Radiation Dose, Risk, Health Effects and Protection
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What is absorbed dose?
Direct measurement of radiation (S.I. unit is GRAY - Gy)
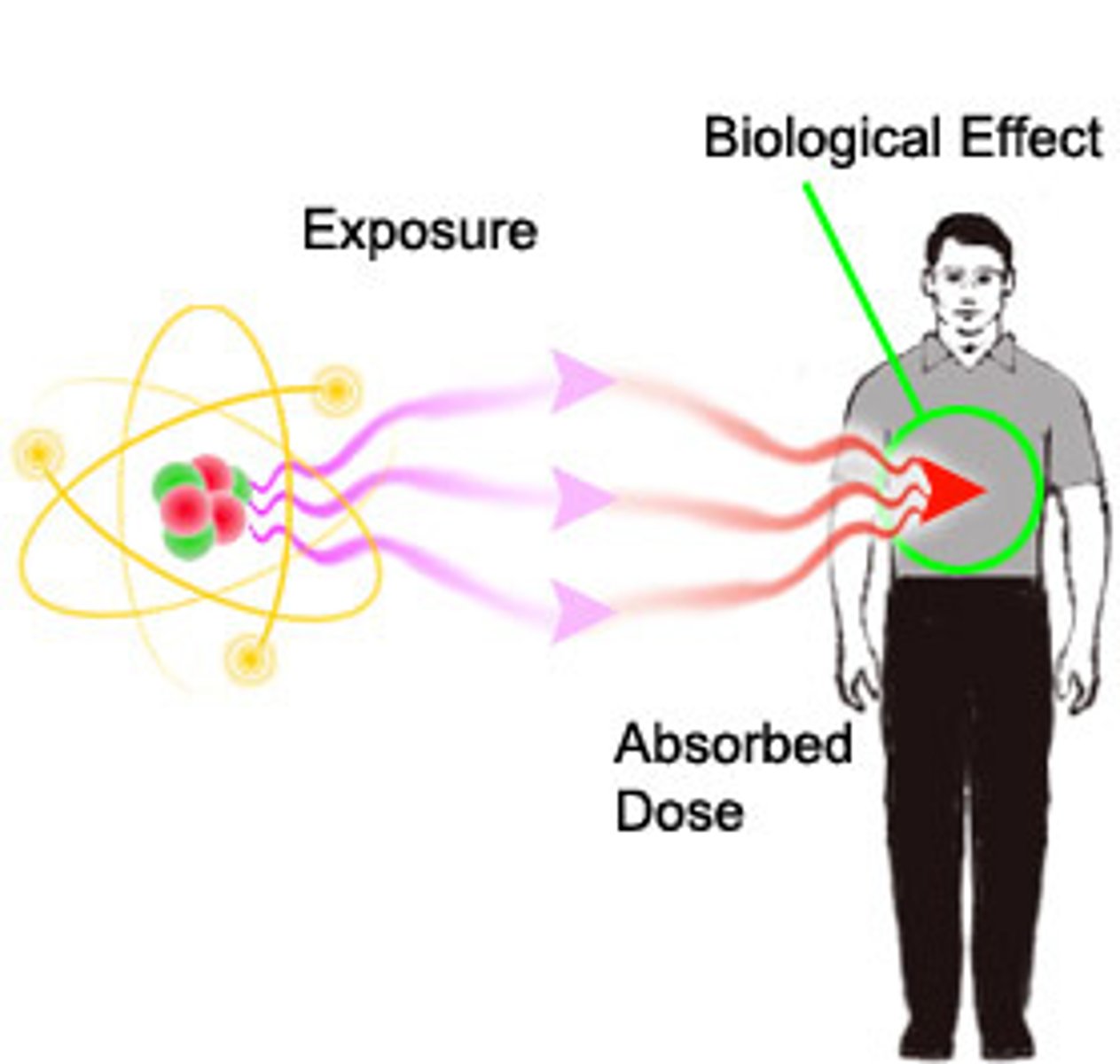
What is the effective dose?
Measure of risk (i.e. chance or probability) of damage, such as cancer, to the whole body (S.I. unit is Sievert - Sv)

What is 1Gy defined as?
The absorption of one joule of radiation energy per kilogram of matter (gas, liquid, solid)
What would happen if 3-5Gy was absorbed by the whole body?
