Online practical 1- is blood real
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
what volume of liquid can a P10 pipette hold + tip colour
0.5-10ul
white tip
what volume of liquid can a P50 pipette hold + tip colour
5-50ul
yellow tip
what volume of liquid can a P200 pipette hold + tip colour
50-200ul
yellow tip
what volume of liquid can a P1000 pipette hold + tip colour
100-1000ul
blue tip
what happens when you forget to press pipette plunger to 2nd stop when expelling liquid
inaccurate pipetting (not enough liquid)
what happens when you press the pipette plunger to the 2nd stop before putting the tip on
inaccurate pipetting (too much liquid)
what happens when you hold the pipette horizontally/with the tip pointing up when theres some liquid in there
damage to the pipette
what happens when you release the plunger too quickly/unevenly when taking liquid in
creates air bubbles in the tip (not enough liquid)
what is spectrophotometry
identifies compounds & their conc based on wavelengths of absorbed light
more advanced colorimeter
what is the visible range of wavlengths
340-700nm
what light can molecules with conjugated bonds absorb + why
UV & visible range
double bonds can combine & electrons spread all over the atoms
energy needed to promote outer electrons is lowered
5 conjugated molecules
pigments
vitamins
nucleic acids
proteins
Hb
what does a spectrophotometer measure
amount of light absorbed by a sample at particular wavelengths of light
relationship between absorbance & conc of absorbing molecules
absorbance is proportional to the concentration of the absorbing molecules in solution
how to work out absorbance (beer-lambert)
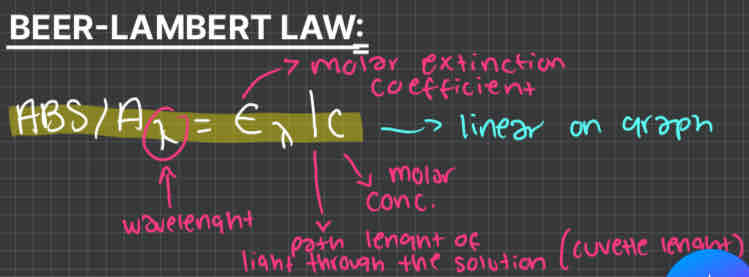
how to work out dilution factor
total volume/ initial volume of stock solution
initial solute concentration/ final solute concentration after dilution