DEN 7127 Extraoral Projections and Anatomy (eliz)- mz
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Extraoral projections
Why do them?
• Examine areas not fully covered by intraoral films
• Evaluate the cranium, face (Mx +Mn), cervical spine, trauma or pathology
• Evaluate the patient's complaints and clinical signs prior to prescribing individualized extraoral projections
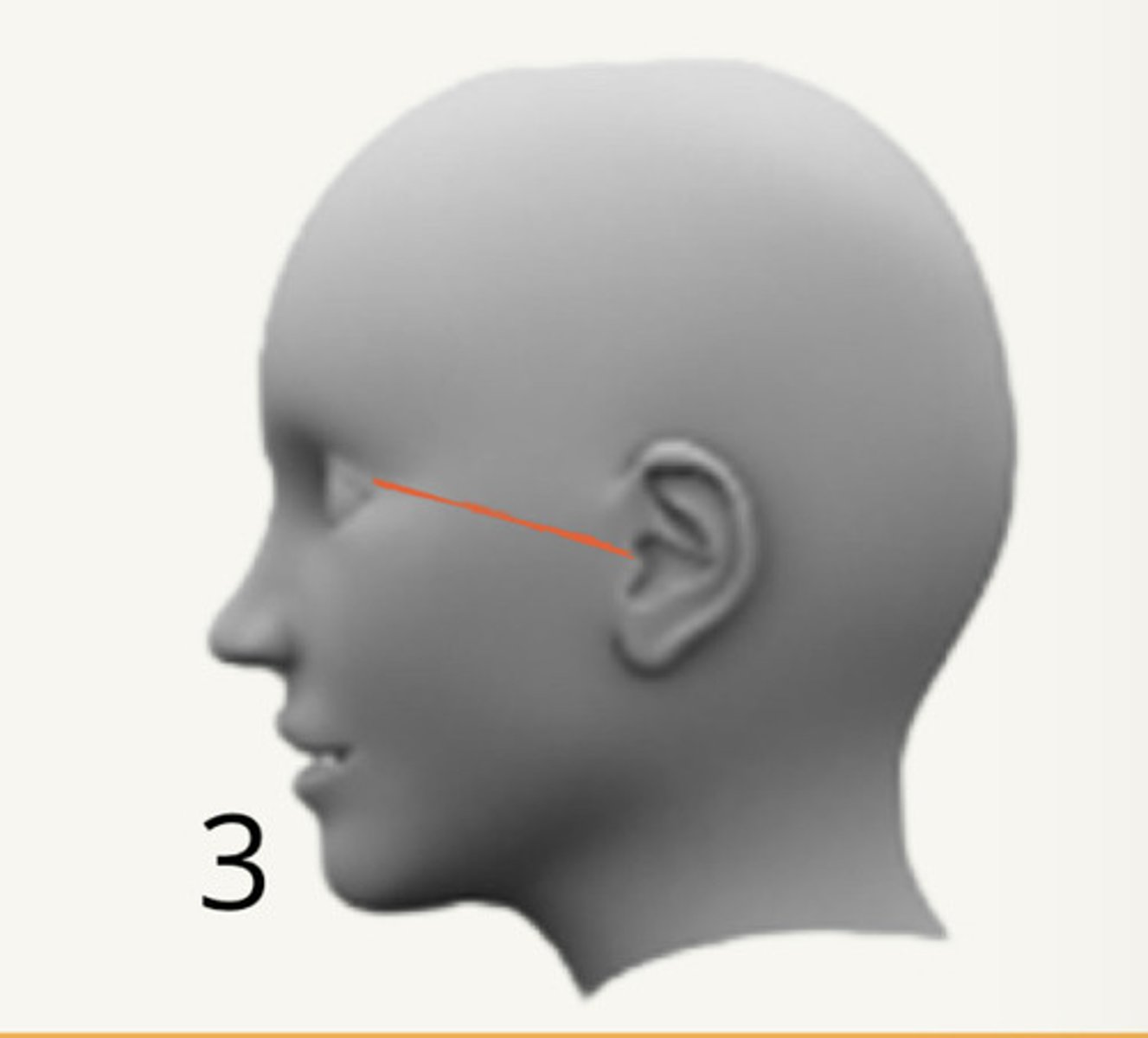
Canthomeatal line:
lateral canthus of the eye to center of external auditory meatus. Forms 10-degree angle with the Frankfort plane
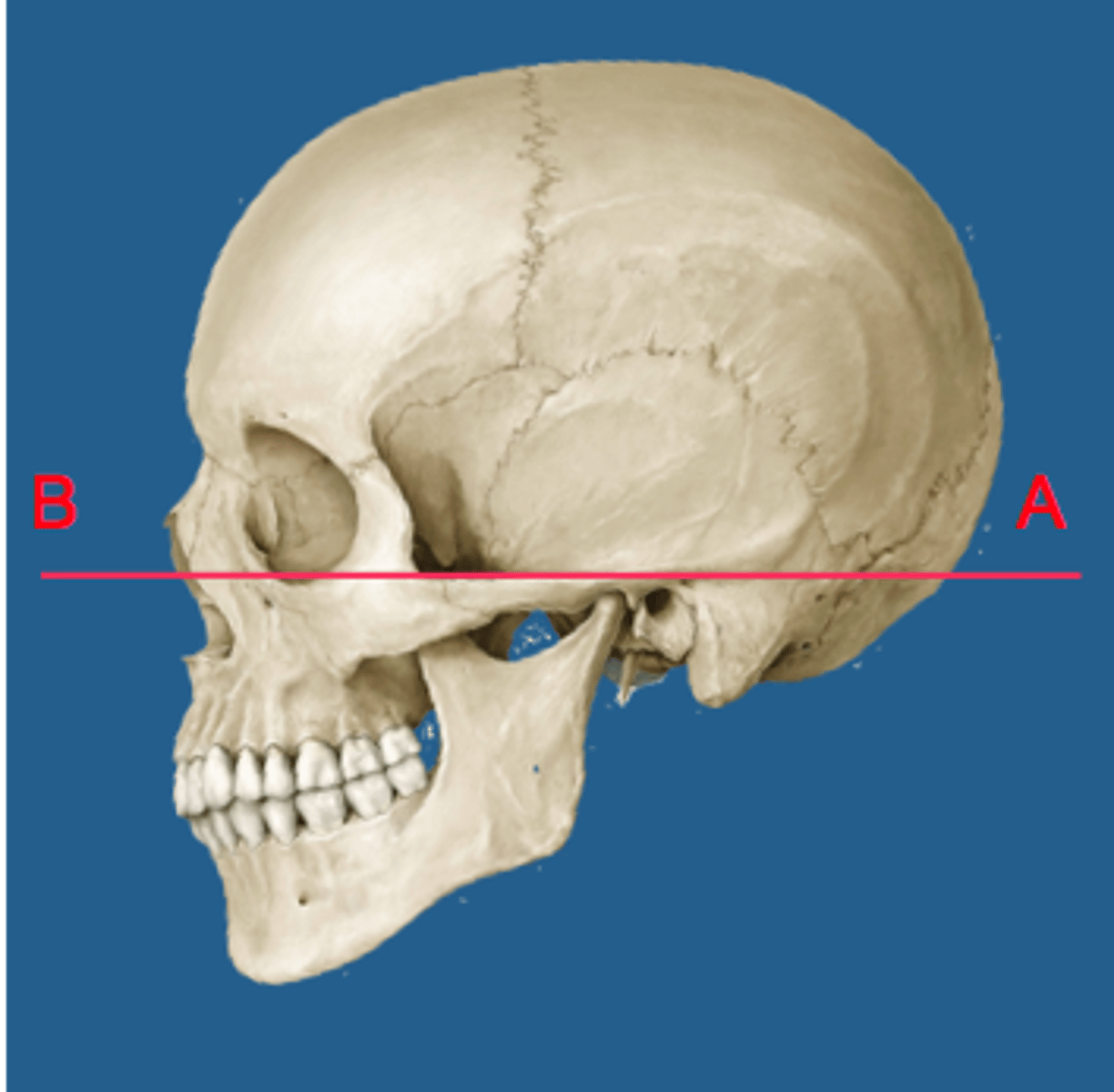
Frankfort plane:
superior border of external auditory canal to infraorbital rim
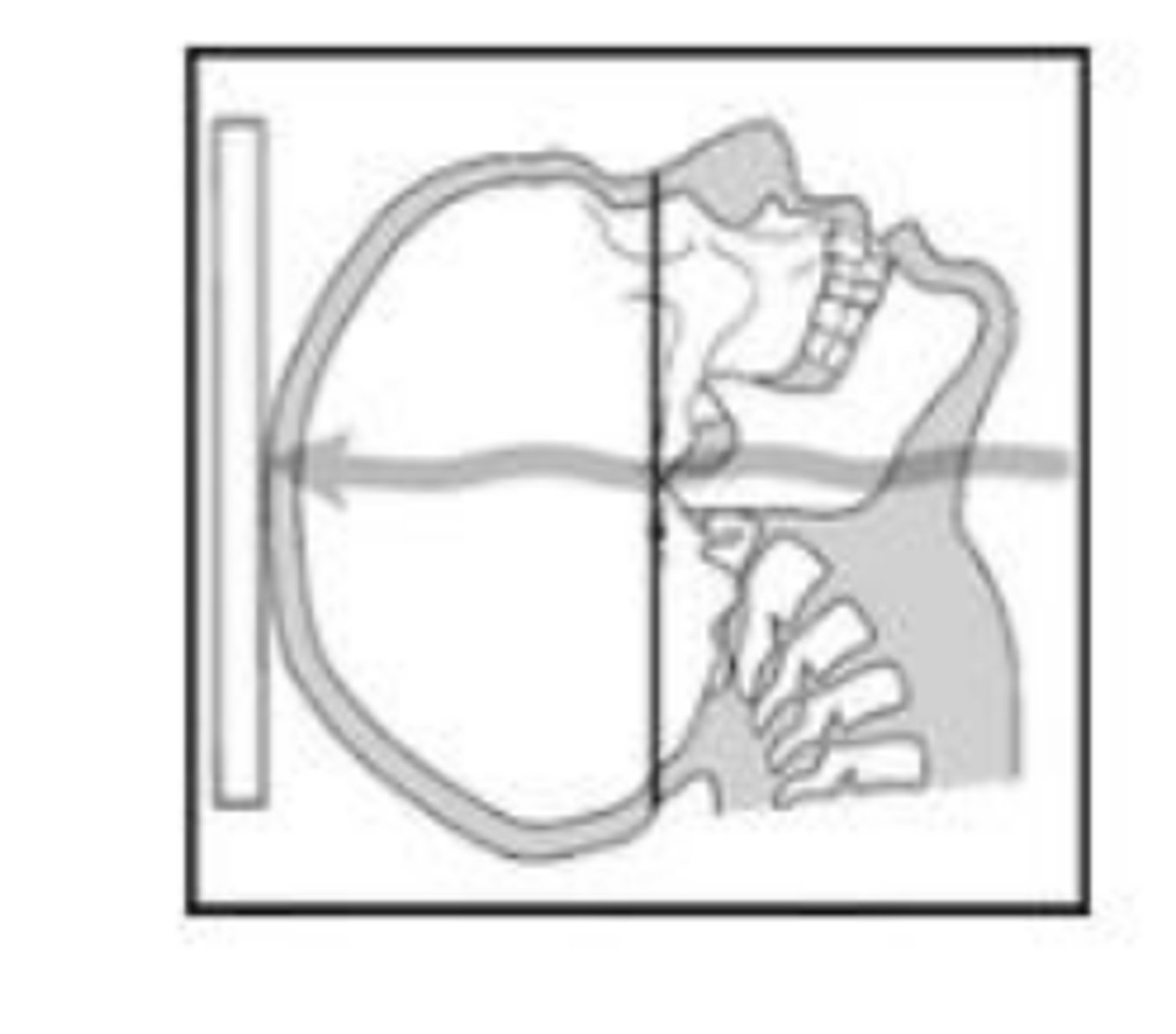
lateral CEPH
film parallel to midsagittal plane
