Midterms final v
1/397
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
398 Terms
What is an organic compound
A compound made of carbon
What is an example of a organic compound?
hydrocarbon and glucose
structure formula vs. molecular formula
Shows the types of bonds, and the type of elements used. Shows only the elements used and how much of it
Valance shell vs. valance electrons
The area where you are likely to find valance electrons. Outermost electrons
what are the difference between structural, cis-trans, and enantiomer isomers?
structural isomers differ in arrangement, cis-trans depend on the location of the attached molecules, enantiomer isomers are mirrored isomers
Draw a hydroxyl
ok
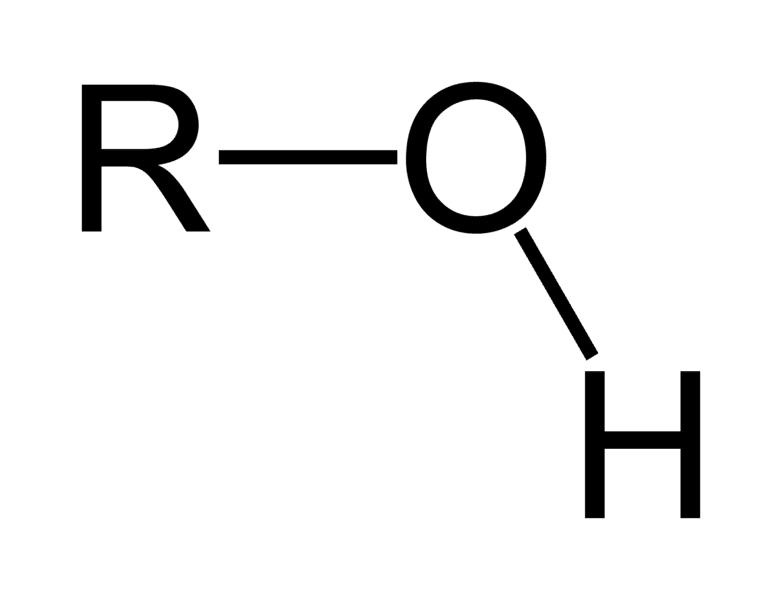
Draw a carbonyl
ok
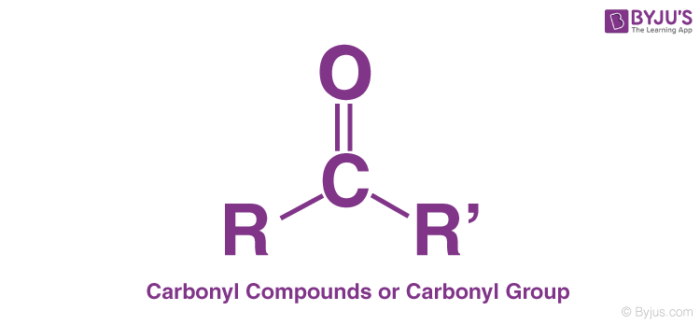
draw a carboxyl
ok
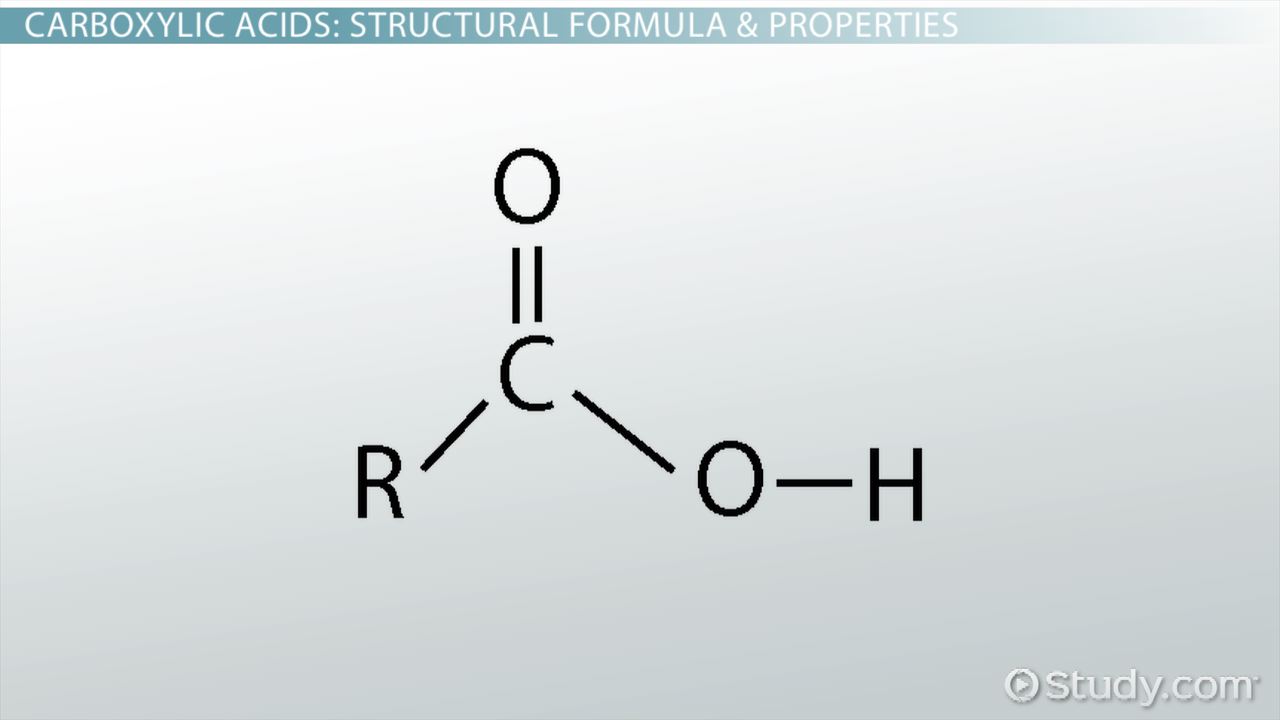
draw an amino
ok
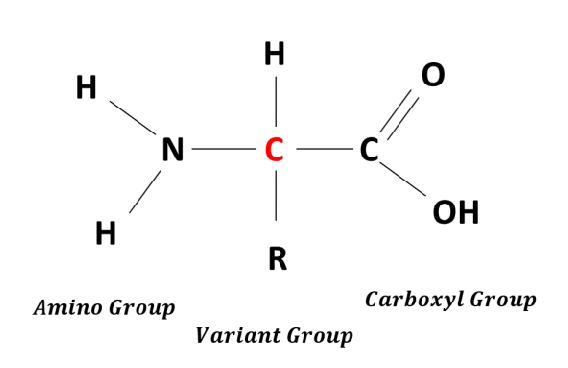
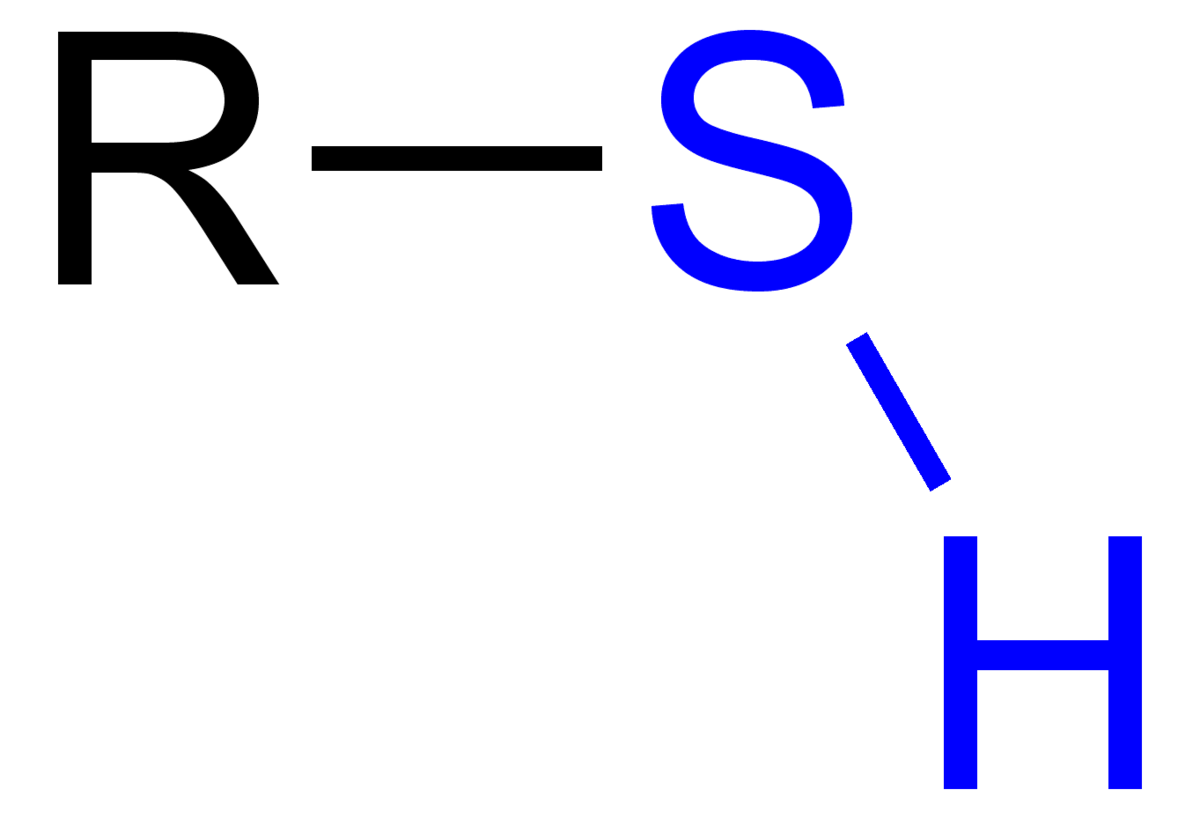
