Arthritis and Finger Deformities - Mod 4
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Osteoarthritis (OA) is characterized by
erosion of articular cartilage and a decrease in the synovial fluid.
Osteoarthritis is also called
Degenerative Joint Disease (DJD)
Osteoarthritis is seen in what joints?
DIP, PIP, and CMC joints of the UE
Rheumatoid Arthritis is characterized by
progressive, chronic systemic disease in which the immune system attacks the joints
inflammatory changes of the joints, tendons, and their sheaths
results in pain, weakness, and dysfunction
Rheumatoid Arthritis results in
pain, weakness, and dysfunction
T or F. Rheumatoid arthritis can affect any joint of the UE.
TRUE
OA Clinical Presentation
localized inflammation
pain in joint
loss of flexibility
soft tissue contractures
osteophytes
loss of joint congruity (when severe)
Osteophytes are
new bone growth
Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Presentation
windswept fingers, instability, subluxation, or complete dislocation of joints, and muscle imbalance
periods of exacerbation and remissions
small joints are the most affected
Rheumatoid Arthritis Progression
muscle imbalance, instability, subluxation or complete dislocation
in advanced state - tendon rupture and weak ligaments
What is the most common type of arthritis in children under 16?
juvenile RA
What is the focus of treatment in RA patient population?
address the symptoms but also work on improving function and protection of the limb long term
T or F. RA is an acute disease.
FALE - longterm
Arthritis of the Elbow joint symptoms
same as the other joints mentioned with the addition of - loss of motion in proximal and distal radioulnar joints which affects flexion/extension and pronation/supination, flexion contracture present, collateral ligament laxity, and bursitis.
Loss of motion in the proximal and distal radioulnar joint affects
flexion/extension and pronation/supination
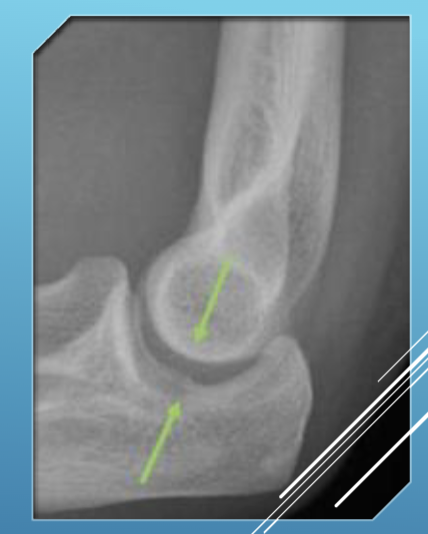
Drop Sign
The elbow joint space being larger than 4 mm of space indicates arthritis
Arthritis Presentation in the Hand
wrist will deviate radially
fingers will deviate ulnarly
may include finger deformities
‘windswept fingers’
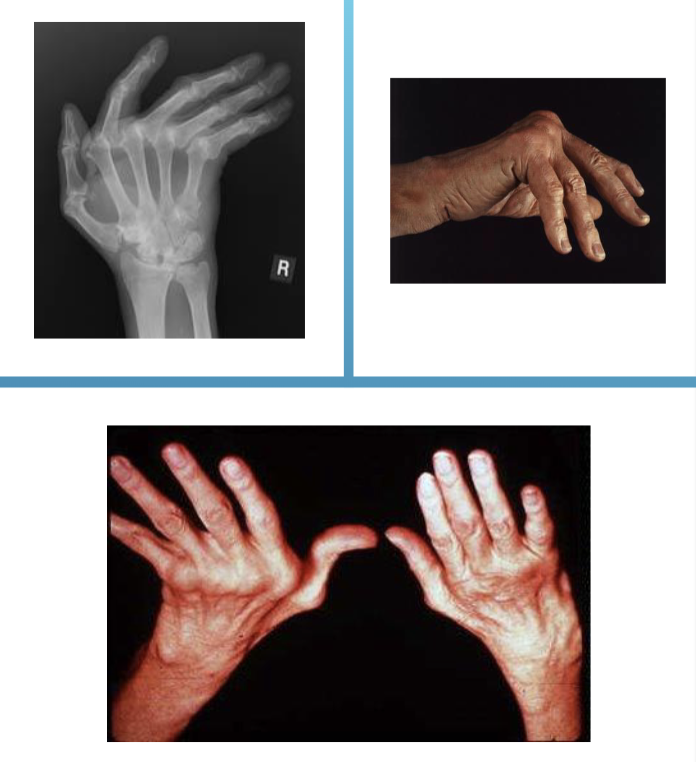
T or F. OA causes more finger deformities than RA.