SMV
canthomeatal line parallel to receptor
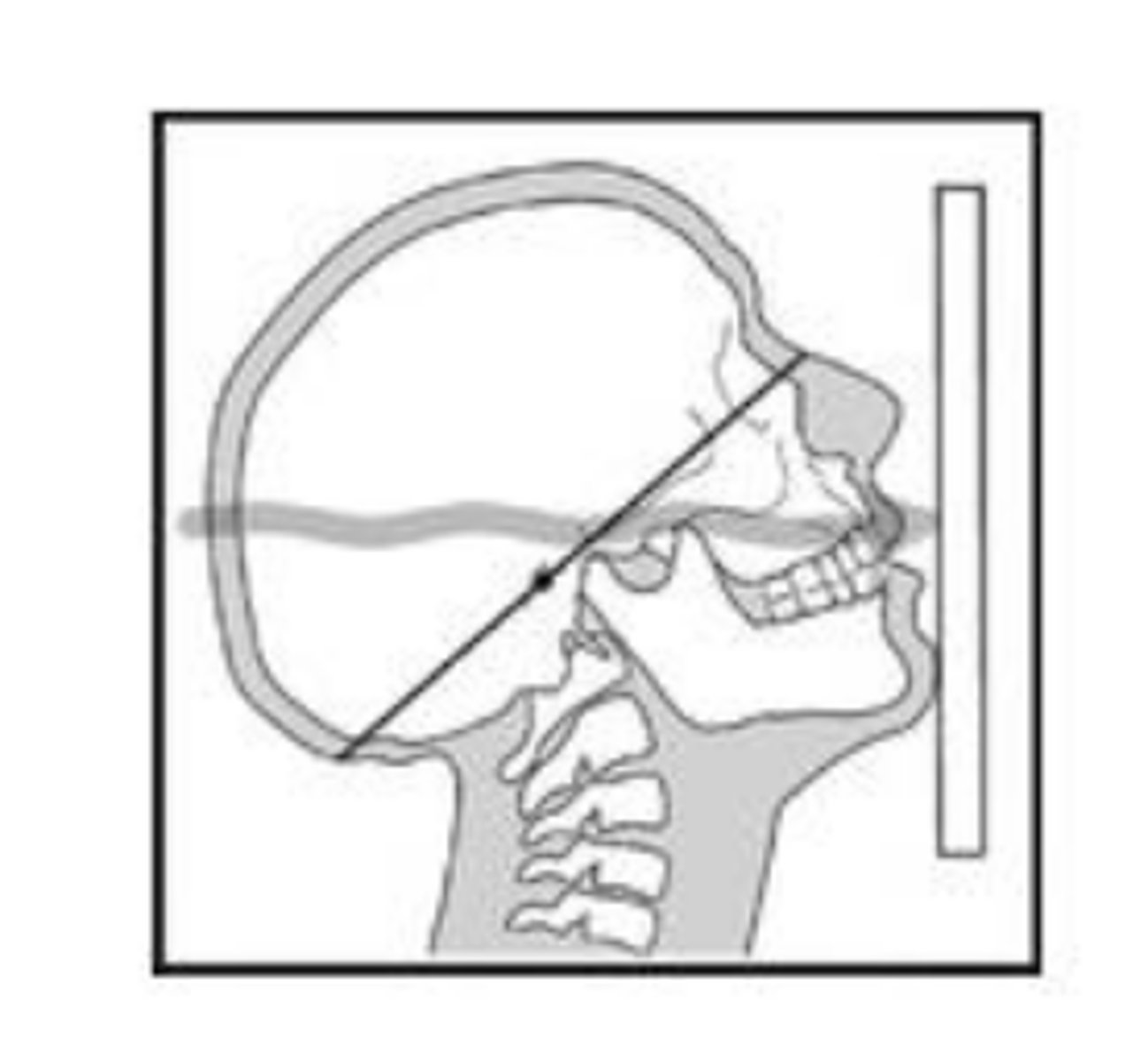
Waters
cantomeatal line 37 degrees with receptor
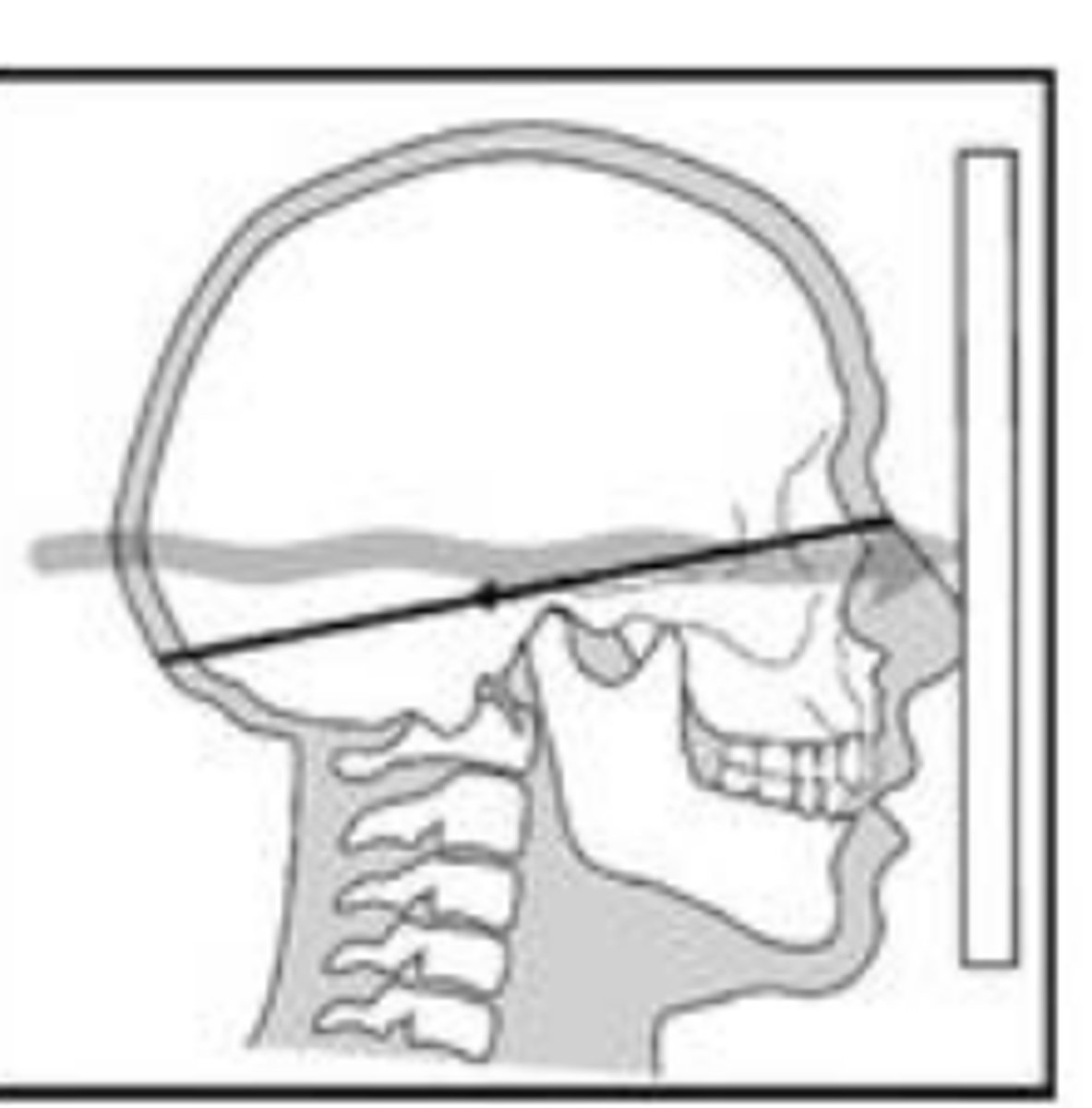
PA Ceph
canthomeatal line 10 degree with receptor
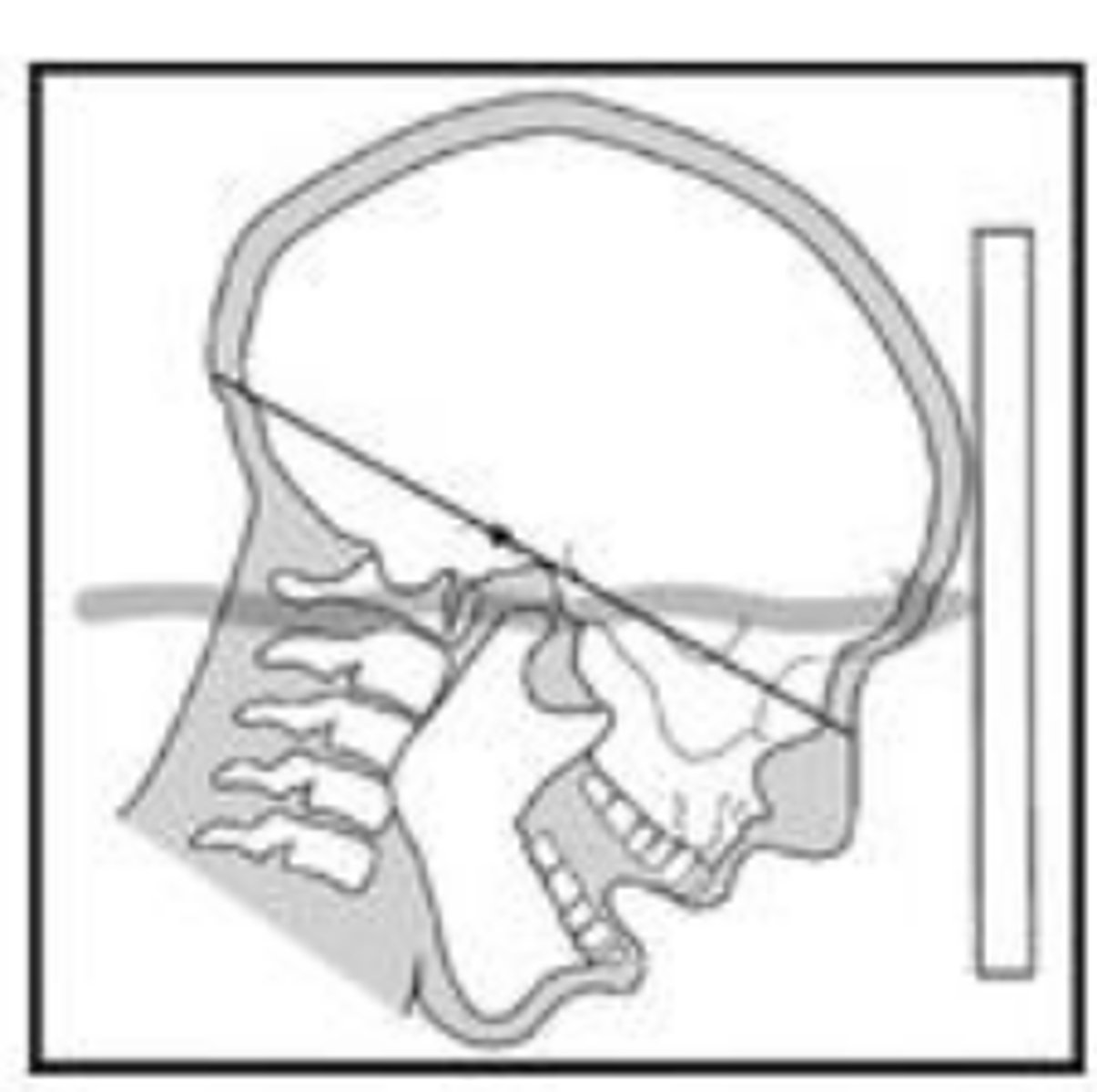
Reverse Towne Projection
canthomeatal line -30 degrees with receptor
Used to identify fractures of the condylar neck and ramus
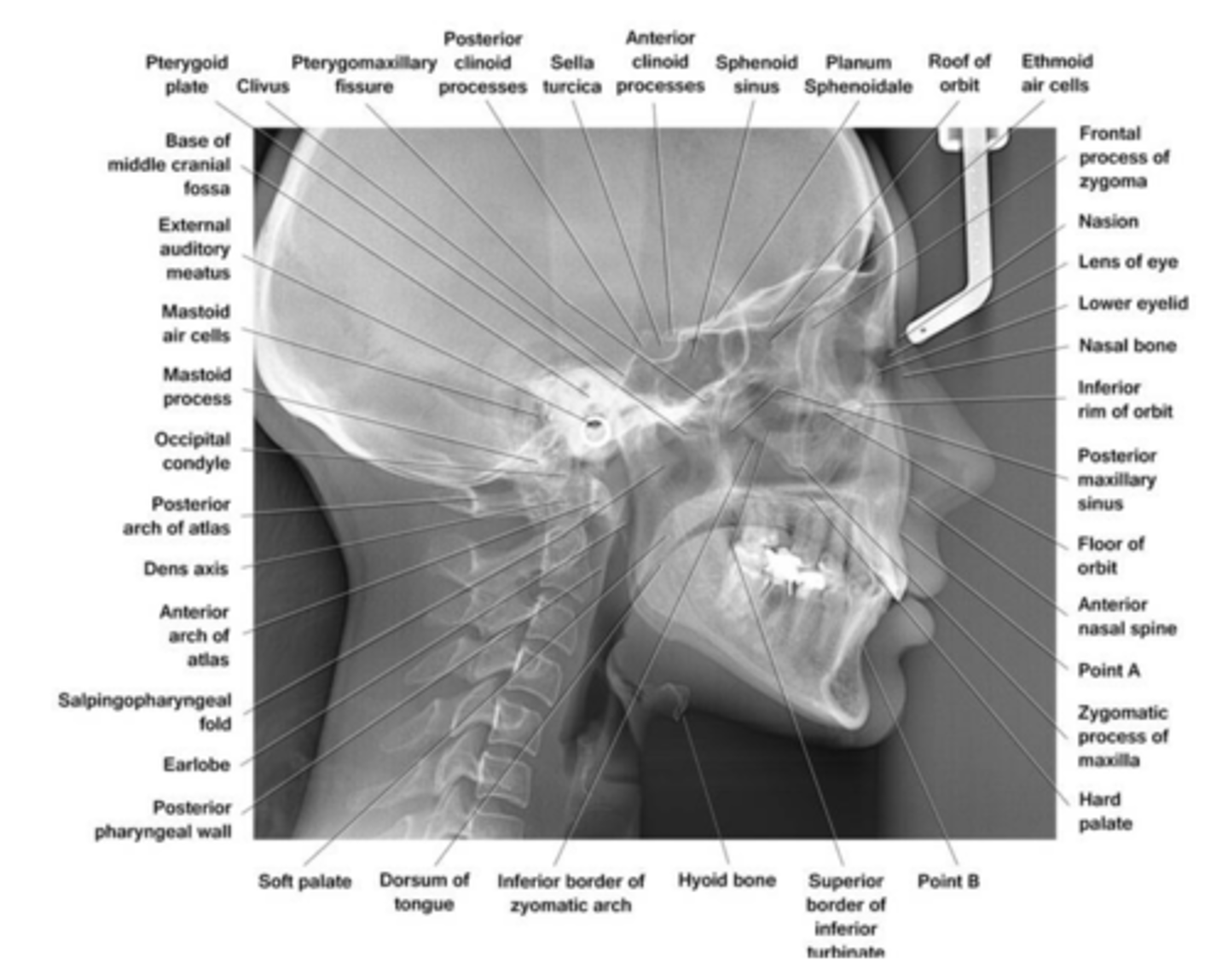
Lateral Cephalometric Projection
The central beam is___________________ to the midsagittal plane of the patient.
perpendicular
Lateral Cephalometric Projection
Evaluate the anteroposterior (AP) relationships between_________, __________ and ___________
maxilla, mandible and cranial base
Lateral Cephalometric Projection
Assess ______________ and______________ relationship
skeletal and soft-tissue
Lateral Cephalometric Projection
Monitor progress of _______________ and ______________ out comes
treatment and treatment outcomes
Lateral Cephalometric Projection
A wedge filter absorbs some of the radiation to allow visualization of ________________________________
soft tissue of the face.
Lateral Cephalometric Projection
Exact superimposition is impossible due to ________________________________________________________________
magnification of the structures on the far side from the receptor
don't need to learn every single landmark
not soft tissue
just obvious boney landmark structures
Posteroranterior(PA) skull projection
Evaluation of
Why do you do this?