50% of the population would die :/
How do DAP meters measure a radiation dose?
Uses an 'ionisation chamber' - measures the amount of air ionised by the radiation multiplied by the absorbed dose

What isn't the absorbed dose useful for as diagnostic radiographers?
- Doesn't indicate risk (probability, chance) of health effects from radiation
- Does not consider the radiosensitivity of different organs
- Doesn't consider the type of radiation (alpha, beta, gamma, x)
- Can't communicate the risk of inducing harm from absorbed dose alone
What is the equivalent dose?
- A weighting factor related to the type of radiation (i.e. alpha, beta, gamma or x)
- For X-rays, the weighting factor = 1
- Measured in Sievert (Sv)
What is the equivalent dose for plain film radiography?
Equivalent dose = ABSORBED dose
What type of effects does the absorbed dose measure?
Absolute (deterministic) effects
What type of effects does the effective dose measure?
RISK (probability or chance) = STOCHASTIC
What is the effective dose useful for?
- Considers organs irradiated and their sensitivity to radiation
- Measure in Sv (mSv at diagnostic radiation doses)
- Relates to stochastic effects
What is the tissue weighting factor of gonads?
0.08
What 6 organs/biological structures have the tissue weighting factor of 0.12?
Bone marrow, colon, lung, stomach, breasts (and rest of body)
What is the tissue weighting factors for the brain, salivary glands, bone surface and skin?
0.01
What is the tissue weighting factor for the bladder, liver, oesophagus and thyroid?
0.04
What is the risk of fatal cancer in 10-15yrs following a lumbar spine X-ray?
1 in 15,000 (very low)
What is indirect damage?
When radiation interacts with non-critical atoms or molecules, especially water which results in production of free radicals
What is direct damage?
When radiation interacts directly with the DNA causing ionisation of the atoms in the DNA molecule which leads to disruption of DNA
What are free radicals?
Ionised atoms - do not have a neutral charge
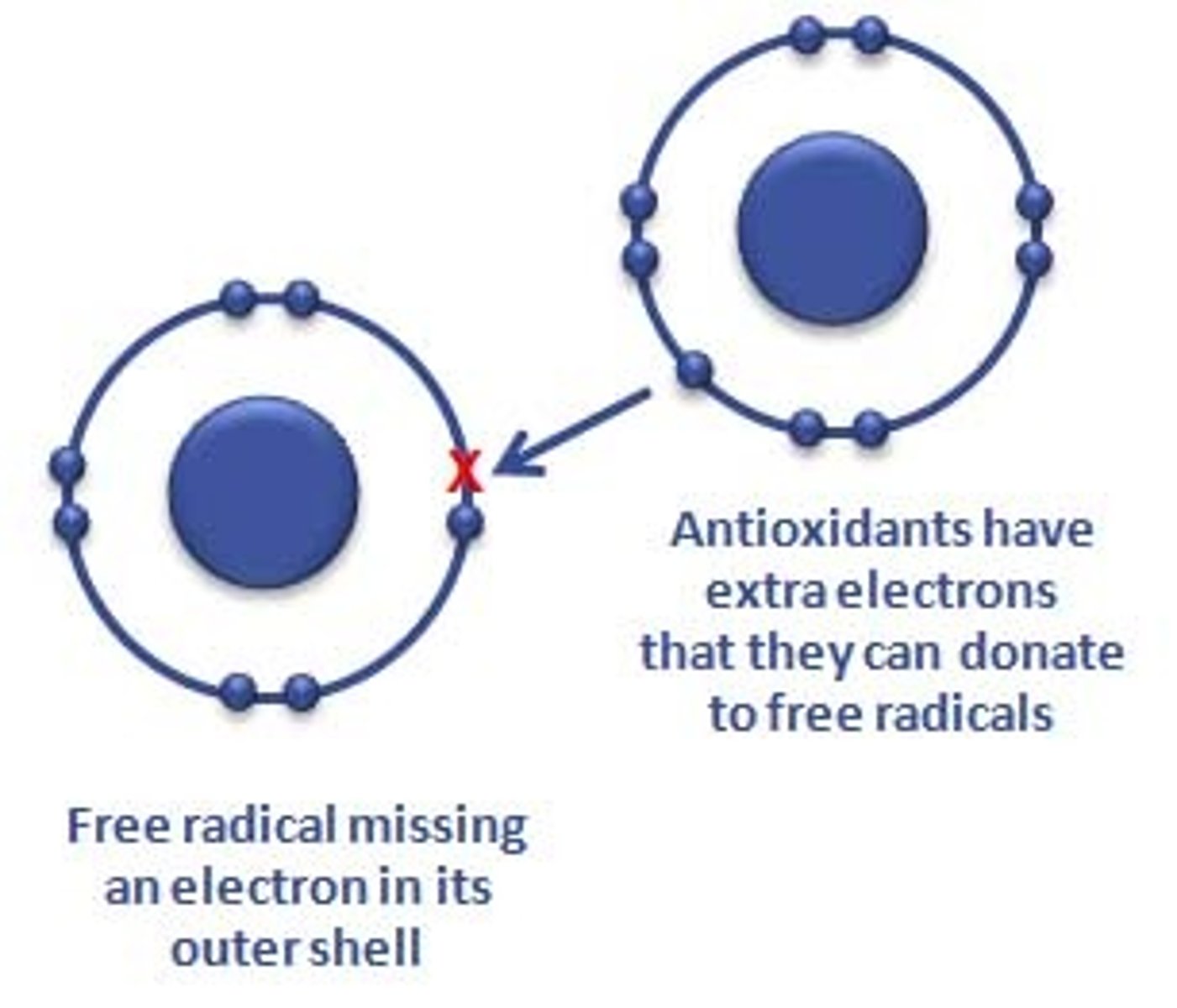
How do free radicals affect biological functioning of the cell?
- Disrupting fatty membranes responsible for intracellular transport (diffusion)