FALSE opposite is true
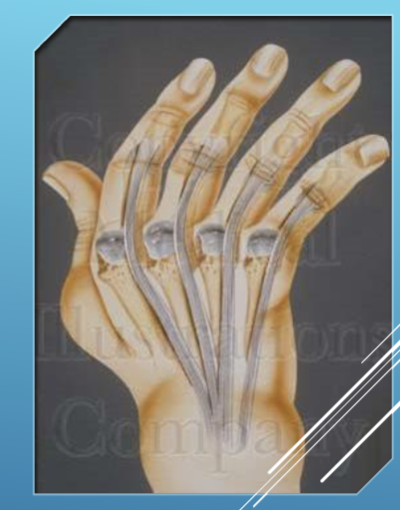
Arthritis in the Metacarpal Phalangeal Joint
Deformities are usually manifested by palmar subluxation and increasing ulnar deviation.
the extensor tendons often sublux ulnarly into the valleys between the MCP joints
the flexor tendons may also slip ulnarly when the collateral ligaments are stretched by the inflamed and edematous joint.
Arthritis in the Proximal Interphalangeal Joints
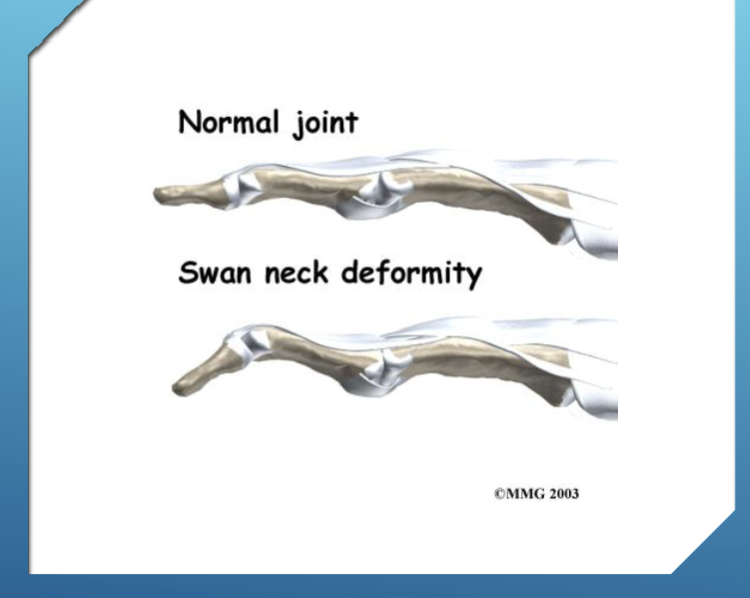
Deformities are usually Boutonniere or Swan Neck.
Synovitis of the joints leads to a shortening of the collateral ligaments and stretching of the joint capsule.
lateral bands displace palmarly thus the Boutonniere deformity.
lateral bands are displaced dorsally thus the Swan neck deformity
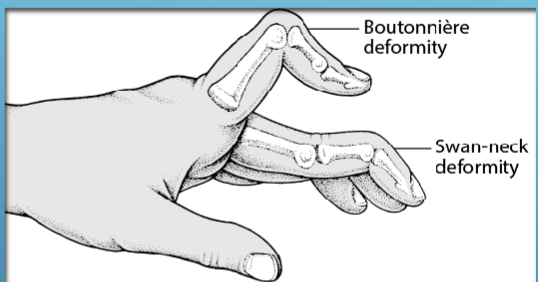
Boutonniere =
button hole in french - because the slit in the tendon looks like a button hole with a bone sticking through
Boutonniere Deformity
Extension of MCP, Flexion of PIP, and Extension of the DIP
Way to remember flex/ext. in Boutonniere Deformity.
