Unit 1 AP Human Geography: The Power of Geovisualization
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Human Geography
The study of variation in patterns and processes in space + human interaction with their environment
Physical Geography
The study of the structure, process, & location of Earth's natural phenomena (climate, soil, plants, animals, topography)

Spatial Analysis
Examining locations, attributes, & relationships in spatial data to answer a question or gain info
Spacial Data
Info tied to a location in space
Quantitative Data
Statistical, mathematical data backed up by formally collected info
Qualitative Data
More humanistic data (interviews, observations, or interpretations of texts, artwork, maps, & archives)

Reference Maps
Maps showing absolute location & geographic features determined by a frame of reference (latitude and longitude)
Road Map
Map with highways, airports, cities, tracks, & major points
Plat Map
Map with individual lots’ boundaries
Political Map
Map with man-made boundaries, countries, & cities
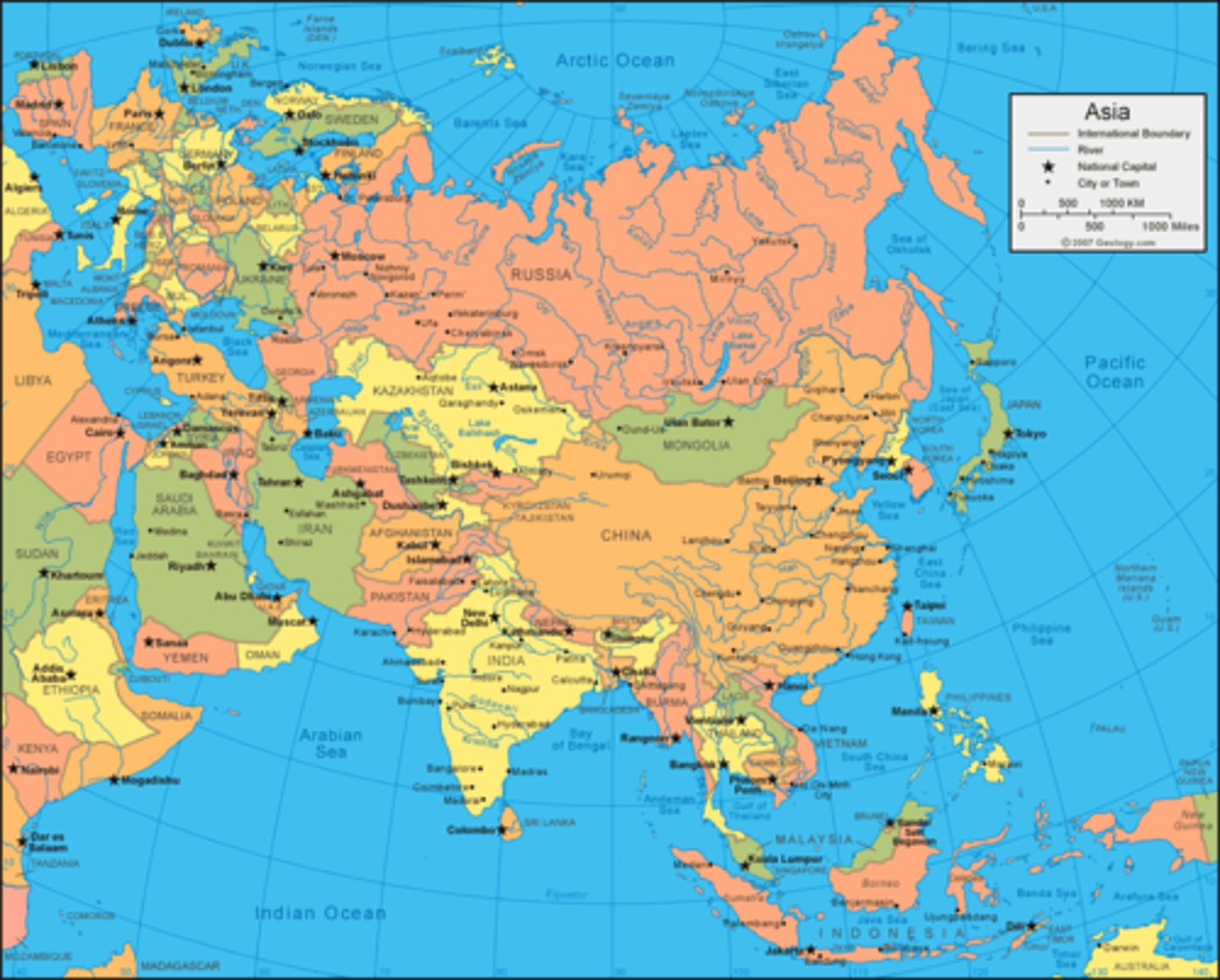
Physical Map
Map with physical features (mountains, hills, plains, rivers, lakes, oceans)
Locator Map
Map in books, newspapers, & ads to show locations mentioned
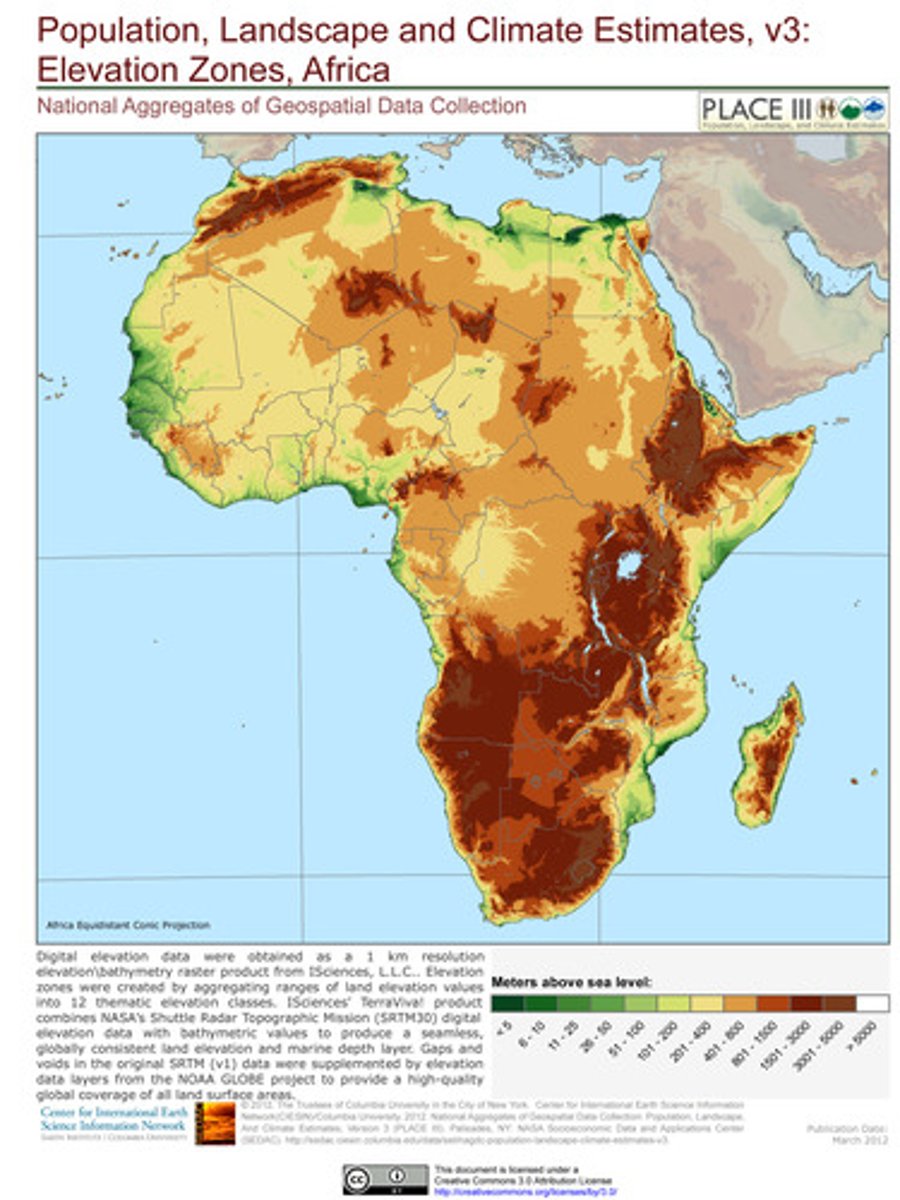
Thematic Maps
Maps showing distribution, flow, or connection of characteristics
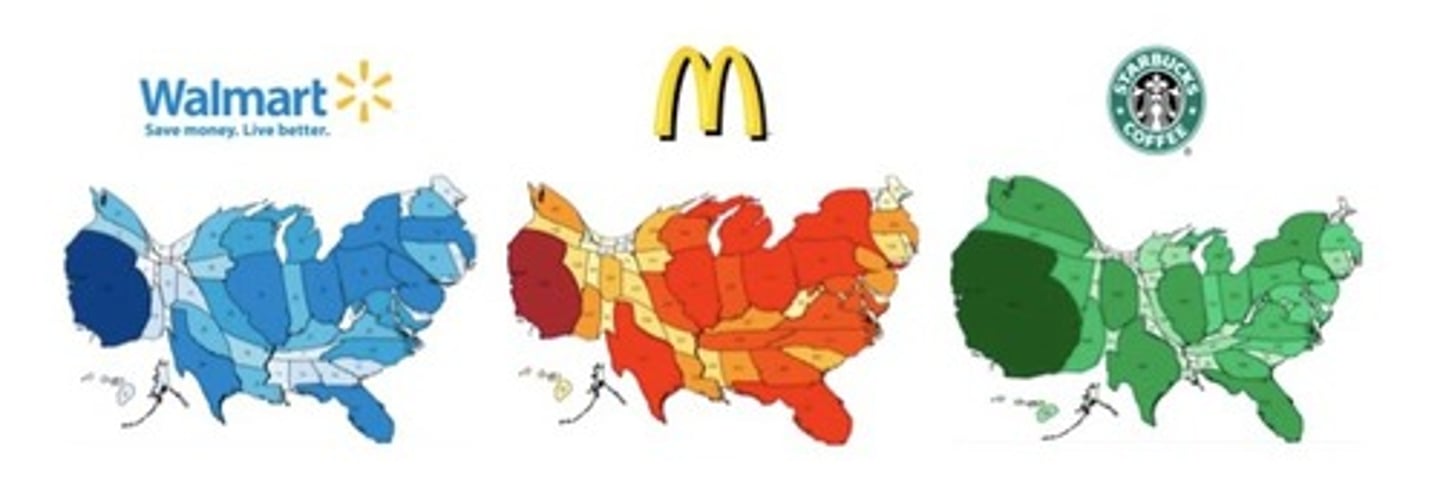
Choropleth Map