- Disrupting protein molecules
- Damaging lysosomes (sacs containing degenerative enzymes)
- Damaging chromosoins and nucleic acids (damage to DNA = cancer)
What are some of the deterministic effects of radiation dose?
- Cataracts (<0.5Gy)
- Skin erythema (0.5-2Gy) + skin cell death with scarring (necrosis)
- Reproductive organ - permanent infertility
- Hair loss (2-5Gy)
- Bone marrow damage/reduction of blood cell production
- GI mucosa lining loss
- CNS tissue damage
- Death (3-5Gy)
What are some of the stochastic effects of absorbed radiation?
- Cancers - increased radiation exposure increases risk
- Heritable effects to offspring - if reproductive cell DNA is damaged and causes mutation
What is the radiation hormesis model?
A cell or response that is biphasic to increasing amounts of stress, beginning with favourable and moving to unfavourable
What are the deterministic effects of X-raying a pregnant female?
- Foetal death
- Foetal malformation
- Growth restriction
- Mental impairment
What are the stochastic effects of X-raying a pregnant female?
- Childhood cancer
- Heritable effects (negligible risk)
From which age should you ask whether your patient could be pregnant or not?
10 years old
What is immobilisation?
Elimination of movement essential to reducing patient dose

How do you reduce patient dose with positioning?
- Radiographic projection (collimation)
- Immobilisation
How do you reduce patient dose with technical factors?
- Interrelationship with prime factors
- Kilovoltage range
- Milliamperage and time
- Distance
- Focal spot size
- Filtration
- Field size
- Subject part density
- Grids
- Gonad shielding (controversial!!)
How do you decrease patient dose with kilovoltage range ?
Increase in kVp with compensation in mAs
How do you reduce patient dose with milliampere-seconds (mAs) ?
Keep the mAs at the lowest level possible
How do you estimate ESE?
- Maximum exposure to the body (calculated at minimum SOD)
- Apply inverse square law (derive mR1 from mR/mAs chart - derive SOD from SID and object to receptor distance (OID))
- Better to overestimate exposure
What is the inverse square law?
