TFS Week 6
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
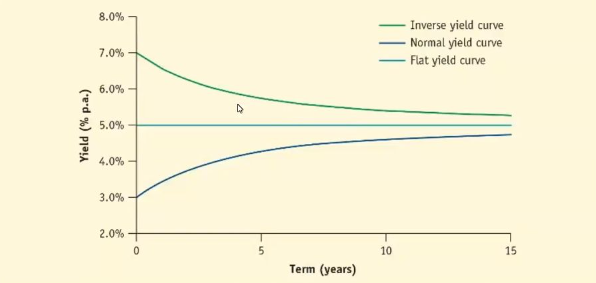
Describe the yield curve graph
On the x axis is the time till maturity of different instrument. On the y axis is their respective interest rates.
What are the yield curve shapes and describe their characteristics?
Inverse yield curve - Short-term interest rates are higher than long-term interest rates
Flat yield curve - All interest rates are the same
Normal yield curve - Short term interest rates are lower than long-term interest rates
What direction is the slope of the yield curve usually?
Upward sloping. The shorter term interest rates on the left are lower than the longer term interest rates
What does the yield curve tell market participants?
It tells them future market conditions and monetary policy
What is the term structure of interest rates?
Refers to the relationship between the interest rates of various financial instruments with different maturities
What term is used interchangeably with term structure?
Yield curve
When does a normal yield curve occur?
Indicating expected economic growth and stable inflation.
When does a flat yield curve occur?
Usually only happens for a short time period. Usually a transitory period between the other to types of yield curves and recession and growth in the economy. Investors are uncertain about the economy
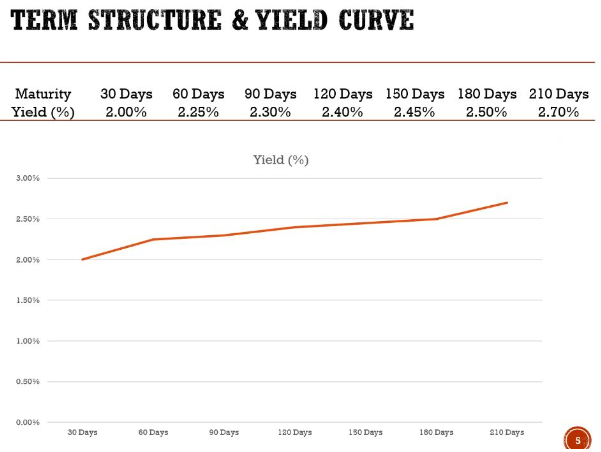
What are yield curves constructed on?
They have to be traded securities rather than bank deposits
They need to have little or no credit and liquidity risk (BAB’s, NCD’s and Treasury Bonds)
The yields need to be calculated on single payment instruments
What are inverse yield curves associated with in the economy?
Recession.
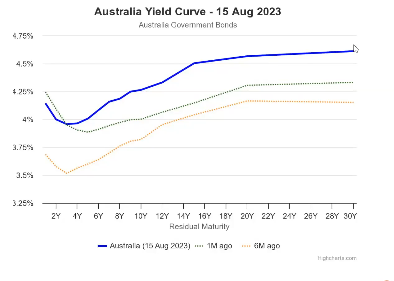
What does the dip at the beginning of the Australian Yield Curve mean.
Investors are confident that in the short term that we will be facing a recession. Over the long term, it is expected that the economy will be normal
What are spot interest rates?
Current rate of interest for a range of terms. Also called the 0 coupon rate
What is the notation for spot interest rates?
The r represents the rate

What is a forward interest rate?
Commences at a future date and extends for a specified term. An interest rate that two parties can agree upon today for a future period based on the prevailing market conditions.
What is a forward contract?
Agreement between two parties to exchange an asset at a future date at a predetermined price
What are the yield curve theories?
Unbiased expectations hypothesis
Liquidity Premium Theory
What is the unbiased expectations hypothesis?
Forward rates are based on the market’s expected future rates. Expected return on long term bonds should be equal to the average return on short term bonds over the same time period.
What does the unbiased expectations hypothesis assume about securities with different terms?
It assumes borrowers and lenders are unbiased in the choice between securities with different terms.
What is an example of the indifference of borrowers and lenders between two securities of different terms?
A two-period investor is indifferent between a two-period security or two successive one-period securities
What is the liquidity premium theory?
Long term interest rates are higher than short-term interest rates because investors demand a premium for the increased risk in holding long term bonds. The liquidity premium compensates investors for the potential loss of liquidity from holding a long term bond.
