Unit 3: Absolutism and Constitutionalism Vocab (ID's)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Sultan
Name for the hereditary ruler of the Ottoman Empire.

James I
The first Stuart king of England, believed in the divine right of kings, known today mostly for his translation of the Bible which omitted the reference to kings as tyrants.

Hobbes
English philosopher who wrote Leviathan around the time of the English Civil War, arguing for a social contract but also absolutist government to maintain order.

Locke
English philosopher who had a more positive view of mankind and argued for natural rights and the right of the people to alter or abolish their government, wrote around the time of the Glorious Revolution.

Junkers
The Prussian nobility given extensive power over serfs and given favorable positions in the military in exchange for granting greater taxation power to the crown.

Cavaliers
Term for the royalist supporters of King Charles I in the English Civil War.

Charles II
Became the new king of England in 1660 as a result of the Stuart Restoration, signed the Treaty of Dover.

Janissaries
Christian slaves recruited to be elite soldiers in the Ottoman Empire.

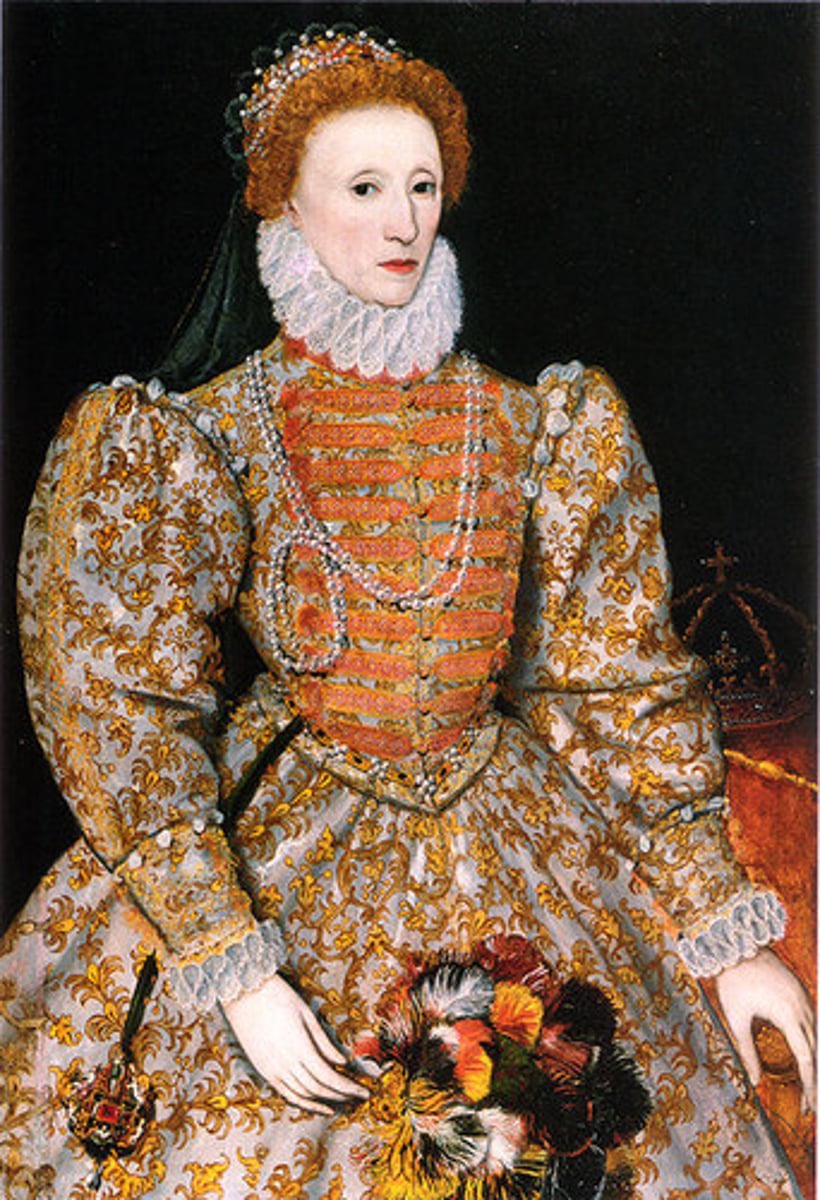
Elizabeth I
The last Tudor monarch, whose death led to the succession of Stuart kings.