Uses shades of a color to show spatial data as average values per unit area with only 1 data set measured
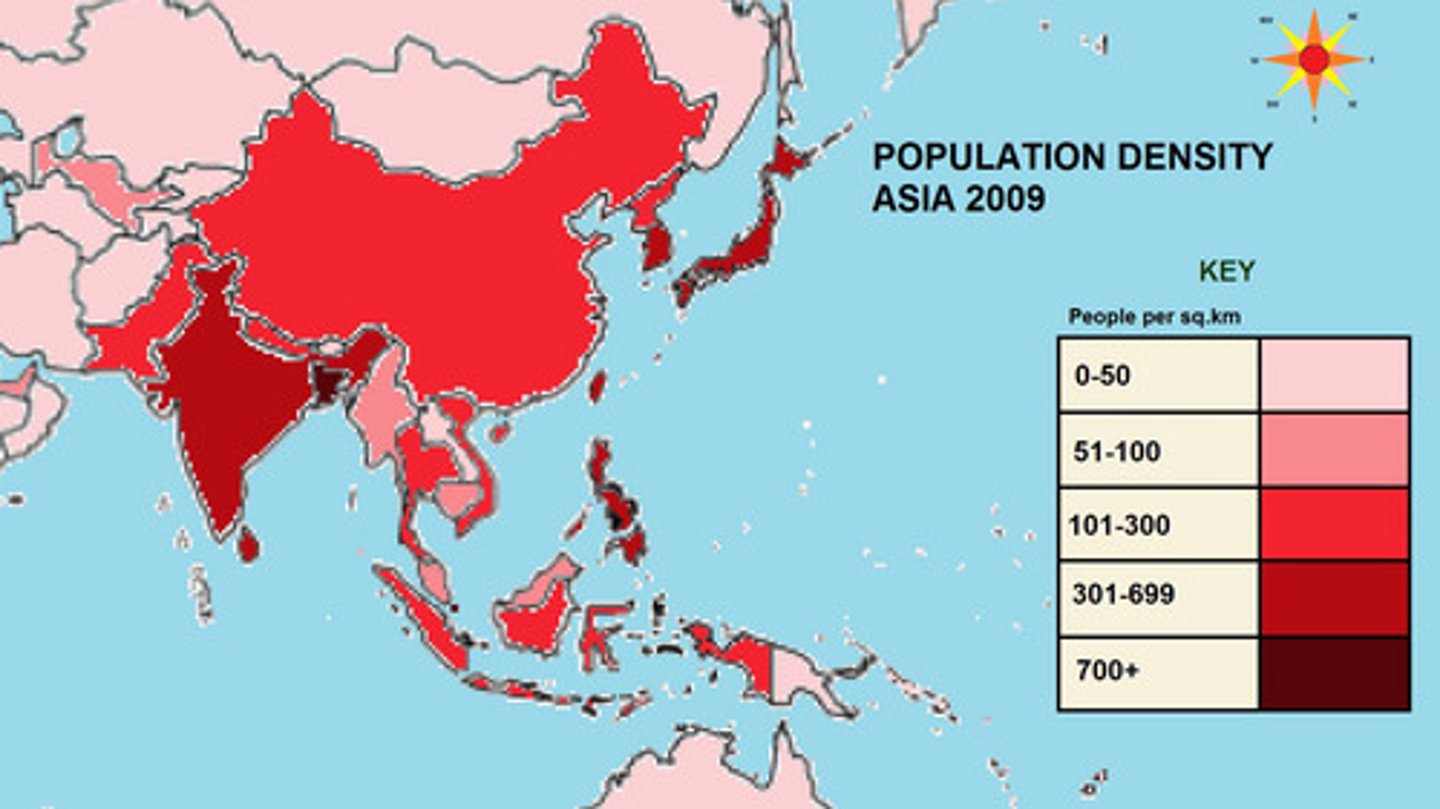
Categorical Map
Uses colors to show multiple categories
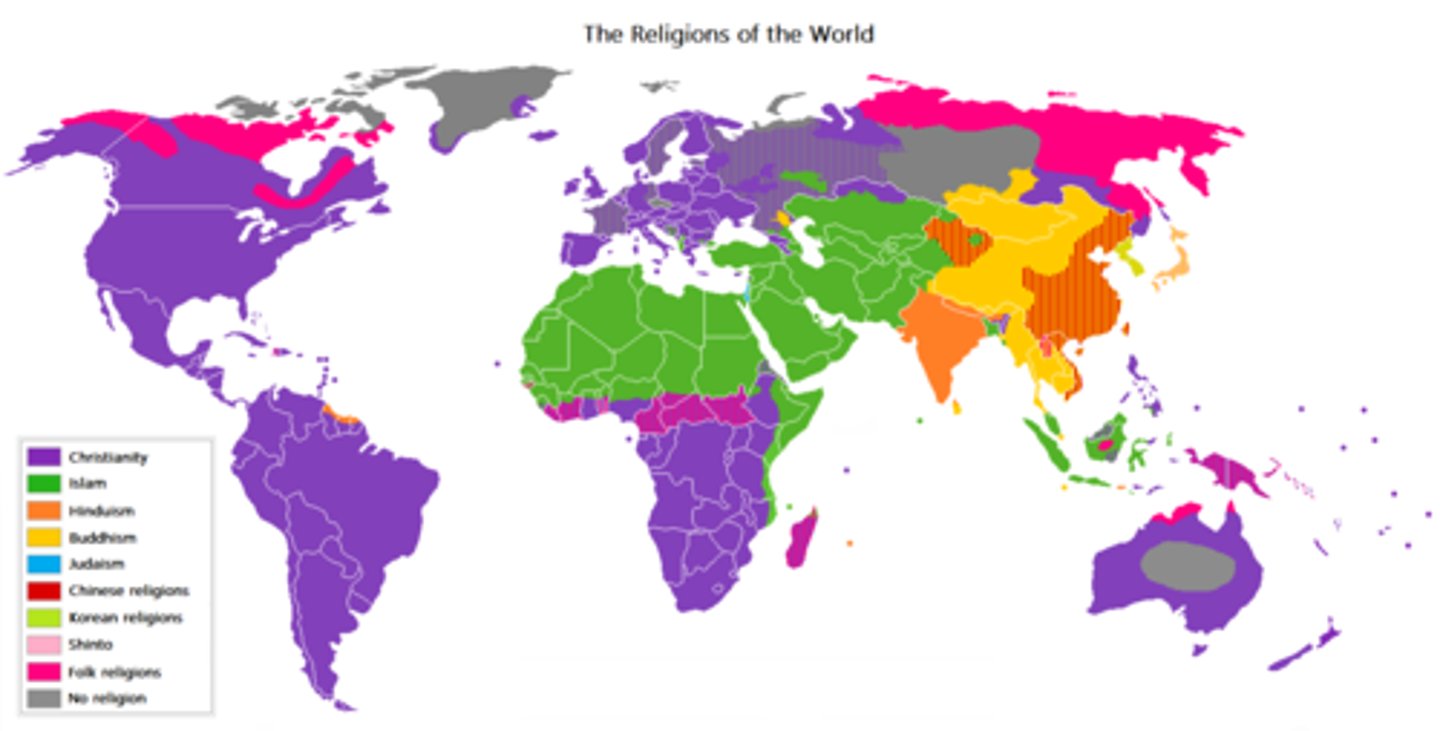
Isoline Map
Map with lines connecting points with equal values
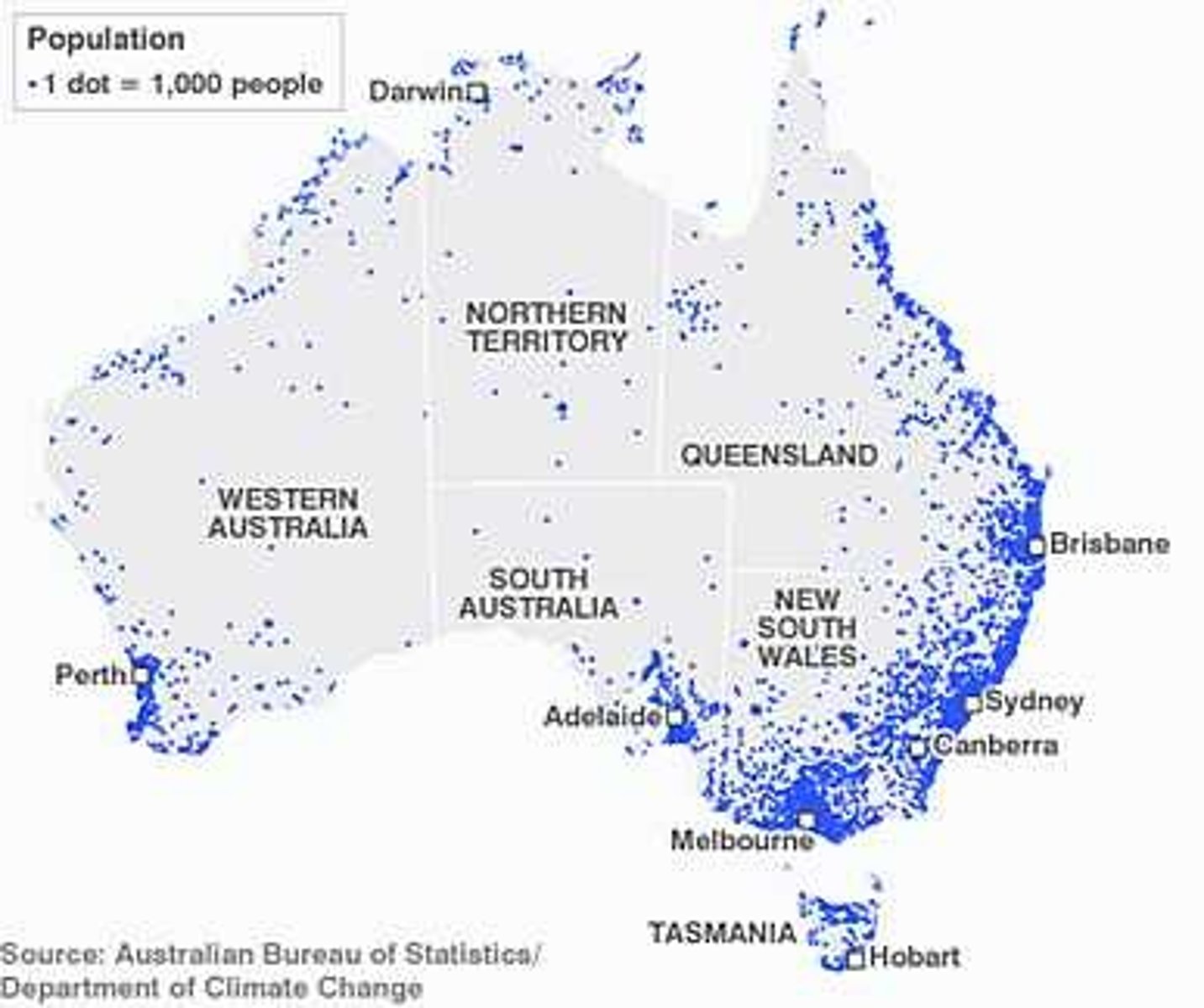
Dot Distribution Map
Dots used to show frequency of a phenomena
Cartogram Map
Map with the shape/size distorted to show a variable
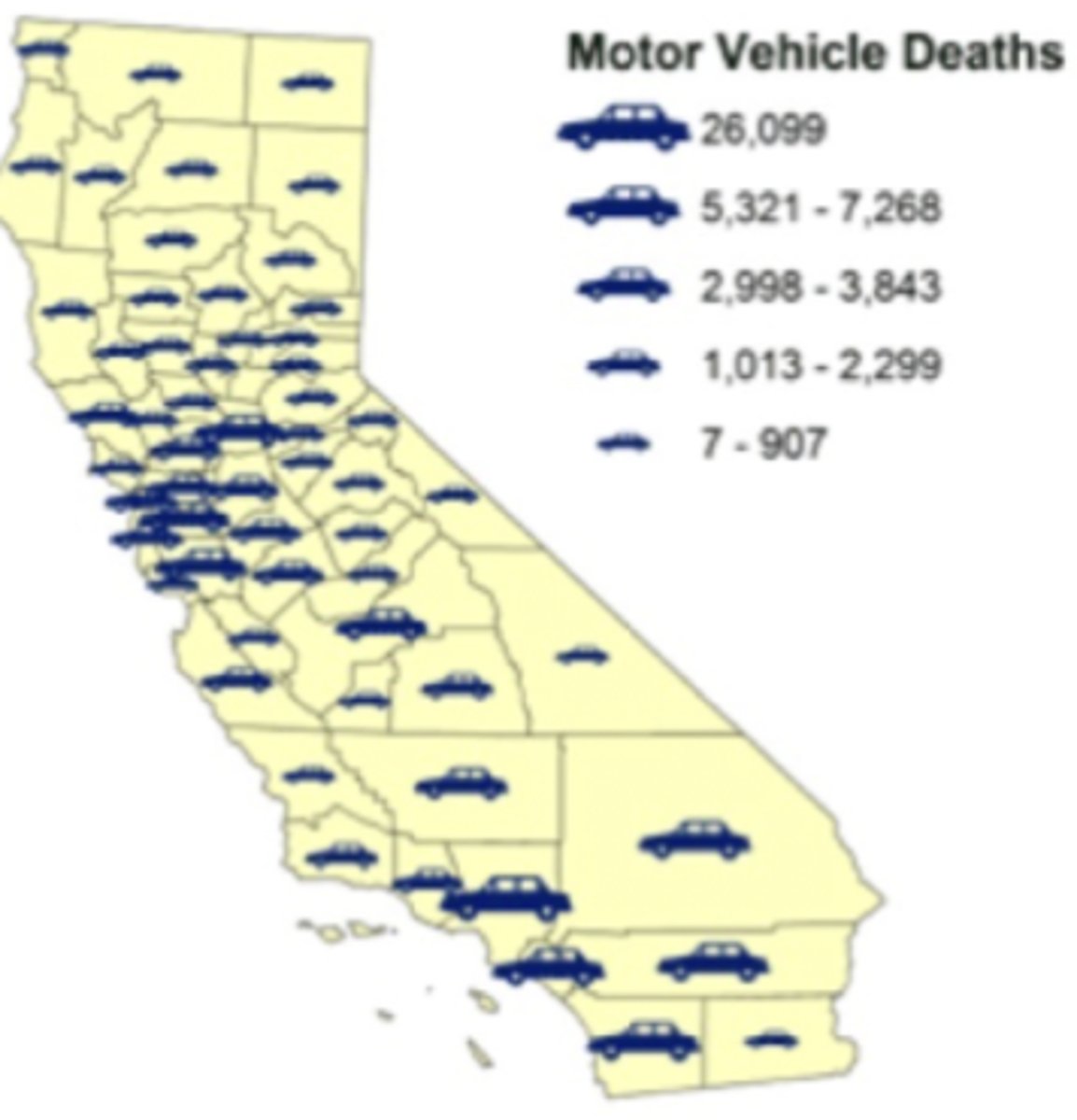
Graduated Symbol Map
Map with symbols changing size by value
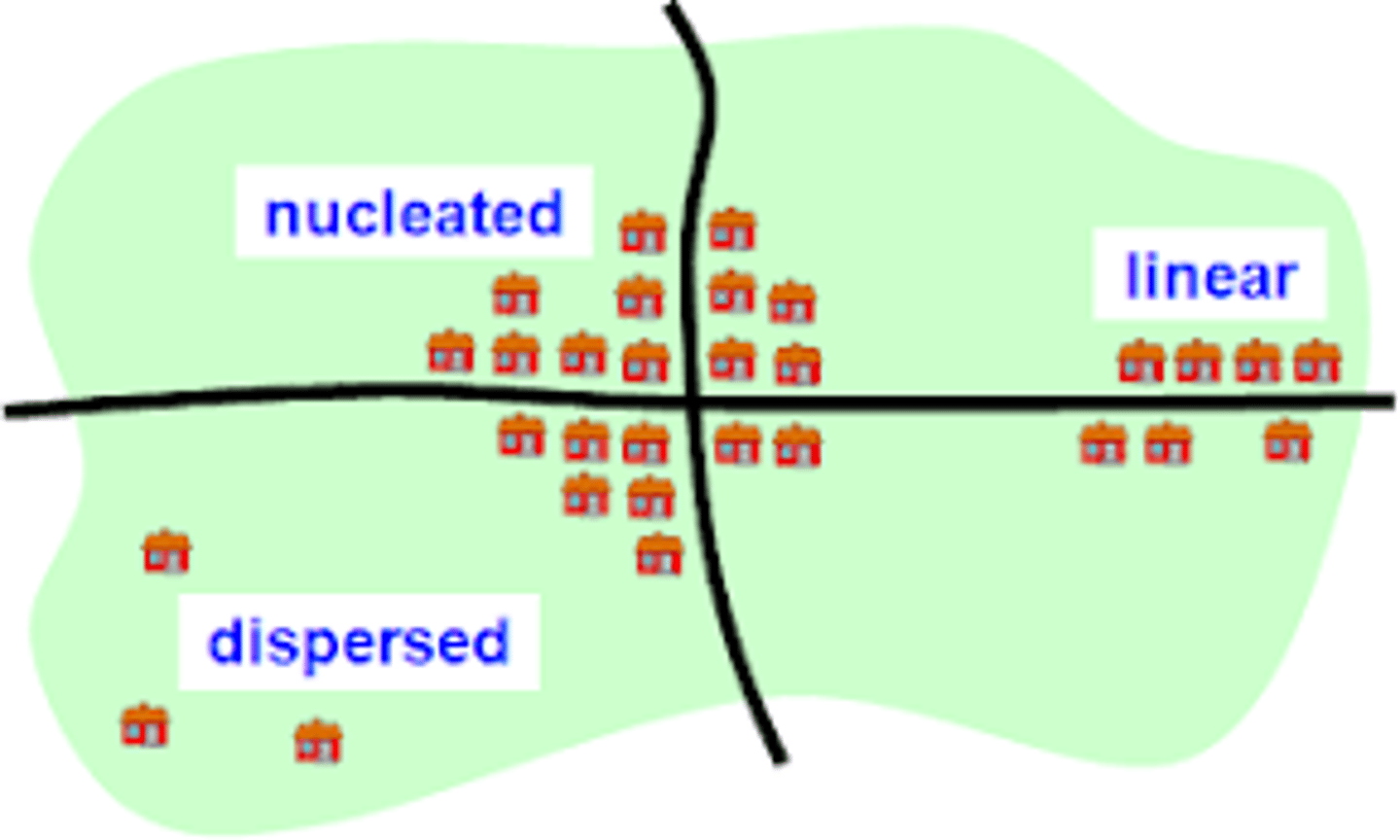
Clustered Phenomena
Concentrated or nucleated
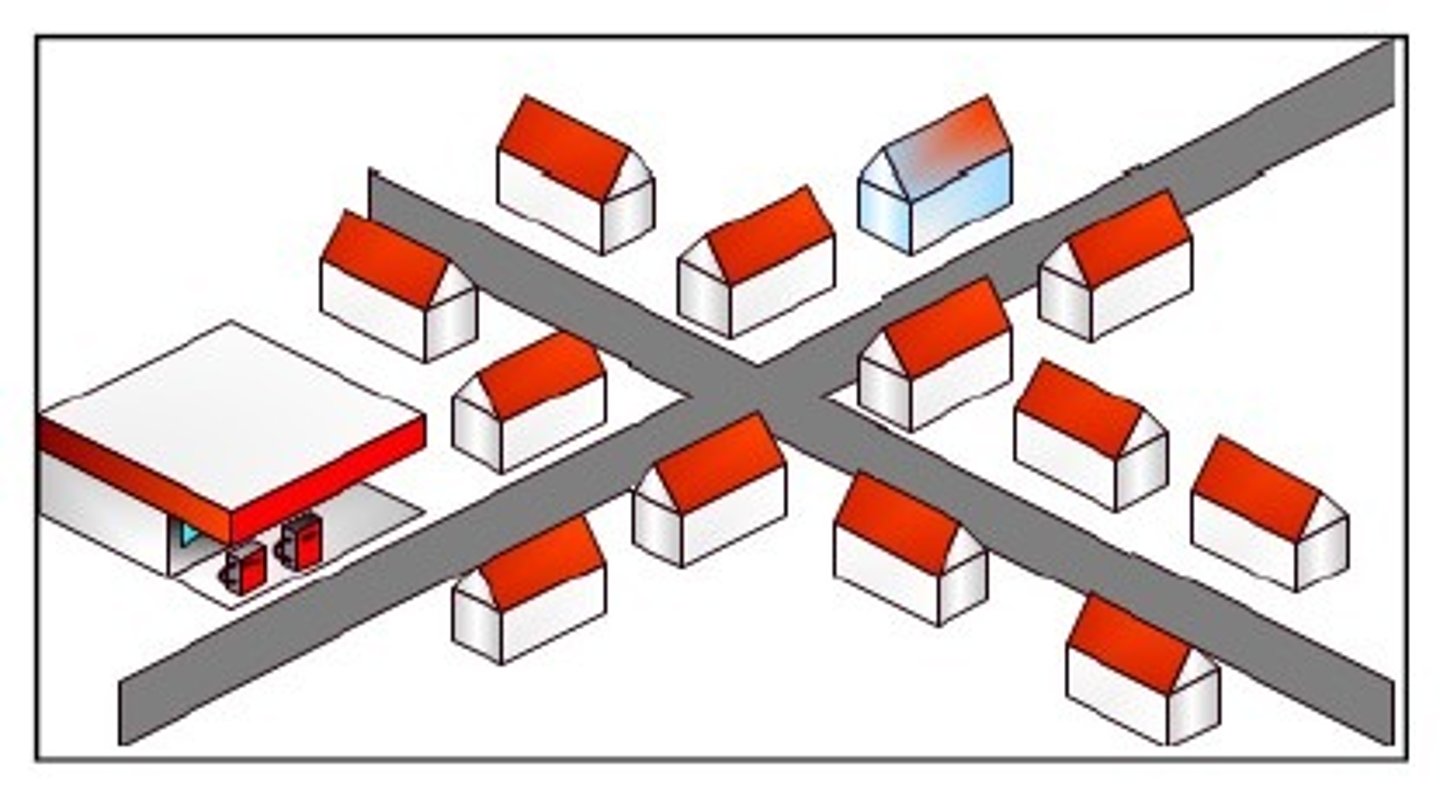
Linear Phenomena
Arranged in a straight line

