Postmortem Changes
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
postmortem
_____________: after death
antemortem
__________________: before death
perimortem
_________________: around death
autopsy
________________: self-examination (human)
necropsy
_________________: death examination
cause of death, extent of disease
What does autopsy/necropsy hope to determine?
dissection, observation, interpretation, documentation
Necropsy involves a careful process of _______________, _____________, _______________, and ________________.
autolysis
___________: decomposition of cells that takes place after somatic death; Breakdown of the body by endogenous substances / enzymes by ITS OWN SUBSTANCES
Putrefaction
_____________: decomposition of organic matter by bacterial or fungal digestion
postmortem predation/scavenging
________________: animals feeding on bodies after death
decomposition
________________: Process by which dead organic substances are broken down into simpler organic or inorganic matter
autolysis, putrefaction
postmortem degeneration is the result of _________ and ______________
true
True/false: one of the main challenges of necropsy is differentiation antemortem cell death from postmortem cell degeneration
liver mortis/hypostatic congestion
______________: Gravitational pooling of blood on the dependent (down) side of the carcass
dependant side (down)
where is blood sent in hypostatic congestion?
pale-skinned, non hairy animals; organs on the down side
where do you see hypostatic congestion most?
0.5-2 hours
How long until hypostatic congestion starts?
blanches (to make pale/move the blood around)
What happens initially on palpation after livermortis has started?
8-12 hours
How long until liver mortis is "fixed" on one side?
smooth and shiny, lack of lamination, lack of attachment to endothelial surface of the vessel
Describe a postmortem clot.... (3 things)
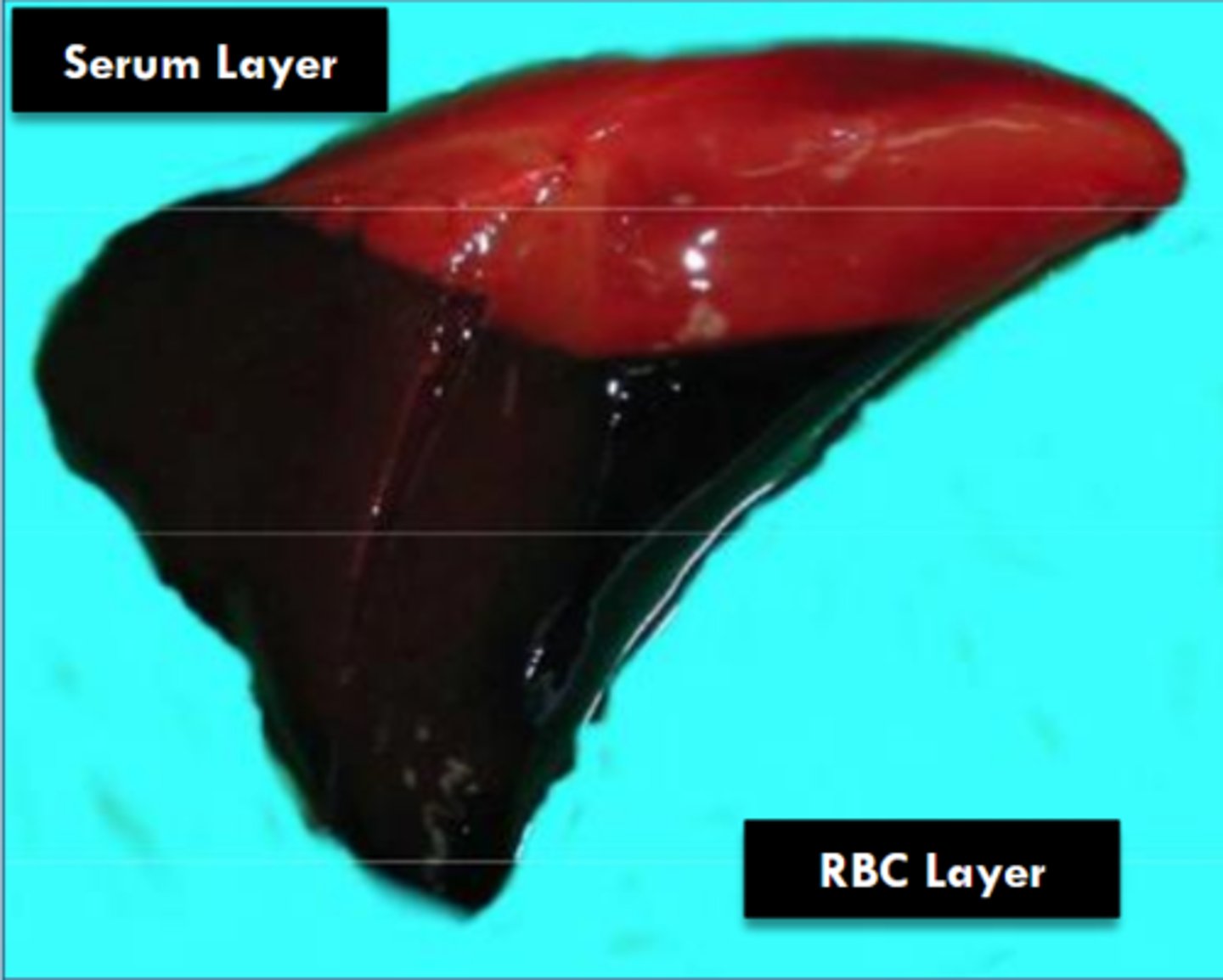
RBCs at the bottom, buffy coat of leukocytes, clotted serum at the top
When blood settles in a dead body, what is meant by a "chicken fat" or "black currant clot"?
horses, high errythrocyte sedimentation rate
What species is a "chicken fat clot" common in?
Why?
chicken fat/black currant clot
What is this pattern?
inflammation
increased sedimentation rates indicate ____________ in the animal
anticoagulant rodenticide toxicity, hereditary coagulopathies
decreased sedimentation rates indicate...(2)
rigor mortis
generalized contraction of skeletal muscle
1-6 hours, 2+ days
When does rigor mortis start? How long does it persist?
Muscles need ATP to relax, run out of intracellular stores of glycogen after death
why does rigor mortis occur?
only autolysis, need complete breakdown of proteins, not just the corss-bridges
How is rigor reversed?
antemortem exertion, seizures, antemortem hyperthermia
What can cause accelerated rigor?
Aseptic
Autolysis is a [septic/aseptic] process
putrefaction
_____________: Involves the action of bacteria on the tissues or body
postmortem bacilli, fermentation
putrefaction is done by ________________ and can result in ____________.
severe softening, gas, not suitable for microscopic exam
Implies presence of __________ and ___________ in tissue
May suggest samples are:
true
true/false: another cahllenge of necropsy, is that there is limited data or evidence to hep determine the postmortem interval
long interval between death and necropsy
high ambient temperature
large body size
heavy hair or wool
continued fermentation in GI tract (equine and ruminants)
antemortem hyperthermia,
antemortem bacteria
what things INCREASE autolysis? (7, but she said to make sure we knew this stuff :.)
short interval between death and necropsy
rapid cooling of carcass postmortem (lower ambient temp/fridge)
thin animal (reduced fat/muscle)
High levels of tissue antibiotics
What can REDUCE autolysis? (4, again KNOW THESE)
20 minutes
Autolysis develops within ________ in the rumen or intestine
pH drops
what happens to the rumen postmortem that causes quick autolysis?