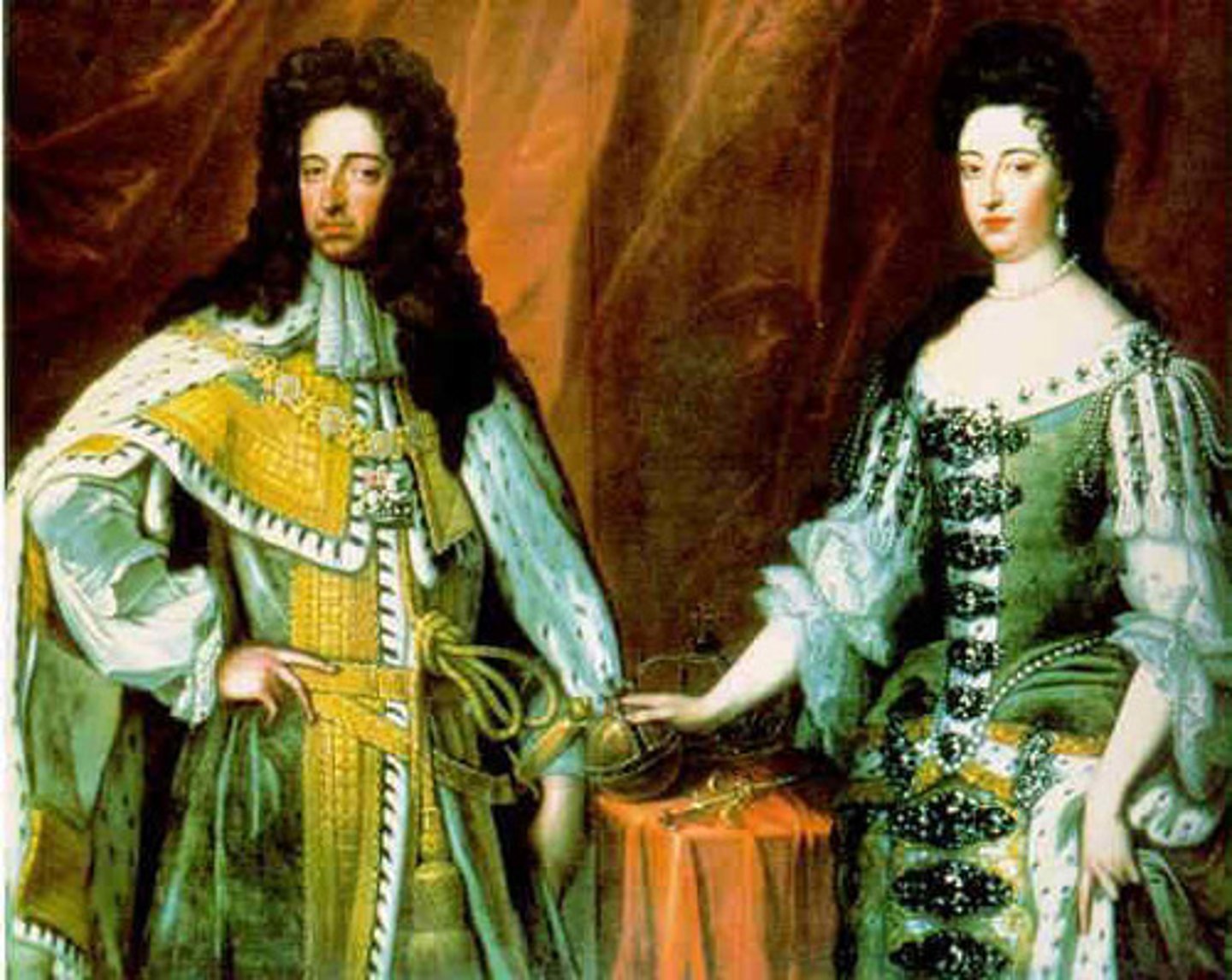
William & Mary
Protestant monarchs who assumed the English throne as a result of the Glorious Revolution.