Dispersed Phenomena
Spread out over a large area
Circular Phenomena
Equally spaced from a central point (circle)
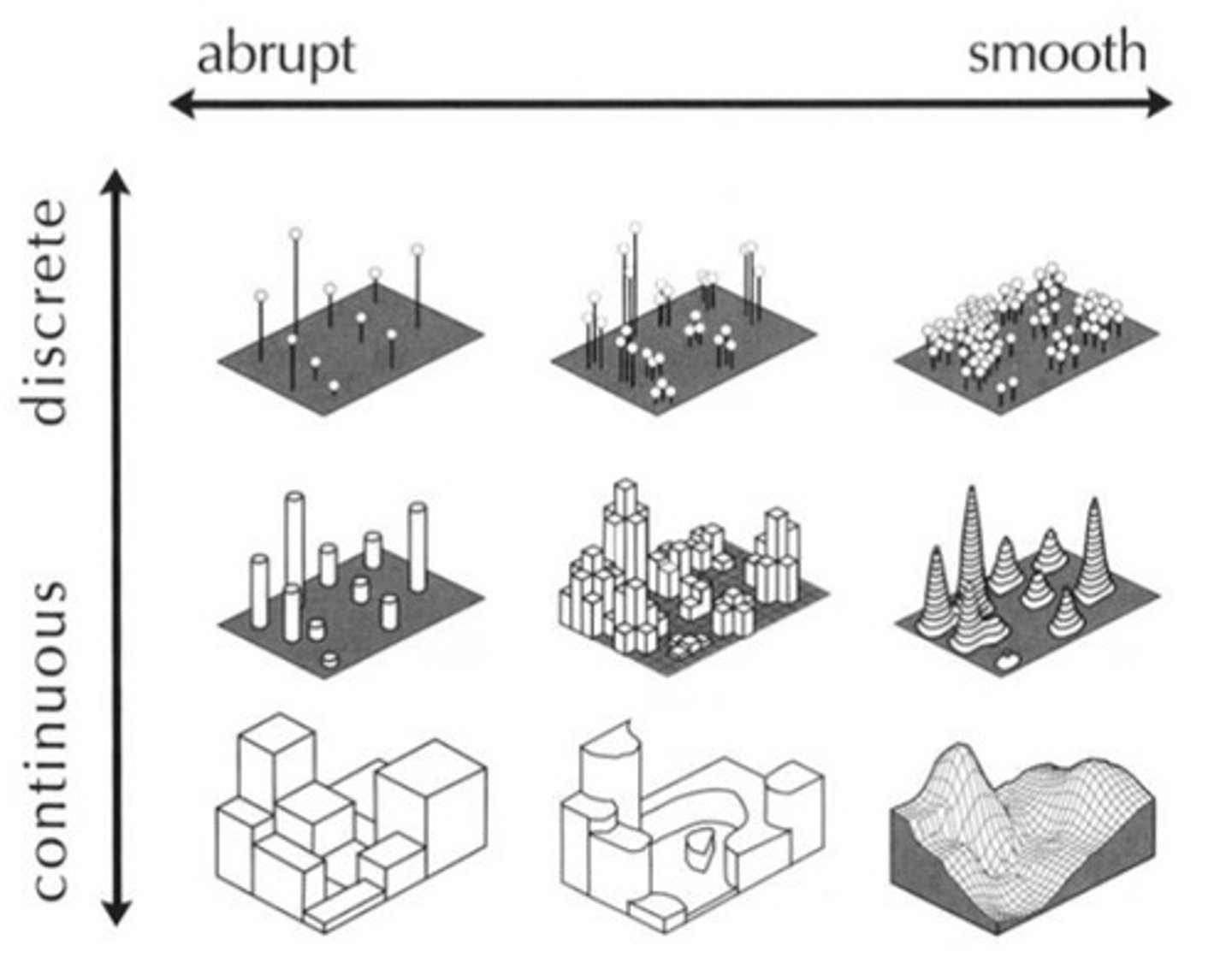
Geometric Phenomena
A regular arrangement

