1. Physical examination exemplars: eyes/exemplars: head, face, neck, and regional lymphatics/exemplars: skin, hair, and nails
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Anyone have singed hair on their face
needs to be very cautious of their airway
Skin, hair, nails: age related changes (older adults)
elasticity loss
thin, dry, wrinkled appearance
thin and flattened epidermis
collagen loss associated with shearing, tearing injury risk
decrease in sweat and sebaceous gland function and number associated with dry skin
decreased thermoregulation associated with increased risk of heat stroke
senile purpura
skin breakdown associated with delayed wound healing
Senile purpura
so-called areas of dark red discoloration, associated with minor trauma
Alopecia
impressive amount of hair loss
Hirsutism
excessive hair
Jaundice
normal finding in a newborn
abnormal finding in older adults associated with hepatic disease (hepatitis, cirrhosis), typically severe and chronic in nature
abnormal increased amounts of bilirubin in blood
noted as change in skin coloration and both eyes
Skin, hair, nails objective data: ABCDEF mnemonic
Asymmetry
Border irregularity
Color variation
Diameter (6mm+, size of pencil eraser)
Elevation/evolution
Funny looking (so-called ‘ugly duckling’ sign), lesion in local area different in appears to local nevi)
Objective data: evaluate temperature (hypothermia)
associated with:
shock
peripheral arterial insufficiency
raynauds syndrome
Objective data: evaluate temperature (hyperthermia)
associated with:
hyperthyroidism
Inspection and palpation of the skin: evaluate texture, thickness, edema
note: anasarca
Anasarca
bilateral extremity or so-called generalized edema
Skin tenting
may occur where pinched skin stands by itself
Scleroderma
so-called “hard skin” associated with chronic connective tissue ailment and decreased mobility
Inspection and palpation of the skin: evaluate vascularity (bruising)
cherry angiomas (senile)
contusion
Cherry angiomas (senile)
bright red dots, slightly raised, smooth, small in size and a normal finding in adults 30+ years old
Contusion
term for bruise
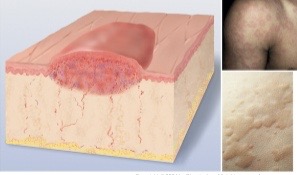
Skin, hair, nails objective data: primary lesions
macule
papule
patch
plaque
nodule
wheal
Primary lesions: macule
flat, circumscribed, less than 1cm and strictly a color change
ex: freckle, petechiae
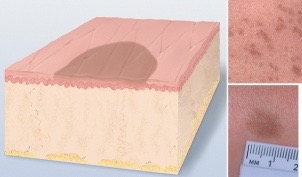
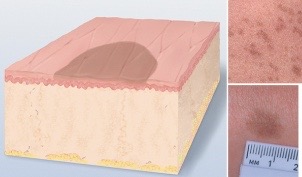
Primary lesions: papule
lesion that can be felt due to epidermis superficial thickening
ex: wart (verruca)
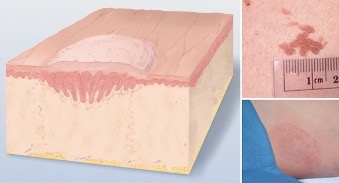
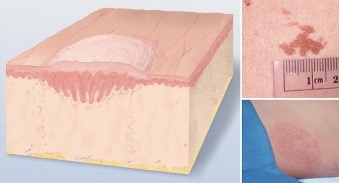
Primary lesions: patch
macules with size (1cm+)
ex: vitiligo
Primary lesions: plaque
papule with a surface elevation greater than 1cm in width
ex: psoriasis
Primary lesions: nodule
greater than 1cm in size, solid and elevated; can extend deeper than a papule into the dermis