EFE
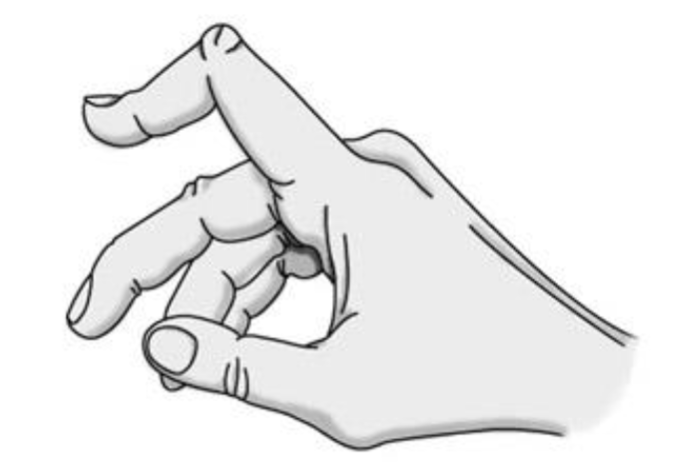
Swan Neck Deformity
Flexion of MCP, hyperextension of the PIP, and flexion of the DIP
Way to remember the flex/ext. of the Swan Neck Deformity.
FEF
Swan Neck Deformity of the thumb
Flexion of CMC, Hyperextension of MCP, and Flexion of the IP
Boutonniere Deformity of the thumb
Extension of the CMC, Flexion of MCP, Extension of the IP
Deformity of the _______ joint will be flexion or hyperextension depending on the ___________ at the MCP and PIP joint.
Distal Interphalangeal (DIP), pathomechanics
Indications for Splinting
decrease inflammation
properly position joints - further deformity
rest and support weakened structures
improve function through better stability and position
aid in postoperative rehab
Orthosis Design Considerations
biomechanical 3 point force system
moment arm - smaller in UE (more force)
pressure - small surface area
shear - suspension (biggest struggle for us)
