Topic 2 - Structure and Bonding
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Define Ionic bonding
the electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions
what determines the strength of an ionic bond?
ionic radius
ionic charge
stronger when ions are smaller/higher charge
Explain the trend in ionic radius down a group
ionic radii increases going down the group. Ions have more shells of electrons and so the outermost electron experience less pull from positive nucleus
explain the trend in ionic radius for set of isoelectronic ions
proton number increases
same number of electrons
so the nucleus attraction between the outermost electrons and nucleus increases and ions get smaller
define covalent bonding
electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of electrons and two nuclei
define metallic bonding
electrostatic attraction between the positive metal ions and the sea of delocalised electrons
in what type of solvents do ionic lattice dissolve?
polar solvents e.g. water
Why are ionic compounds soluble in water?
water has a polar bond
hydrogen atoms have a delta positive charge
oxygen have a delta negative
these charges are able to attract charged ions
what is the effect of multiple covalent bonds on bond length and strength?
double/triple bonds exert greater electron density and so the attraction between nucleus and electron is greater resulting in a shorter and stronger bond.
what is a lone pair?
Electrons in the outer shell that are not involved in the bonding.
What is a dative bond?
A bond where both of the shared electrons are supplied by one atom
Draw the bonding structure diagram for Al2Cl6
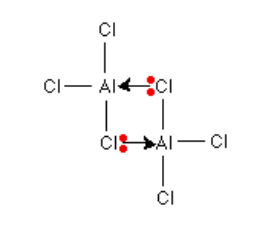
what does expansion of the octet mean?
When a bonded atom has more than 8 electrons in the outer shell.
Describe bonding in simple molecular structure
Atoms within the same molecule are held by strong covalent bonds and different molecules are held by weak intermolecular forces
dissolve in non polar solvent
How does graphite conduct electricity?
Delocalised electrons present between the layers are able to move freely carrying the charge
name shapes of molecules
linear
trigonal planar
tetrahedral
trigonal bipyramid (5 bonded pairs)
Octahedral (6 bonded pairs)
pyramidal (1 lone pair, base tetrahedral)
bent (2 lone pairs)
shape of molecules/ions determined by the repulsion between the electron pairs that surround a central atom
define electronegativity
the ability of an atom to attract the pair of electrons in a covalent bond
measured on Pauling scale
what does it mean when the bond is non-polar?
the electrons in the bond are evenly distributed
How is a polar bond formed? Why some molecules are non-polar
Bonding atoms have different electronegativities
They are symmetrical, which means dipoles cancel out, there is no overall dipole. Or have a lone pair of electrons
define intermolecular force
Attractive force between neighbouring molecules
describe permanent dipole- induced dipole interactions
describe permanent dipole-permanent dipole interactions
when a molecule with a permanent dipole is close to other non polar molecules it causes the non polar molecule to become slightly polar leading to attraction
some molecules with polar bonds have permanent dipoles - forces of attraction between those dipoles and those of neighbouring molecules
describe london forces/ how its formed
caused by fluctuations in electron density around the molecule
leads to instantaneous dipoles
instantaneous dipole induces a dipole in nearby molecules
induced dipoles attract one another, weak force of attraction between dipoles
greater force in larger molecules due to more electrons
affect by number of protons/electrons and whether the molecule is branched
why is ice less dense than water?
In ice, the water molecules are arranged in a orderly pattern. It has open lattice with hydrogen bonds.
In water, the lattice is collapsed and molecules are closer together.
Why does solubility depend on chain length?
Insoluble when long chain - non-polarity of C-H bond takes priority
Expanding the Octet
from P onwards (period 3)
able to hold extra electrons in the empty d subshell as it is easily accessibly
close in energy to p subshell
endothermic - compensated by making more bonds
Factors affecting bond length
atomic radii
nuclear charge
single/double bonds - larger number of electrons shared so stronger force of attraction
why do lone pairs repel more than bonding pairs
lone pairs bigger and shorter, more concentrated distribution of negative charge held closer to the nucleus
Ione pairs pushed electrons by 2.5 degree, caused by repulsion of electrons
Why shapes of molecules?
number of bonding pairs/bonding regions/lone pairs
electron pairs repel to be as far apart as possible to maximise separation to minimise repulsion
lone pairs repel more strongly than bonding pairs, bonding pairs repel each other equally
the repulsion between lone pair and bonding pair is stronger than bonding pair and bonding pair
so the molecule adopts the shape
difference in electronegativity
small difference (0-0.4)- covalent bonding
medium difference (0.4-1.7) - polar covalent bonding
large difference(>=1.7) - ionic bonding - electrons are completely transferred to the more electronegative atom
Explain the trend in boiling temperatures of hydrogen halides
as group goes down, atomic radii increases(further distance between valence electrons and nucleus)
electron number of halides increases
stronger London force
so higher boiling point, more energy required to weaken London force
Why magnesium chloride has a higher solubility in water than lithium fluoride
hydrogen bonding in water must be overcome
attraction between ions must be overcome
water molecules hydrate the ions (i.e. O2- to cations and H+ to anions)
the energy released when ions are hydrates compensates for the energy needed to overcome the lattice energy in ammonium nitrate
magnesium ions have a 2+ charge whereas lithium ions have a + charge
ions in magesium chloride are more strongly hydrated
this compensates for the strong forces that must be overcome
Why is fluorine more electronegative than boron
greater nuclear charge/protons
smaller atomic radius
so greater pull from nucleus on bonding electrons
which bond is stronger, B-Cl or B-F
B-F because this has a shorter bond length
because F has a smaller atomic radius/less shielding
What happens when an ionic compounds have a huge difference in electronegativity
less covalent character
more ionic character
Suggest how a chemical process could have a higher yield but a low atom economy
Has a higher yield if there is a good conversion of reactants to product, but has a lower economy if waste produce may be produced
How to form hydrogen bonds
caused by water having a permanent dipole on the OH bond
oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen
hydrogen bond is formed between molecules
Why is PCl5 possible but not NCl5
Phosphorus can expand its octet, but Nitrogen does not have a (2)d orbitals, so can only accommodate 8 electrons in valence shell