Malignant Diseases of Uterus/Cervix
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
Hormone secreted by the placental trophoblastic cells
Found in urine and blood of pregnant women
Elevated levels are found with GTN
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
Inherited disorder characterized by the presence of polyps of the small intestine and melanin pigmentation of the lips, mucosa, fingers and toes
Anemia from the intestinal polyps is common
Polypoid
Containing more than two normal sets of chromosomes
Teratogenic
Causing congenital anomalies or birth defects
What is the most common site of pelvic malignancy in developed countries?
Endometrium
3 main Uterine cancers:
Endometrial Carcinoma
Leiomyosarcoma
Carcinoma of the cervix
Endometrial Cancer
2x as common as cervical cancer
Ultrasound is very effective in staging endometrial and cervical cancer (when advanced) (TV)
CT and MRI are good at evaluating lymphatic spread for staging
Endometrial Carcinoma
Most commonly encountered malignancy of the female genital tract
Usually found in post-menopausal women
Over age 50
Increased risk with high estrogen levels
Estrogen has a proliferative effect on the endometrium
Thickened endometrium spreads to adjacent areas and into the myometrium
Earliest change in endometrial cancer is thickened endometrium
Endometrial Carcinoma is associated with:
Ackerman’s Triad
Obesity, diabetes, and HTN
Nulliparity
PCOS
Dysfunction Uterine Bleeding (DUB)
Endometrial Hyperplasia
Granulosa-theca cell tumor
late menopause (after 52 y/o)
adenomatous polyps
women on HRT
African Americans
Tamoxifen
Treatment for breast cancer
Can increase chance of endometrial cancer, especially in post-menopausal women
Can change the appearance of the endometrium
Endometrial Carcinoma symptoms:
Usually asymptomatic
Abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge after menopause
Bleeding within the endometrial cavity may cause uterine pelvic pain
What provides endometrial carcinoma diagnosis?
D&C (Dilation and Curettage) with endometrial biopsy
Endometrial Carcinoma Staging:
Stage 1 - Limited to the endometrium
Stage 2 - Spreads to Cervix
Stage 3 - Spreads to adnexa, vagina, pelvic, and periaortic lymph nodes
Stage IV - Bladder and bowel mets as well as distant mets
Endometrial Carcinoma Treatment:
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy
Bilateral Salpingo-Oophrectomy
Radiation Therapy
Stage IV may include chemotherapy or hormone therapy
Endometrial Hyperplasia
Endometrial thickening not specific to endometrial cancer
May be a precursor to endometrial cancer
25% of pt’s with atypical endometrial hyperplasia progress to endometrial cancer
In post-menopausal female, must be considered cancer until proven otherwise
May be due to prolonged estrogen stimulation
Abnormal bleeding
Associated w/ Tamoxifen
Endometrial Hyperplasia U/S appearance:
Thickened endometrium
>14 mm suggests hyperplasia
In post-menopausal female, 8mm is upper limits of normal
Leiomyosarcoma
RARE, fast growing malignancy of fibroids
Aggressive growth
Rarely diagnosed prior to surgery
Localized re-growth and metastasis are common
Associated w/ perimenopausal or postmenopausal growth of fibroid
Requires serial ultrasounds to check growth
Common leiomyosarcoma metastasis sites:
Lung is common sites
Others include:
Bone
Brain
Abdomen
Leiomyosarcoma risk factors:
nulliparity
increasing age
perimenopausal
postmenopausal
in the 5th decade of life
obesity
history of pelvic radiation
exposure to tamoxifen
Leiomyosarcoma symptoms (in women over 40):
Abnormal vaginal bleeding (56%)
Palpable pelvic mass (54%)
Pelvic or abdominal pain (22%)
Leiomyosarcoma prognosis:
B/c uterine LMSs are extremely aggressive, prognosis depends on tumor stage and grade
Greater survival in:
