What happens in the __Exhaustion__ Stage?
If the threat persists, eventually the body will give out.
21
New cards
How can we __Cope__ with Stress?
* Relaxation
* Reappraisal
* Social Support
* Reappraisal
* Social Support
22
New cards
What does __Relaxation__ have to do with Coping?
* Involves low arousal
* Incompatible with stress
* Biofeedback
* Incompatible with stress
* Biofeedback
23
New cards
What is __Biofeedback__?
* When people are given feedback on their body’s state through a machine
* May result in __Perceived Control__ and may reduce stress-related tension and pain
* May result in __Perceived Control__ and may reduce stress-related tension and pain
24
New cards
What does __Social Support__ have to do with Coping?
* Support from others, often in the form of comfort, caring, or help can lead to a healthy immune system and less stress
* Beneficial in reducing stress since more social support is associated with lower mortality rates
* Pet support can lead to less doctor trips and lower heart attack deaths
* Beneficial in reducing stress since more social support is associated with lower mortality rates
* Pet support can lead to less doctor trips and lower heart attack deaths
25
New cards
What does __Reappraisal__ have to do with Coping?
* Cognitive Appraisal
* A large part of the stress reaction is psychological
* Using therapy and take a positive outlook on situations
* A large part of the stress reaction is psychological
* Using therapy and take a positive outlook on situations
26
New cards
What are Individual Differences to do with Stress?
* Perceived Control
* Personality Differences
* Personality Differences
27
New cards
What is __Perceived Control__?
* How much control one can see/believe they have over situations
* Having high perceived control reduces stress and has health benefits
* Having high perceived control reduces stress and has health benefits
28
New cards
What are __Personality Differences__?
* Optimism and Pessimism
* Optimism is associated with faster recovery after surgery, better immune system functioning, and a lower mortality rate
* Optimism is associated with faster recovery after surgery, better immune system functioning, and a lower mortality rate
29
New cards
What are some __Physical Consequences__ of Stress?
* Stress may weaken the immune system
* “fight or flight“ → increased blood pressure
* Stress is linked to higher blood cholesterol
* Personality Types play a role in the consequences
* “fight or flight“ → increased blood pressure
* Stress is linked to higher blood cholesterol
* Personality Types play a role in the consequences
30
New cards
What role do Personality Types play in the Physical Consequences of Stress?
* Type A: Impatient, Ambitious, Easily Annoyed; Low on “Agreeableness“
* A person can easily get angry, and when stressed they may show it; this component is linked with a high risk of cardiovascular diseases
* Type B: Patient, Laid Back, Flexible, Clam, Easy Going
* A person can easily get angry, and when stressed they may show it; this component is linked with a high risk of cardiovascular diseases
* Type B: Patient, Laid Back, Flexible, Clam, Easy Going
31
New cards
What are some __Psychological Consequences__ of Stress?
If stress is intense enough, or lasts long enough, psychological problems can result. These include Depression, Anxiety, or PTSD.
32
New cards
What is __Problem Drinking__ and how does it affect Health?
* Binge drinking
* There are __Physical effects__ (increases in cancer, liver problems, pregnancy complications, brain shrinkage)
* There are __Cognitive effects__ (is a depressant, but inhibits or reduces anxiety; **Alcohol Myopia**)
* There are __Physical effects__ (increases in cancer, liver problems, pregnancy complications, brain shrinkage)
* There are __Cognitive effects__ (is a depressant, but inhibits or reduces anxiety; **Alcohol Myopia**)
33
New cards
What is __Alcohol Myopia?__
* The idea that intoxication may cause narrowed *perceptual* and *cognitive* functioning that can lead to aggressive behaviour; this increases with dosage
* (Narrowed Attention) They may ignore information that is significant or substantial
* (Narrowed Cognitive) May act against social norms without thinking; influenced by immediate cues without considering the long term consequences
* (Narrowed Attention) They may ignore information that is significant or substantial
* (Narrowed Cognitive) May act against social norms without thinking; influenced by immediate cues without considering the long term consequences
34
New cards
What are some __behaviours that Promote Good Health__?
* __Aerobic Exercise__ (improves cardiovascular fitness, releases mood-altering neurotransmitters, and may increase perceived control)
* Thinking about Stress __Positively__
* Thinking about Stress __Positively__
35
New cards
What does it mean to “Make Stress your Friend?“
* High-stress levels are linked with an increased risk of dying, but only for people who think of stress in a negative way
* __Oxytocin__ makes you “tend and befriend”
* Makes us seek support from other individuals
* Social connections are key to health benefits
* __Oxytocin__ makes you “tend and befriend”
* Makes us seek support from other individuals
* Social connections are key to health benefits