Random Phenomena
No order or pattern of distribution
Four-Level Analysis
4 steps to study phenomena. Comprehension, identification, explanation, & prediction
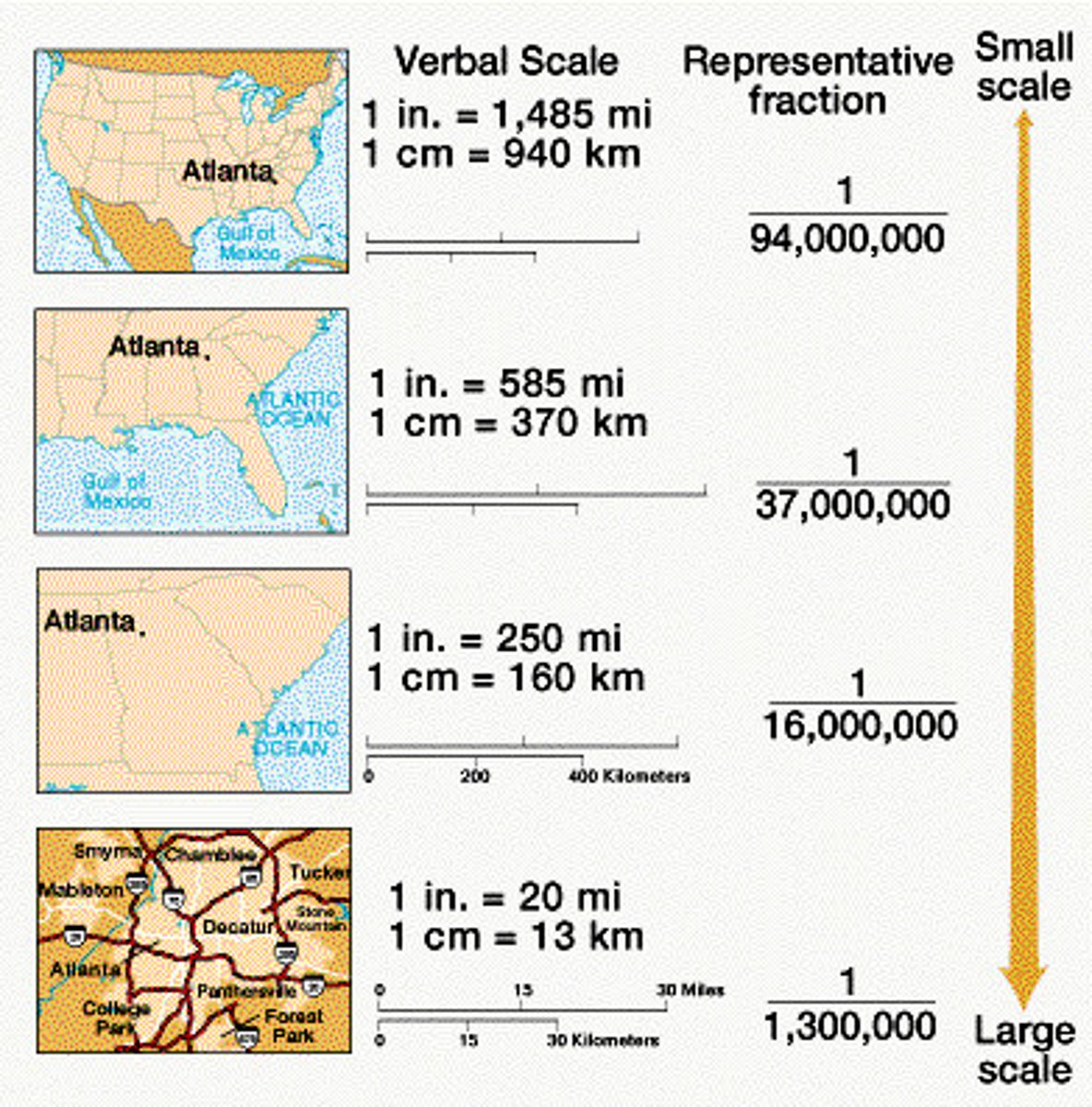
Scale Analysis
Determines what is being studied by size of area. Zoom in = large scale, zoom out = small scale.
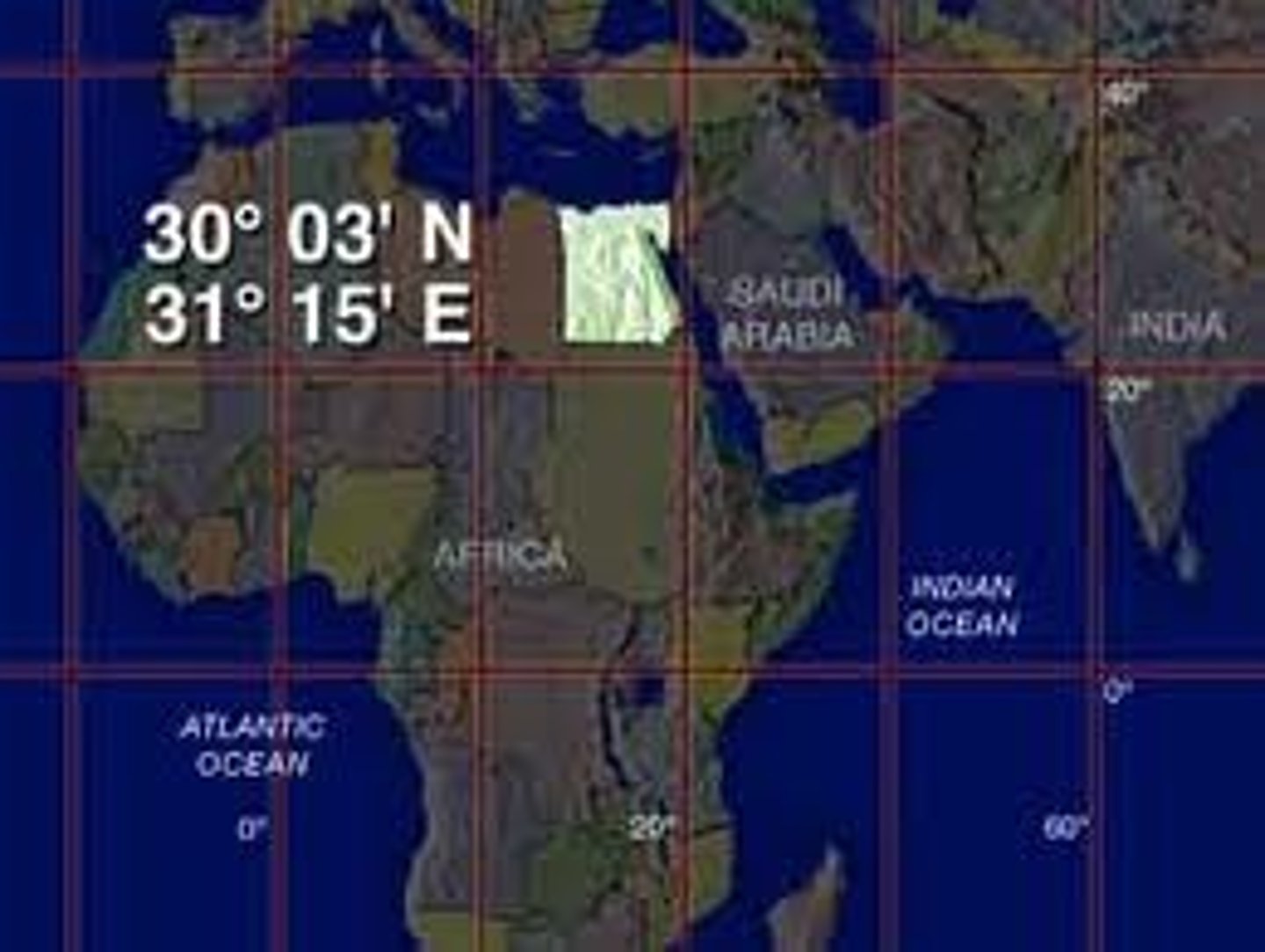
Relative Location
The location of a place relative to other places