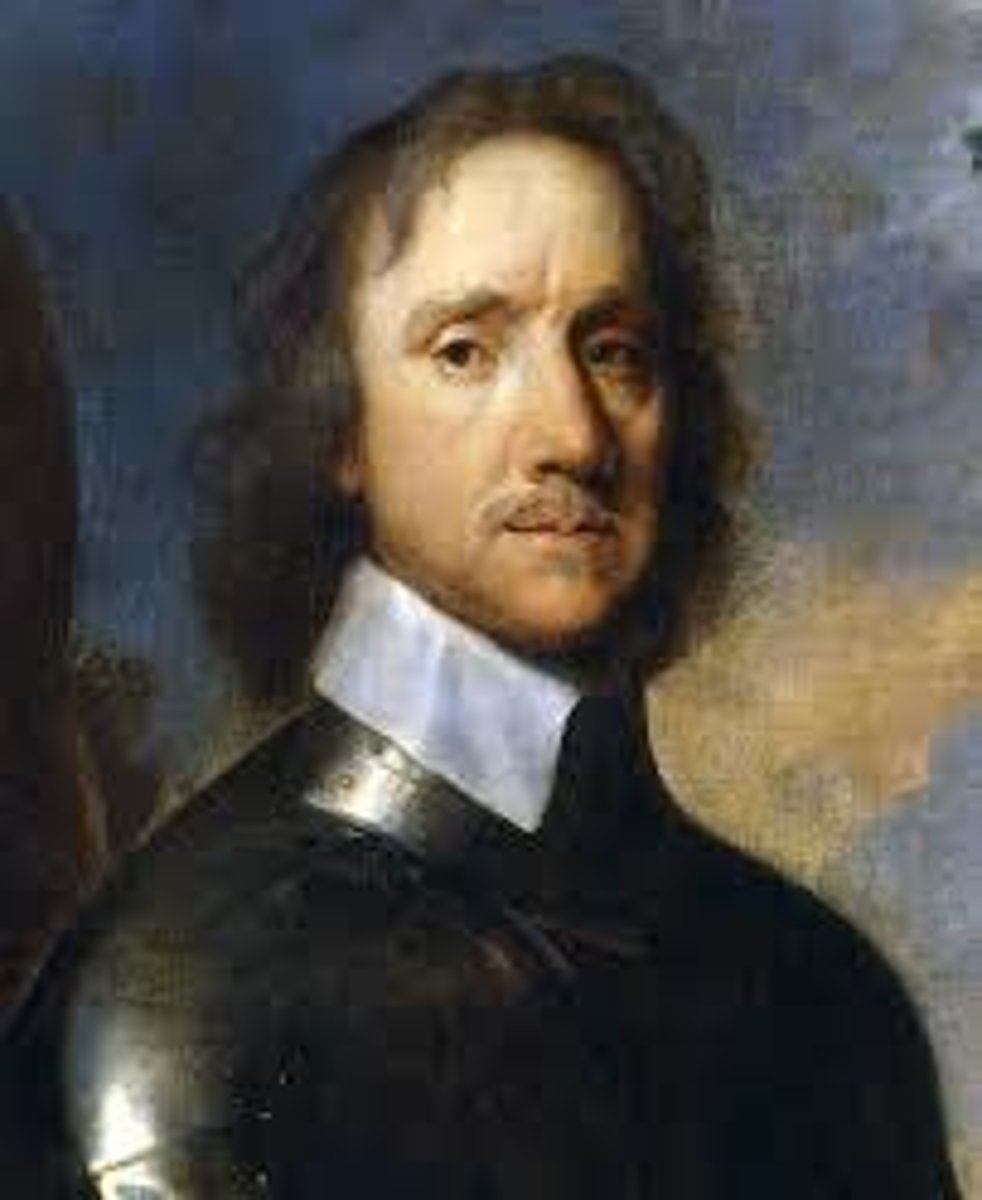
Cromwell
Brilliant general of the New Model Army, named Lord Protector of England.