draw a sulfhydryl
ok
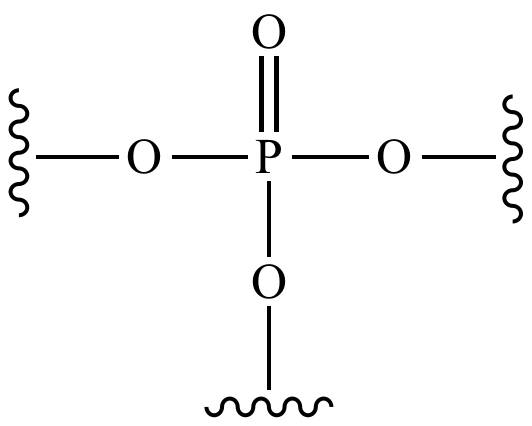
draw a phosphate group
ok
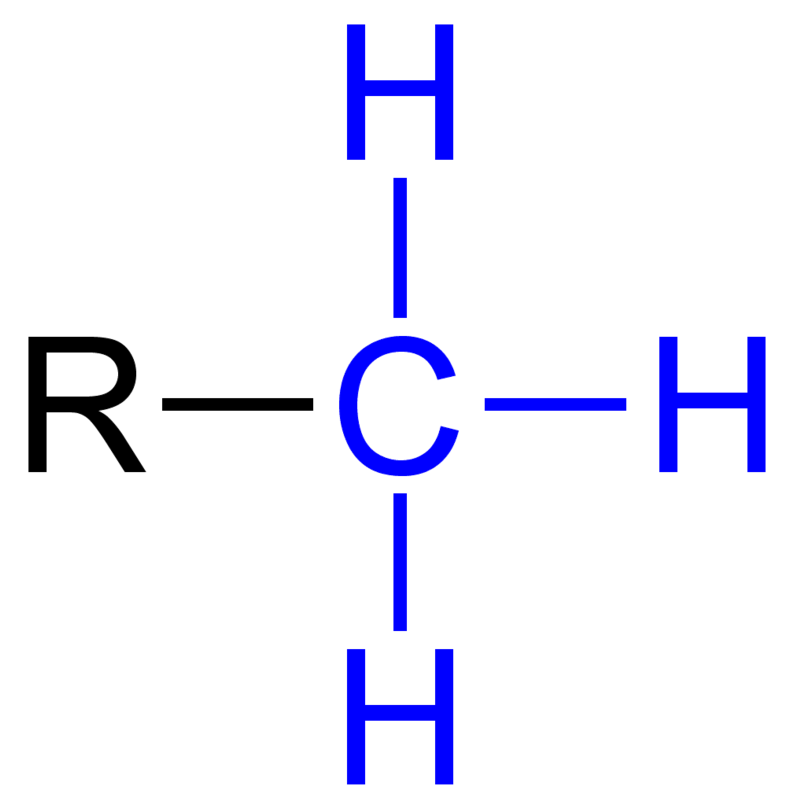
draw a methyl group
ok
what are the 4 main classes of biological macromolecules?
Protein, lipids, nucleic acid, and carbohydrates
lipid structure
Not true polymers and smaller than a macromolecule
what is a purpose of a protein
structure
lipid purpose
energy storage
nucleic acid purpose
store information
purpose of carbs
energy production
What are polymers made of
made of monomers
what are monomers made of?
atoms and molecules
What happens in hydrolesis?
a covalent bond between 2 monomers are broken because water is added
What happens in dehydration?
Covalent bond between 2 monomers with the loss of a water
What are monosach, disach, and poly sach?
sugars
what does monosaccharides do?
quick energy
what does disaccharides do?
Transport
What do poly saccharides do?
storage
What is a special characteristic of lipids?