What yield curve does the liquidity premium theory explain?
Normal yield curve. Because long term interest rates are higher than short term interest rates
What does a payoff diagram look like (risks for a borrower)?
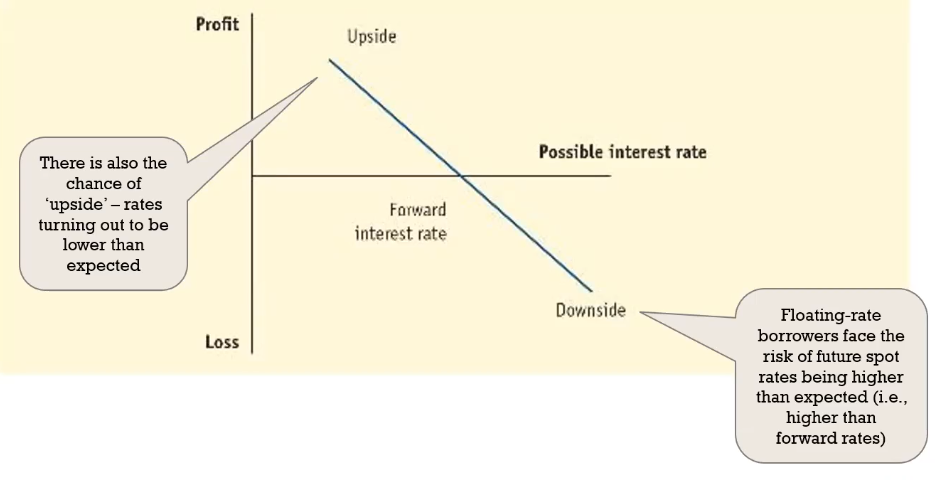
What does a payoff diagram look like (risks for a lender)?
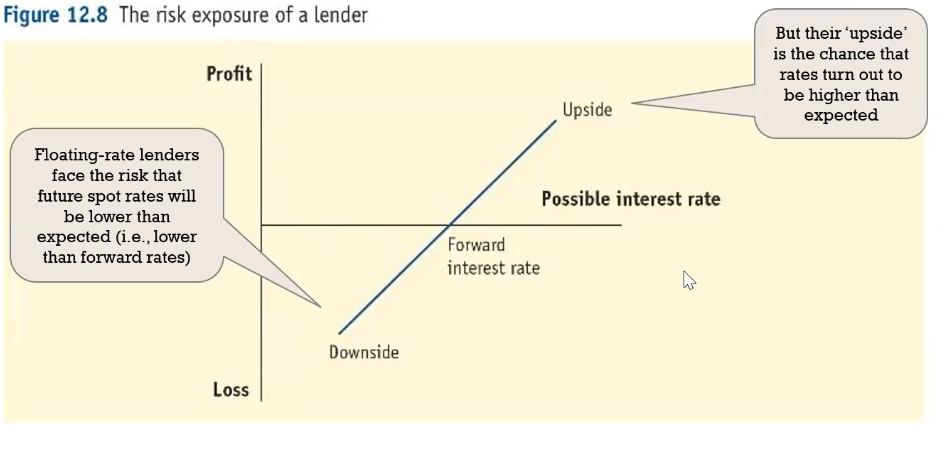
What are derivatives?
Financial instrument whose value is derived from the value of an underlying asset. They are used to hedge against potential losses.
What are the outcomes of hedging?
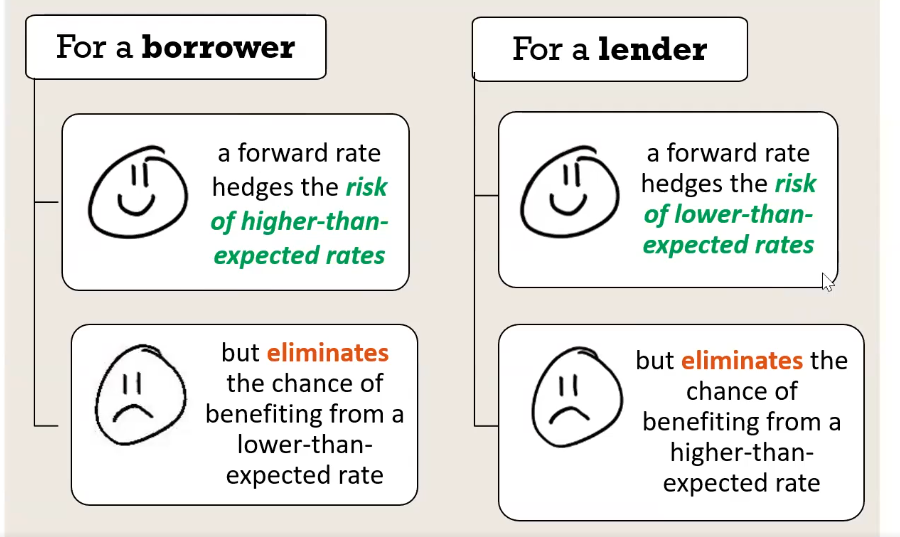
What is a Forward Rate Agreement (FRA)?