material properties
degree of deformity - may indicate custom fabrication
T or F. UE orthoses are harder to suspend than LE orthoses.
TRUE
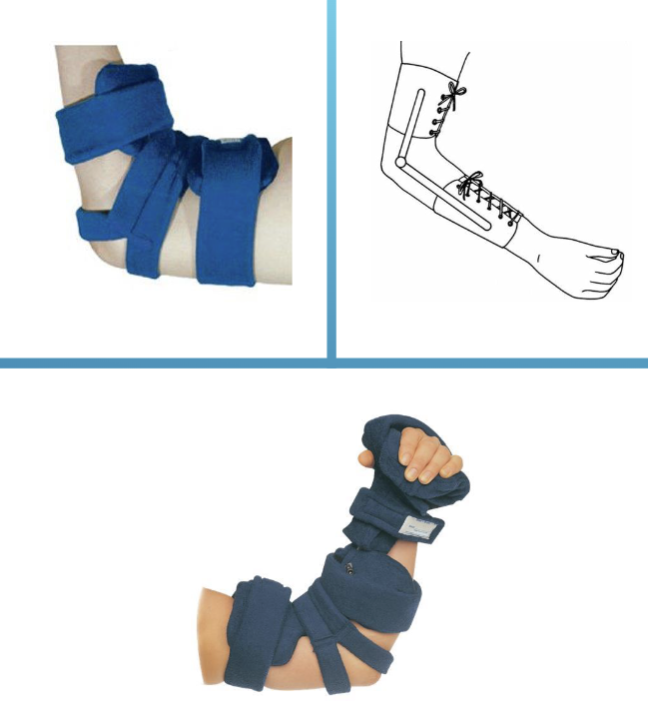
Elbow Orthosis Considerations
Custom fit or custom - EO, EWHO
Consider joint position for function
with or w/o elbow joint
set screws or pins to adjust ROM
locks, springs
Joint alignment
w/in 1 cm from apex of humeral epicondyle
may prevent migration/ mal alignment
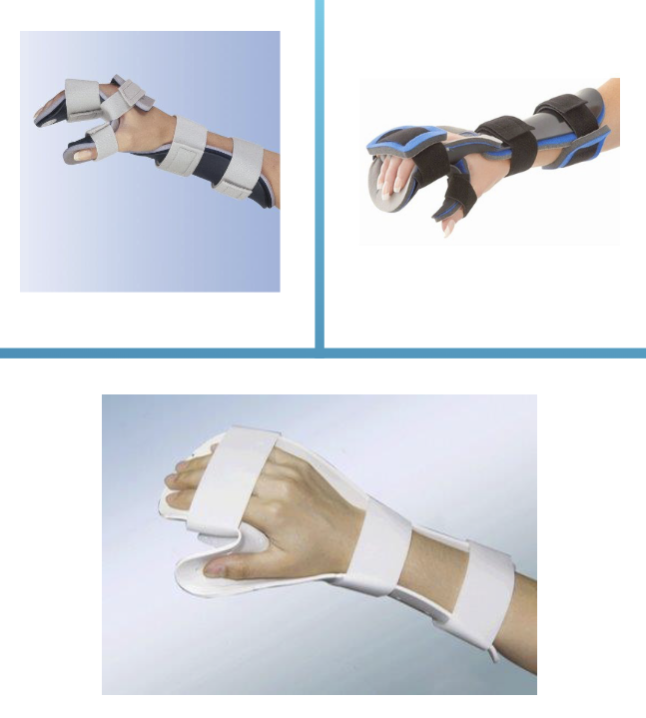
Resting Hand Splint positioning
static positioning of the wrist and digits during acute episodes to decrease pain and to align the joints.
Wrist in 10-20° extension and 5° ulnar deviation.
Thumb abducted and opposed.
Fingers in flexion.
Wrist Orthosis
wrist cock-up splint
10-30° of extension
OTC, custom-fit, or custom fab
with or without a thumb spica
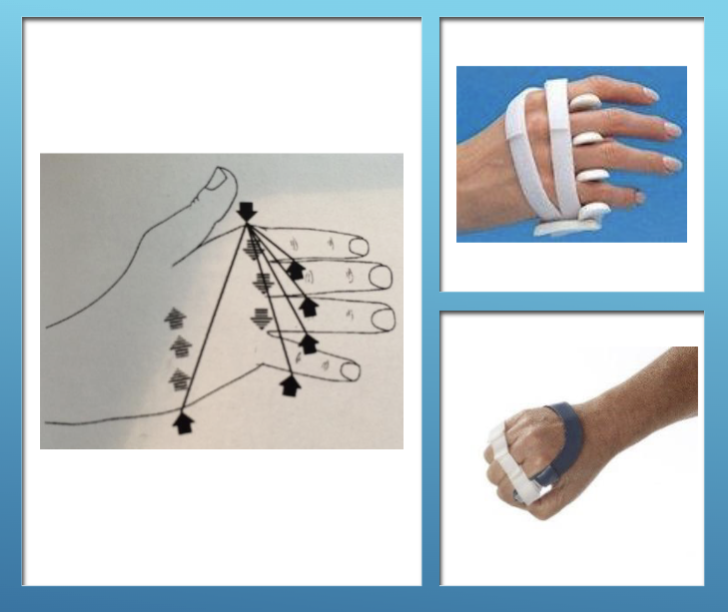
Ulnar Deviation Orthosis