They are hydrophobic and are not true polymers
What are lipids made of?
made of mostly hydrocarbon molecules
what are the three major types of lipids
Fats, phospholipids, and steroids
Structure of a fat
glycerol and 3 fatty acids
structure of a phospholipid
glycerol, 3 fatty acids, and phosphorous group
Structure of a steroid
What is a unique characteristic of fats?
no double bonds
unique charect. of a unsaturated fat
one or more double bonds
Cis fats vs. trans fats
kinked (bent and liquid at room temp), straight (solid at room temp)
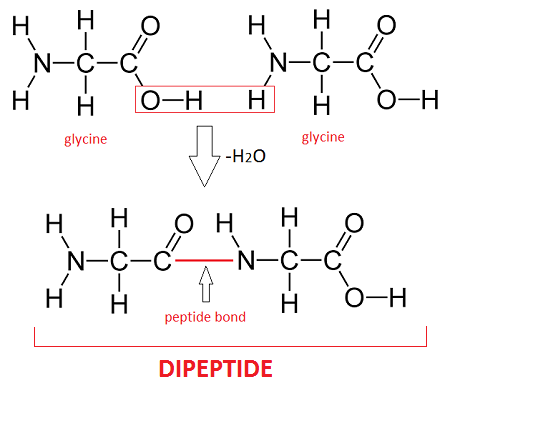
What holds amino acids together?
peptide bonds
Draw a dipeptide
ok
What are the 4 major groups of amino acids?
non polar, polar (uncharged), positively charged (basic), and negatively charged (acidic)
what is a property of non polar groups and an example
hydrophobic, glycine
what is a property of polar (uncharged) and an example
hydrophilic, and serine
what is a property of positively charged (basic) and an example
has a side chain that can attract protons, amino acids
what is a property of a negatively charged (acidic) amino acid and an example
has carboxyl groups, and aspartic acid
Describe a primary level
A linear sequence of amino acids
describe a secondary level
Coiled polypeptides stabilized by hydrogen bonding
describe a tertiary level
3d, held by hyd and ionic bonds
describe a quaternary level
assembly of mult poly peptides
Dna vs. rna
double helixed with deoxyribose, single helixed with ribose
Purpose of dna vs. rna
dna is blueprint of genetics and rna is a messenger
What are polymers?
Made of many monomers (SIMILAR COMPOUNDS)
what connects nucleotides?
Phosphodiester (phosphate group connects to a 3’ carbon)
What does antiparallel in DNA mean?
one helix goes one way, the other goes the opposite way
What are the 5 basic functional groups?
Hydroxyl, Carbonyl (Ketones, Aldehydes), Carboxyl, Amino, Phosphate,
What functional group is this?
hydroxyl (alcohol)
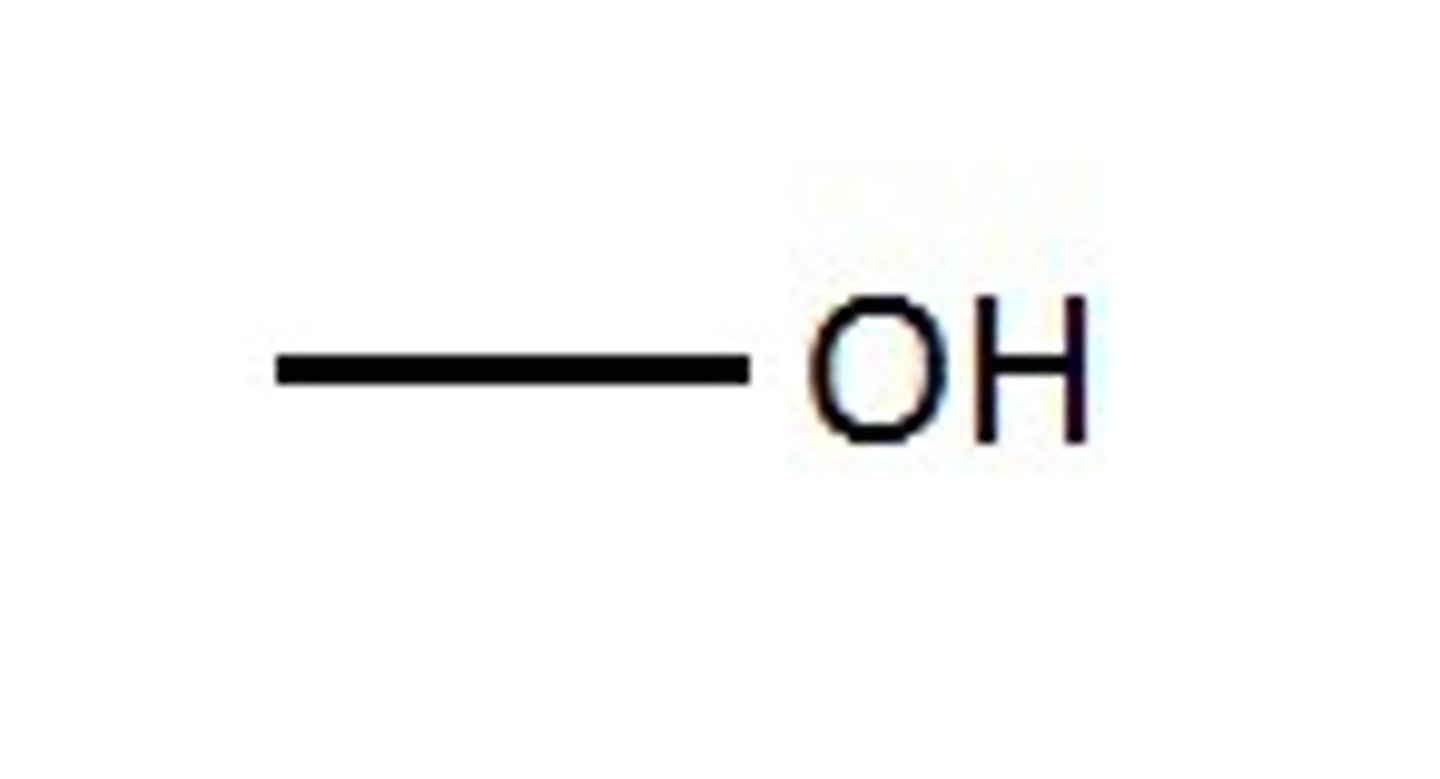
What functional group is this?