brain, spinal cord
_______ adn ________ are tissues quick to autolyze
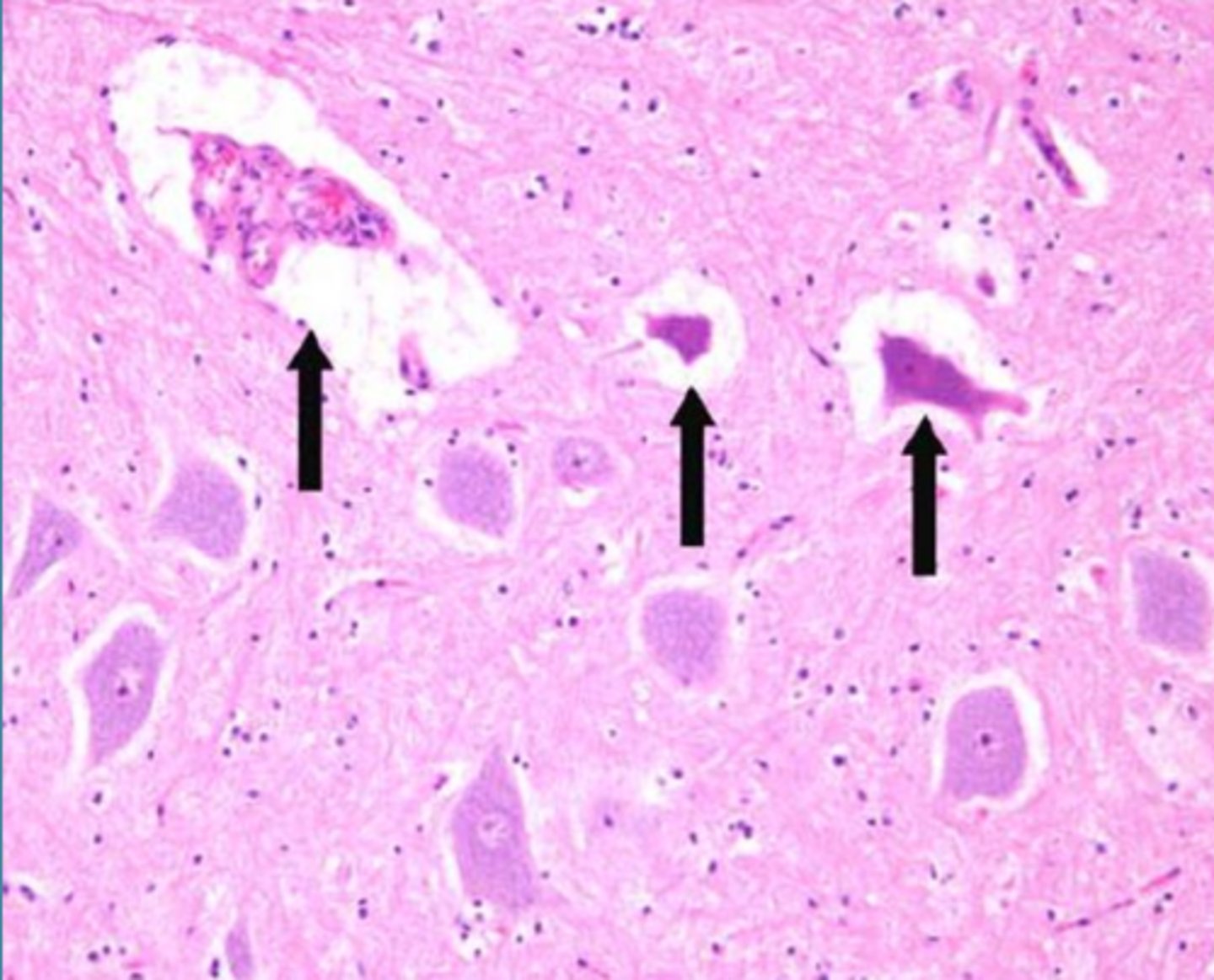
dark neurons
handling artifact in brain tissue on necropsy
False; it retains the ability to contract
true/false: skeletal muscle once dead... is dead man, it doesn't move
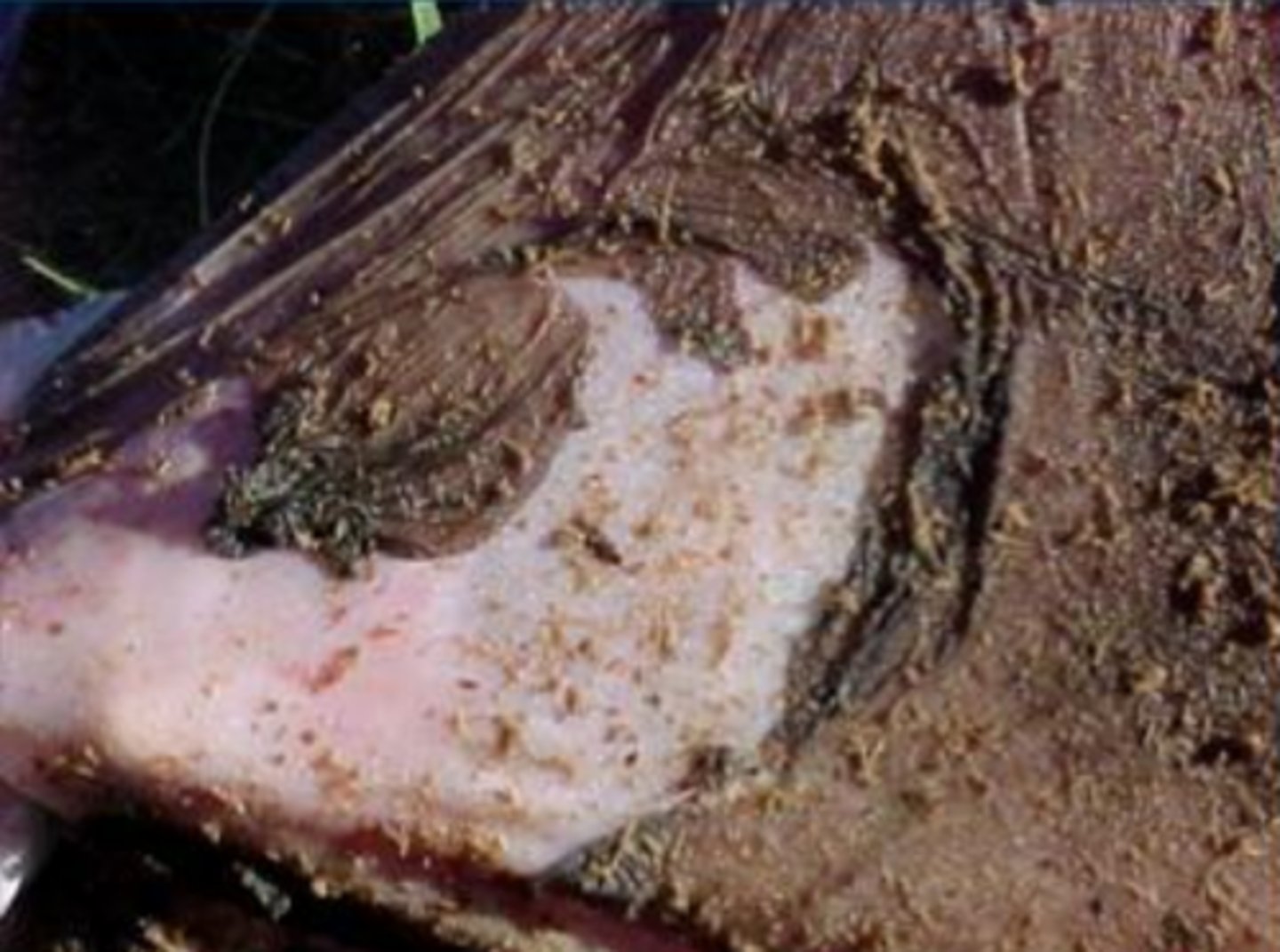
mucosal sloughing
What is happening in this image?
Dark neurons
What are these?
bloating, rectal/vaginal prolapse, tissue softening/discoloration and gas bubbles
what are some postmortem changes you would see on a carcass that'd been lying out for a while? Like a cow by the road
putrefaction
What do we know we have if gas bubbles are present in dead tissue?
gaseous distension
result of increased gas producing bacteria in a carcass
Gi tract, diaphragm, entire carcass
what can rupture if the carcass is bloating
displacement of abdominal viscera, eversion of rectal mucosa through anus, vaginal eversion, phimosis, protrusion of the tongue
WHat else can bloating cause besides rupture?
postmortem rods
What are these?
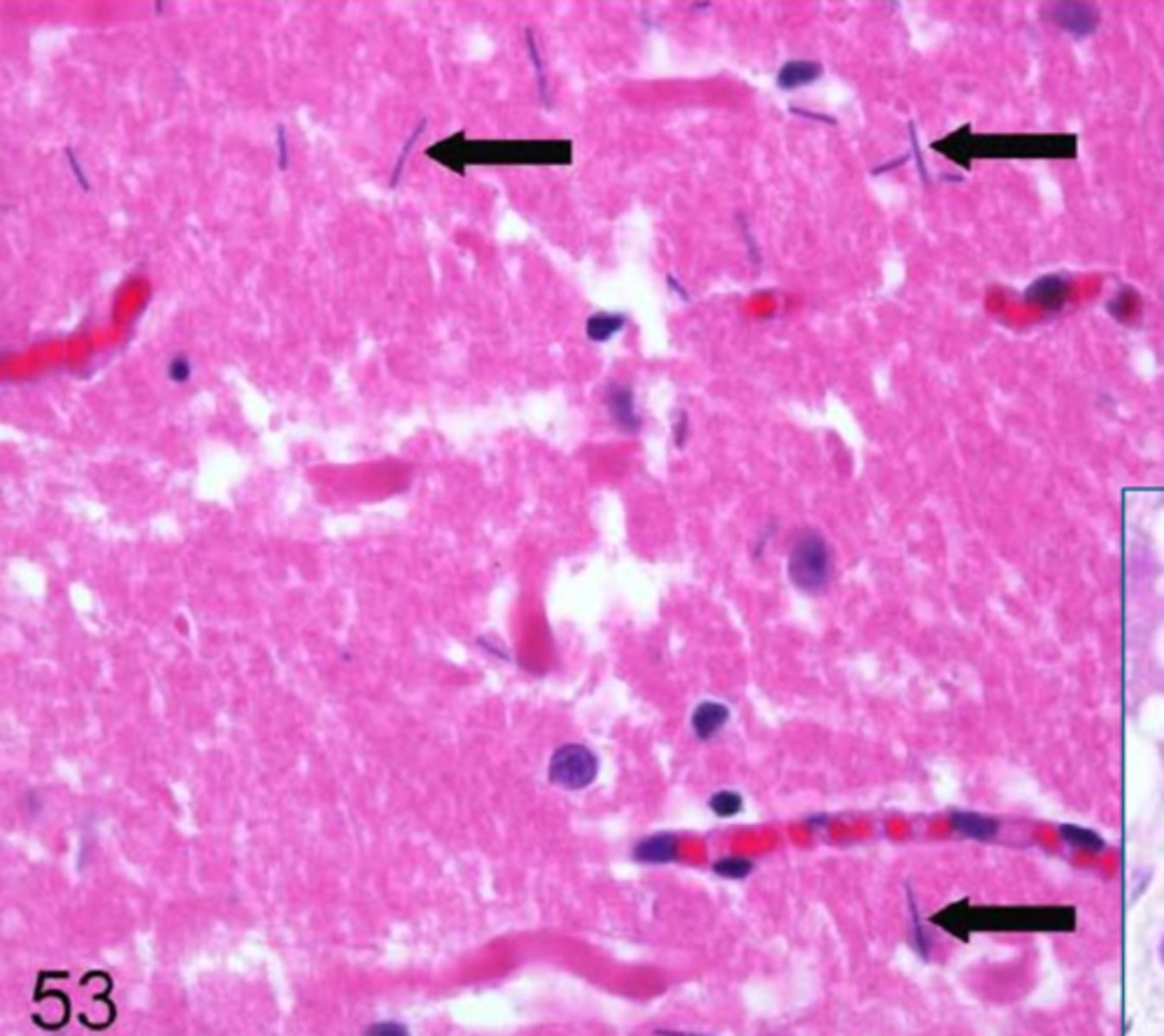
gas producing bacteria
what caused this "swiss cheese brain"?