Evaluation of craniofacial asymmetry
it make the face more clear
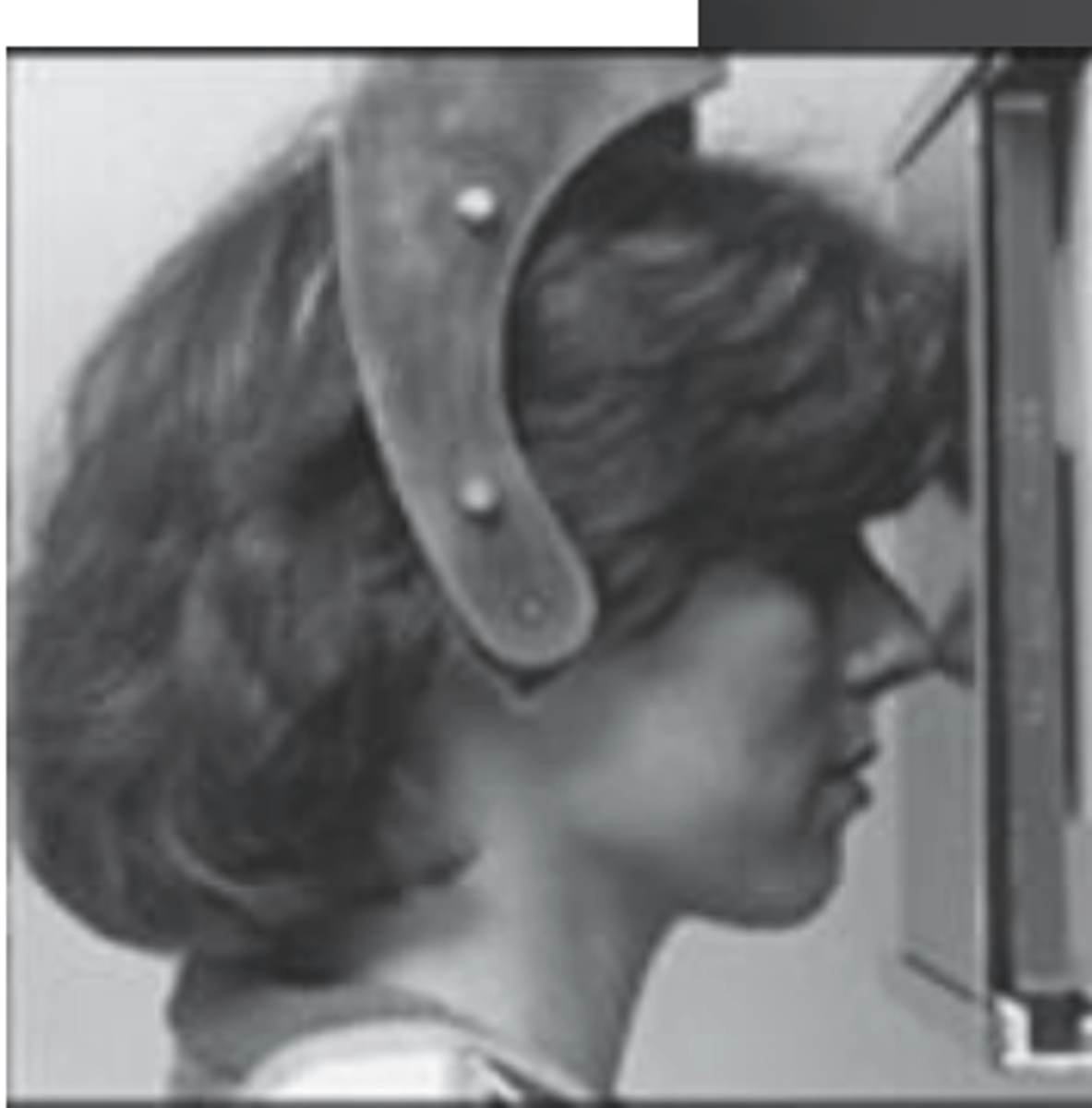
Posteroranterior(PA) skull projection
Monitor progress of _____________ and ____________________________
treatment and treatment outcomes
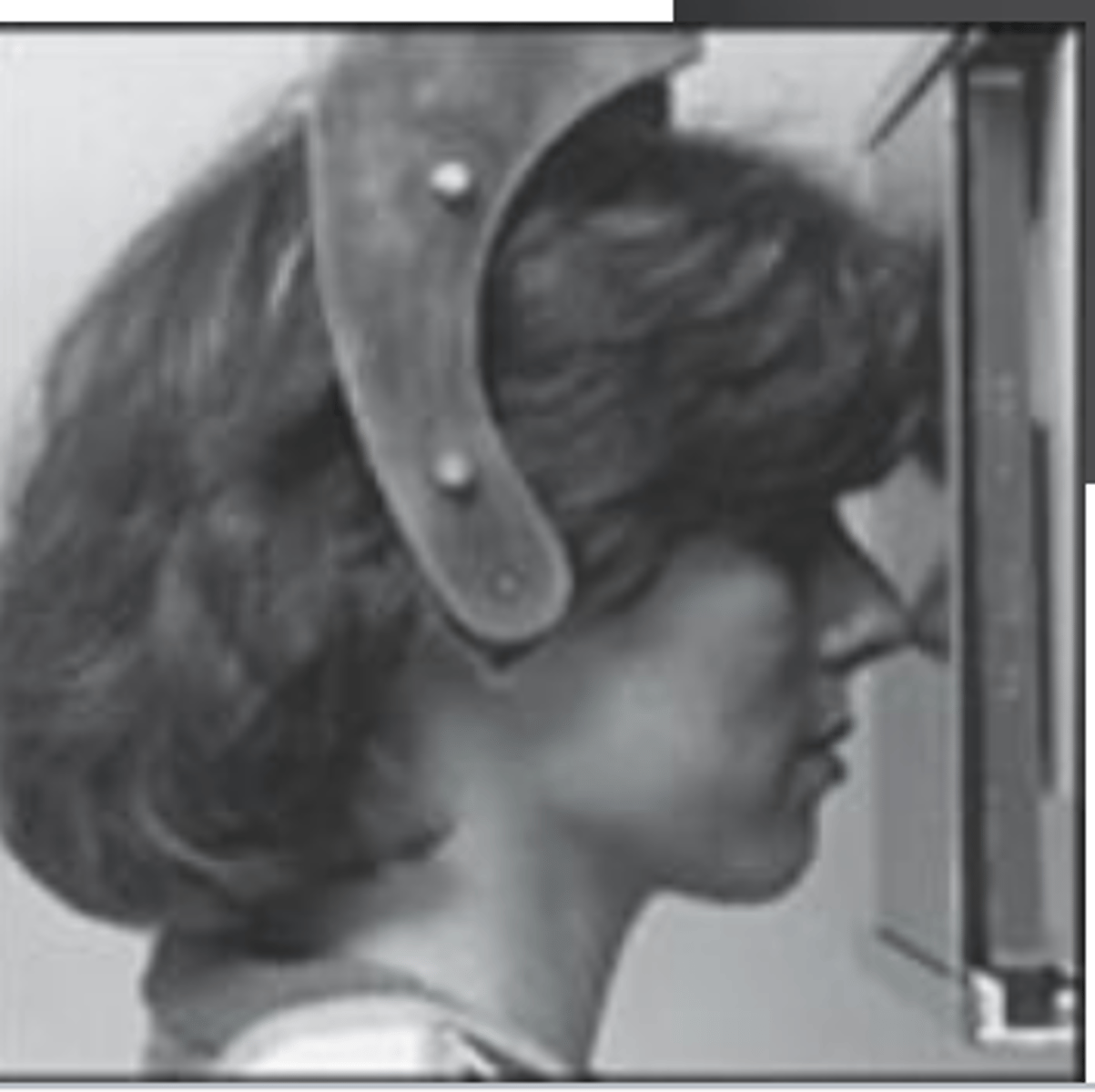
Posteroranterior(PA) skull projection
Positioning:
• Frankfort plane = ___________
• Canthomeatal line = _____________________