Carbonyll
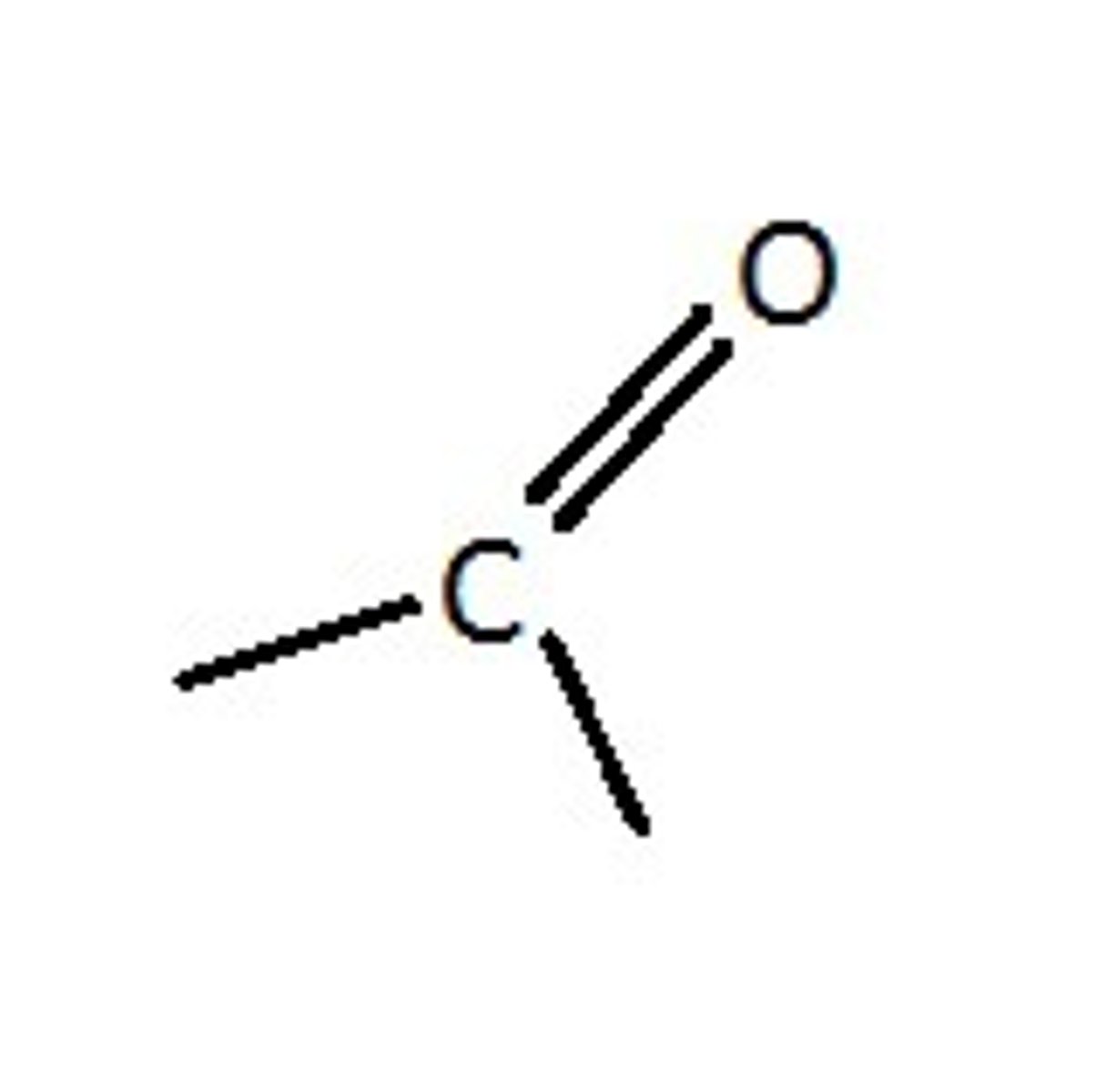
What functional group is this?
Carboxyl
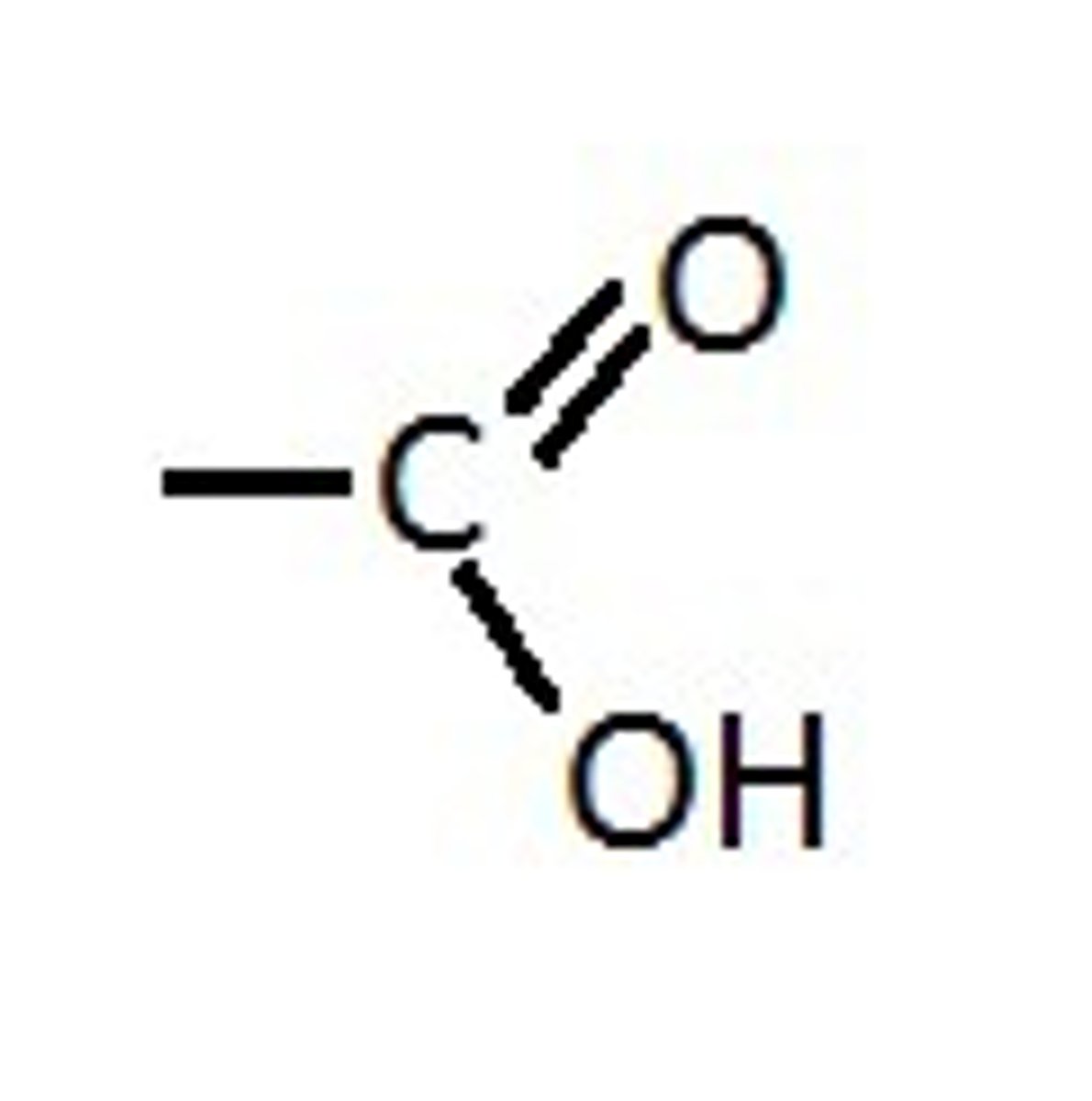
What functional group is this?