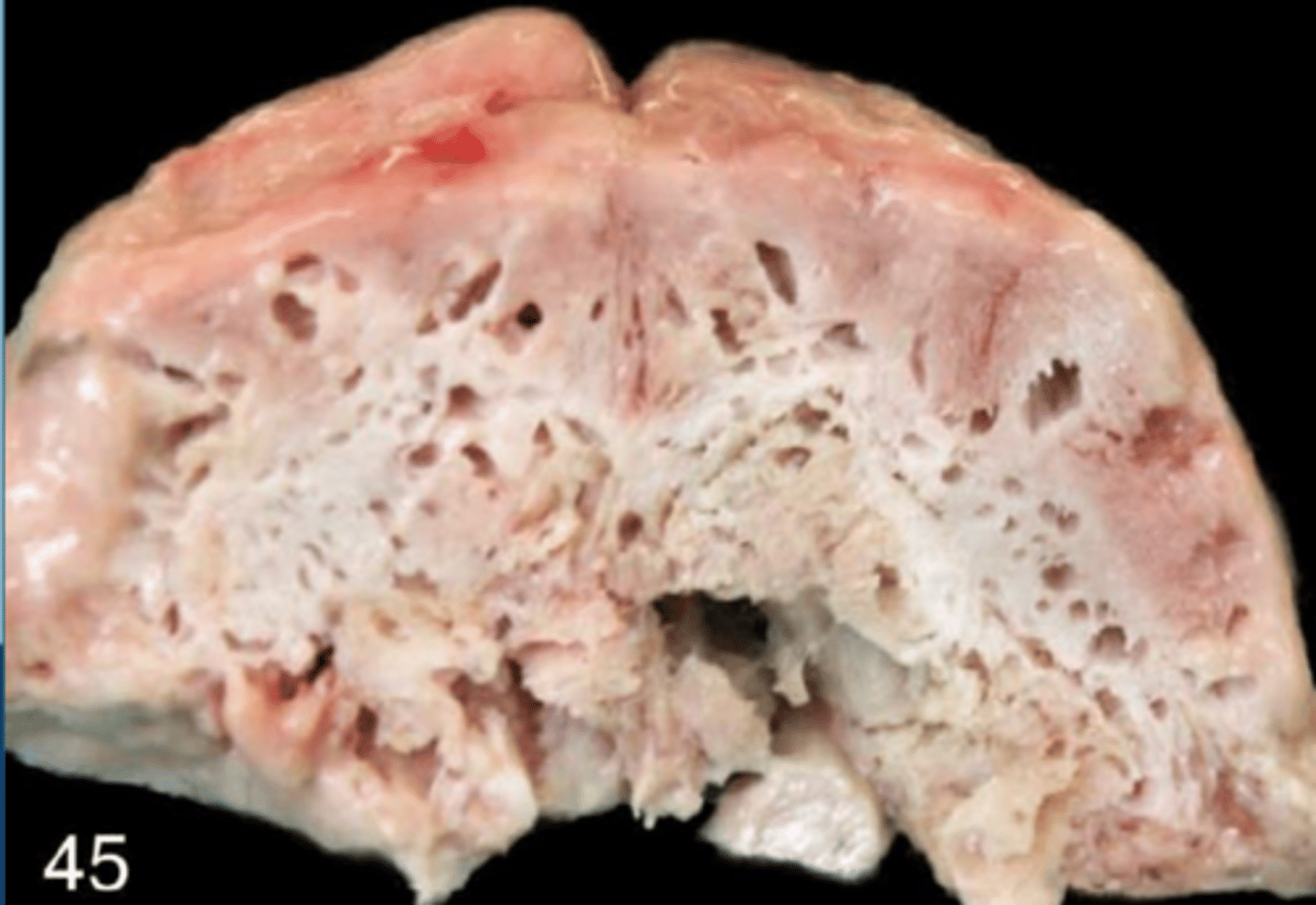
diffuse, pallor, soft/pulpy/gas filled tissue
Grossly, autolysis looks like what?
friable, reddish fluid, hydrogen sulfide, methyl mercaptan
grossly, autolysis causes tissue to be [tough/rubbery/friable], the tissue oozes __________________ and has a strong odor due to the _______ and _______________--
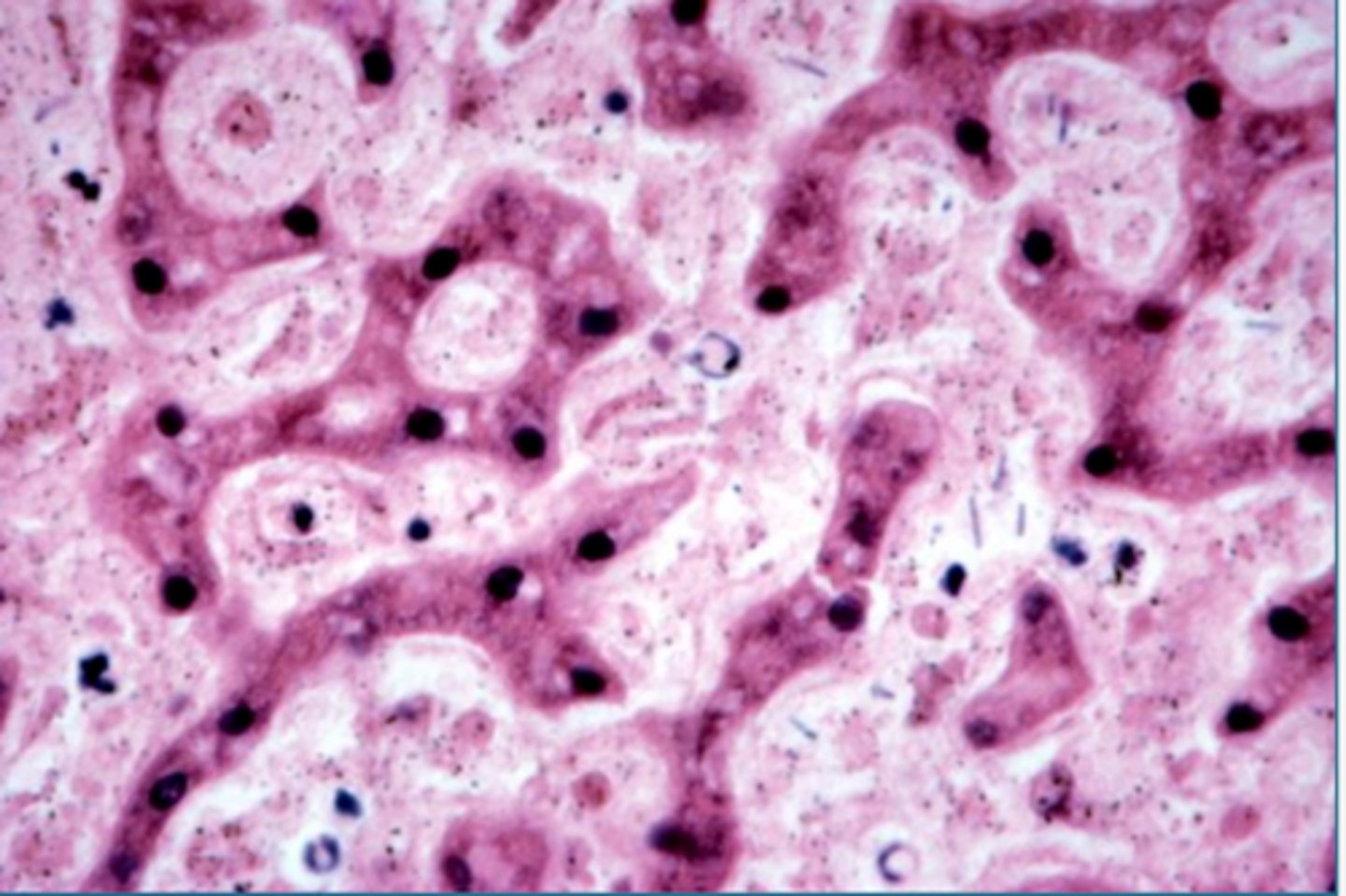
pale, nope, cadaver bacilli
Microscopically, due to autolysis, the tissues stain ____________.
Is there inflammatory response seen?
What bacteria is there?
errythrocytes not preserved, loss of tissue pattern, cells release from basement membrane
Describe the microscopic appearance of autolysis
autolysis
what is happening?
