TOPIC 3: The Bacterial Cell
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
196 Terms
Morphology
The study of the internal structure
Shape
Size
What are ways to categorize bacteria?
Cocci (Round/Spherical)
Bacillus (Rods)
Spirillum & Spirochete (Spiral)
What are the major shapes/forms of bacteria?
Cocci
Round or spherical bacteria
Diplococci
Round or spherical bacteria that is in pairs and facing each other and may also come in a lanceolate (leaf-like) or coffee-bean form
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Provide an example of lanceolate (leaf-like) shaped bacteria.
Neisseria Gonorrhoeae
Identify the coffee-bean shaped bacteria.

Streptococci
Round or spherical bacteria in chains and occur along a single axis

Streptococcus Pyogenes
What is an example of a streptococci?
Staphylococci
Round or spherical bacteria that has an irregular shape or grape-like clusters

Staphylococcus Aureus
What is an example of a staphyloccoci, which is known to be a causative agent of acne and food poisoning?
Tetrad
Round or spherical bacteria that come in groups of 4
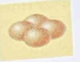
Gaffkya Tetragena
What is an example of a tetrad?
Sarcina
Round or spherical bacteria that are in cubical pockets of 8 (may look like 4 under a microscope but has a shadow at the back to differentiate from a tetrad)

Sarcina Lutea
What is an example of a sarcina, which is known to be a normal flora of the skin and large intestines?
Bacillus
Rod shaped bacteria
Fusiform Bacillus
Rod shaped bacteria that are spindle-like in shape
Wide in the middle and tapers at both ends
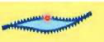
Diplobacilli
Rod shaped bacteria that occur in pairs

Snapping
Type of diplobacilli that is v-shaped

Slipping
Type of diplobacilli that is parallel

Streptobacilli
Rod-shaped bacteria that occurs in chains

Bacillus Subtilis
What is an example of a streptobacilli, which does not cause any disease and is a common lab contaminant?
Coccobacilli
Rod-shaped bacteria that is plump and oval
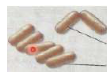
Escherichia Coli
What is a type of coccobacilli, which is normal flora of the lower intestine?
Vibrio
Rod-Shaped bacteria that is comma shaped/curved rod
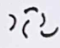
Vibrio Cholerae
What is an example of a vibrio, which causes cholera?
Spirillum
Spiral organisms that remain rigid in motion
Camplyobacter Jejuni
What is an example of a spirillum, which is a causative agent of diarrhea?
Spirochete
Bacteria with a spiral shape with long axis that bends when in motion; different genus are differentiated by the tightness of the coiling
Genus Treponema
Genus Leptospira
Genus Borrelia
Types of spirochete genus
Genus Treponema
Type of spirochete genus that is tightly coiled with the characteristics corkscrew appearance

Treponema Pallidum
What is an example of a corkscrew shape bacteria that causes syphilis, STD?
Genus Leptospira
Type of spirochete genus that is less tightly coiled with sharp hook like bends at the ends of the cell
Leptospira interrogans
What is an example of a leptospira bacteria?
Genus Borrelia
Type of spirochete genus that is much less tightly coiled which have the appearance of an extremely long, undulating, bacillary form

Borrelia burgdorferi
What is an example of a borrelia, which causes lime disease, virus, ticks?
Micron (μ)
What is the old unit for measuring bacteria size?
Micrometer (μm)
What is the metric system unit for measuring bacteria size?
1/1000th mm
1/25000th in
1 μm = ____ mm or ____ in
Width: 0.25-1 μm
Length: 1-3 μm
What is the size of bacteria generally?
0.4-2 μm
Size of cocci (in μm)
0.2-4 μm x 0.5-20 μm
Size of bacilli (in μm)
Haemophilus influenzae; 0.3-1 μm
What is the smallest known pathogenic bacilli and what is its size?
Bacillus anthracis; 1.5 μm across by 4 μm long
What is the largest known pathogenic bacilli and what is its size?
1-14 μm
Size of spirals (in μm)
External Structures
Ultrastructures of Bacteria
Flagellum
Long, whiplike structures that extend beyond the surface of the cell and glycocalyx and propel the cell through its environment
Proteus Species
What bacteria species sometimes swarm as a thin film of growth?