floor
10 degree from the floor
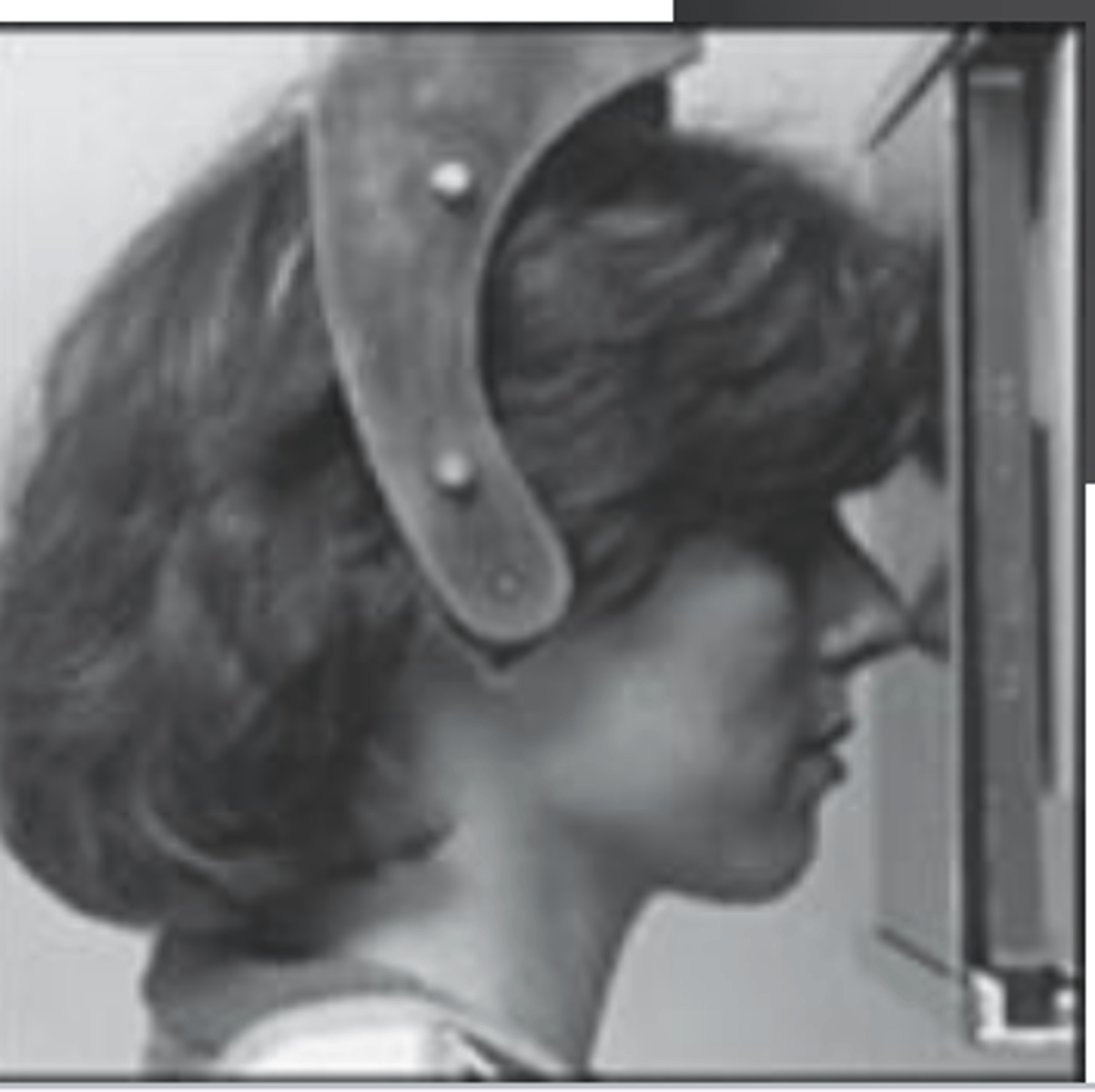
Posteroranterior(PA) skull projection
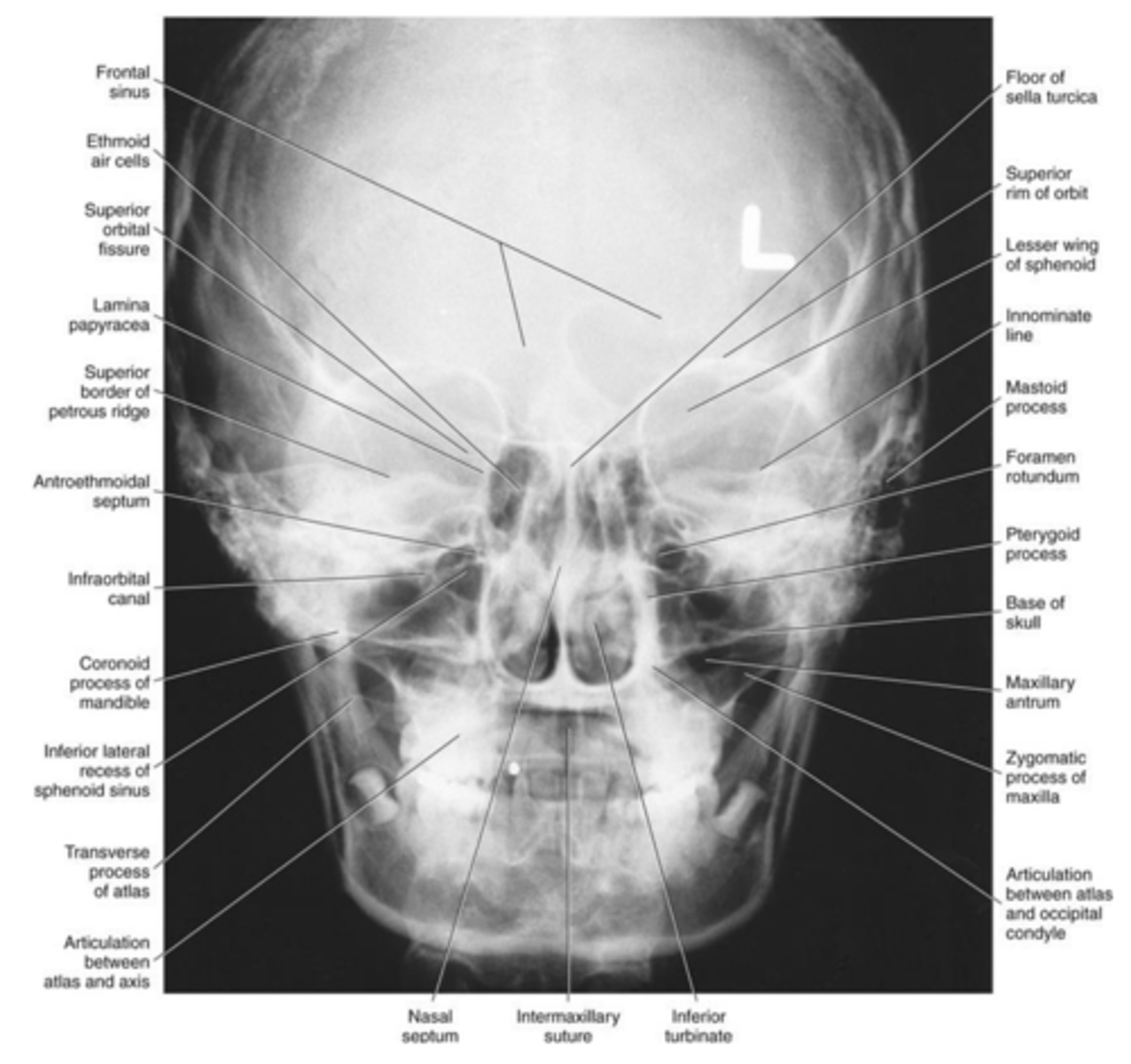
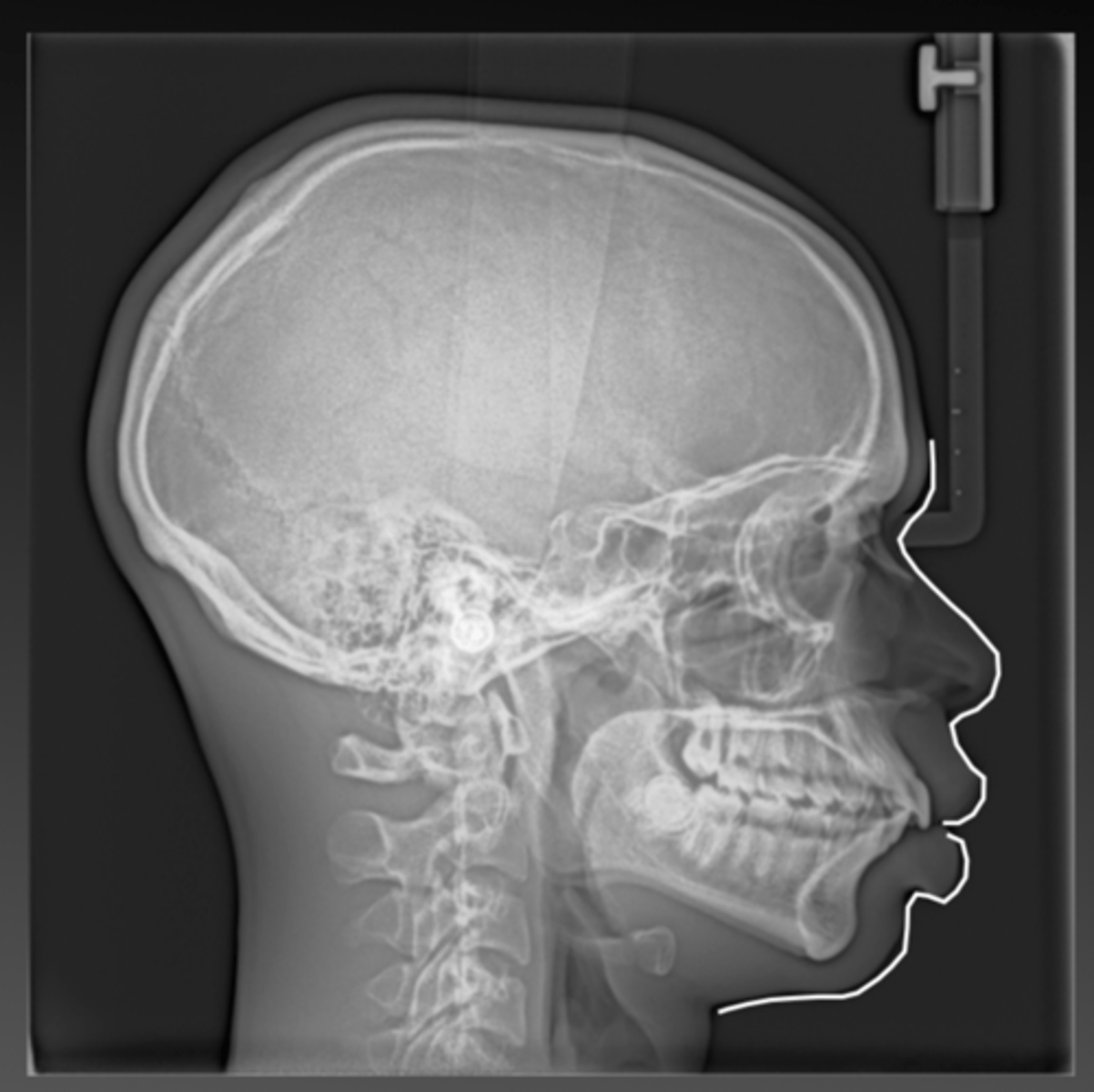
Submentovertex projection
• Can be useful in
-evaluating fractures of the zygomatic arches
-aeration of sphenoid sinuses
-osseous changes from skull base tumors
Is this image over or under exposed?