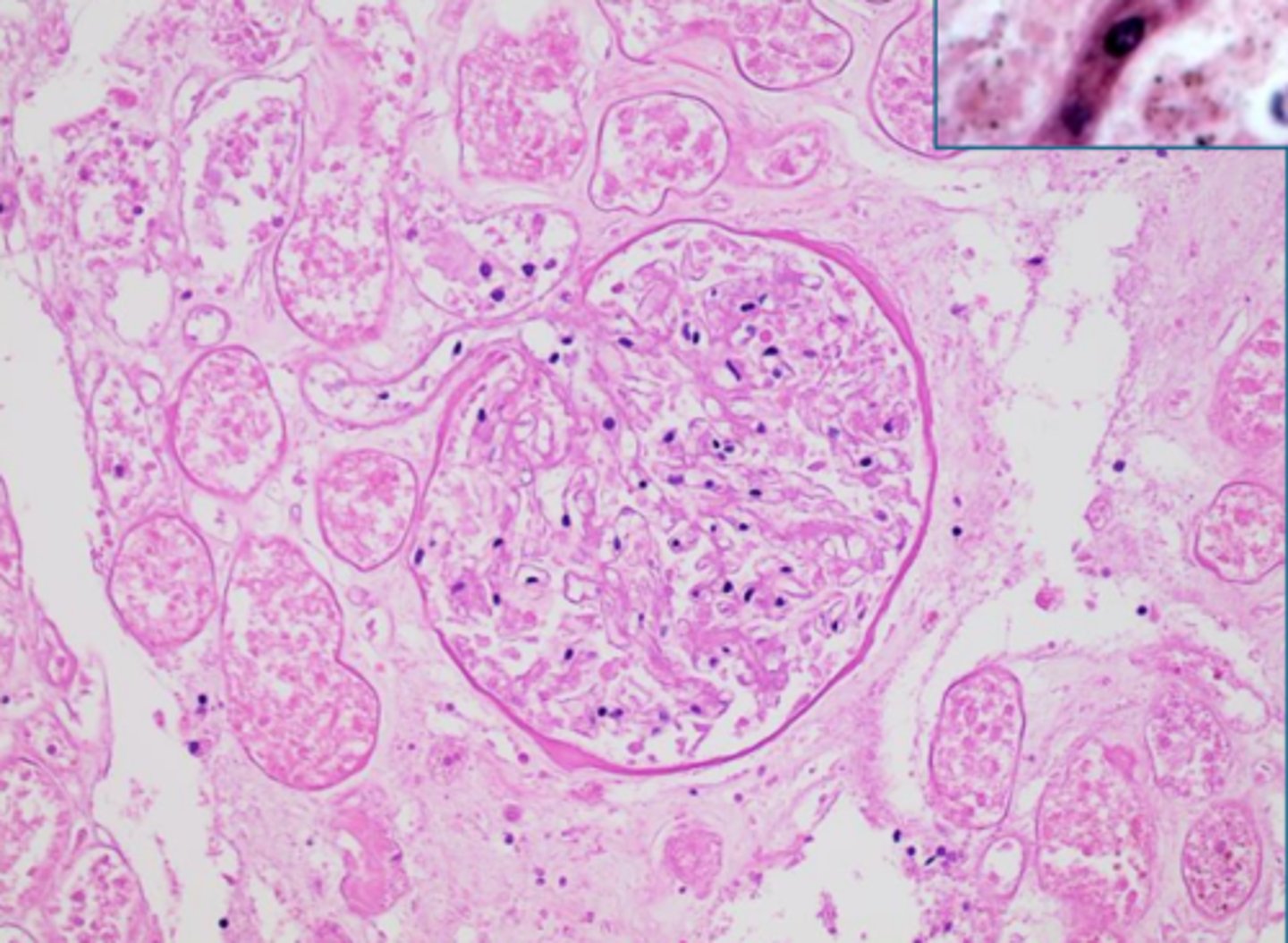
autolysis
what is happening?
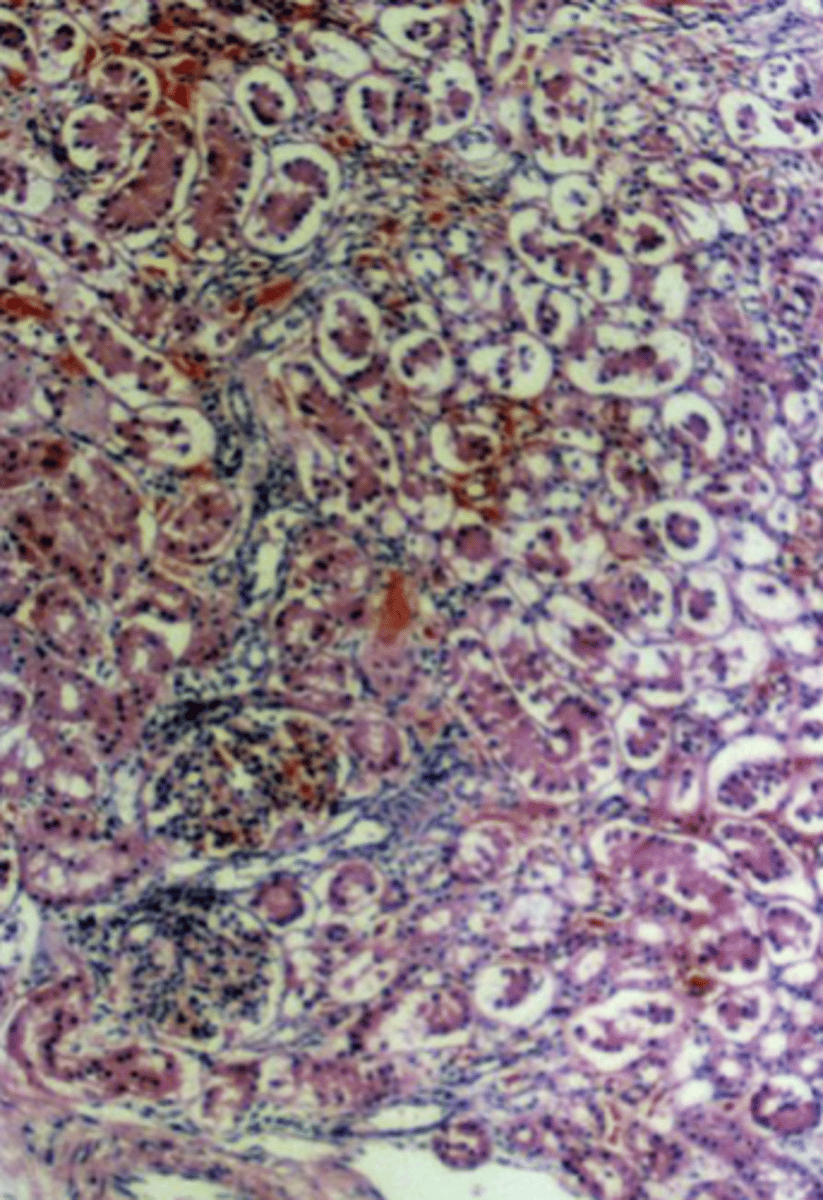
water
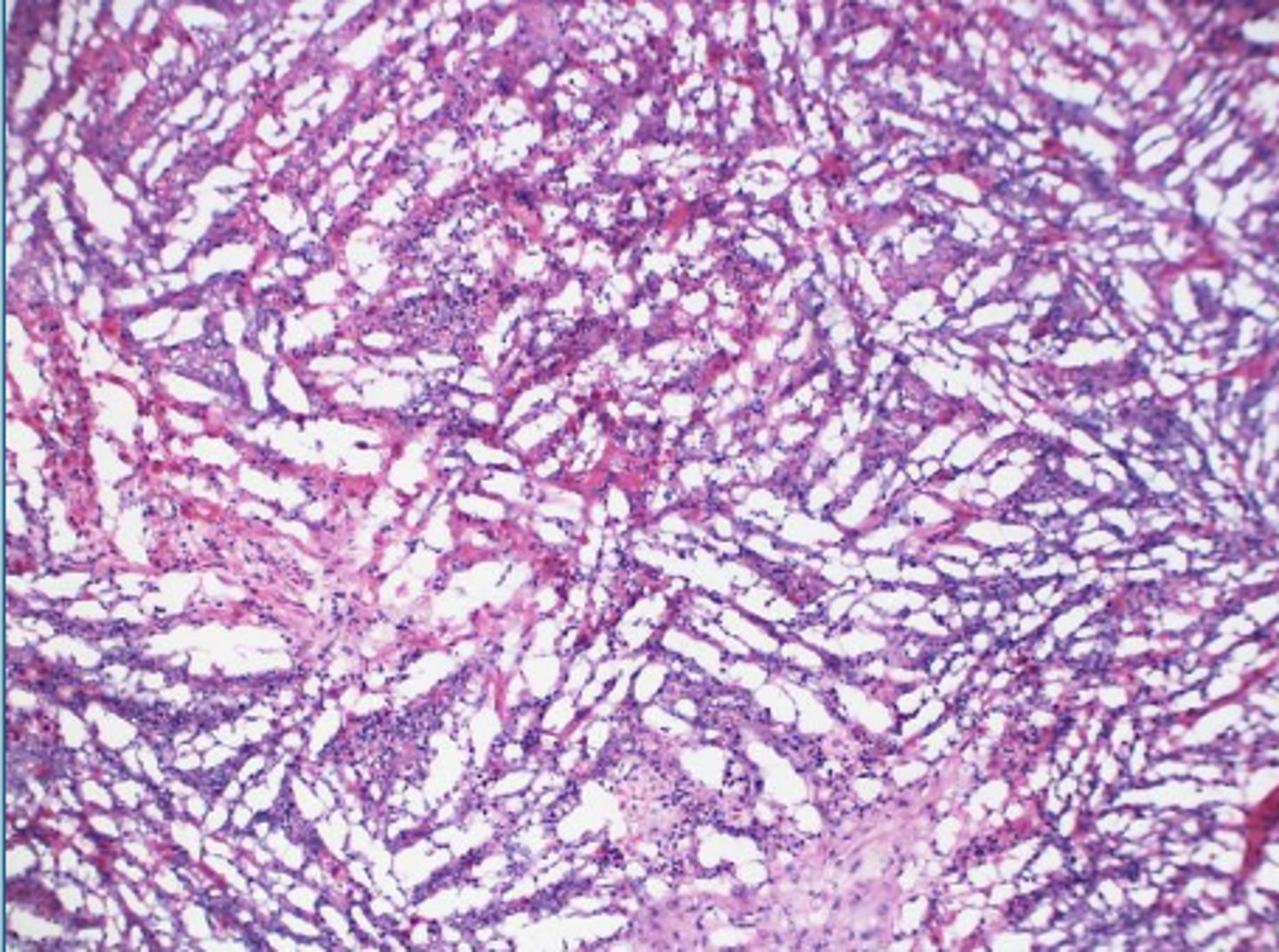
what histological artifact?
