C25 - Electric Potential
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Electric potential difference
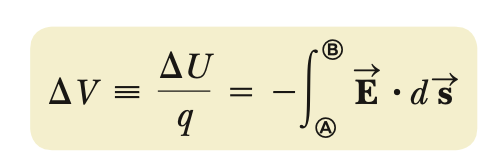
positive particles move towards lower e-potential
negative particles move towards higher e-potential
electron volts (eV)
1 eV = 1.6 × 10-19 C • 1 V = 1.6 × 10-19 J
The energy change resulting in moving one e-charge (±1.6 × 10-19 C) through a distance of 1 V
Electric potential (uniform field)
∆V = -Ed
∆U = -qEd
d = parallel distance across field line
E-field lines always point towards DECREASE in potential energy ↓ ↓ ↓
Electric potential & energy (point-charge)
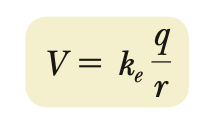
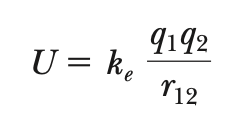
total potential energy (multiple point-charges)
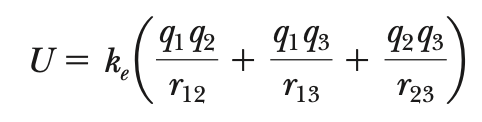
Electric potential (continuous distribution)
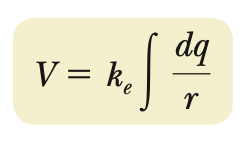
equi-potential surface
surface/area on which all points have equivalent V
electric field from potential
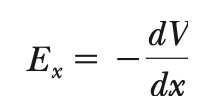
*-∇V
corona discharge
visible heat & light radiation from conductors near an E-field in high-voltage systems
ionization