underexposed
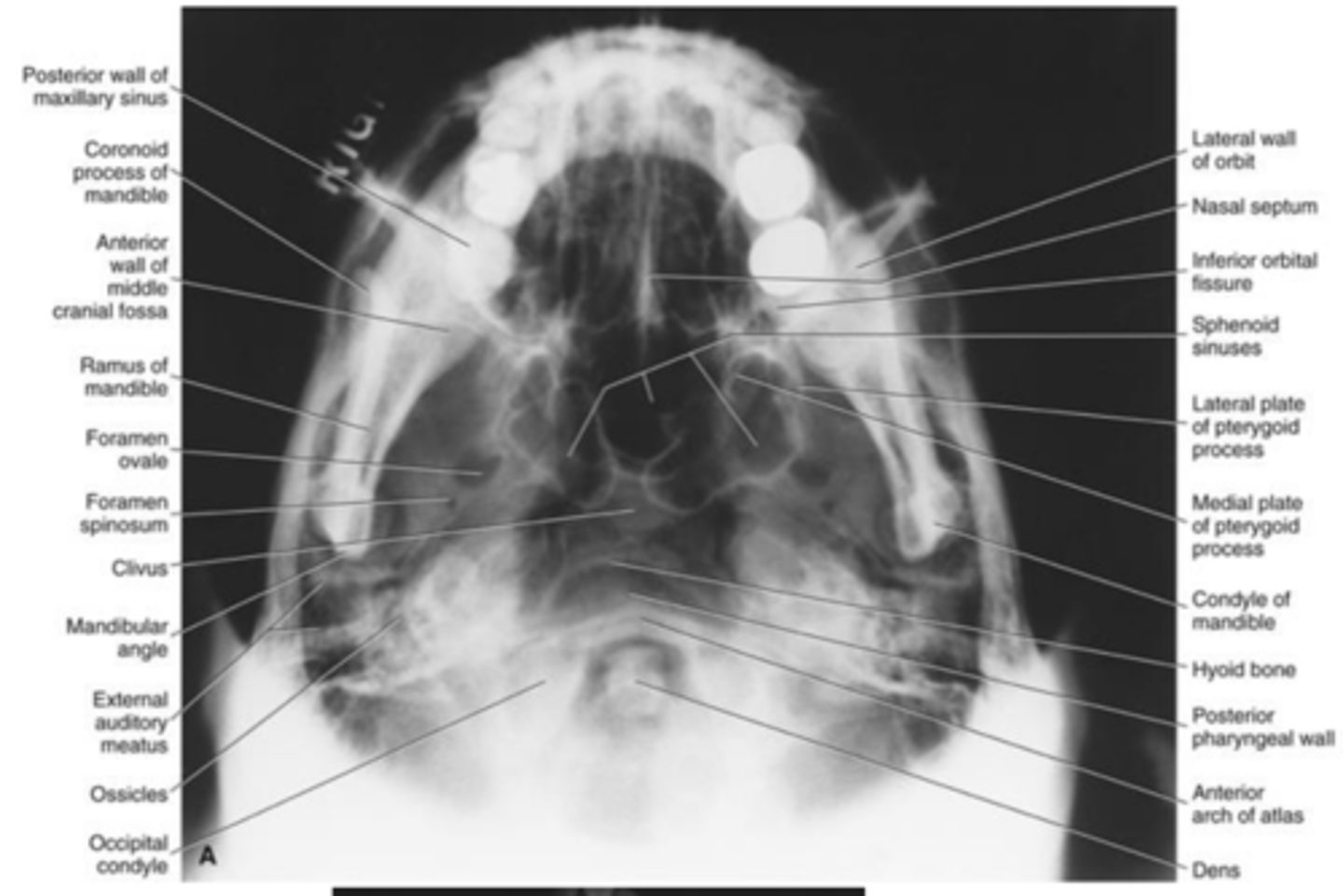
Submentovertex projection
Indications are largely achieved by _______
CT
Waters projection
Evaluation of
sinuses, predominantly the maxillary sinus and a lesser extent the frontal sinus and ethmoid air cells, midfacial fractures
Waters projection
Diagnostic objectives are accomplished by______
CT
Reverse-Towne projection
• Helpful to evaluate
condyle and condylar neck fractures
Reverse-Towne projection
Diagnostic objectives are achieved by ______
CT
radiation dose
amount of ionising radiation a person receives
Absorbed dose
• Total energy absorbed by ionizing radiation per unit mass of irradiated material
• Absorbed Dose = _______/___________
• Absorbed Dose = Energy/ Mass
Absorbed dose-SI unit:
Gray, where 1 Gy = 1 J/kg
Absorbed dose -Traditional unit:
rad (radiation absorbed dose)
Conversion
• 1 rad = _____Gy
• 1 Gy= _____ rad
0.01
100
Equivalent (radiation-weighted) dose
Not all types of ionizing radiation cause the same biological damage
1 Gy of alpha particles cause (more/less/the same) biologic damage than 1 Gy x-ray photon
more
Radiation weighting factor established by ________________________________________________________ to account for the relative effect of producing biologic damage
ICRP (International Commission on Radiological Protection)
Equivalent dose =
Absorbed dose * Radiation weighting factor
Equivalent dose SI unit : Sievert [Sv] = [J/kg]
Equivalent dose Traditional unit:
rem (roentgen equivalent man)
Conversion
• 1 rem = _______
• 1 Sv = _______
0.01 Sv
100 rem
Who causes more damage? Tyson (heavy charged alpha particle) or Mayweather (x ray photons)?
Tyson
Tyson is equivalent to alpha particle or x-ray photon?
alpha particle
Mayweather is equivalent to alpha particle or x-ray photon?