frozen before fixation
What histological artifact?
hemoglobin imbibition
reddish discoloration of tissue from lysed erythrocytes; Leakage of hemoglobin from blood vessels after death;
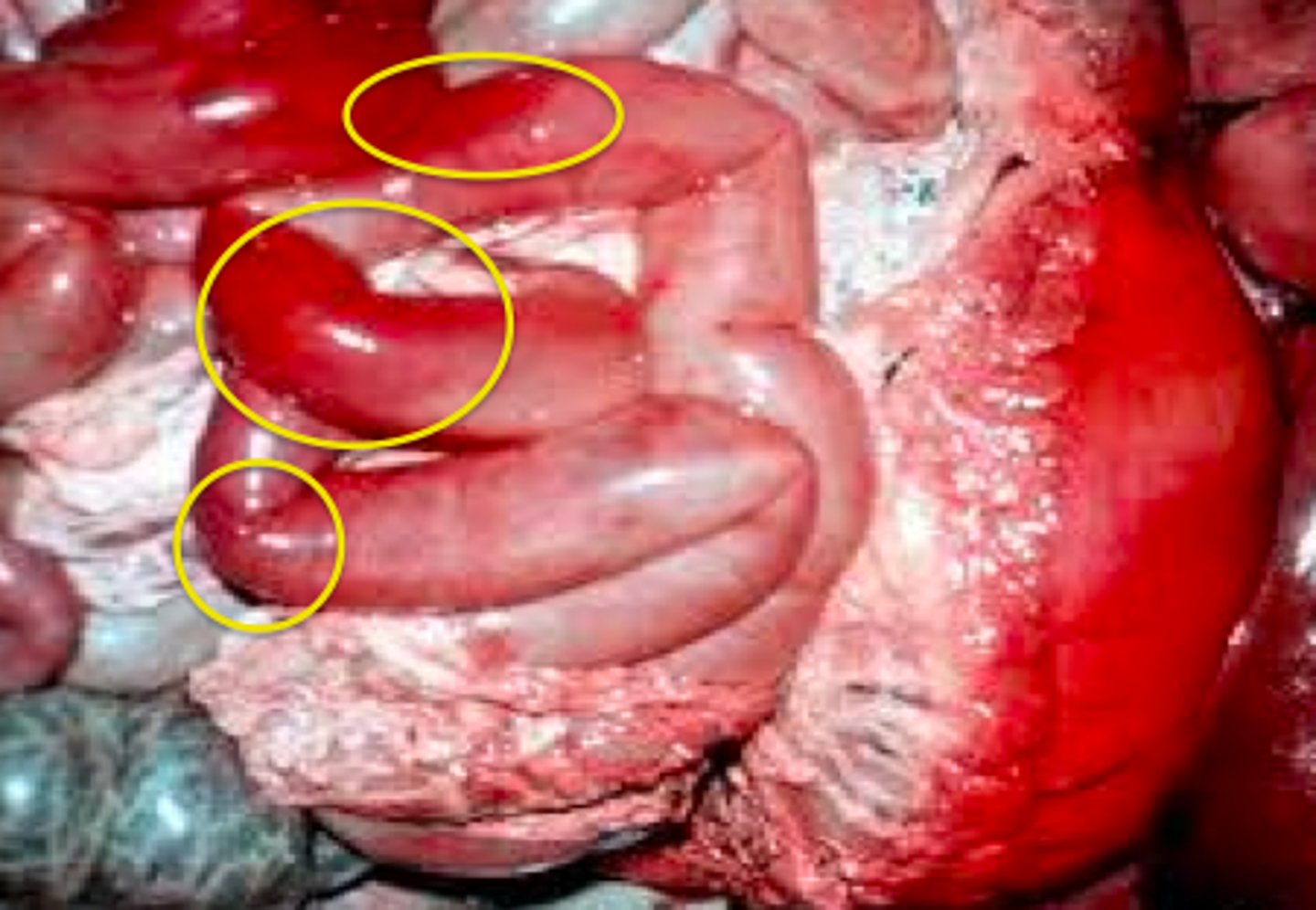
intima, endocardium, surrounding tissues
where would you see hemoglobin imbibition
hemoglobin imbibition
what is causing his deep red pigment on this aorta?
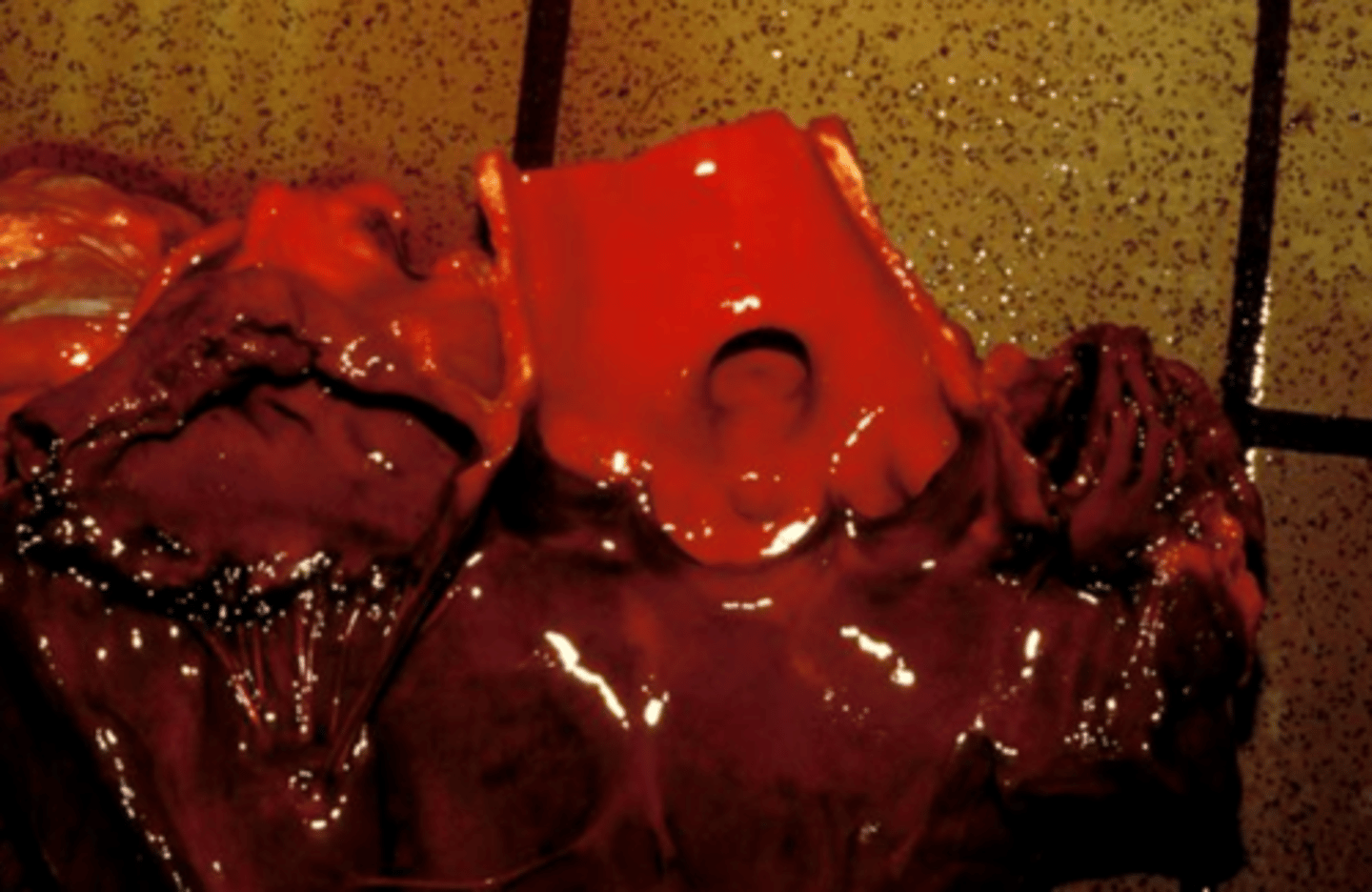

hemoglobin imbibition
What is causing the deep red pigment on the top of this organ?