An FRA is a contract with a bank that serves to establish a forward interest rate for a specified future date on a nominal principal for a set period, FRA’s do not have any upfront cost
Where are FRA’s traded?
OTC markets. The main dealers are the big 4 banks
What is a 1:4 FRA @5.00%?
Sets a rate of 5% for 3 months (90 days) starting in one month
What are the main advantages of FRA’s?
Meet each client’s requirements
Are convenient to arrange because of standard documentation
Pose low default risk (on the settlement payment)
Given the spot rates of 0r1 = 6.4% and 0r2 = 6.5% calculate the forward rate implied for the second period (1r2)
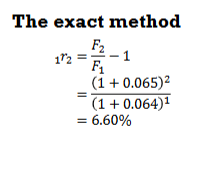
What is the formula for the approximate method to calculate forward rates?
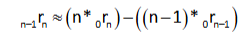
Given 0r1 = 7%, 1r2 = 7.6% and 2r3 = 8.1%, find 0r2
and 0r3
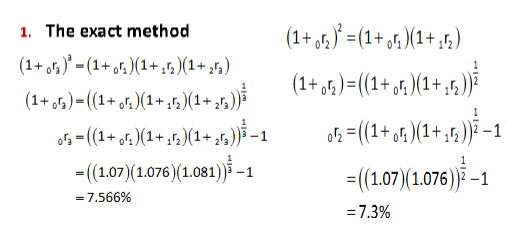
Given 0r1 = 7%, 1r2 = 7.6% and 2r3 = 8.1%, find 0r2
and 0r3 using the approximate method
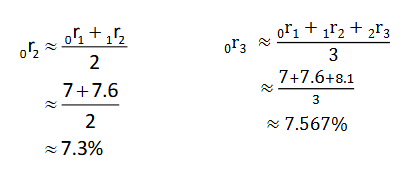
What is settlement in a forward rate agreement?
The net cash flow exchanged between the parties occurs on the contract expiration date, based on the difference between the agreed-upon fixed rate and the actual floating rate at that time.
What is the equation for settlement in a FRA?
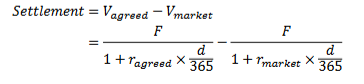
A company plans to issue $50m worth of 90 day bills next month and enters a 1:4 FRA at 6.6%. Next month the spot rate is 6.6%. What is the settlement?
If the settlement was positive it would have been the bank paying the borrower
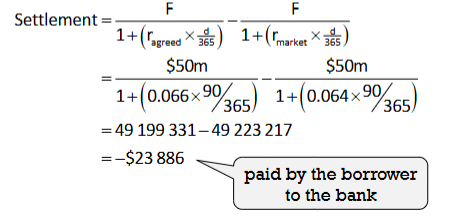
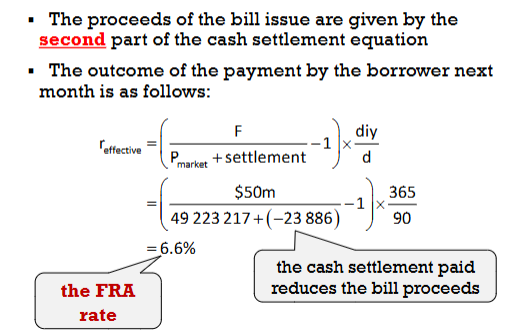
A company plans to issue $50m worth of 90 day bills next month and enters a 1:4 FRA at 6.6%. Next month the spot rate is 6.6%. Idek anymore big bro
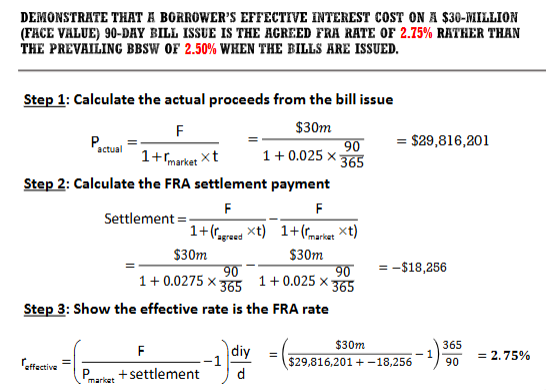
Demonstrate that a borrower’s effective interest cost on a $30 million (face value) 90 day bill issue is the agreed FRA rate of 2.75% rather than the prevailing BBSW of 2.50% when the bills are issued?