x-ray photon
Radiation weighting factor
X ray photons =___
Alpha particle (heavy charged particle) =___
1. 20
Biologic damage
10 mGy from alpha radiation =______mGy of x ray
200
Effective dose
Used to estimate...
estimate the risk in humans
- account for different radiosensitivity of different tissues
- in terms of the risk for stochastic effects (cancer induction and heritable effects)
Tissue weighting factors established by the ______
ICRP
Effective dose = sum of products of equivalent dose to each organ or tissue and the corresponding weighting factor =
= equivalent dose (Ht) * tissue weighting factor (Wt)
Effective dose
SI unit : Sievert [Sv] =_____________
[J/kg]
Effective dose
Traditional unit: ____________________________
rem (roentgen equivalent mam)
1 Sv = _____ rems
100
Tissue weighting factor established by
ICRP
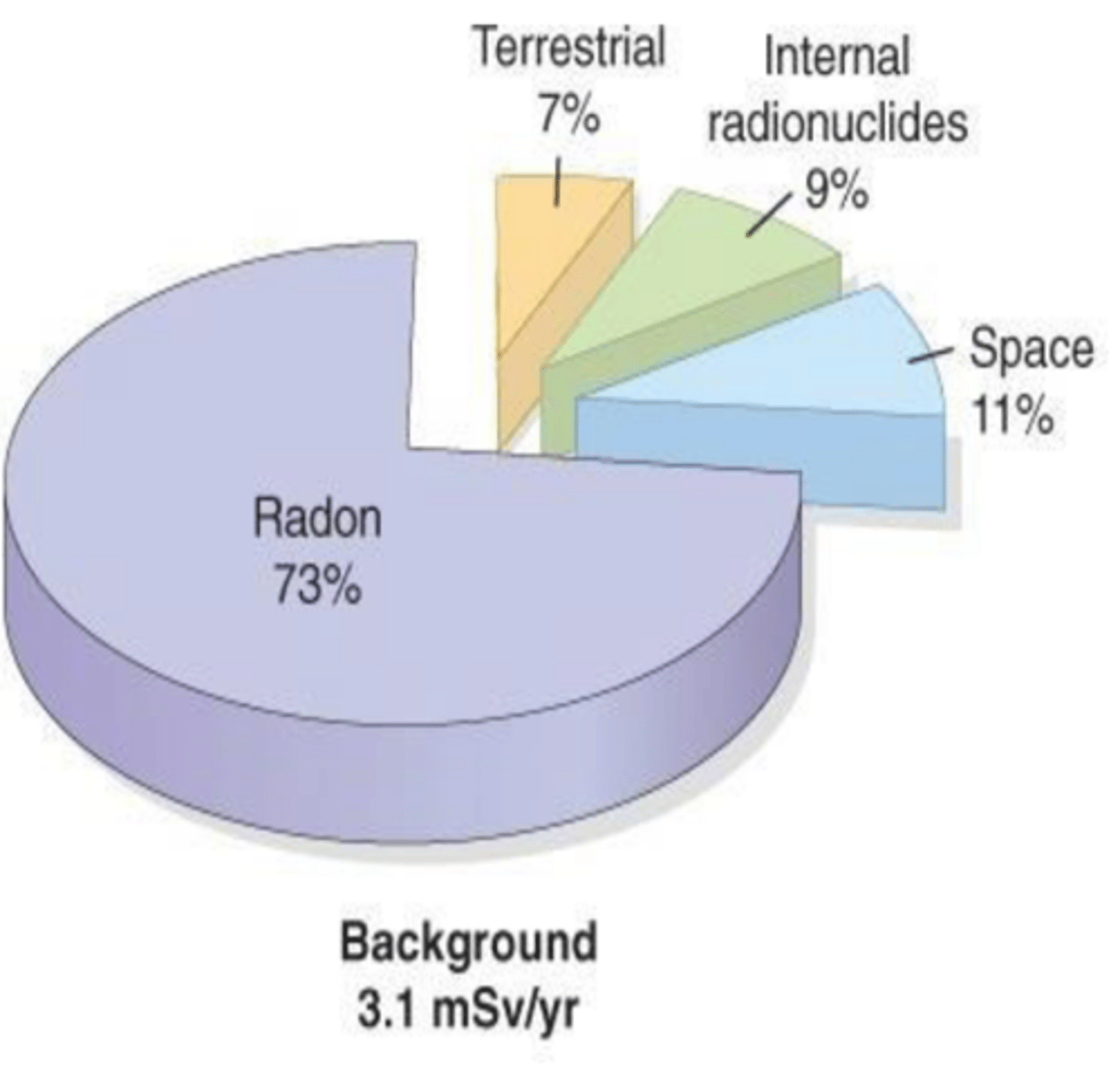
Background radiation (United States)
Naturally occurring radiation exposure
_____ mSv = Average annual per capita effective dose in the US in 2006 (NCRPreport No. 160)
3.1
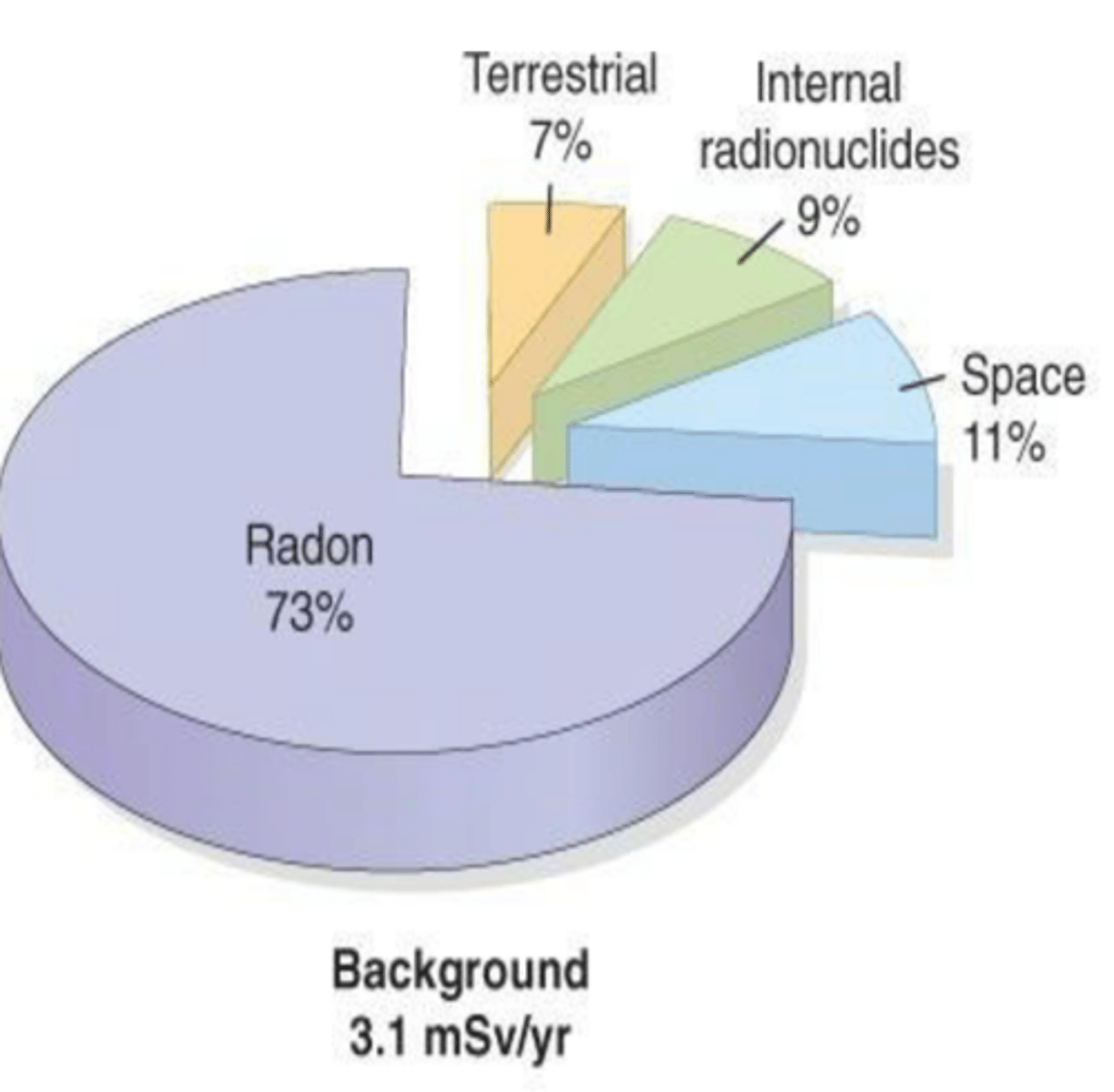
Background radiation sequence
Radon (73%) > Space (11%) > Internal radionuclides (9%) > Terrestrial (7%)
• Radon-222:
Naturally occurring radioactive elements in earth's crust.
- produced in the uranium-238 decay chain
emits alpha particles, which can be inhaled.
• Space/cosmic radiation:
comes from sun or cosmic rays. Composed of protons, helium nuclei, and nuclei of heavier elements. Function of altitude, doubling with each 2000m increase in elevation. Sea level 0.33 vs Denver 0.5 mSv/yr
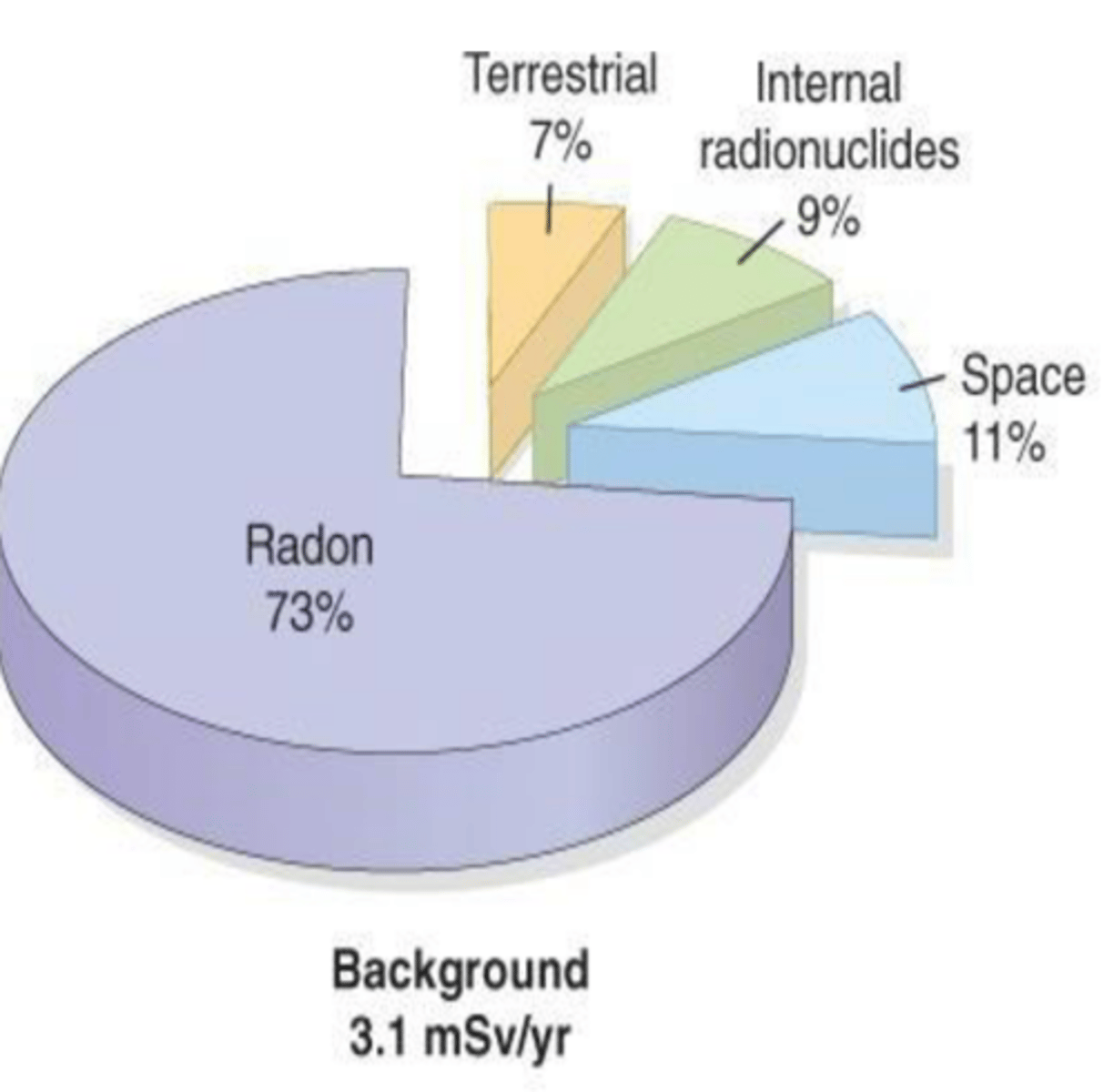
Internal radionuclides:
Ingestion of food and water containing radioactive material such as uranium and thorium and etc.