Amino
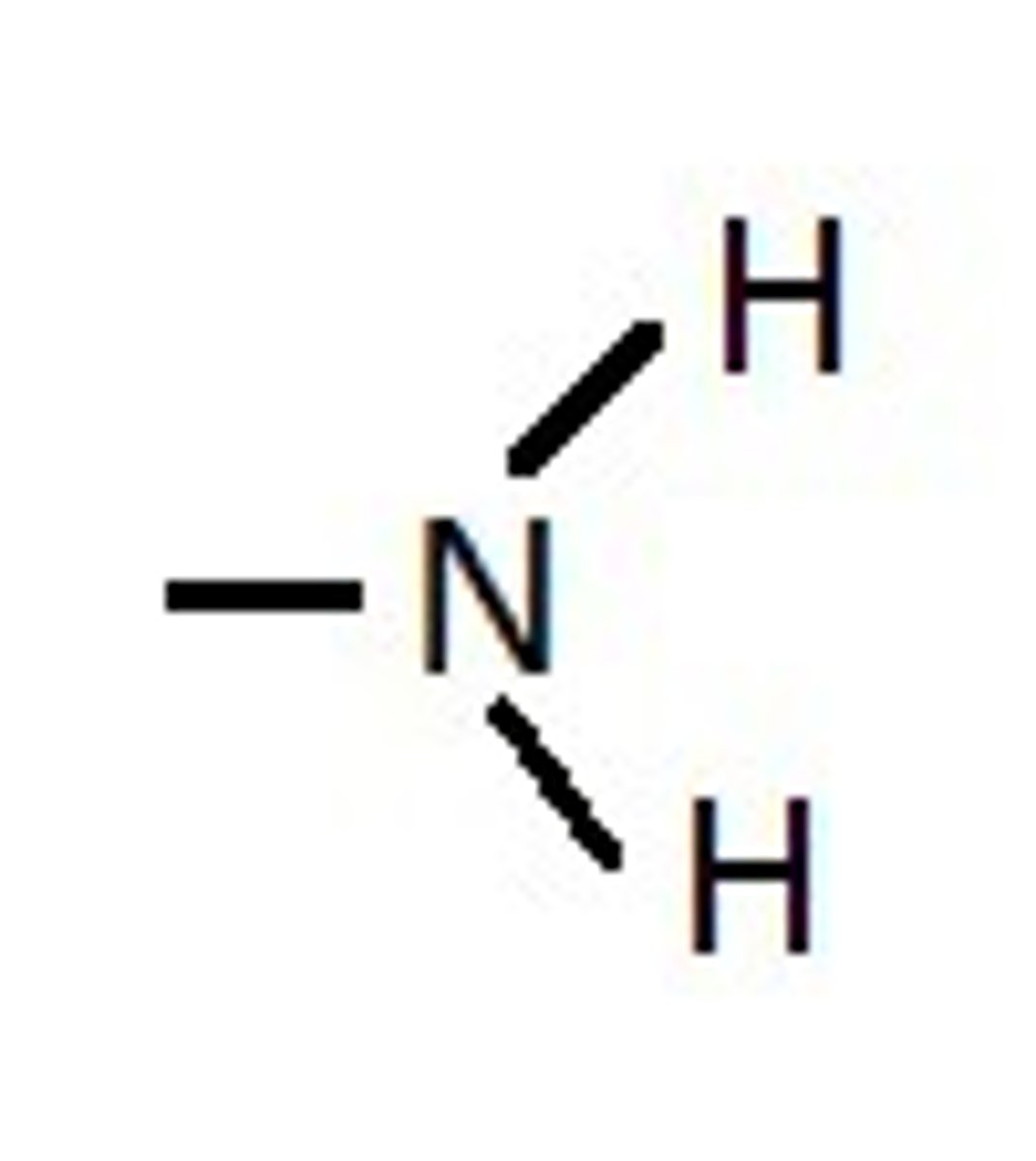
What functional group is this?
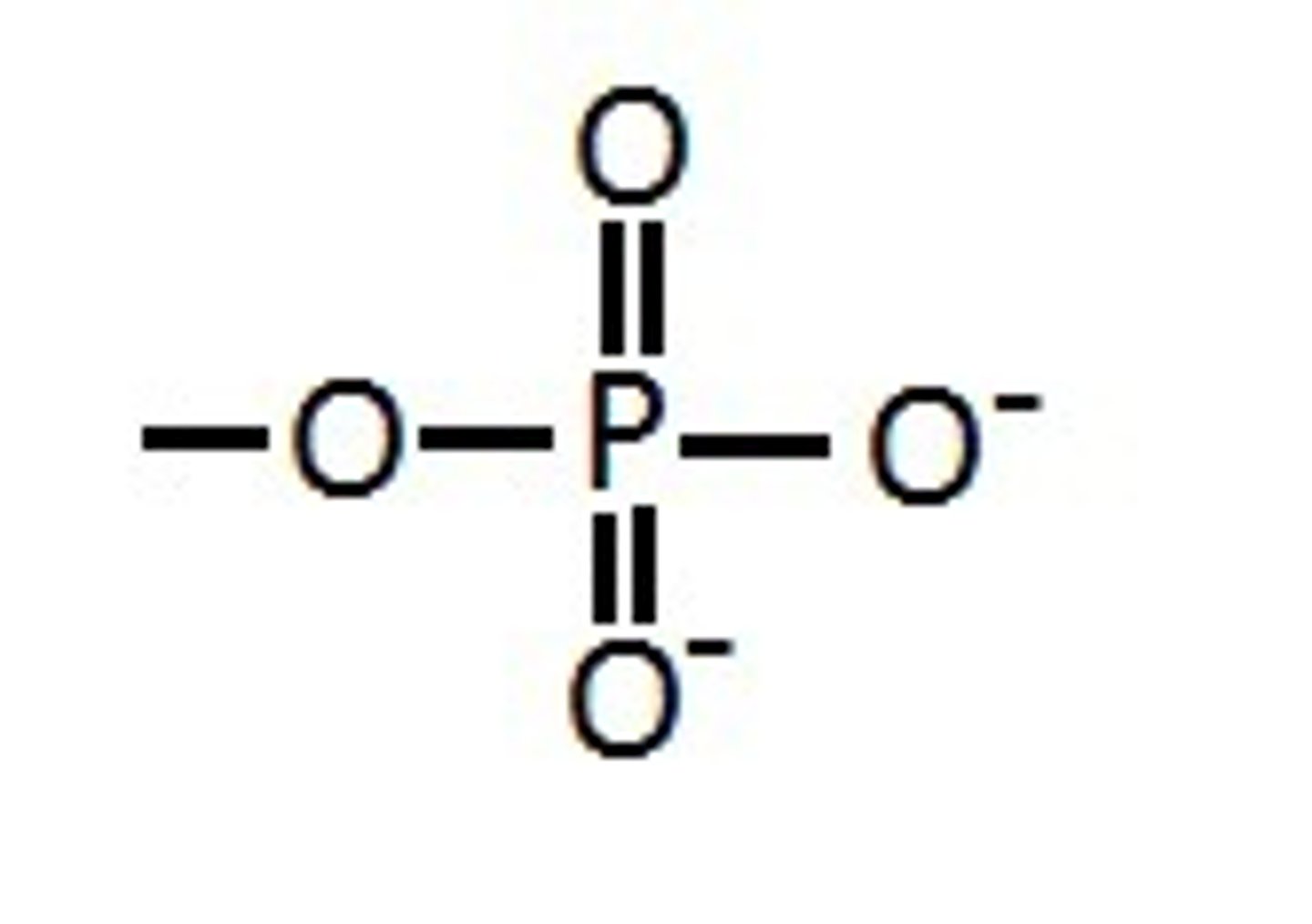
Phosphate
What do you call a molecule carrying a hydroxyl group?