Intendants
Royal officials and representatives of the king in France who acted as the "eyes and ears" of the monarchy and ensured that regional governments and nobles were following the king's decrees.

Divine Right
Theory that a monarch is appointed directly by God and is not subject to the will of the people.

Versailles
Palace built by Louis XIV in France which helped enhance the monarchy's power over the nobility.

Charles I
Stuart king of England who was beheaded in 1649 as a result of the English Civil War.

Constitutionalist
A government which is limited by a written set of laws.

Amsterdam
Wealthy capital in the Netherlands known as a center of commerce and banking.

Absolute Monarchy (Absolutist)
Louis XIV's system of government was known as this, opposite of a Constitutional Monarchy.

New Model Army
The name for the Parliamentary military forces led by Oliver Cromwell.

Fronde
Series of uprisings by peasants and nobles in France opposed to royal taxation and growing royal power when Louis XIV took the throne.

Mazarin
The cardinal who tutored Louis XIV and continued the policies of Louis XIII.

French Academy of the Arts
Louis XIV established this so that he could censor art while glorifying French culture and his own prestige, had strict guidelines about art, architecture, and literature.

Edict of Fontainebleau
Louis XIV issued this in his pursuit of religious unity, which forced thousands of Huguenots in France to flee.

Nine Years' War
One of Louis XIV's wars after the Glorious Revolution in which he faced the Grand Alliance of Spain, England, the Dutch, and HRE (Holy Roman Empire) for nearly a decade.

Vienna
The Austrian Habsburgs were able to defeat an Ottoman siege at this Austrian city in 1683 with Poland's help, ending the Ottoman expansion into Europe.
Great Northern War
Russia fought Sweden during this, which resulted in Russia gaining territory along the Baltic coast.

Frederick William the Great Elector
The Prussian prince who pursued absolutism and effectively centralized the Prussian state, though he was not yet declared a king.

Mercantilism
The Navigation Acts in England were an example of this economic theory, also used by Jean-Baptiste Colbert.

War of Spanish Succession
Several European states, including England, formed an alliance to stop Louis XIV from gaining power over Spain after the death of Charles II in this war.

Petition of Right
English Parliament asserted its rights in 1628 with this, which protects some basic liberties.

Sun King
Louis XIV called himself this, a reference to the Greek god Apollo.

Stadtholder
The name for the elected executive of the Dutch government who mostly oversaw military affairs and had a limited role.

Colbert
Louis XIV's finance minister who pursued mercantilist policies and built a more efficient system of taxation for the king (Hint: He's not a cardinal).

Gibraltar
By the Treaty of Utrecht in 1714, Britain took control of this key island, which acts as a gateway in and out of the Mediterranean.
Poland
This modern state failed to centralize power and was eventually divided, or partitioned, between stronger states like Russia, Austria, and Prussia by 1795.
Peter I (the Great)
Tsar of Russia known for his modernization of Russia's military and "Westernization" of Russia.

Tory (Tories)
Before the Glorious Revolution, the name for Parliamentary supporters of King James II.

Baroque
Highly elaborate and ornate style of art and architecture associated with artists like Peter Paul Rubens and common in Catholic areas after the Counter Reformation, featured less focus on realism and greater emphasis on emotion, drama in the 17th century.

Jacobites
The Irish and Scots who rebelled against William & Mary after the Glorious Revolution were called this, believing that James II was the legitimate king.
English Bill of Rights
Landmark document signed by William & Mary in 1689 which established many of the basic liberties we know in our government today and effectively limited the power of the monarchy.

Test Act of 1673
Law passed by Parliament during the reign of Charles II of England, which ensured that all English government officials had to be a member of the Anglican Church.

Treaty of Union (1707)
This act finally brought together England, Wales, Ireland, and Scotland into the United Kingdom.