ex: xanthoma

Primary lesions: wheal
dark skin
somewhat irregular shape associated with edema, superficial, transient, erythematous, and raised
ex: mosquito bite
Skin, hair, nails objective data: evaluate lesions
tumor
urticaria (hives)
vesicle
bulla
cyst
pustule
Evaluate lesions: tumor
a few centimeters or greater in diameter, may be soft or firm, can be benign or malignant
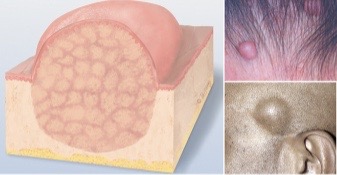
Evaluate lesions: urticaria (hives)
light skin
extensive pruritic reaction of several wheals in a collection coming together

Evaluate lesions: vesicle
cavity of so-called free fluid, elevated and up to 1cm in size, ‘blister’
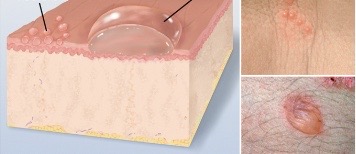
Evaluate lesions: bulla
cavity of free fluid that is larger than 1cm and can rupture with ease
ex: burn, contact dermatitis
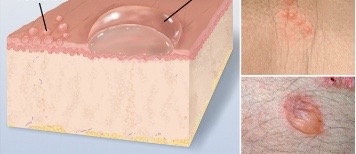
Evaluate lesions: cyst
fluid filled cavity enclosed by a capsule within the dermis or subcutaneous tissue

Evaluate lesions: pustule
cavity containing pus (turbid fluid) that is elevated and circumscribed
ex: acne
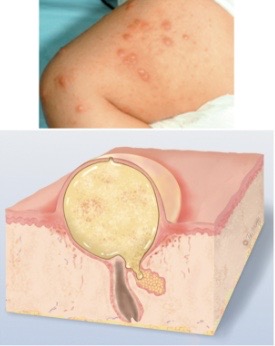
Objective data: secondary lesions
evolution of primary lesion over a period of time with a resultant change
crust, scale, fissure, erosion
ulcer
excoriation
scar
keloid
pressure ulcer
Secondary lesions: ulcer
depression, irregular in shape, potential bleeding and can leave scar upon healing
ex: pressure injury stasis ulcer
Secondary lesions: excoriation
superficial abrasion that is self inflicted, described as scratches from impressive amount of itching
ex: insect bite
Secondary lesions: scar
repaired skin lesion with loss of normal tissue and replacement using collagen (connective tissue); so-called permanent fibrotic change
ex: surgical site (healing or healed)
Secondary lesions: keloid
excess scar tissue outside of original injury site, benign in nature
described as smooth, claw-like, shiny, rubbery in nature and firm
Pressure ulcer
associated with lack of perfusion, oxygenation and interruption of vasculature of body tissue, commonly found over a bony landmark
Staging of ulcer progression: stage 1
non-blanchable erythema
skin intact
redness
no blanch ability of skin
Staging of ulcer progression: stage 2
partial-thickness skin loss
epidermis loss
exposed dermis layer
no visible fat/deep tissue
Staging of ulcer progression: stage 3
full-thickness skin loss
injury to tissue extends within subcutaneous tissue layer
fat and granulation tissue exposed
no visible muscle, tendon or bone structures
Staging of ulcer progression: stage 4
full-thickness skin/tissue loss
all skin layer involvement
supporting tissue involvement
visualization of bone, muscle, tendon
potential for tunneling
can include
slough
eschar
Slough
wound bed so-called stringy matter
Eschar
necrotic tissue
Staging of ulcer progression: stage 5
unstageable
deep tissue injury