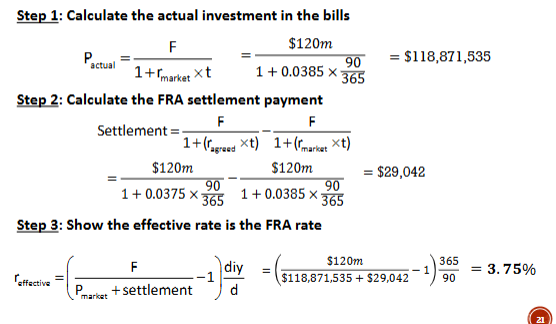
Demonstrate how a 1:4 FRA at 3.75% p.a. locks in the forward lending rate for a fund manager that plans to invest next month in $120 million (face value) worth of 90 day bills. This is assuming that next month the spot rate is 3.85% p.a.
Distinguish between a spot and forward interest rates?
A spot interest rate is today’s interest rate for a specified term whereas, a forward interest rate commences at a future date and applies for a specified term
How are spot and forward interest rates revealed within the financial system?
Spot rates - discovered by the rate at which BABs/NCDs and Treasury bonds are traded in the markets
Forward interest rate - discovered in the futures market
Suppose that in January the BBSW was 3.45% for 30 days, 3.49% for 60 days and 3.53% for 90 days. Calculate the one month implicit forward rates (1r2 and 2r3) using the approximate method

Calculate the implicit forward rate (1r2) using the accurate method (on a compound interest basis) and the approximate method given 0r1 is 4% p.a. and 0r2 is 3.8% p.a.
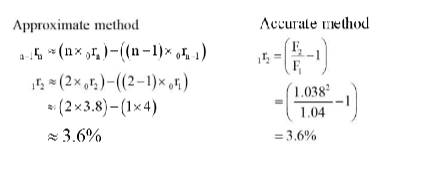
Calculate the one period spot rate given that 0r2 = 4.5% p.a. and 1r2 = 5.5%

Explain the interest rate risk exposure of a borrower under a one year bill facility that uses 90 day bills that start next month
The bills are exposed to interest rate risk each time they are issued because future spot rates are unknown. The risk is that 90 day interest rates will be higher than expected next month and on each rollover date. This would mean the proceeds from the bill issues would be lower than expected and so increase the amount of interest paid by the borrower
Explain how a borrower could use a FRA contract to hedge the interest rate risk posed by a bill facility
To hedge a bill facility a borrower requires a strip of FRAs with settlement dates that coincide with the issue/rollover dates within the bill facility
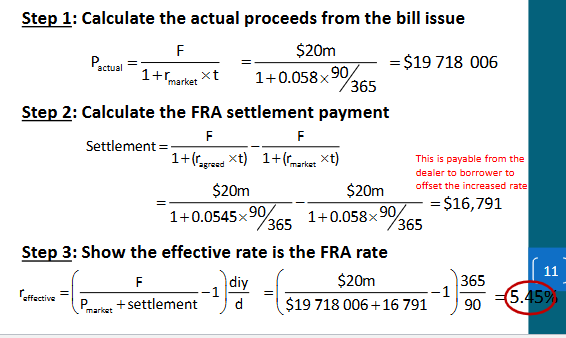
Demonstrate how a 1:4 FRA at 5.45% locks in the effective interest cost on a planned issue next month of $20 million (face value) 90 day bills if the spot rate then is 5.80%
Currently, we are able to lock in the rate of 5.45% (agreed rate) for the next month issue (through the use of FRA) to hedge the interest rate risk (As a borrower, we do not like to see the spot rate to increase yet the future spot rates are unknown). We then discover that the spot rate (5.8%) is higher than expected. That means, under the FRA that we had a dealer, we (as a borrower) are going to receive a cash settlement that makes the effective rate equal to the agreed rate
Demonstrate how a 1:4 FRA at 5.45% locks in the effective interest cost on a planned issue next month of $20 million (face value) 90 day bills if the spot rate then is 5.80%. QUANTITATIVELY