Absolute Location
Exact location of a place on the Earth (global coordinates)
Remote Sensing
The acquisition of data about Earth's surface from a satellite orbiting the planet or other long-distance methods, ie: geothermal data, seismic activity projections.
Global Positioning System (GPS)
A system that finds the position of something on Earth (satellites, tracking stations, & receivers)
Geographic Information System (GIS)
A computer system that stores, organizes, analyzes, and displays geographic data.
Place
A specific point on Earth distinguished by characteristics

Location
Where specific phenomena are located

Site
Physical characteristics of a location

Situation
Location (site) influencing human interactions and connections to other places

Sense of place
Personal, emotional attachment to a place

Toponyms
Name of a place
Time-Space Compression
Technological innovation reduces perceived distance of people (communication, transportation)

Spatial Interaction
Flow of people, goods, & info between locations
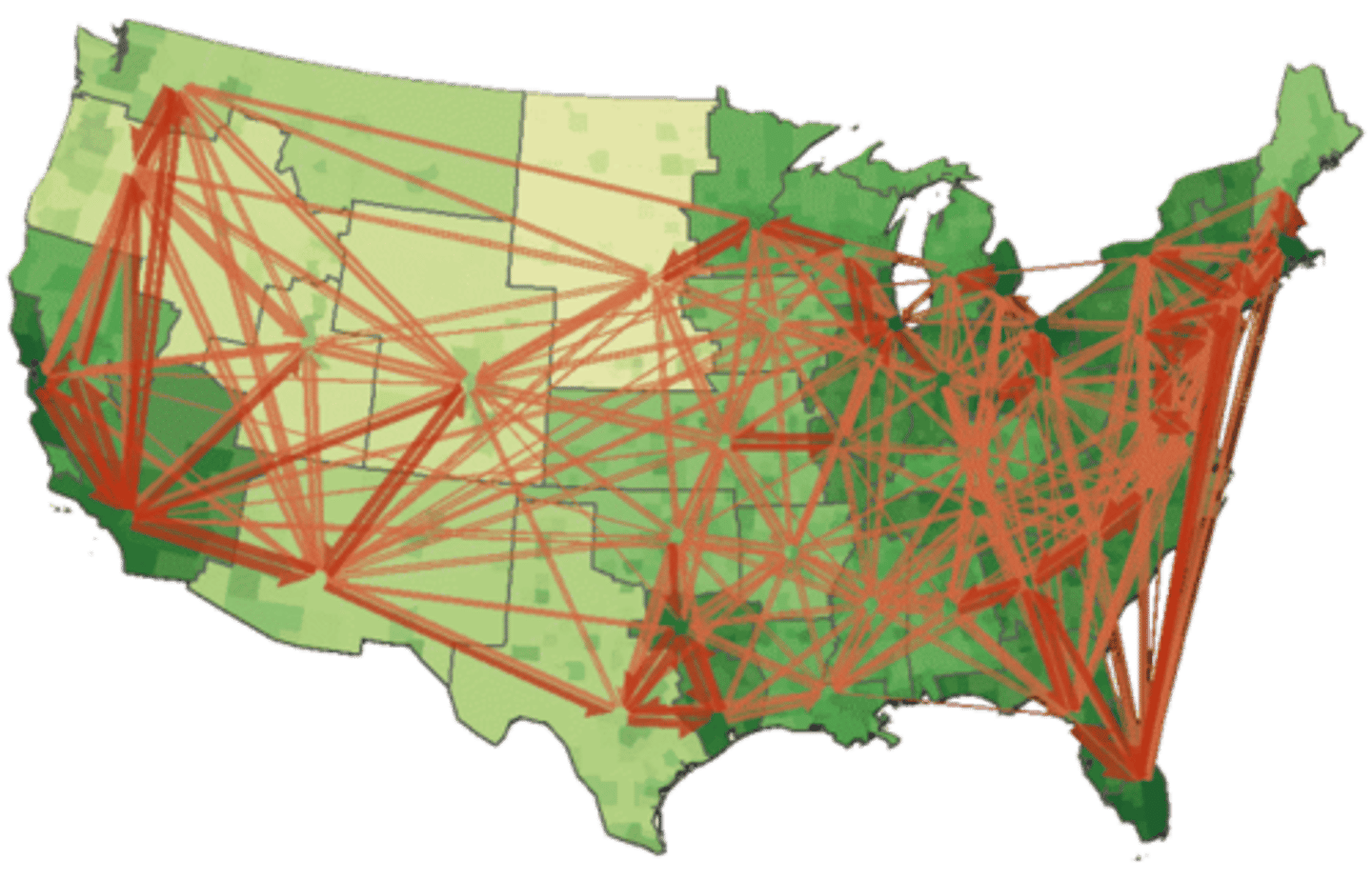
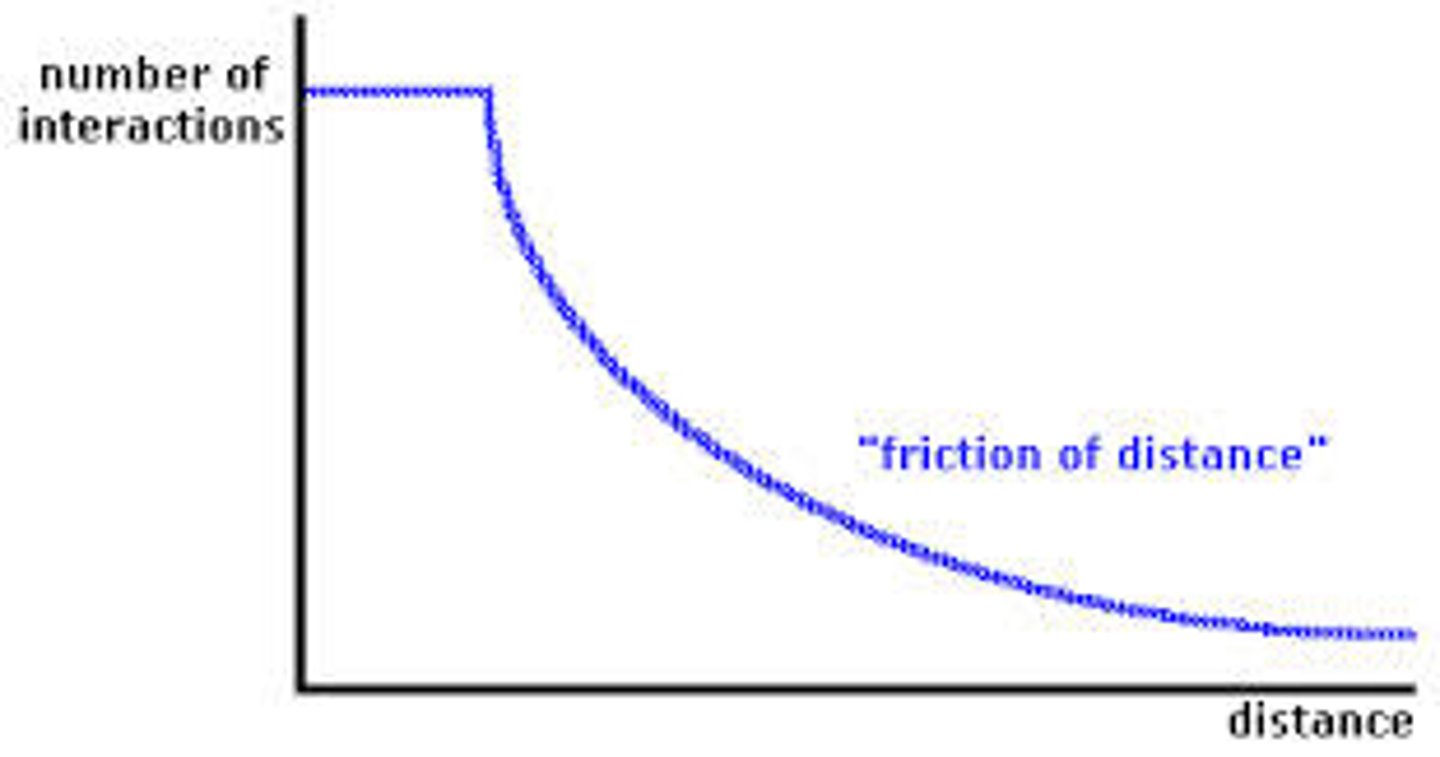
Friction of Distance/Distance of Decay
Farther apart = less connected + less interaction
Spacial Association
When multiple phenomena are related to each other
Renewable Natural Resources
Theoretically unlimited and will not be depleted
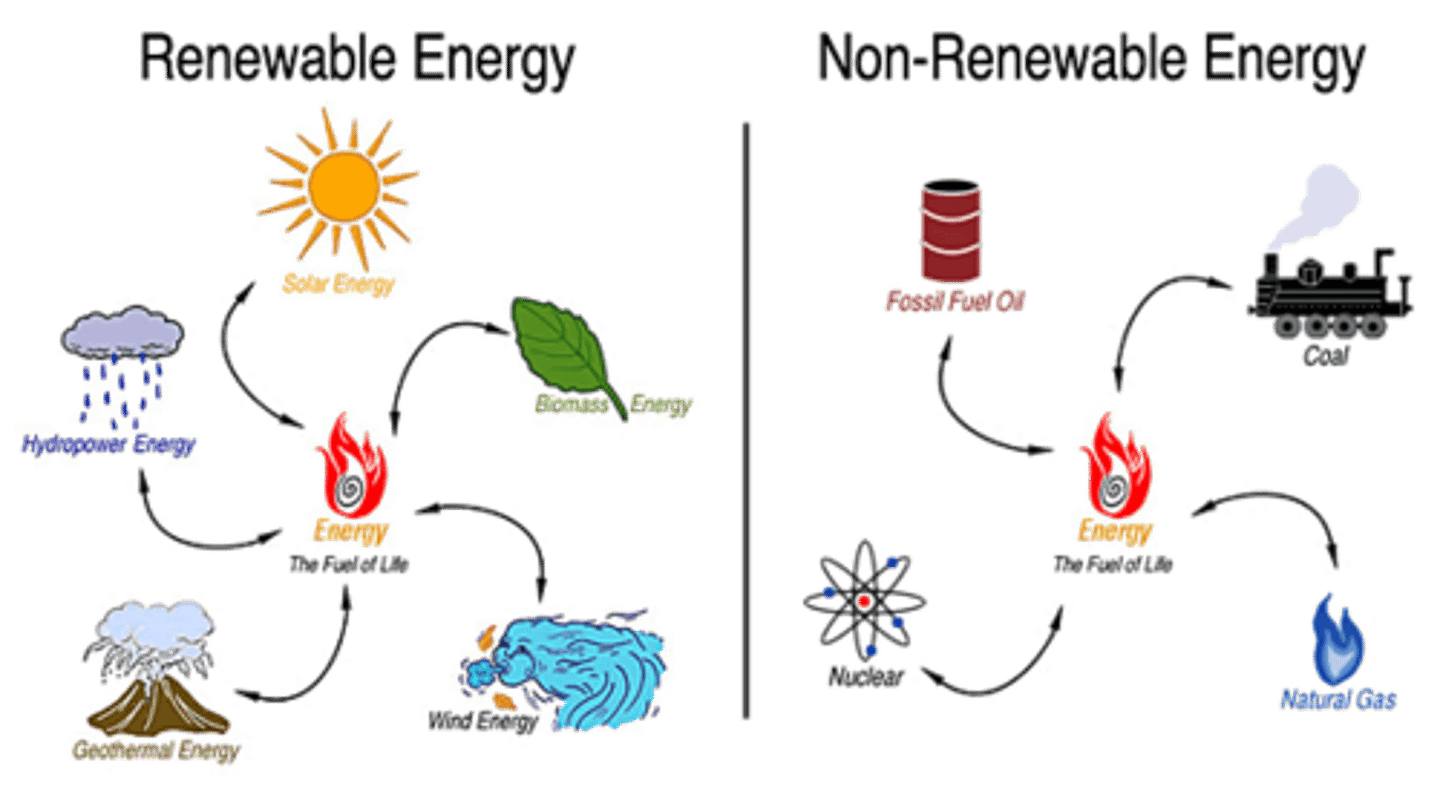
Non-renewable Resources
A resource that cannot be reused or replaced easily
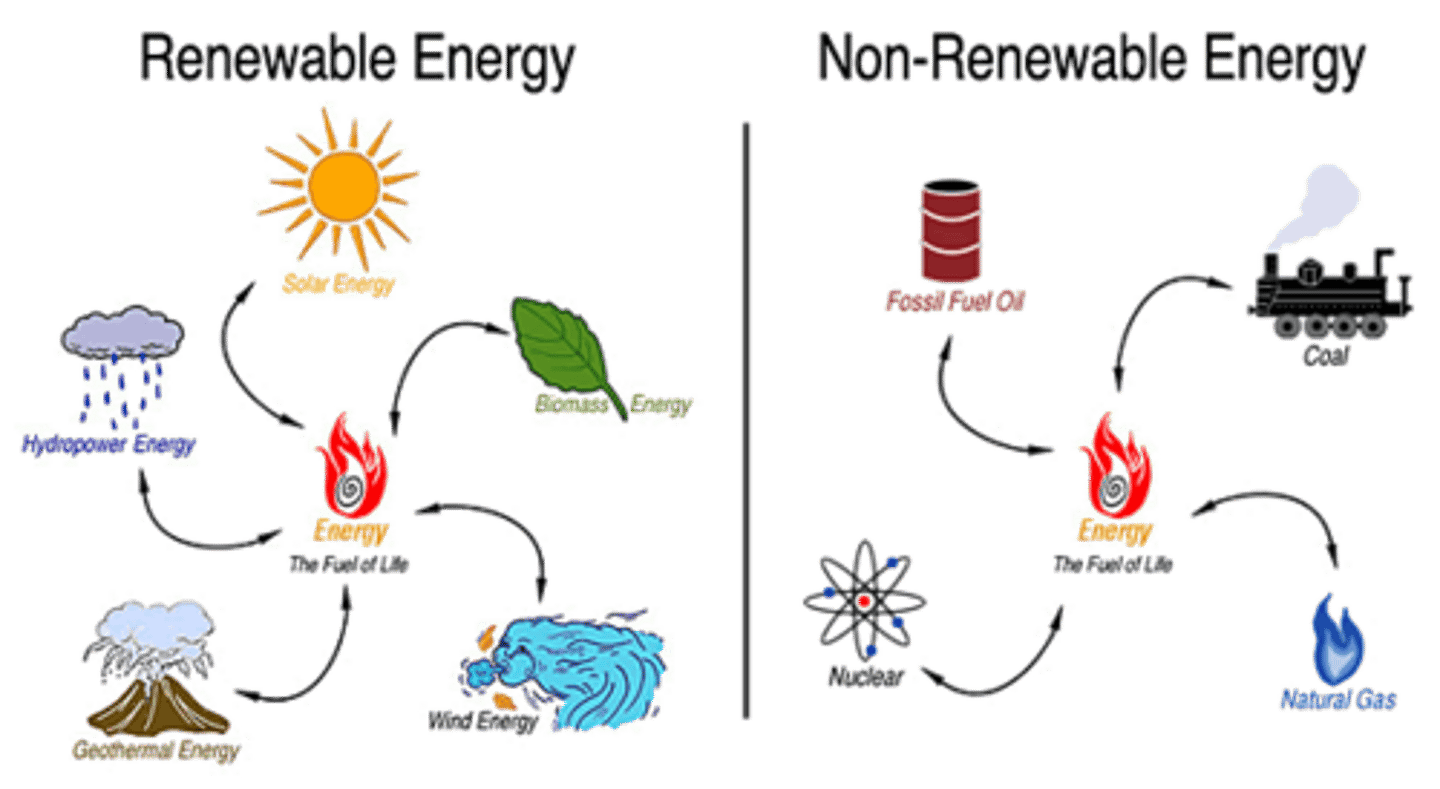
Sustainability
The use of Earth's natural resources to not constrain future use

Land Use
How people use a specific location on Earth’s surface

Built Environment
Landscape created by humans & material culture

Cultural Ecology
The study of how humans adapt to their environment
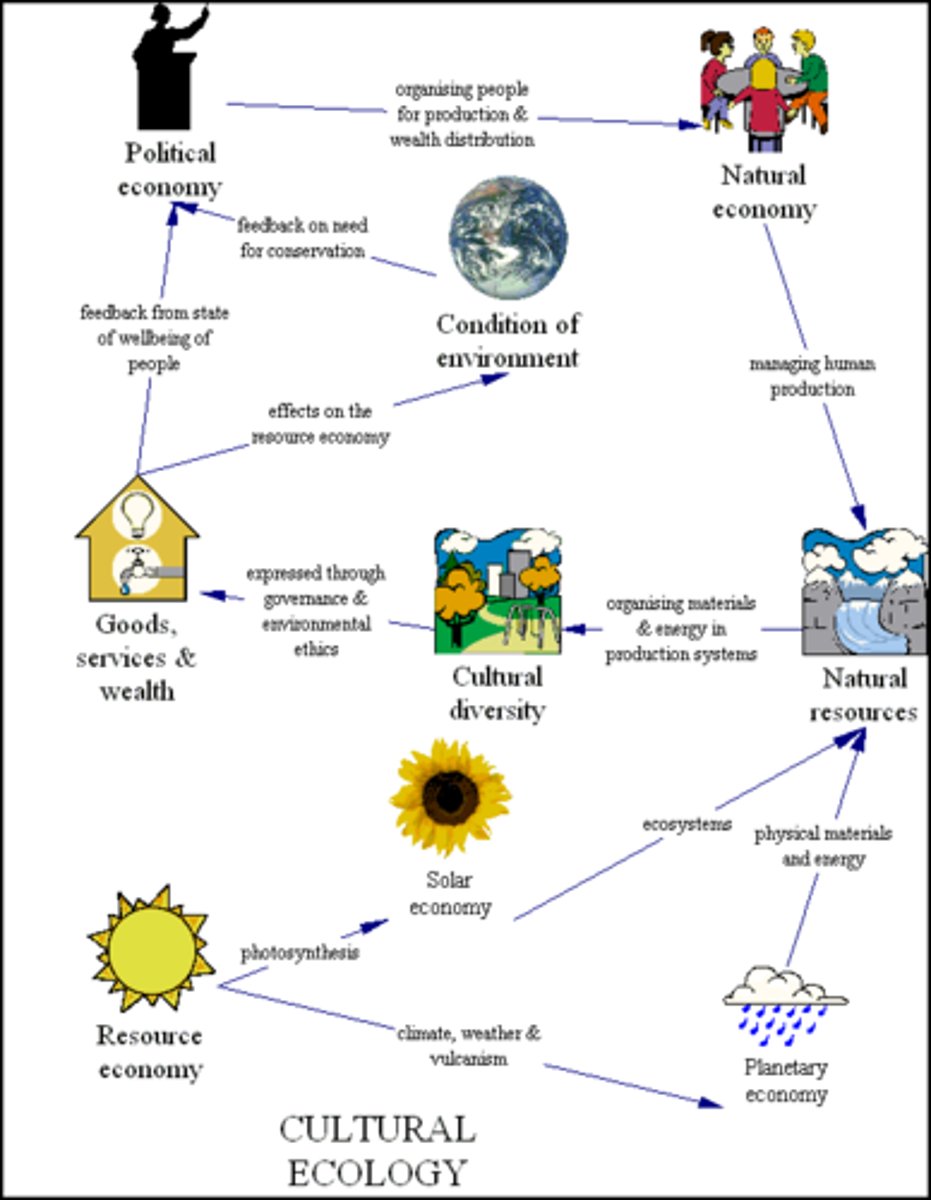
Environmental Determinism
Natural environments influences human life (cultural development)