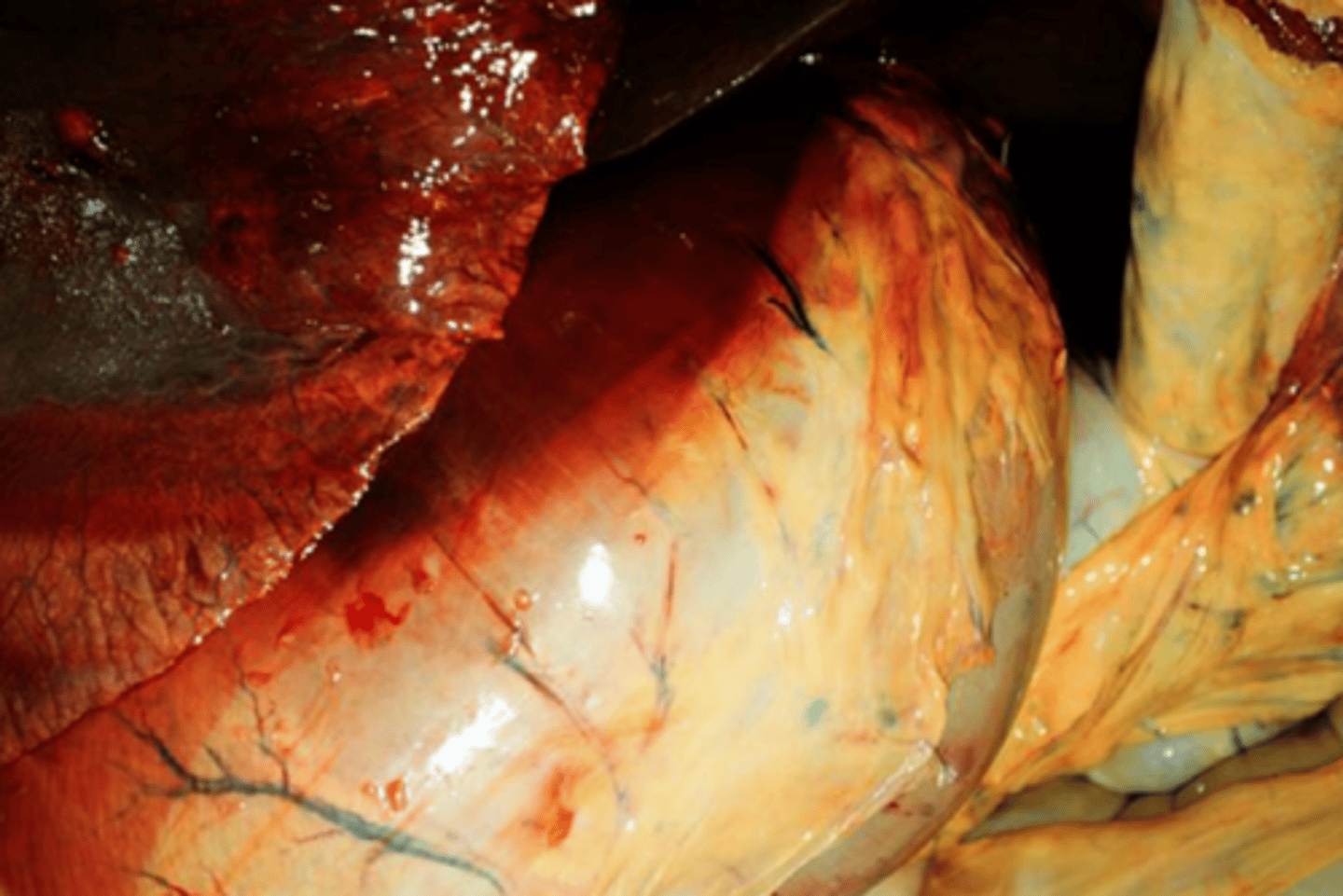
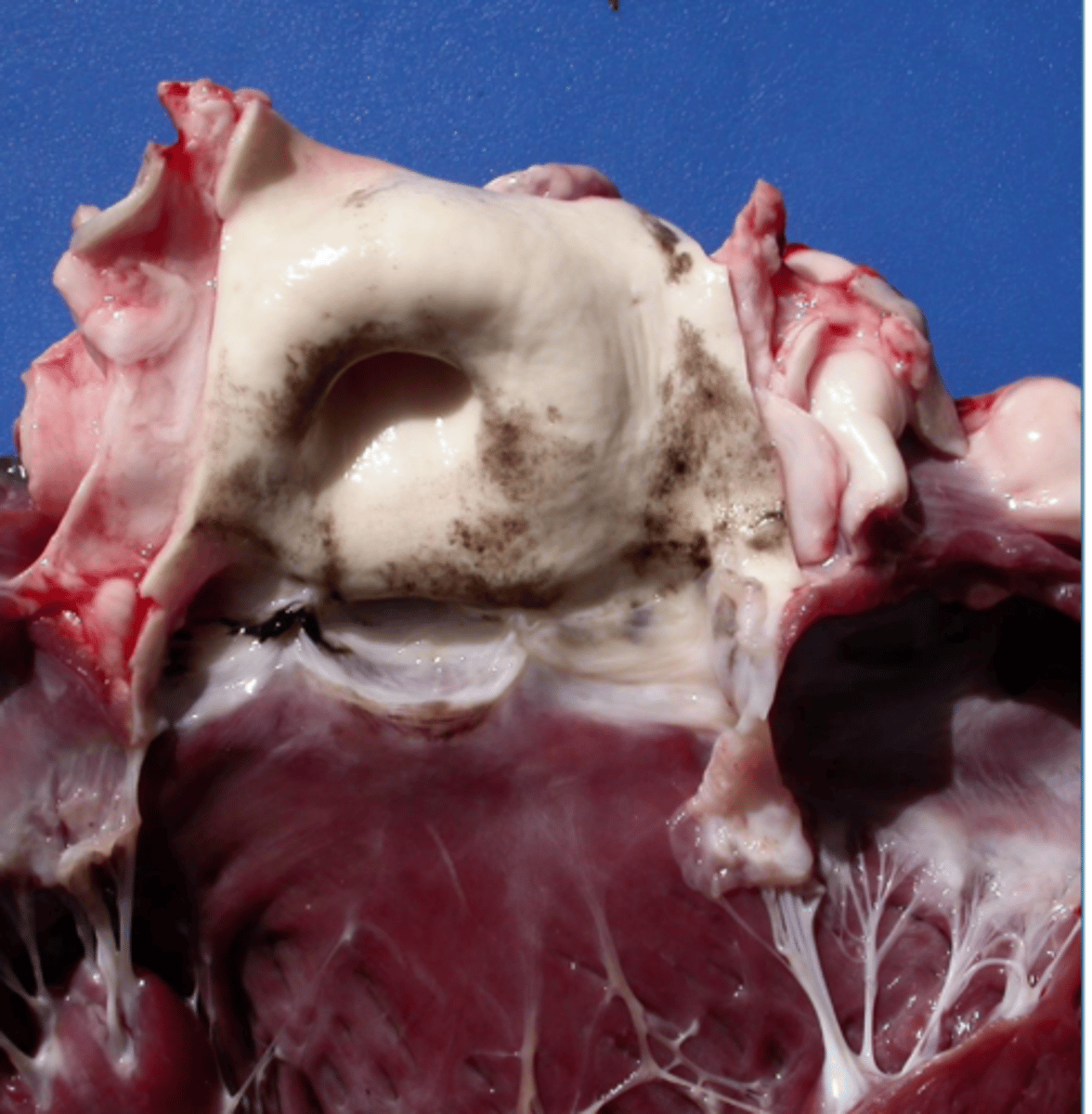
bile imbibition
_____________: Greenish discoloration from leakage of bile through the wall of the gallbladder or bile ducts
bile imbibition
what is the pigment in the gall bladder on the far right?