H (Hauch) Antigen
Flagella antigen; refers to the swarming growth in culture
False
True or False: Flagella can be seen with an ordinary stain.
Long, thin filaments
Hook
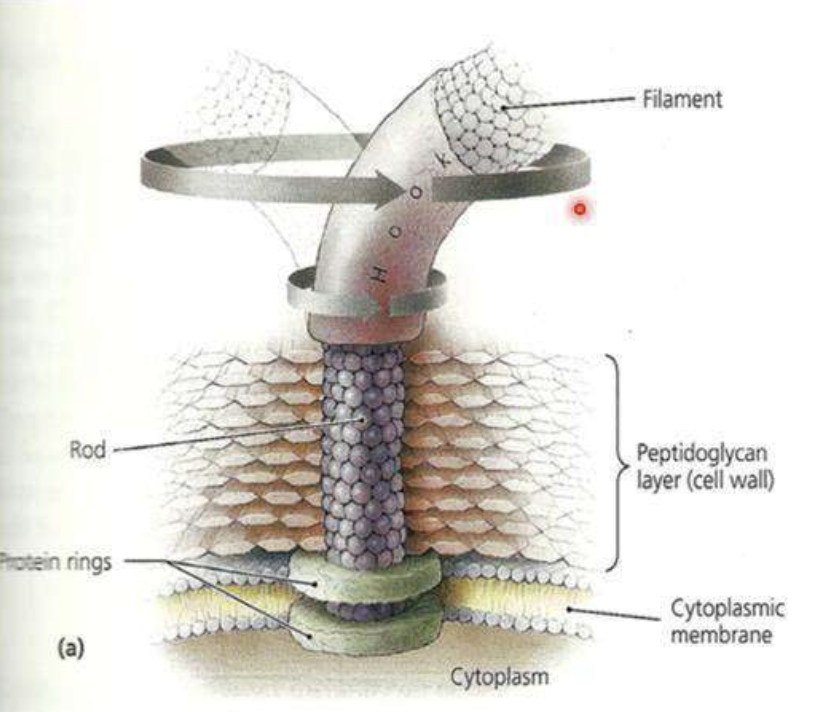
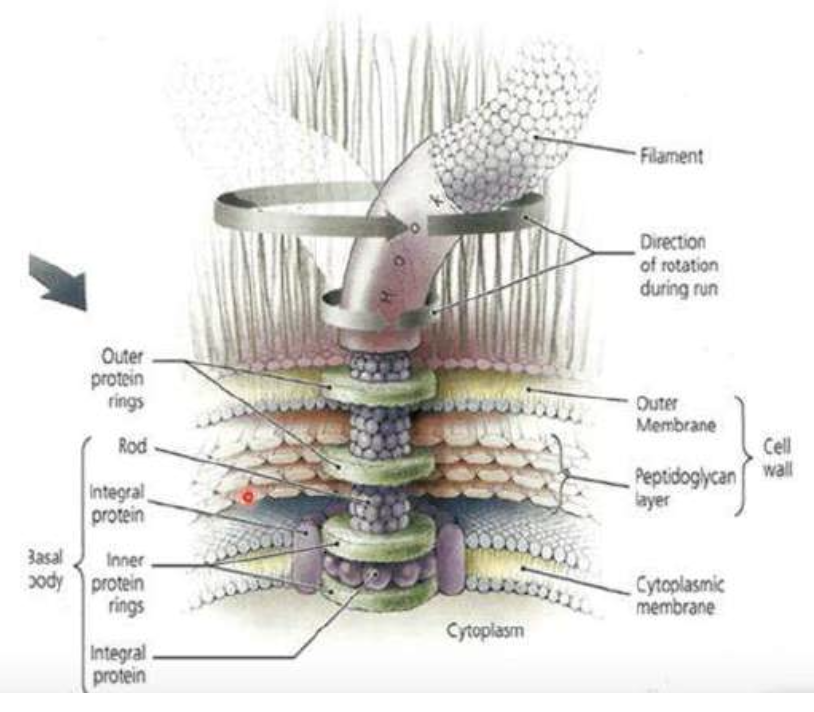
Basal body
Three parts of the flagella
Long, thin filament
Part of the flagella that is the whiplike shaft that extends out into the cell’s environment; composed of many identical globular molecules of a protein called flagellin
Flagellin
What are the identical globular molecules of a protein that composes the long, thin filament of the flagella?
Hook
Part of the flagella that is a curved structure where the base of the filament is inserted
Basal Body
Part of the flagella that anchors the filament and hook to the Cell Wall (CW) by means of a rod and a series of either 2 or 4 rings; Together the hook, rod, and rings allow the filament to rotate 360
Gram Positive Bacteria
The image shows the cell membrane of what bacteria type?
Gram Negative Bacteria
The image shows the cell membrane of what bacteria type?
Messea’s Classification
Classifies the various flagellar arrangements
Monotrichous
Lophotrichous
Amphitrichous
Peritrichous
Atrichous
According to Messea’s Classification, what are the flagellar arrangements prokaryotes may have?
Monotrichous
Flagellar arrangement in which cells have a single flagellum