premenopausal women
women with tumors <5cm
Poor prognosis w/:
vascular infiltration
extrauterine spread
Cervical Carcinoma
Second most common pelvic malignancy in US
Decreased in the last few decades d/t PAP smears (early detection)
Cervical Carcinoma risk factors:
Early sexual activity
Multiple sex partners
HPV
Exposure to DES
DES-exposed daughters are 40x more likely to develop CCA (Clear cell adenocarcinoma) than women not exposed
But b/c this cancer is so rare, its only about 1/1000 of DES daughters that develop Cervical Cancer
DES also increased breast cancer risk
Higher incidence in peri-menopausal women
Cervical lining two layers:
Lower cervix is covered by squamous epithelium - 85-90% of cervical cancer lesions
Cervical canal lines with columnar epithelium - 10-15% of cervical cancer lesions
Junction between 2 cell types is where most cancers occur
Cervical Carcinoma clinical diagnosis:
Occurs at a younger age than endometrial carcinoma
25-40 y/o
Symptoms
None in early stages
difficult to detect with US in stages 1-2
Larger tumors and more advanced stages can be visualized
Diagnosis made by cervical biopsy
Cervical Carcinoma symptoms:
Abnormal bleeding
pain
bleeding after intercourse
weight loss
bladder irritability
low back pain
Pap Test
Speculum is inserted and the cervix is swabbed to remove a small sample of cells
Cells are evaluated for signs of changes in the cells that may lead to cancer
If a PAP test is abnormal, a Colposcopy may be required
Colposcopy
Abnormal PAP results
Provides magnified view (2-60x) of the vagina and cervical tissue so that minor tissue changes can be identified
Acetic Acid (vinegar solution) solution applied to area of interest
Acetic acid reacts differently when it comes into contact with areas of abnormal tissue versus normal tissue
Abnormal areas turn white
Biopsy areas of suspicion
Cervical Carcinoma Treatment:
Treatment determined by the stage of the disease
Cryotherapy
Cone biopsy of cervix
Technique for early stages when fertility preservation is desired
Radiation therapy
Total hysterectomy
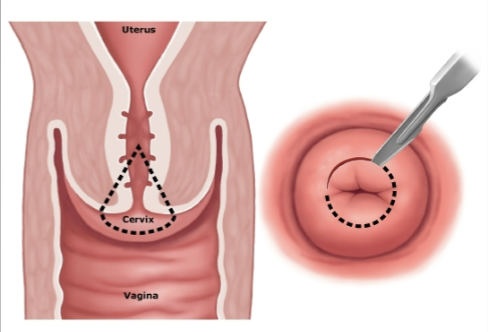
Cone Biopsy AKA:
Cervical Conization
Cone Biopsy
may remove cervical cancer or pre-cancerous tissue
May be used to analyze cells of suspicious lesions
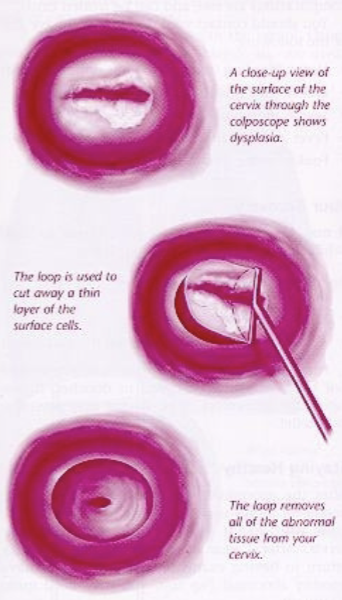
LEEP (Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure)
uses a thin, low-voltage electrified wire loop to cut out abnormal tissue
cut away abnormal cervical tissue that can be seen during colposcopy
remove abnormal tissue high in the cervical canal that cannot be seen during colposcopy
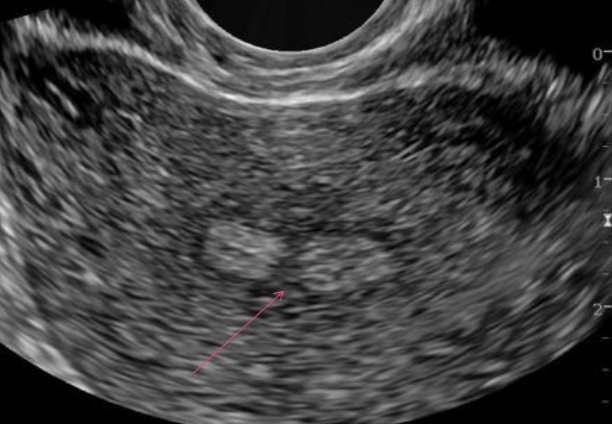
Cervical Carcinoma U/S appearance:
Not usually seen on US in stages 0-II
May see enlarged cervix
Scan kidneys to look for hydronephrosis
indicates stage III disease
Scan for liver mets
Cervical Carcinoma differential diagnosis:
cervical myoma
prolapsed endometrial polyps
Fallopian Tube Carcinoma
Rare → less than 1% of all GYN malignancies
aggressive tumor most commonly in the 6th decade of life
8% are metastatic with primary sites being the ovary, uterus, or GI tract
CA-125 may be suggestive of malignancy
Fallopian Tube Carcinoma risk factors:
infertility
nulliparity
low parity
pelvic inflammatory disease
family hx of ovarian cancer
Fallopian Tube Carcinoma signs / symptoms:
abdominal pain
increased abdominal girth
abnormal vaginal bleeding
palpable pelvic mass
small and hard to detect on pelvic exam
How is Fallopian Tube Carcinoma treated?
Radiation and chemotherapy
Asherman’s Syndrome AKA:
Fritsch Syndrome
Asherman’s Syndrome
Normal endometrium replaced by fibrous adhesions
Secondary to:
Previous D&C
Multiple Abortions
Infections
Can cause absence of menstruation
Asherman’s Syndrome U/S appearance:
Normal appearance
Thickened endometrium