Possibilism
People can adjust to limitations caused by the physical environment

Geographic Scale (Relative Scale)
Refers to the amount of territory that the map represents.
Global, World Regional, National, National Regional, Local, State, County etc. Also referred to as aggregation.
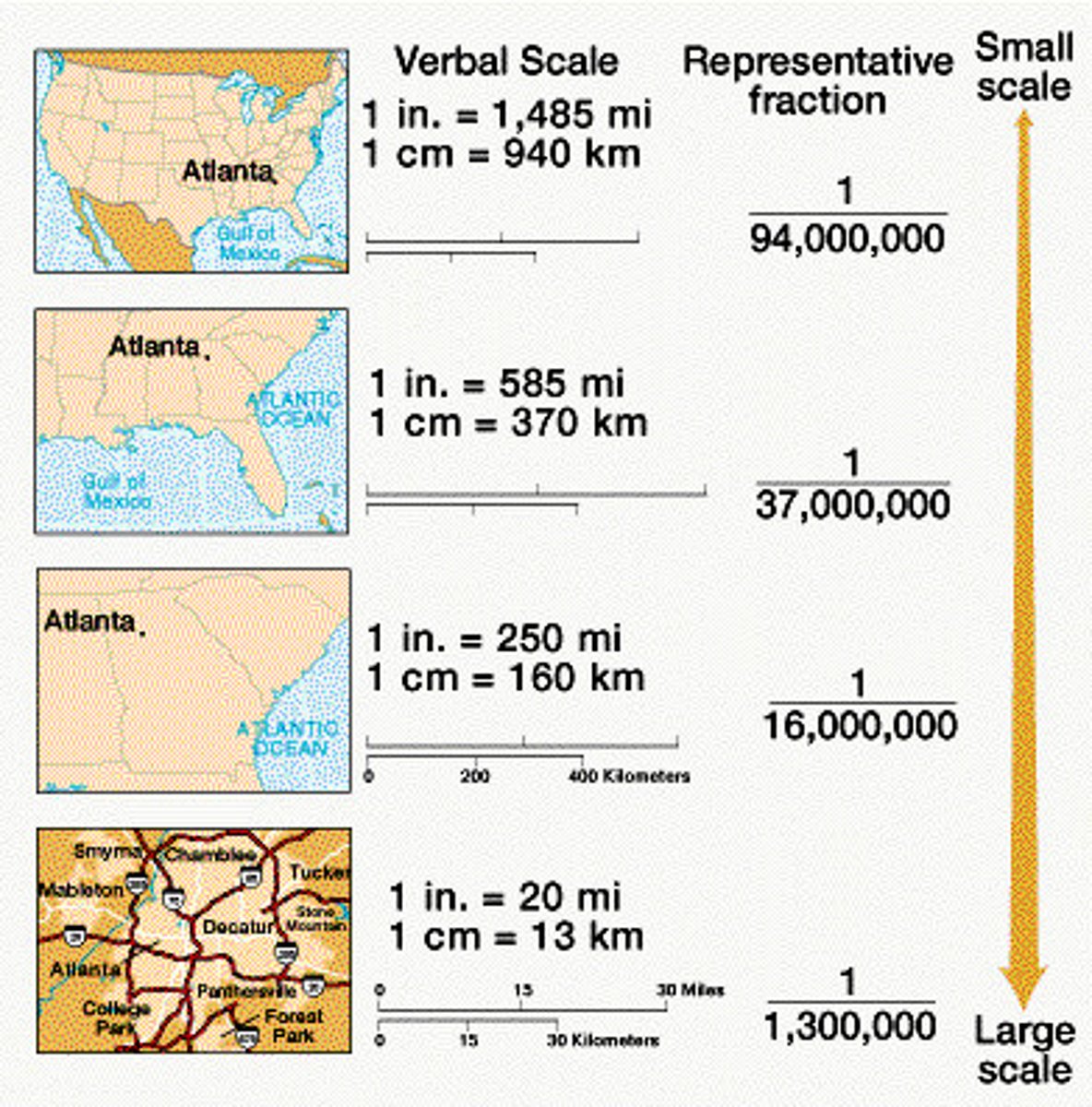
Region
An area of Earth distinguished by cultural & physical features
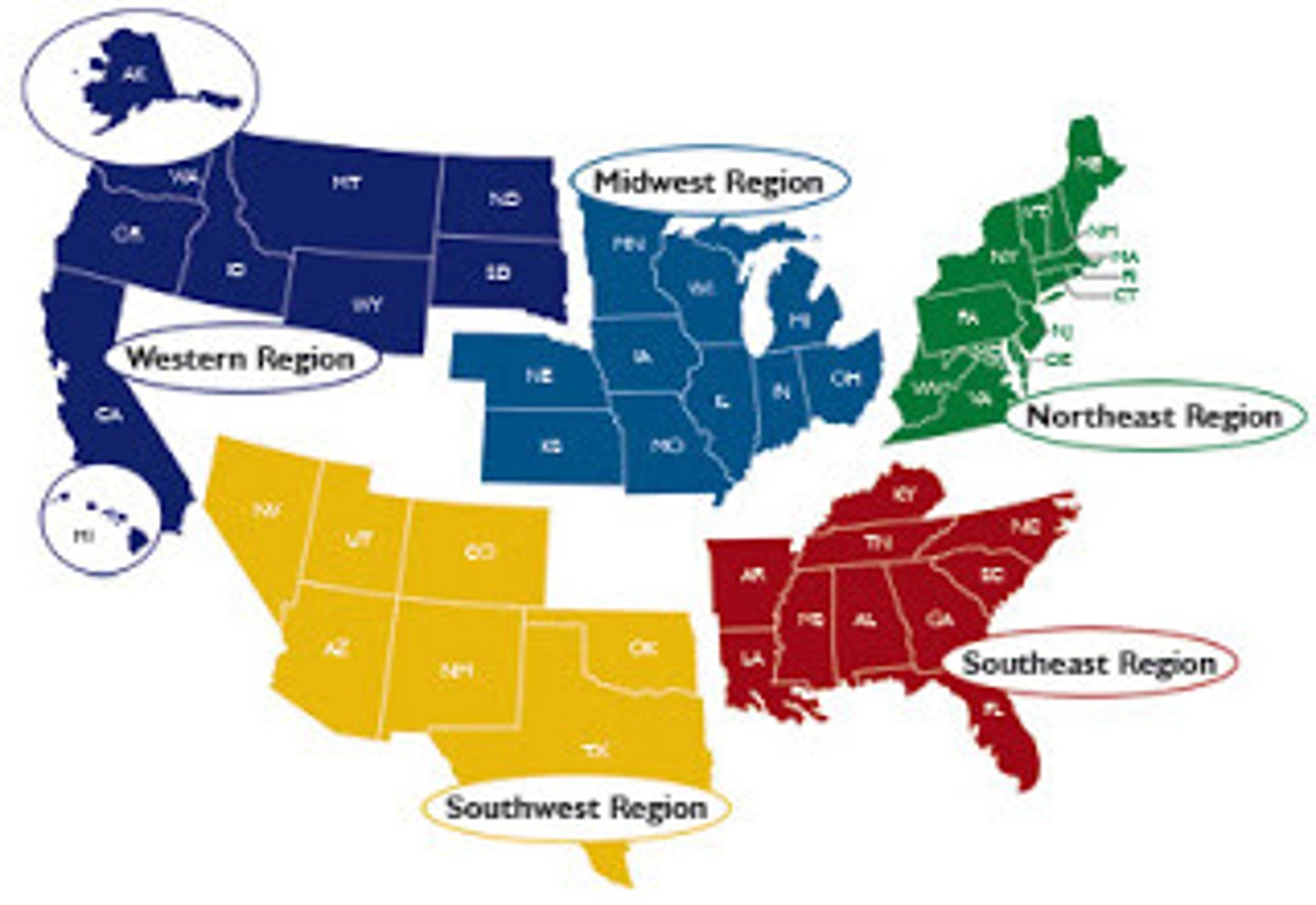
Formal/Uniform/Homogeneous Region
Defined region united by characteristics
Functional/Nodal Region
Region that is united by a central place (transportation, activity)
Perceptual/Vernacular Region
Region defined by feelings & beliefs, not boundaries
Transitional Region
Exhibits characteristics of many regions, but no sharp boundary exists
Overlapping Region
A place is part of over 1 region
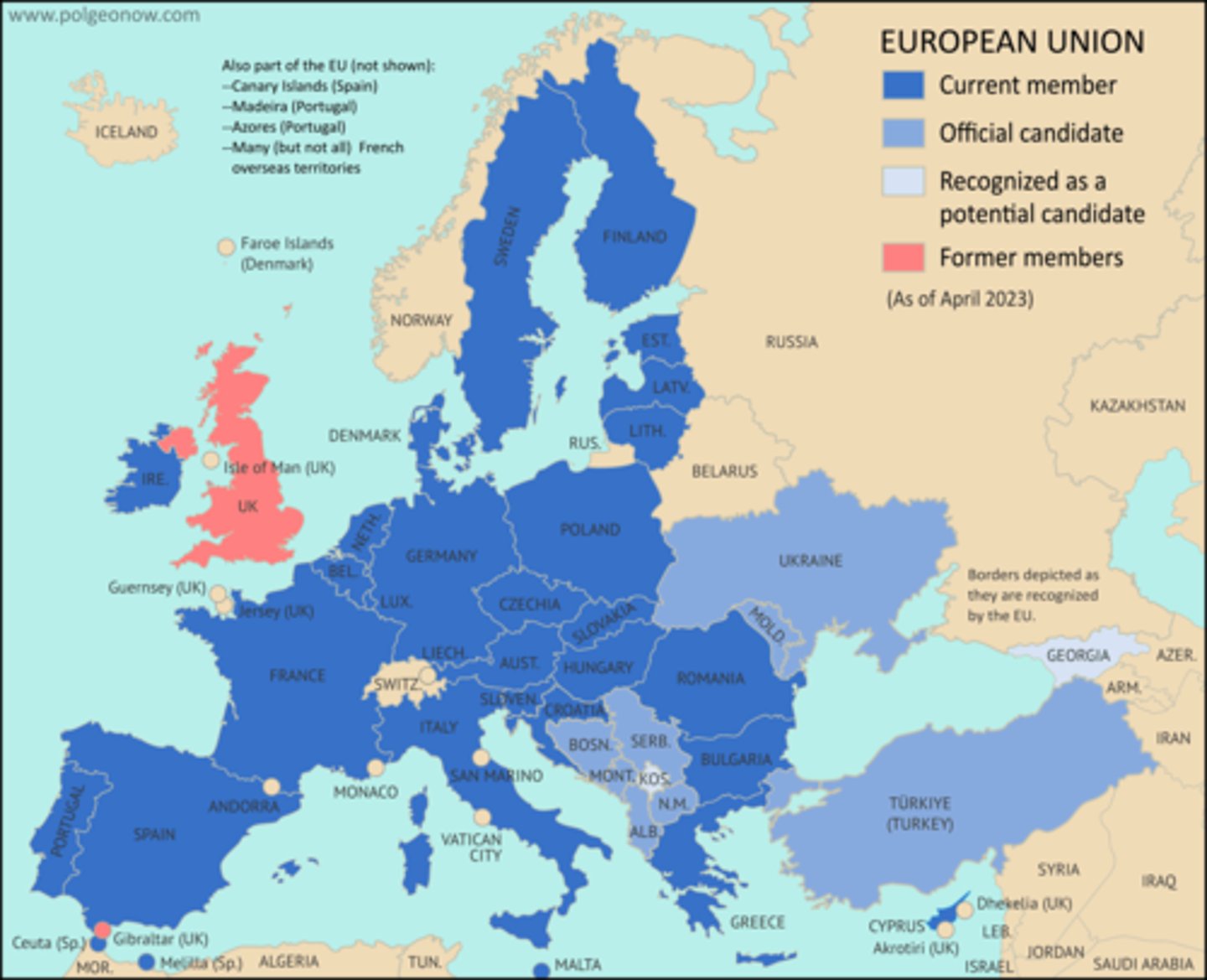
Contested Regional Boundaries
Man-made boundaries are disputed politically (Kashmir, Crimea, Taiwan)
Syncretism
The blending of opposing people, ideas, or practices