Vibrio cholerae
Campylobacter jejuni
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
What are examples of monotrichous bacteria?
Lophotrichous
Flagellar arangement in which cells have a tuft of flagella at only one end of the cell

Amphitrichous
Flagellar arrangement in which cells have flagella at both ends

Pseudomonas species
What species of bacteria are mostly lophotrichous?
Peritrichous
Flagellar arrangement in which flagella cover the surface of the cell

Salmonella typhi
Proteus vulgaris
What are examples of peritrichous bacteria?
Atrichous
Flagellar arrangement that has no flagella

Shigella dysenteriae
Klebsiella pneumoniae
What are examples of atrichous bacteria?
Helical
Some spiral bacteria have amphitrichous flagella that spiral tightly around the cell (instead of protruding into the surrounding environment). This produces what type of movement for spirochetes?
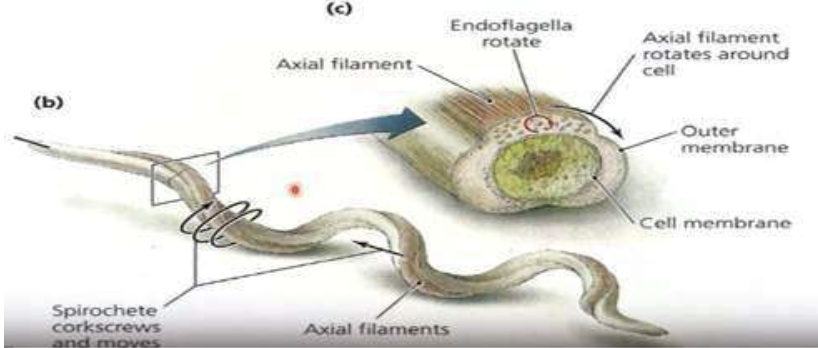
Endoflagella
Some spiral bacteria have amphitrichous flagella that spiral tightly around the cell (instead of protruding into the surrounding environment). This is considered what which form an axial filament that wraps around the cell between the cell membrane and outer membrane?
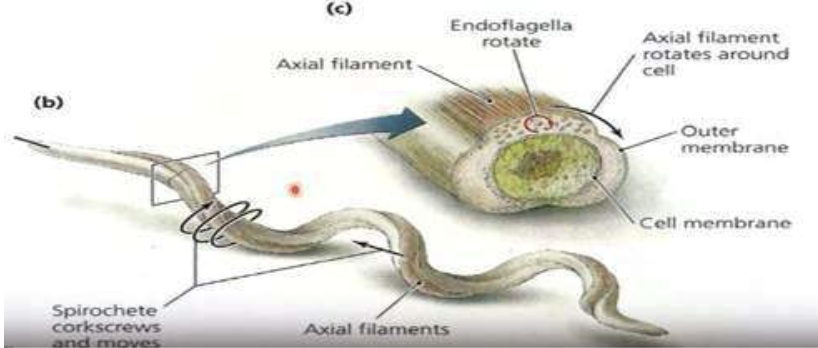
Motility of the cell wherein it can flee from a harmful environment or to a more favorable environment with food and light available
What is the function of the flagella?
Phase Variation
Mechanism in which when bacteria sense that antibodies are developing, it will change to its antigenic structure so that it will not be killed by the antibodies
Microfibrils: Pili & Fimbriae
Nonmotile extensions of prokaryotes unlike flagella