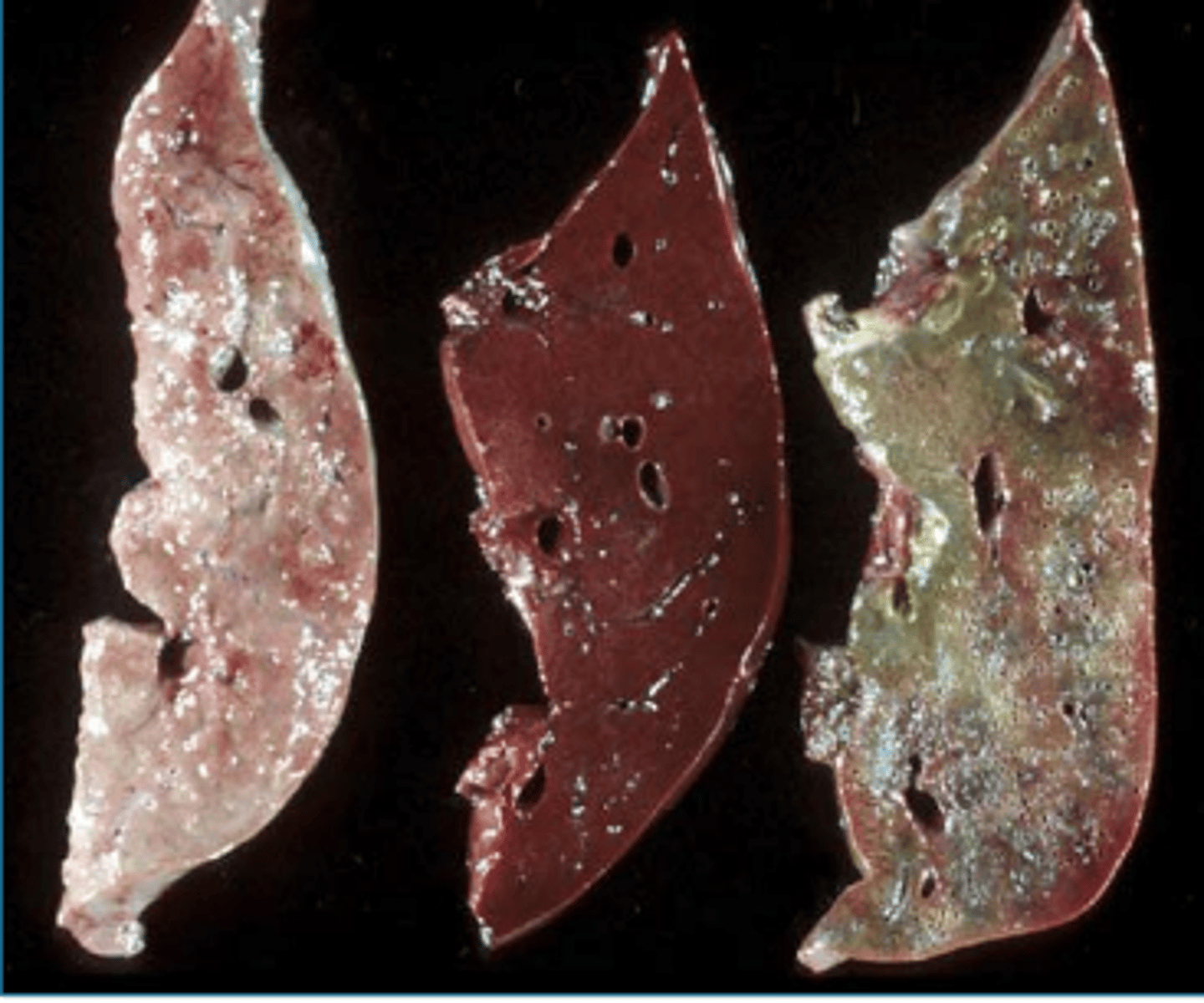
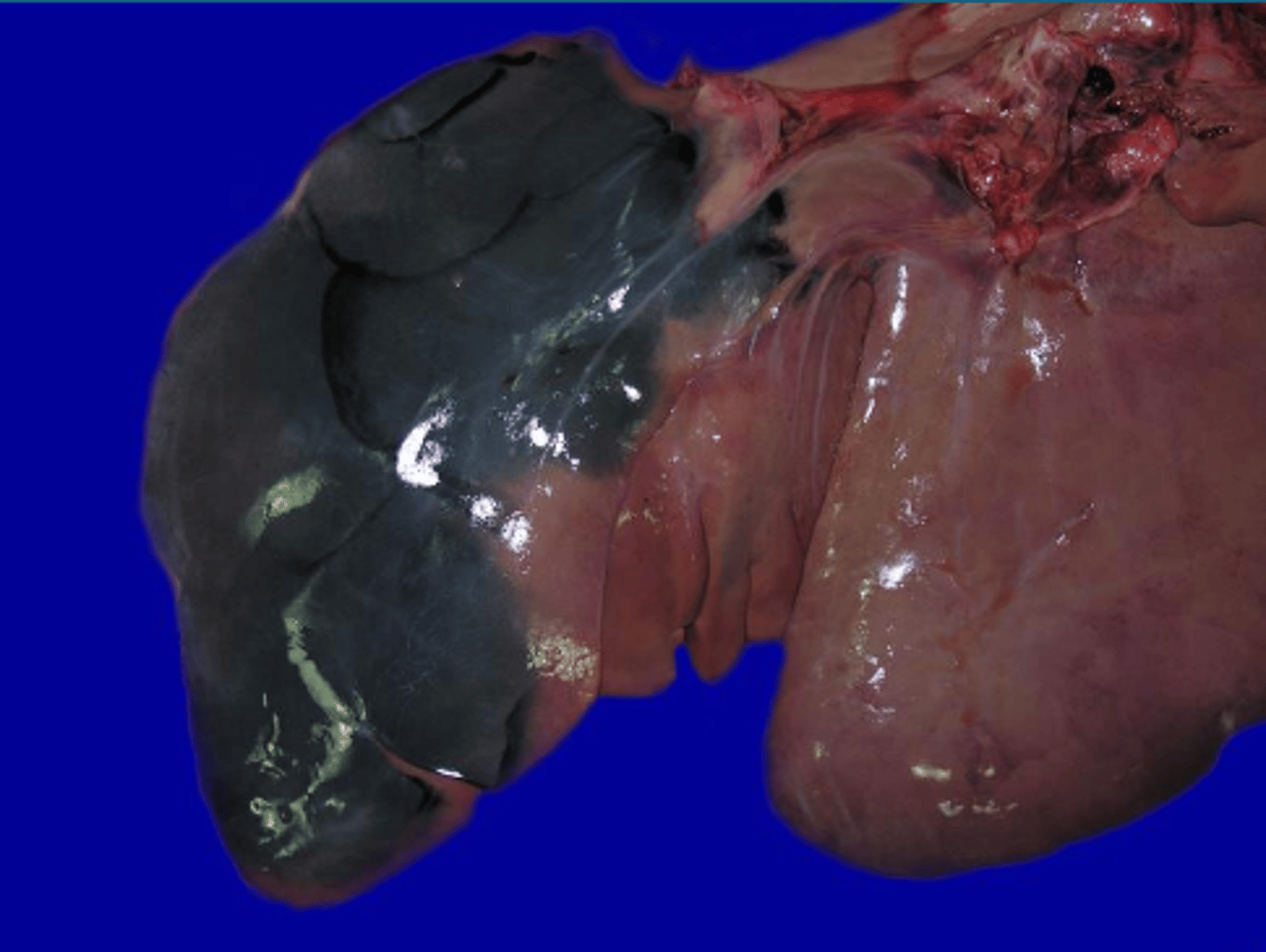
pseudomelanosis
_________________: Blue-green to black discoloration of tissues by iron sulfide deposits
false; pseudomalanosis is not melanin
true/false: pseudomelanosis and melanosis are both the same melanin pigment, just named for different stages of the animals life (or...death ig)
hydrogen sulfide from bacteria reacting with iron in hemoglobin
so if pseudomelanosis isnt melanin... what is it?
severe autolysis
what does pseudomelanosis signify?
antemortem; melanin deposits
is this a postmortem or antemortem pigment change?
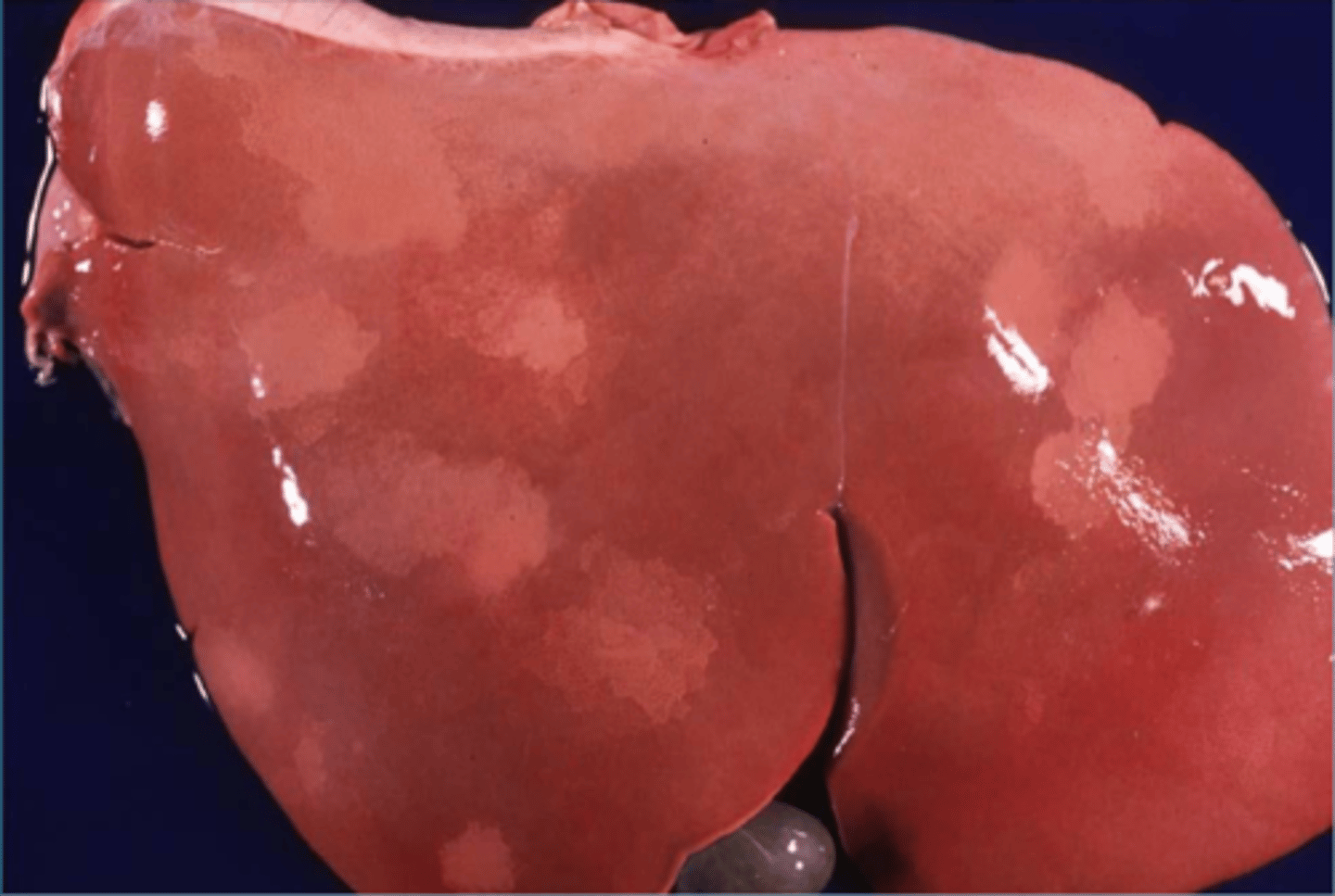
pallor
_________: Postmortem pressure on organs can force blood out of tissues causing "Pale imprints" (like the ribs)
bacterial proliferation, liver
Pallor can also come from localized postmortem _____________ ________________- in the _______________
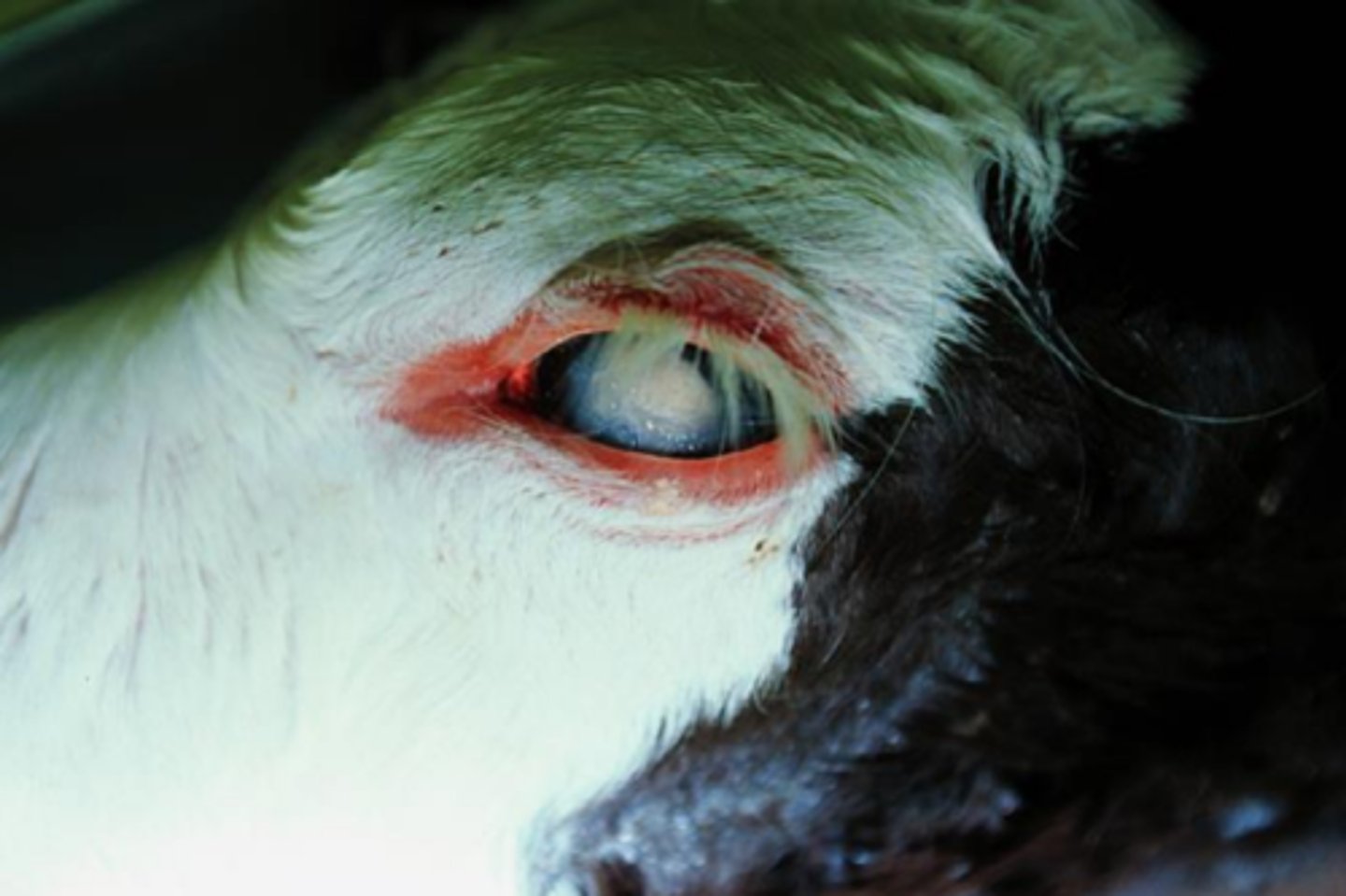
lens artifact
Chilling or partial freezing of the carcass can make the lens opaque and white
cataracts, lens artifacts are from freezing, and so revert to normal on warming (most of the time)