The intensity of radiation is inversely proportional to the square of the distance
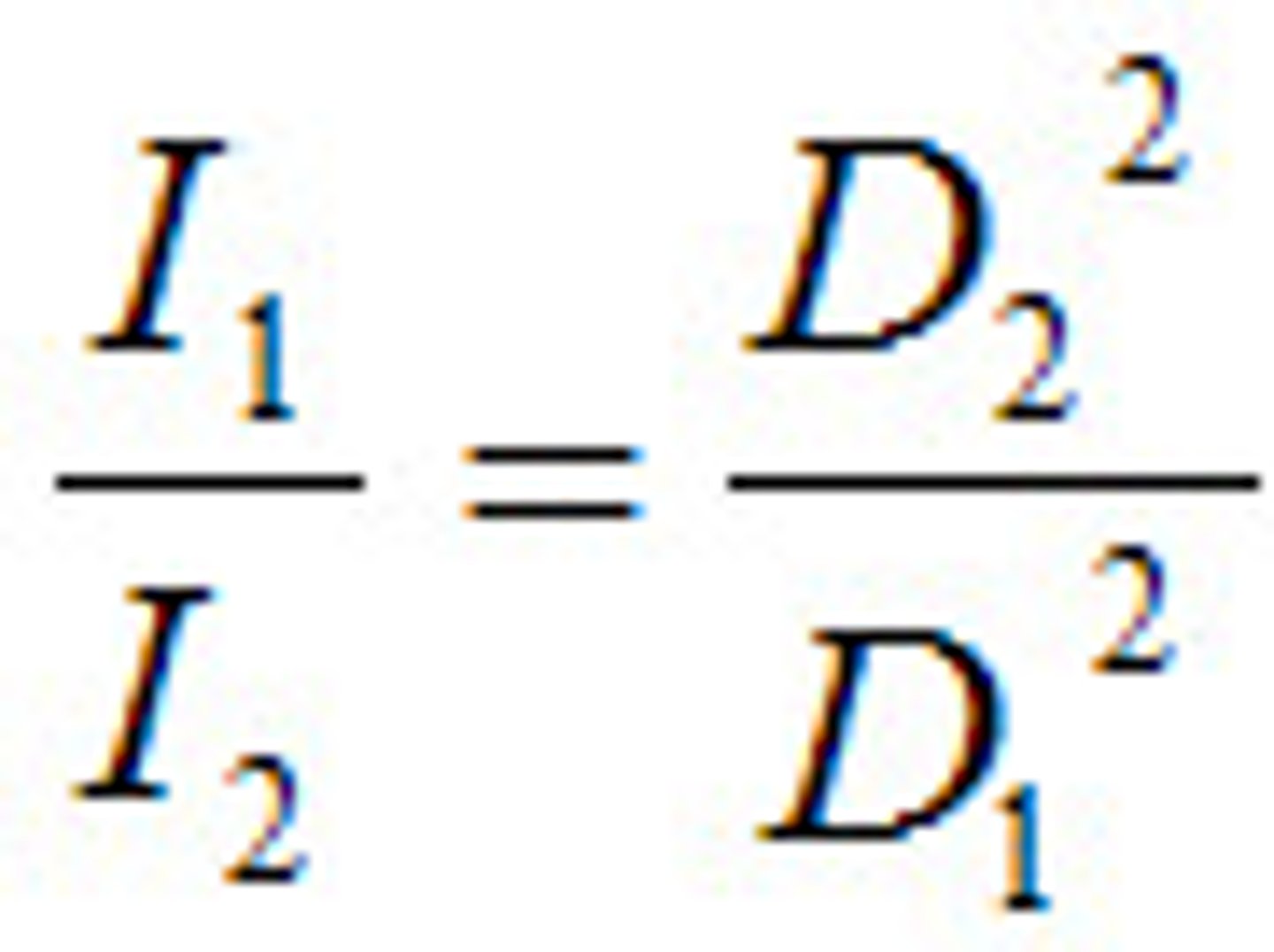
What does I stand for in the inverse square law?
Radiation intensity
What does D stand for in the inverse square law?
Distance
What does IR(ME)R state about patient radiation protection?
1) Limitations
- Do they need this exam?
- Consider previous imaging
- Any other way to answer the question?
2) Justification
- Do the benefits outweigh the risks?
3) Optimisation
- Collimation!
- ALARP (inc. Dose Reference Levels and equipment quality assurance)
What does IRR 17 state about staff radiation protection?
- Keep time of radiation short
- Keep large distance from radiation source
- Insert shielding material between source and worker
How can you decrease ESE with increased filtration?
With modification in kVp
How can you increase ESE with increased filtration?
With modification in mAs
What are the 3 types of accurate shielding for decreasing patient dose?
- Flat contact
- Shadow
- Shaped contact
What happens with a higher ratio grid?
Requires an increase in mAs, and increases patient dose