Lesson 11 - Primates
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What class do primates belong to?
Mammalia
What is the subclass of primates?
Eutheria
What order do primates belong to?
Primata
What are key physical features of primates?
Opposable Thumbs
Frontally-directed eyes with binocular vision
Large and convoluted brains
Complex social behavior
The earliest primate (Prosimian) arose 65 MYA when dinosaurs went extinct
When did the earliest primate (Prosimian) arise?
65 million years ago when dinosaurs went extinct.
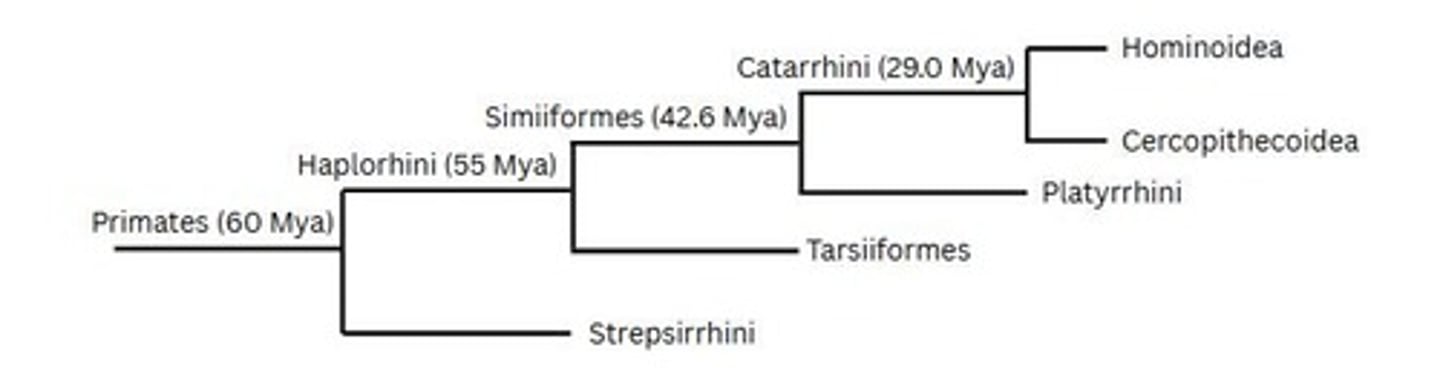
What is the suborder that includes prosimians?
Suborder Prosimil.
What are the two new classifications of prosimians?
Suborder Strepsirrhini and Suborder Haplorhini
non-tarsier prosimians
Suborder Strepsirrhini
tarsiers and anthropoids
Suborder Haplorhini
What characterizes the skull of prosimians?
Large orbits, a reduced brain case, an elongated snout, and well-developed olfactory and auditory regions.
What does the suborder Anthropoidea include?
Monkeys and apes, including humans.
How do anthropoids differ from prosimians in terms of sensory reliance?
Anthropoids rely more on sight and less on the sense of smell.
What is the new classification for anthropoids?
Infraorder Simiiformes.
What are the two parvorders under the infraorder Simiiformes?
Parvorder Platyrrhini and Parvorder Catarrhini.
New World Monkeys
Parvorder Platyrrhini (
Old World Monkeys and Apes
Parvorder Catarrhini
What distinguishes monkeys from apes?
Monkeys have tails, while apes do not.
Where are Old World Monkeys primarily found?
Africa and Asia.
What are the characteristics of Old World Monkeys?
Tails are not prehensile, nostrils face downward, and they can be arboreal or ground-dwelling.
Where are New World Monkeys found?
Central and South America.
What are the characteristics of New World Monkeys?
Tails are prehensile, nostrils face sideways and are wide apart, and all are arboreal.
Superfamily Cercopithecoidea
Old World Monkeys
What classification do apes belong to?
Superfamily Hominoidea.
What are the two families within the superfamily Hominoidea?
Family Hylobatidae (Lesser Apes) and Family Hominidae (Great Apes).
What distinguishes the Family Hylobatidae?
They are smaller than great apes, have lower sexual dimorphism, and do not form nests.
What are the seven extant species of the Family Hominidae?
Orangutan (Pongo), Chimpanzee (Pan), Man (Homo), and Gorilla (Gorilla).
What percentage of DNA do humans and chimpanzees share?
98.4%.
What are some characteristics that distinguish humans from other apes?
Upright posture, bipedal locomotion, larger brains, language capabilities, symbolic thought, manufacture and use of complex tools, shortened jaw, and shortened digestive tract.
Brachiation
Arm swinging