What is it important to differentiate lens artifacts from? and how can you do this?
traps blood in ridges, mimics intussusception
what patterns (2) does postmortem peristalsis cause in the intestines?
agonal breathing, hemorrhage, euthanasia artifacts, resuscitation artifacts
what are some examples of perimortem changes (4)
interstitial edema, tracheal foam
What changes does agonal breathing cause?
petechial hemorrhage
What perimortem change comes with electrocution?
splenic congestion, pulmonary congestion and edema, dicolored blood, coagulation of endocardium
what are the perimortem artifacts associated with Barbiturate euthanasia (4)
fractured ribs, cutaneous hemorrhage, hemorrhage around injection sites, collapse of lungs if on O2 or anesthetic gas
What are some of the artifacts of ressuscitation?
pseudomalanosis
What is this change?
pallor
What is this change called?
freezing
What is this artifact caused by?
postmortem peristalsis
what causes this change?
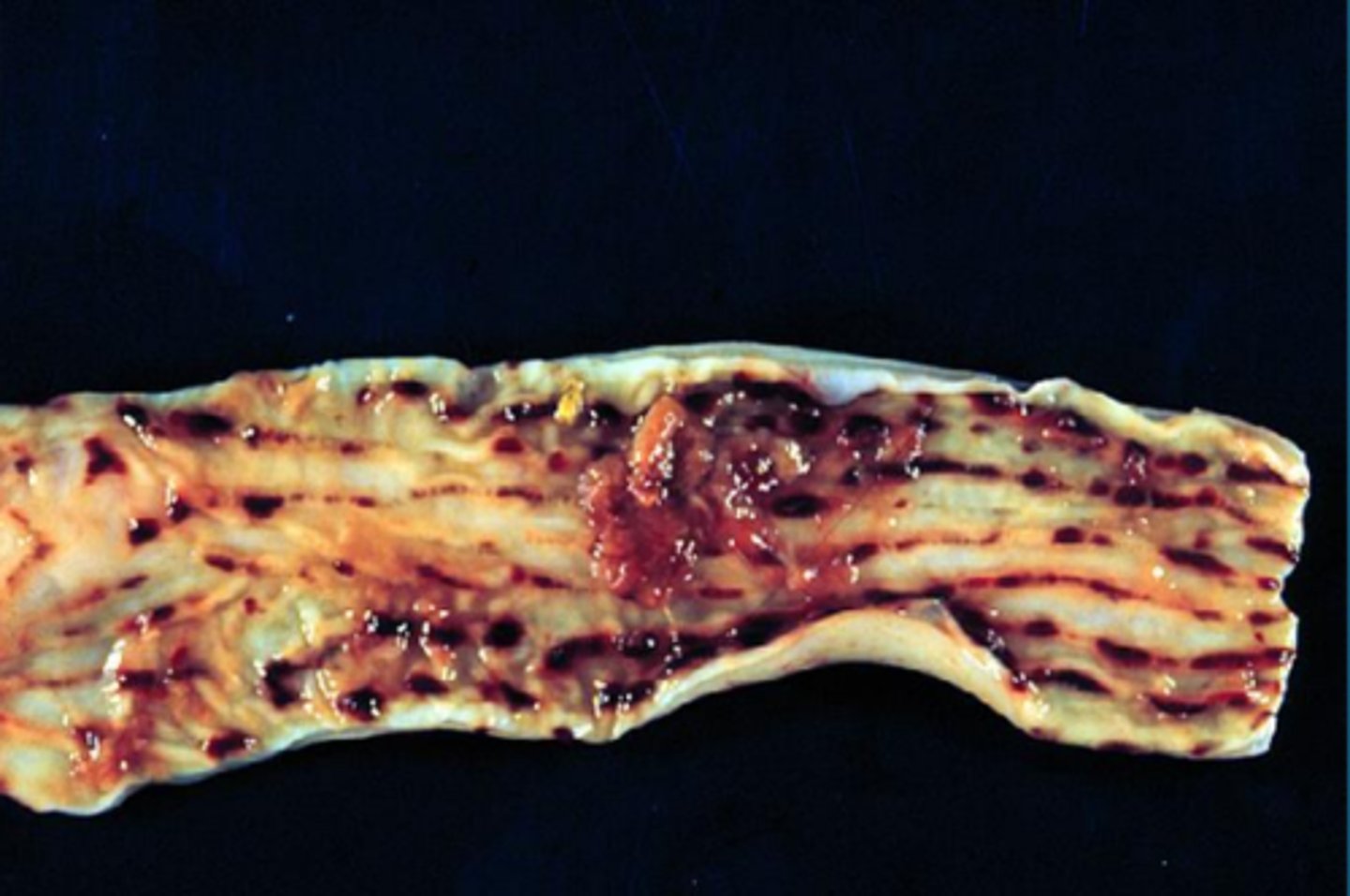
_____________: Greenish discoloration from leakage of bile through the wall of the gallbladder or bile ducts