Alcohol
ethanol, hydroxyl
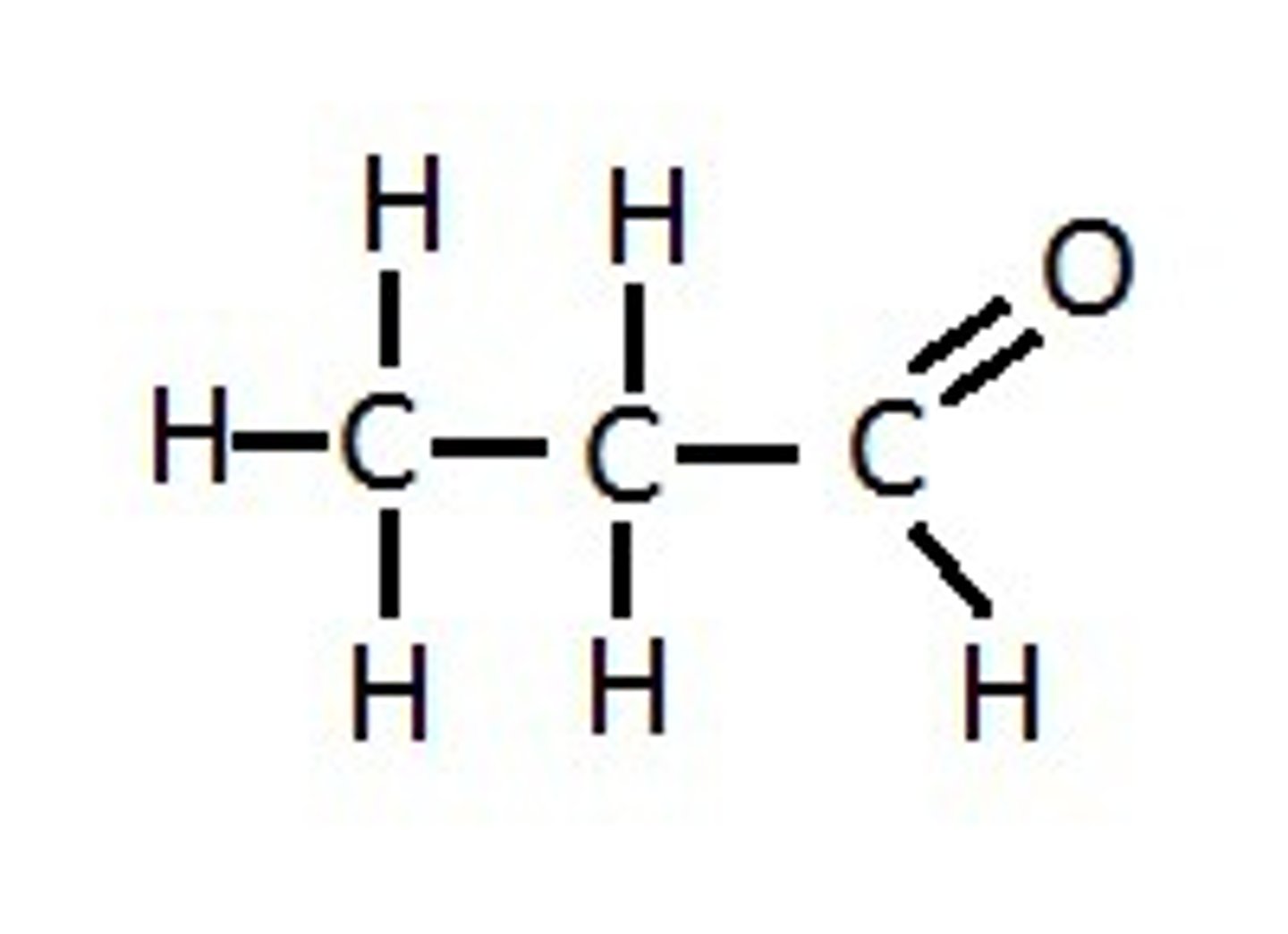
What compound is this and what functional group(s) can you see?
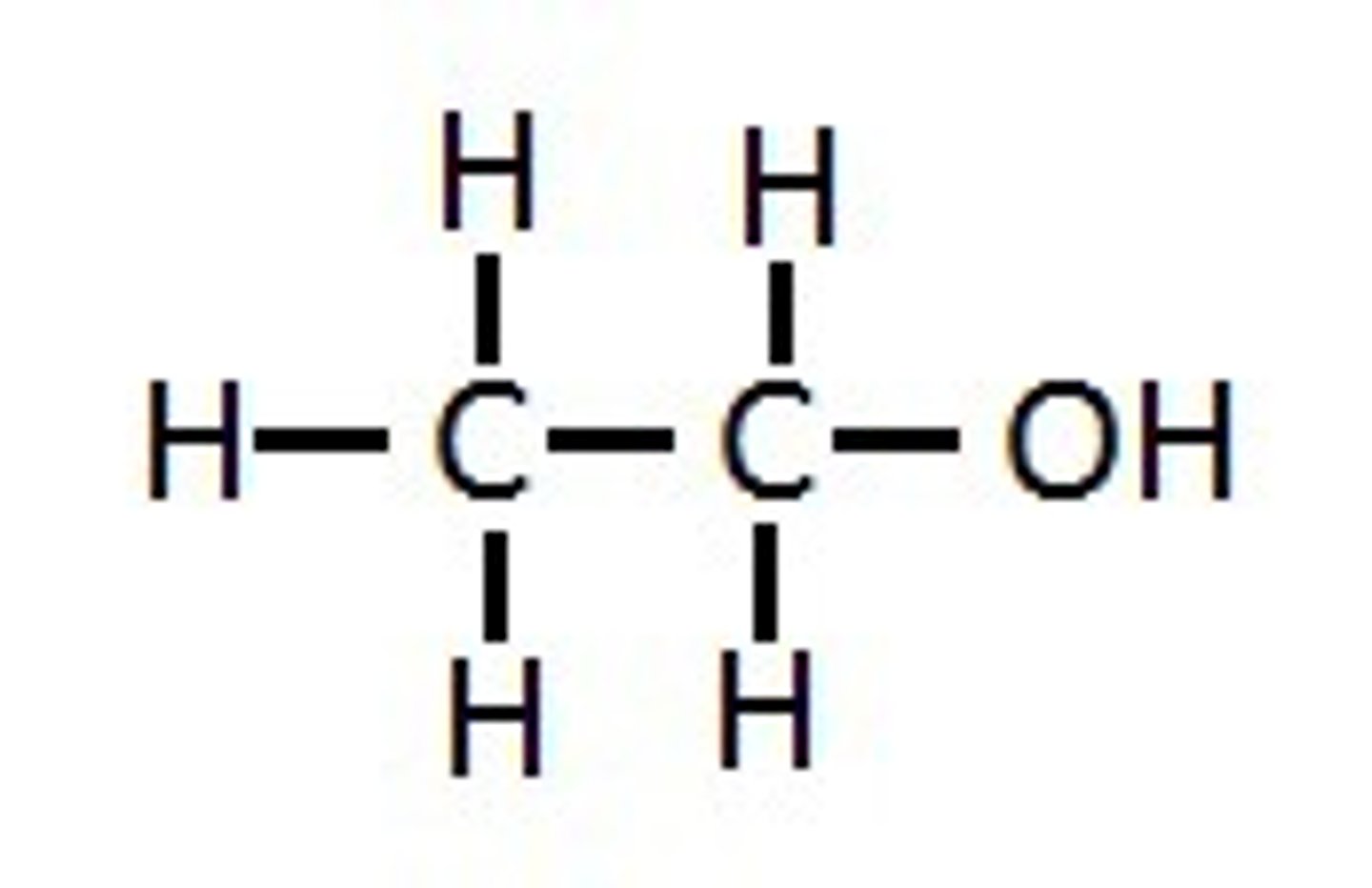
acetone, carbonyl: ketone
What compound is this and what functional group(s) can you see?