Fimbriae
Hairlike, sticky, proteinaceous, bristle-like projections
Used by Gram (-) bacteria to adhere to one another and to substances in the environment (adhesins)
May be hundreds
Usually shorter than flagella
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
What is an example of a bacteria with fimbriae, which adheres to host surfaces like the mucous membranes of the reproductive tract?
Pilus
Tubules composed of a protein called pilin
Longer than fimbriae but shorter than flagella
Typically 1-10 present per cell
Used in moving across a substrate or towards another bacterium
Sex/conjugal -__ mediate the transfer of DNA from one cell to the other
Pilin
What protein is pilus composed of?
Serve as adhesins, lectins
Conduit for the passage of DNA
Surface translocation
What are the importances of microfibrils (fimbriae and pili)?
Adhesins
(Importance of microfibrils)
Proteins that allow bacteria to attach to host cells
Lectins
(Importance of microfibrils)
Any class of proteins which bind specifically to certain sugars and cause agglutination to particular cell types, specific for fimbriae
Conduit for passage of DNA
(Importance of Microfibrils)
Via sex/conjugal pili
Surface translocation
(Importance of Microfibrils)
Slow twitching or gliding motion for non-flagellated material like cocci
Fimbriae.
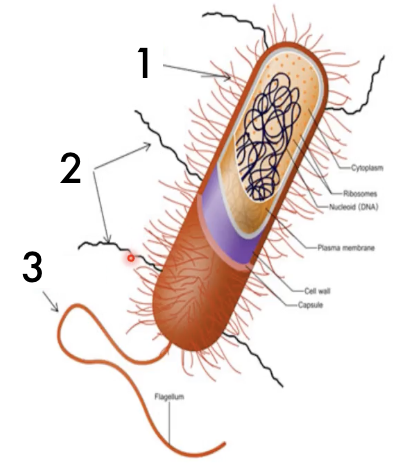
Identify (1)
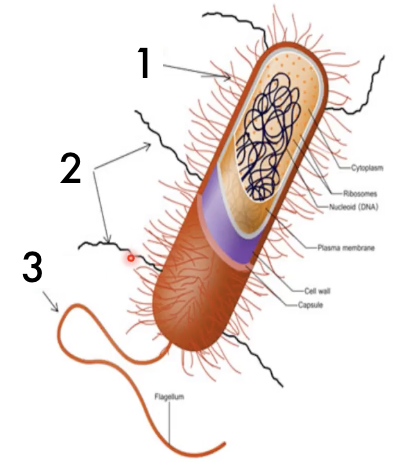
Pili
Identify (2)
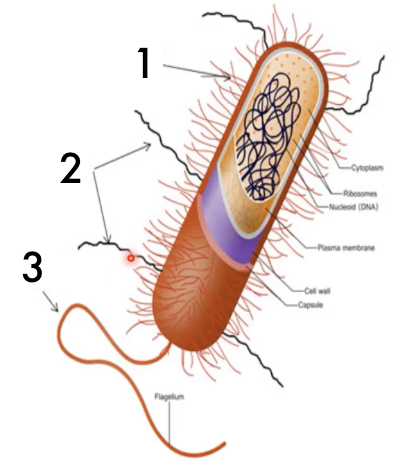
Flagellum
Identify (3)
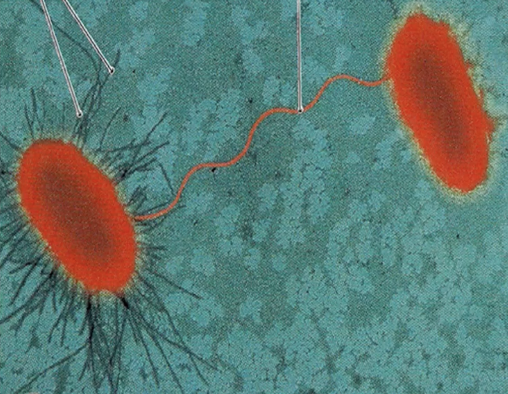
Sex/Conjugal Pili
Identify the structure between the bacteria.
Gram (+) has a thick peptidoglycan layer