Profile sign
nail clubbing associated with congenital heart disease, pulmonary pathology and lung cancer
Lentigines (seniles)
called ‘liver spots’
seen in older adults
not considered malignant and no need for treatment
Keratoses
areas of pigmentation that are thick and raised and may appear crusty, scaly or so-called warty
seborrheic keratosis
Keratoses: seborrheic keratosis
have a so-called ‘stuck on’ appearance and are not associated with cancer
Actinic keratosis
plaques that are scaly and red-tan with raised and roughened edges
associated with sun exposure
premalignant
potential to develop into squamous cell carcinoma
Skin tags
also called acrochordons
so-called normal skin overgrowth that are characterized as polyp-like
Vertigo
spinning sensation of the head
Normocephalic
so-called normal anatomical description including round skull with symmetry that is sized in proportion to overall body habitus
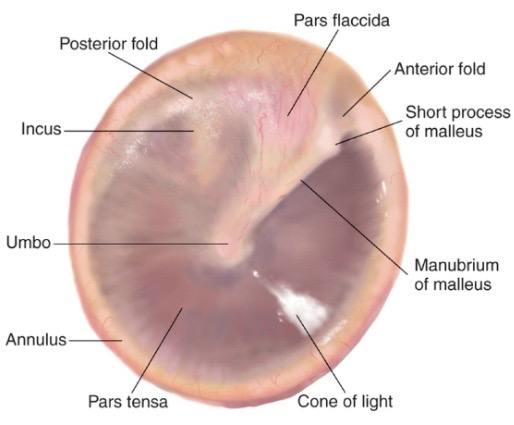
Tympanic membrane
what you look at when looking inside someones ear
Normal finding in tympanic membrane
pearly gray
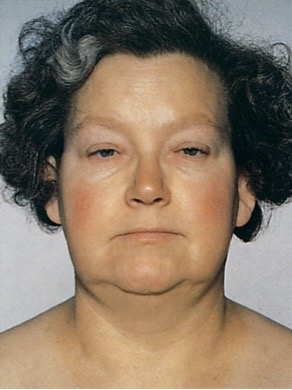
Inspection and palpation of thyroid gland: myxedema
severe form of hypothyroidism
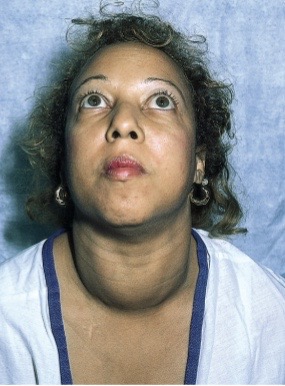
Inspection and palpation of thyroid gland: graves disease
leads to hyperthyroidism
Cachetic appearance
Ears: tympanic membrane
Eyes pupillary light reflex: direct light reflex
pupil constriction of respective eye
Eyes pupillary light reflex: consensual light reflex
light shined on one eye, yet opposite eye has simultaneous pupil constriction
Eyes pupillary light reflex: fixation
eye is attracted reflexively moves toward an object drawing a person’s attention
Eyes pupillary light reflex: accommodation
eye adaptation in setting of near vision
Scotoma
blind spot noted in setting of glaucoma or other pathology
Strabismus/diplopia
two images of one object
deviation of two eye parallel axes
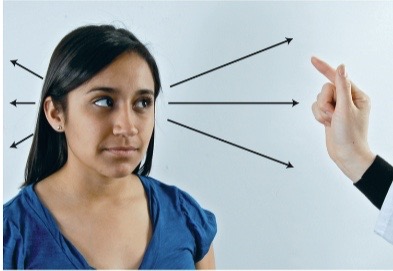
Eyes: confrontation test
screen for peripheral vision loss
Eyes objective data: evaluate via inspection; extra-ocular muscle function
hirschberg test
diagnostic positions test
Eyes: hirschberg test
corneal light reflex
shine light into one eye approximately 12 inches away from eye, note light reflection in same spot of each of the two corneas
Eyes: diagnostic positions test
6 cardinal positions of gaze
normal response: both eyes track object in parallel
Nystagmus
fine oscillating movement around iris
PERRLA
pupils equal, round, reactive to light, and accomodating
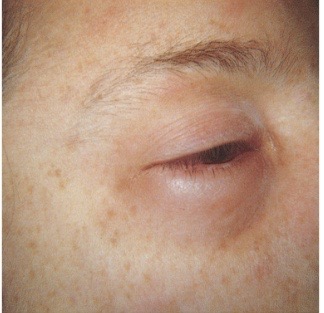
Eyes: periorbital edema
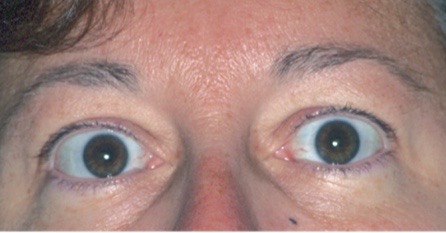
Eyes: exophthalmos
eye protrusion
associated with pathology of thyrotoxicosis
Eyes: mydriasis
associated with trauma, acute glaucoma, CNS injury, deep anesthesia

Eyes: miosis
associated with narcotic use and glaucoma treatment via pilocarpine drops