Mercator Map Projection
Accurate shape + direction, but distorts distance + size
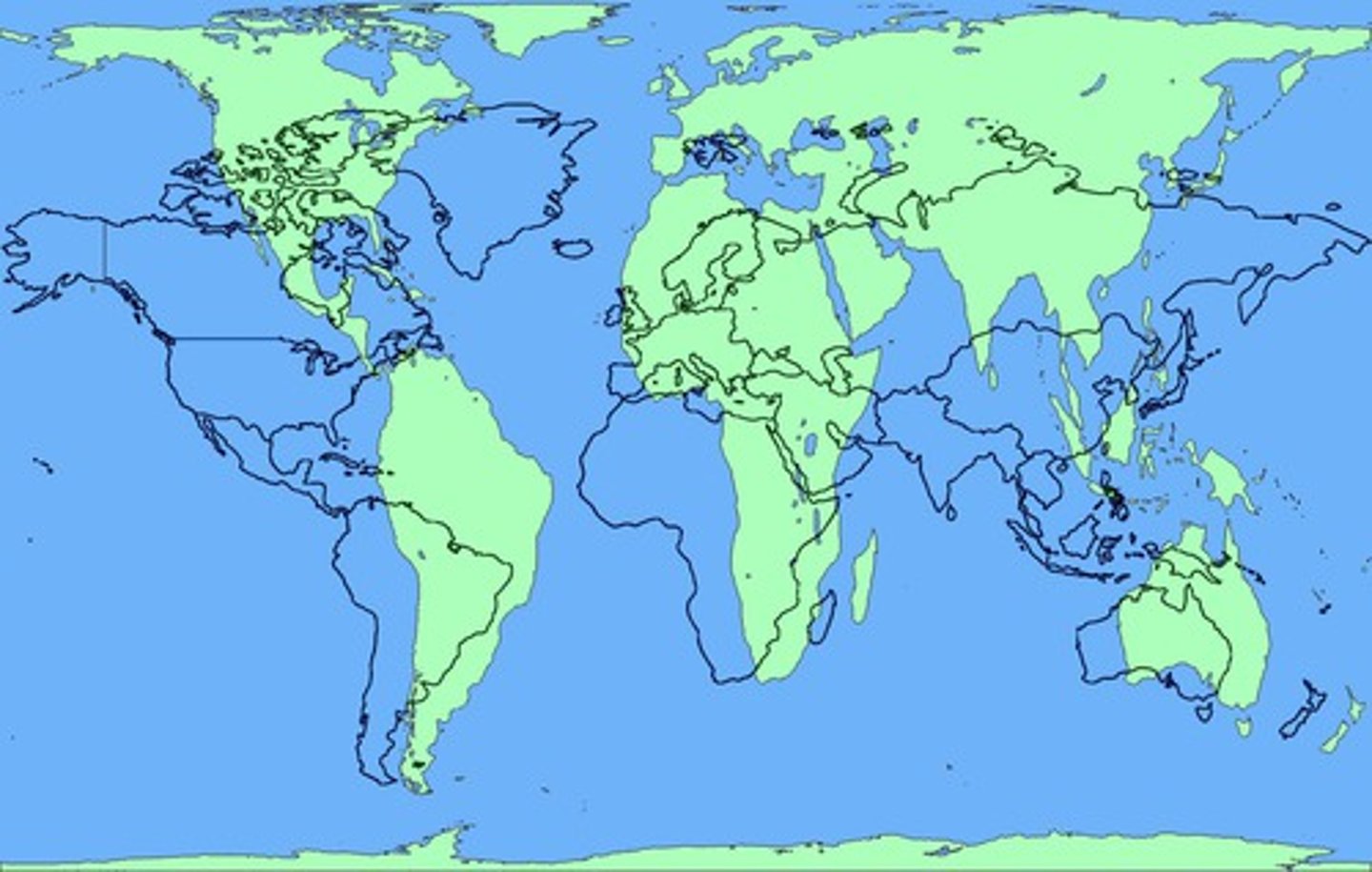
Goode-Homolosine Map Projection
Little distortion of land because of interruptions, but useless for navigation (distorted lines + interruptions in the ocean)
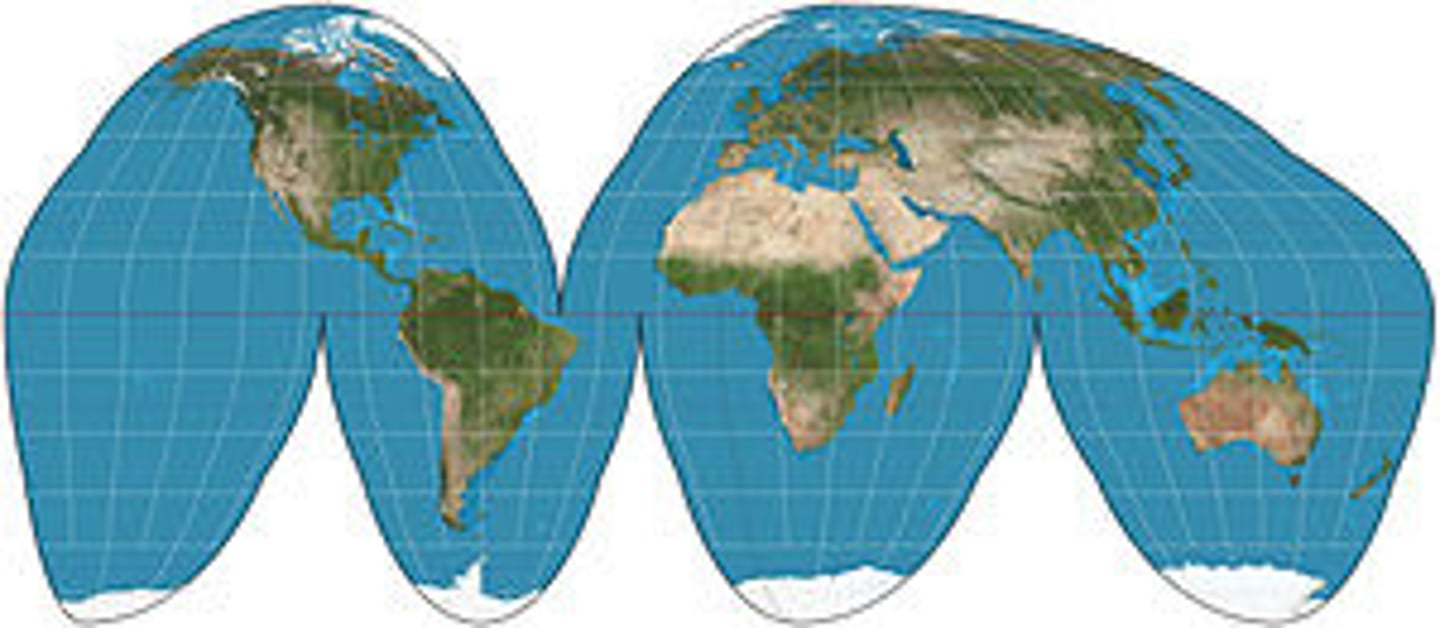
Robinson Map Projection
Less distortion but less accurate direction (curved lines)