What is the difference between the two types of prokaryotic cell wall (Gram (+) and Gram (-) bacteria)?
Cell Envelope
Consists of the membrane structures surrounding the cytoplasm; the outermost structures
Cell Wall/Murein Layer
Periplasm (in Gram (-) bacteria only)
Outer membrane (in Gram (-) bacteria only)
Cytoplasmic/cell membrane
What is the cell envelope compoed of?
Cell Wall/Murein Layer
Component of the cell envelope that is composed of the peptidoglycan macromolecule
Periplasm
Outer membrane
Components of the cell envelope that is only found in Gram (-) bacteria
Cytoplasmic/cell membrane
Component of the cell envelope that encloses the cytoplasm and some produce capsules and slime layers
Glycocalyx (Glycocalyces)
Surface adherence structure that is a polypeptide or polysaccharide, either an amino acid or sugar, enriched coating that covers the outside of many eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells that functions as a barrier between cells and its surroundings
Capsule
Slime Layer
2 Kinds of Glycocalyx
Capsule
Kind of glycocalyx made up of organized repeating units of organic chemicals firmly attached to the cell surface
Slime Layer
Kind of glycocalyx that is loose, water-soluble
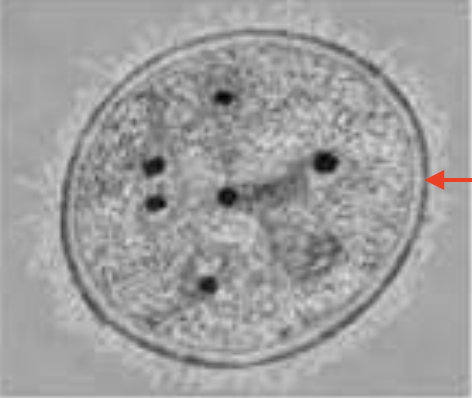
Capsule
Identify the type of glycocalyx.
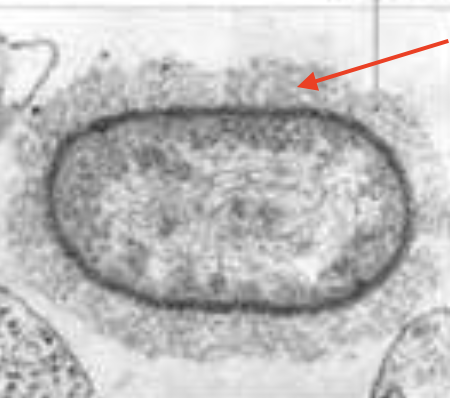
Slime layer
Identify the type of glycocalyx.
Protect the cell from desiccation (removal of moisture)
Feature of numerous pathogenic prokaryotes
Important in organisms’ ability to survive and cause disease
What is the significance of glycocalyces?
Vi antigen
Heat labile somatic antigen of capsules thought to be associated to virulence or severity and harmfulness of a disease in bacteria