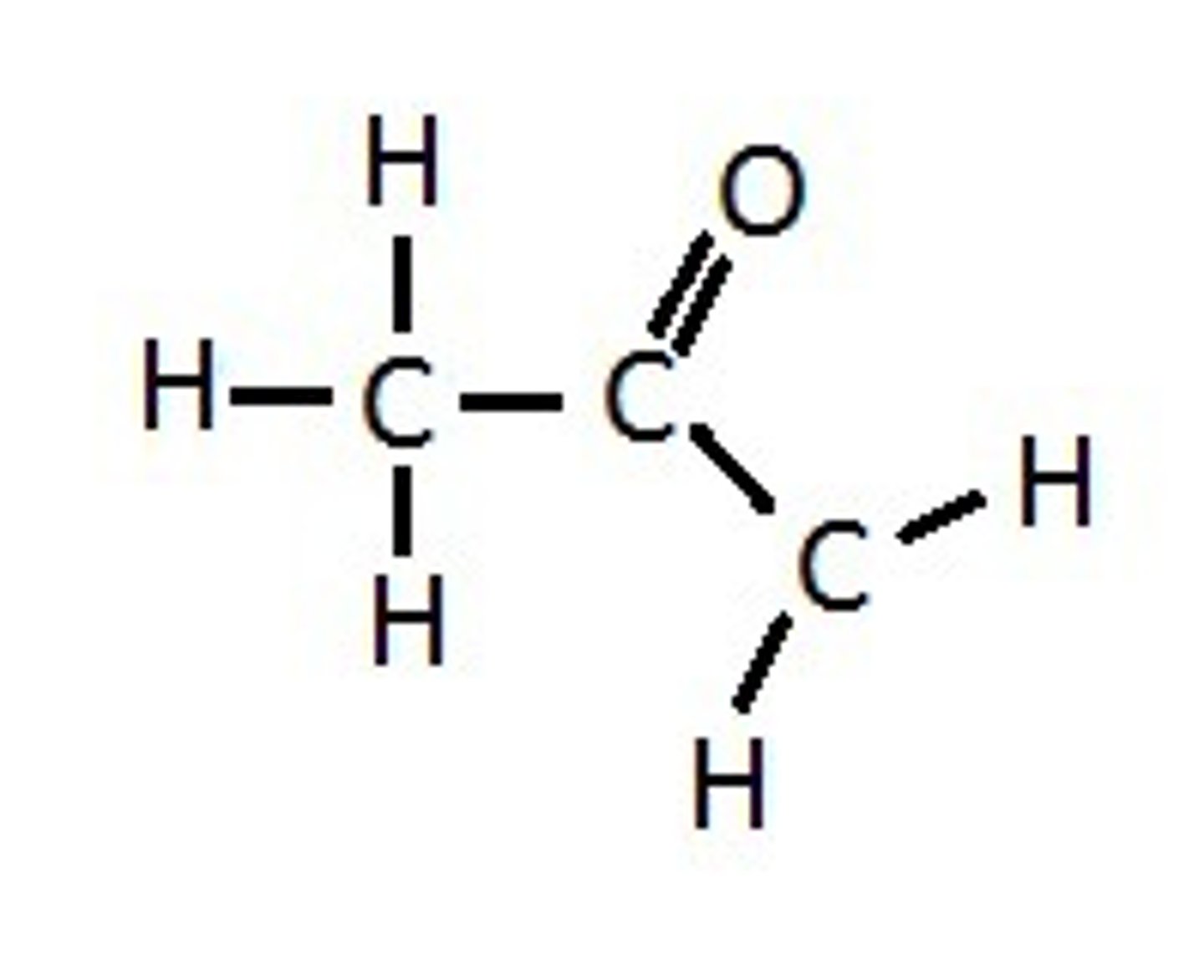
propanol, carbonyl: aldehyde
What compound is this and what functional group(s) can you see?
acetic acid, carboxyl
What compound is this and what functional group(s) can you see?
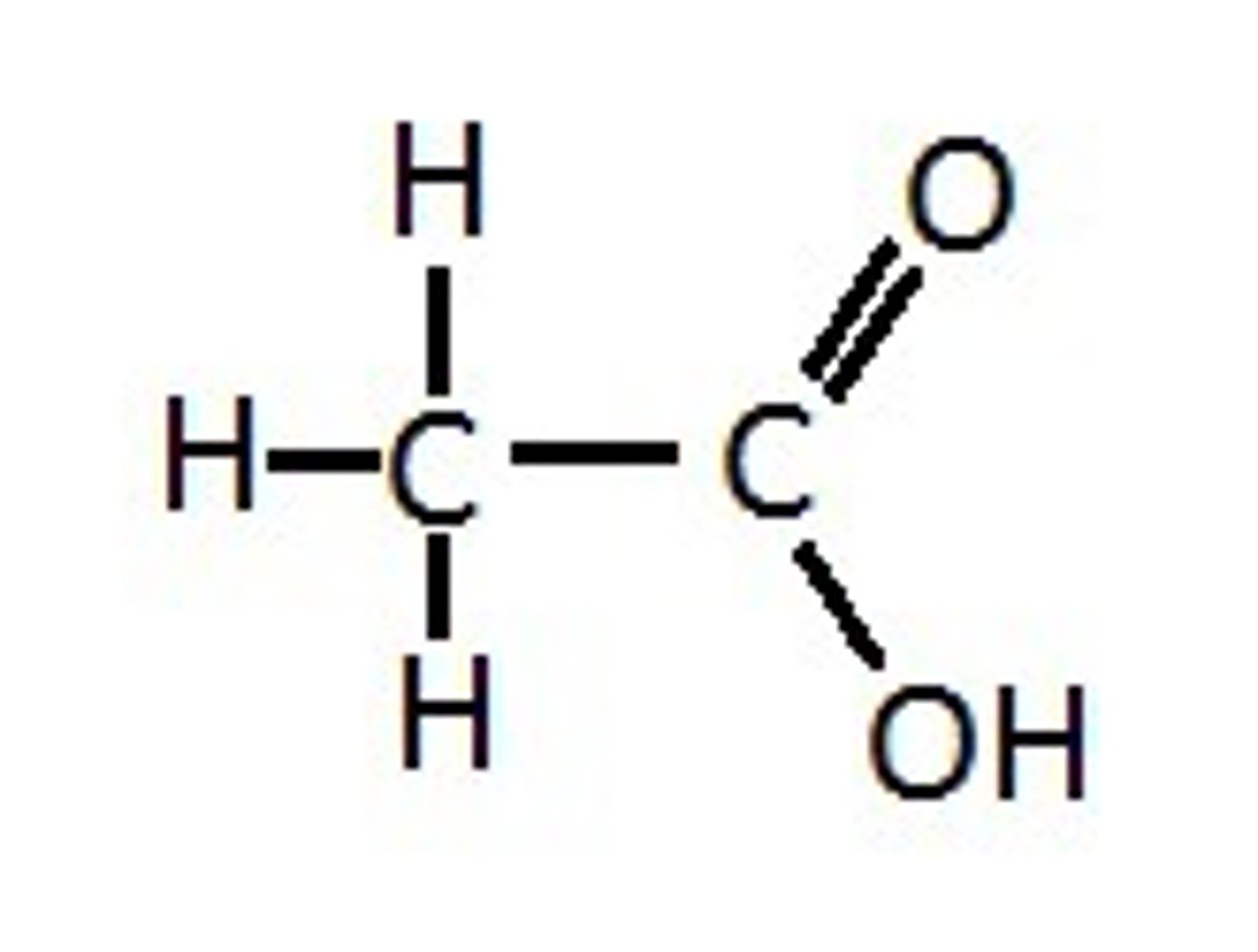
glycine, amino, carboxyl
What compound is this and what functional group(s) can you see?
