Motor Control Theories
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Scientific Theory
“A well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world, based on a body of facts that have been repeatedly confirmed through observation and experiment”.
A good theory should satisfy…
-Must accurately describe a large class of observations
-Must make definite predictions about the results of future observations
A good motor control theory…
-Explain how the nervous system produces coordinated movement such that we are able to successfully perform a variety of motor skills in a variety of environmental contexts.
Coordination
The patterning of head, body, and/or limb motion relative
to the patterning of environmental objects and events
Degrees of Freedom
the number of independent elements or components in a control system and the number of ways each component can vary
e.g., planes of motion of a joint or individual muscles or individual motor units
Degrees of Freedom Problem
Successfully controlling the many independent, redundant components of the musculoskeletal system
What is the goal in understanding the degrees of freedom problem
How can we constrain the system’s many degrees of freedom so that it could produce the specific result
Open-Loop Control systems
a control system in which all the information needed to initiate and carry out an action as planned is contained in the initial instructions to the effector
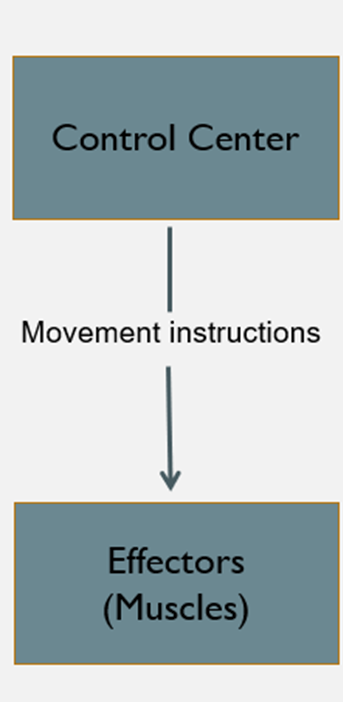
Motor Program
A memory representation that stores information needed to perform an action
(prestructured set of commands that defines and shapes an action)
General Content of Motor Programs
Specification of Anticipatory Postural Adjustments (APA’s)
Postural muscle activation patterns
Anticipation of what the task requires
2) Specification of primary/focal action
Generalized Motor Program Theory
Definition of GMP:
•abstract representation that produces a general class of movements and can vary along certain dimensions (“parameters”)
•GMPs contain the fundamental pattern of a class of actions
•Provides the basis for controlling a specific action within the class of actions
Invariant features of GMP’s
These features are the signature of a GMP and form the basis of what is stored in memory. They are characteristics that do not vary across performances of a skill within class of actions.
•Order of events/components (ie. spatial pattern)
•Relative Timing
•Relative Force
Parameters of GMP’s
Parameters: movement-related features of the performances of a motor skill that can be varied from one performance to another.
•Muscle Selection
•Overall Duration
•Overall Force