Supports the MCP joints and provides radially directed force
3 point forces are on the picture
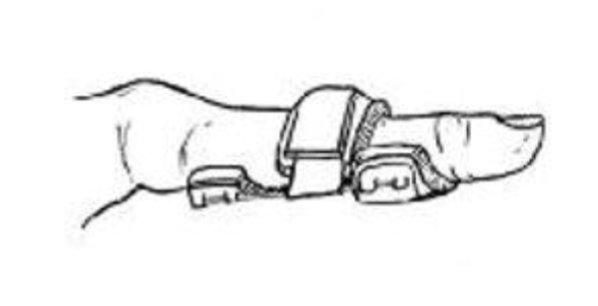
Thumb Spica Splints
hand or forearm based
provide support to the CMC and MCP joints for acute Rheumatoid Arthritis or Osteoarthritis
JUST ON RADIAL SIDE
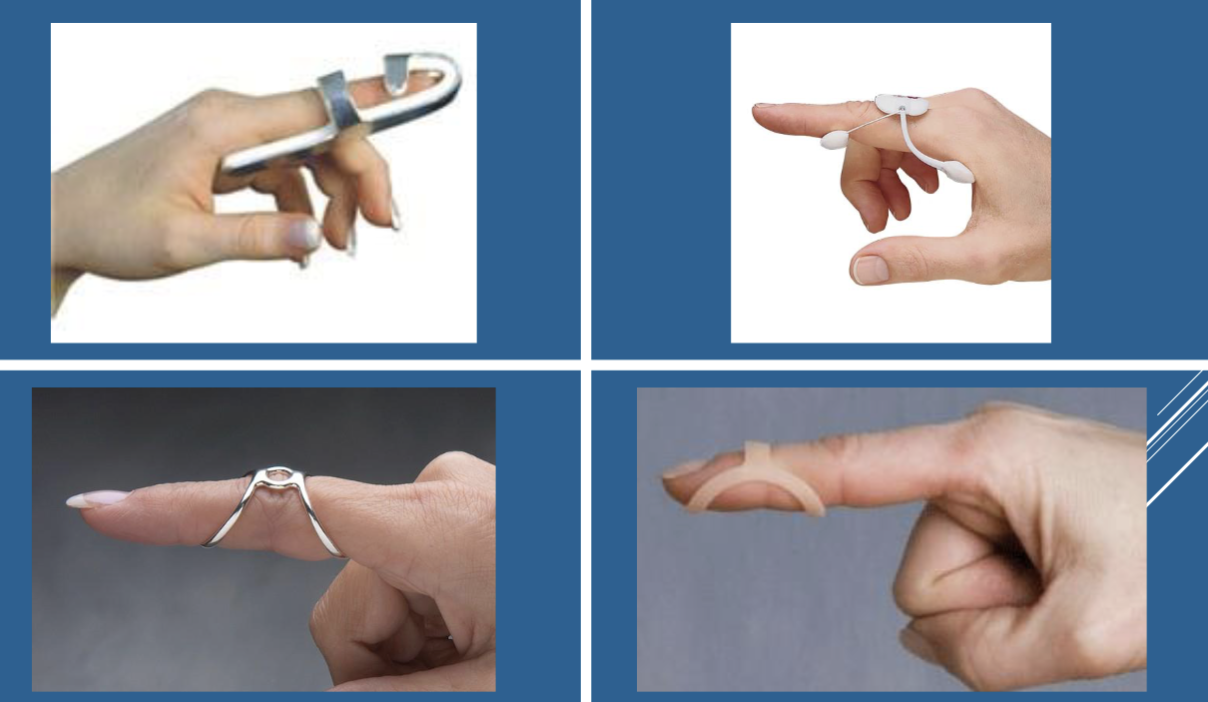
Interphalangeal Boutonniere or Swan Neck Splints
position opposite of the deformity
Casting for a WHFO
Mark landmarks - radial and ulnar styloids, MCP and IP joint, CMC and IP joints of the thumb, any bony prominences
Measure - ML at the styloids and MCP joints
Circumferences at the wrist, MCP
Lengths - wrist to fingertip, wrist to elbow
Modifying a WHFO
remove - roping from the mold
draw - trimlines
accentuate - palmar arch
apply - build ups on styloids and joint inside the trimlines, buildups on the trimlines
build out - finger pan to keep to ML measured at MCP joint