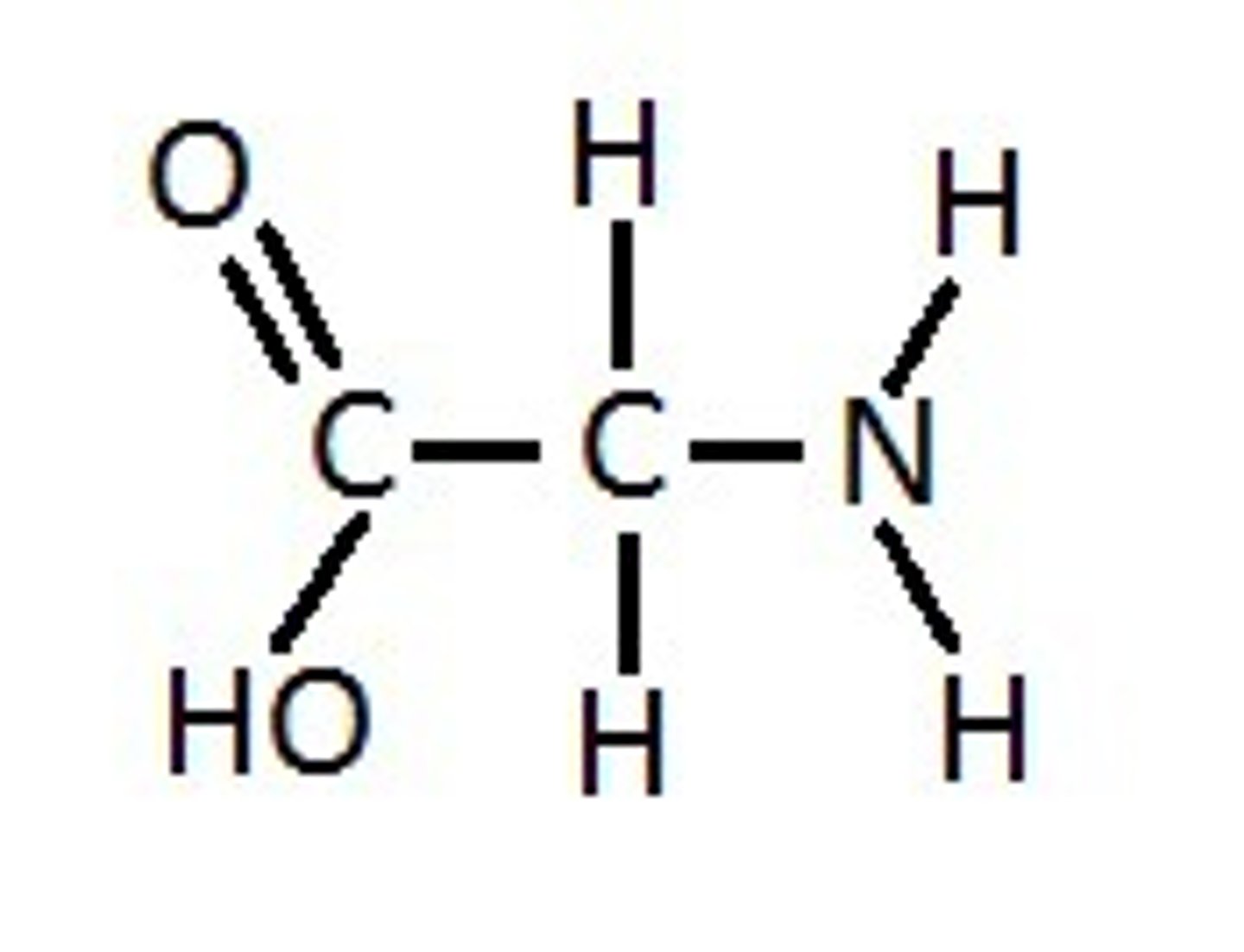
glycerol phosphate, phosphate, hydroxyl
What compound is this and what functional group(s) can you see?
What are the functional properties of hydroxyl groups?
Polar and can form hydrogen bonds
What is the major functional property of carboxyl groups?
Acts as an acid
What are the functional propertie(s) of amino groups?
Act as a base
what are the functional properties of sulfhydryl groups?
Stabilize protien structure
What are the functional propertie(s) of phosphate groups?
Gives a negative charge
What are the functional propertie(s) of methyl groups?
Affects gene expression and hormones
What makes carboxyl groups aicds?
The polar covalent bonds
Based on your knowledge of polarity of water molecules, the solute molecule (X) is most likely
Nonpolar
Which of the following is not a polymer? Why? a. RNA b. starch c. DNA d. glucose
d.glucose. polymers contain monomers of identical structure. glucose = c6h12o6
What is starch?
Polysaccharide found in plants
What is cellulose?
Structural polysaccharide found in plants
What would be the molecular formula for a glucose molecule made by linking three glucose molecules together by dehydration reactions?
C18H32O16
What are unique characteristics of lipids?
Lipids mix poorly with water
What is the primary function of an RNA molecule?
Function in the synthesis of proteins
Draw the structural formula of two fatty acids: one saturated and the other cis-fatty acid
cis-fatty acid has a kink
Characteristic of a fatty acid
carboxyl alpha carbon and a bunch of C with H
what are macromolecules
Protiens, lipids, and nucliec acid’s connected together
what are monomers?
The building blocks of polymers.
What are enzymes and what do they do?
They speed up the process for chemical reactions and synthesis
What is a condensation reaction?
A formation of covalent bonding formed through a loss of a small molecule.
What is a dehydration reaction?
The formation of covalent bonding through the loss of a water
Define hydrolysis
The breaking of covalent bonds through the addition of water
What breaks the bond between monomers?
H2O
Why are a basically infinite number of polymers possible?
Arrangement
What are carbohydrates purpose?
primary energy. Structure
What is a disaccharide?
2 monosaccharides joined by covalent bonding
Monosaccharide formula
CH2O
Draw a hydroxyl group
—OH
The location of a carbonyl determines if a sugar is a
Aldose or ketose
What is a major nutrient of all cells?
glucose
Why is glucose 6 sided gon?
most stable
What is cellular respiration?
Cells break down gluecos’s energy
Monosaccharides are not only used for energy but for what?
Synthesis of other organic molecules
how is a disaccharide constructed?
2 monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkage
What is a glycosidic linkage?
a bond between 2 monosaccharides
What is a polysaccharide made of?
a molecule made of hundreds or thousands of monosaccharides