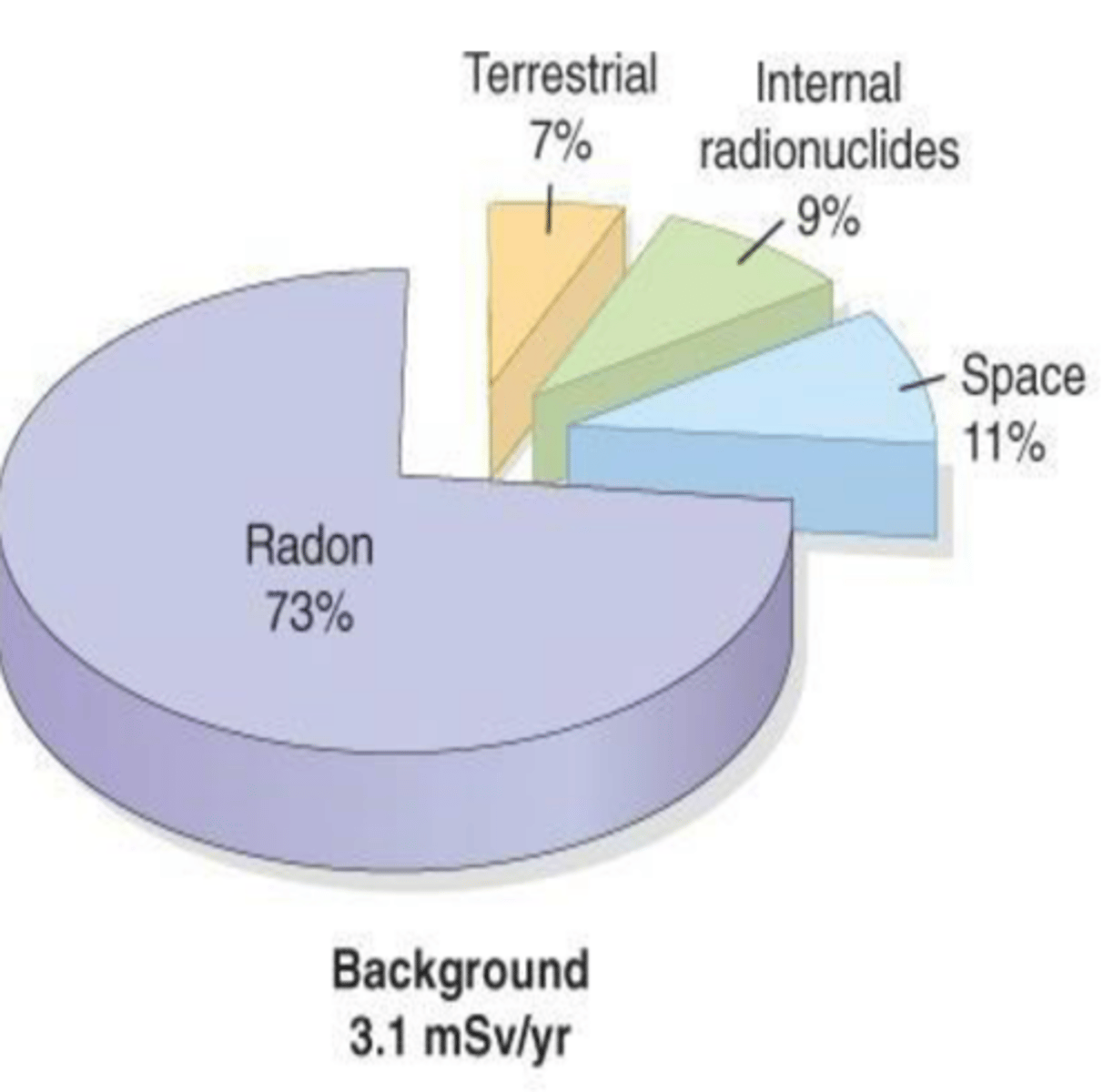
Terrestrial:
radioactive materials in the soil. Potassium-40, thorium-232, uranium-238, radium. In brick, concrete, granite
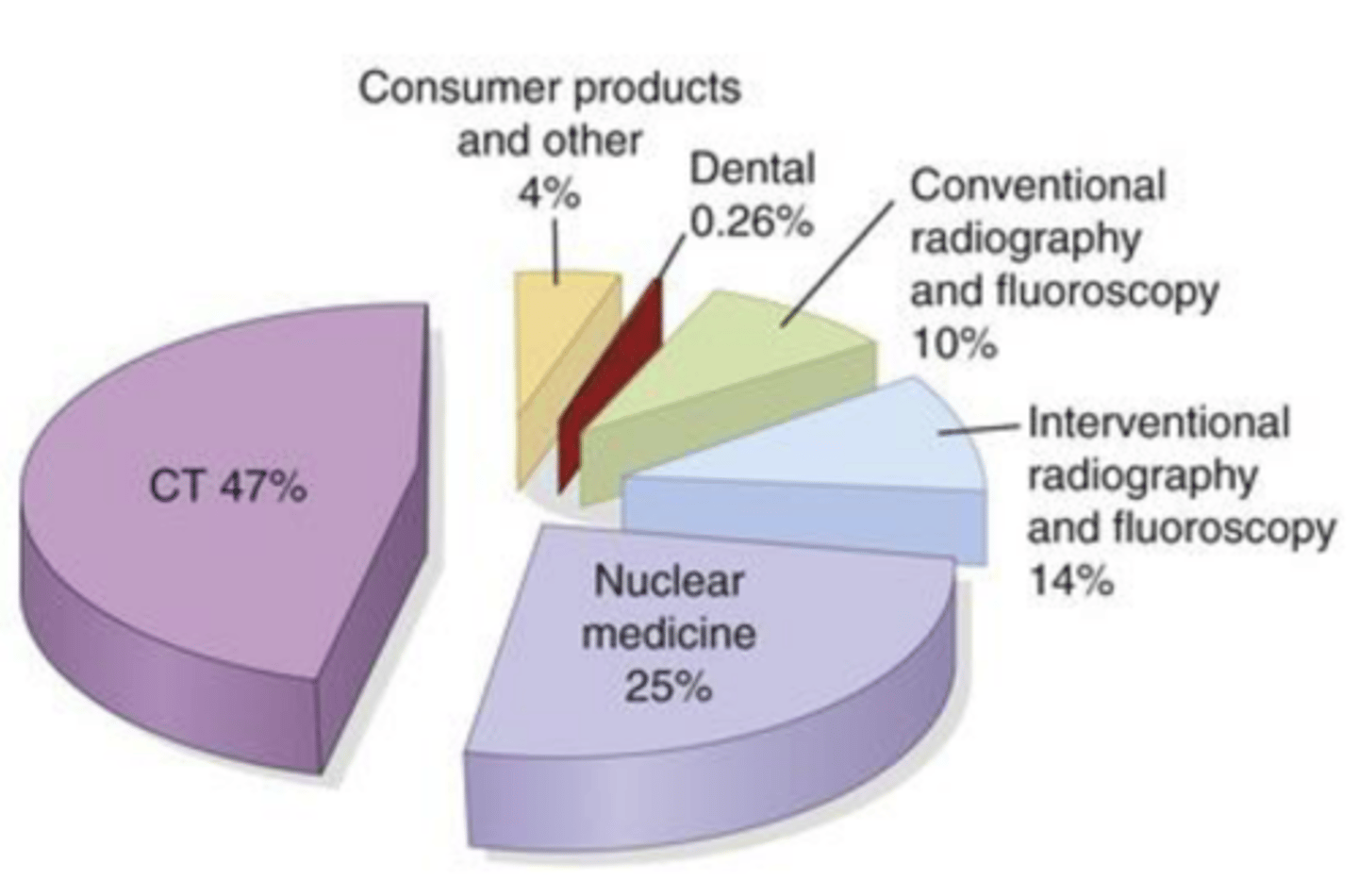
medical, and consumer products _____ mSv/year
3.1
CT: Computed tomography
Nuclear medicine
Interventional radiography and fluoroscopy
Conventional radiography and fluoroscopy
Consumer products and other: Cigarette smoking, Air travel, Mining, agriculture, and combustion of fossil fuels e.g., flight of 5 hours cruising at an altitude of 12km results in an exposure of 25 microSv
_____ billions x-ray and nuclear medicine exams done annually worldwide. ___% of these are dental radiographic exams.
3.6, 14
• Daily background dose = _____ microSv
8.5
Does 3D image have more radiation than 2D?
yes, but it's not that much different.
Communicating radiation risk to patients
Allow the patient to
fully express his/her thoughts. Acknowledge their concerns
Explain the patient
why you need radiographs as part of the patient's personal diagnosis (caries, extent of bone loss, periapical infection and information that can only be obtained by radiographic examination)
Reassure the patient
you make efforts to minimize the radiation (digital sensor, thyroid collar, rectangular collimation, individualized imaging parameters)
Convey the relative magnitude of the dose that the patient is likely to receive (compare to _________________________________________)
natural background radiation or airline flight
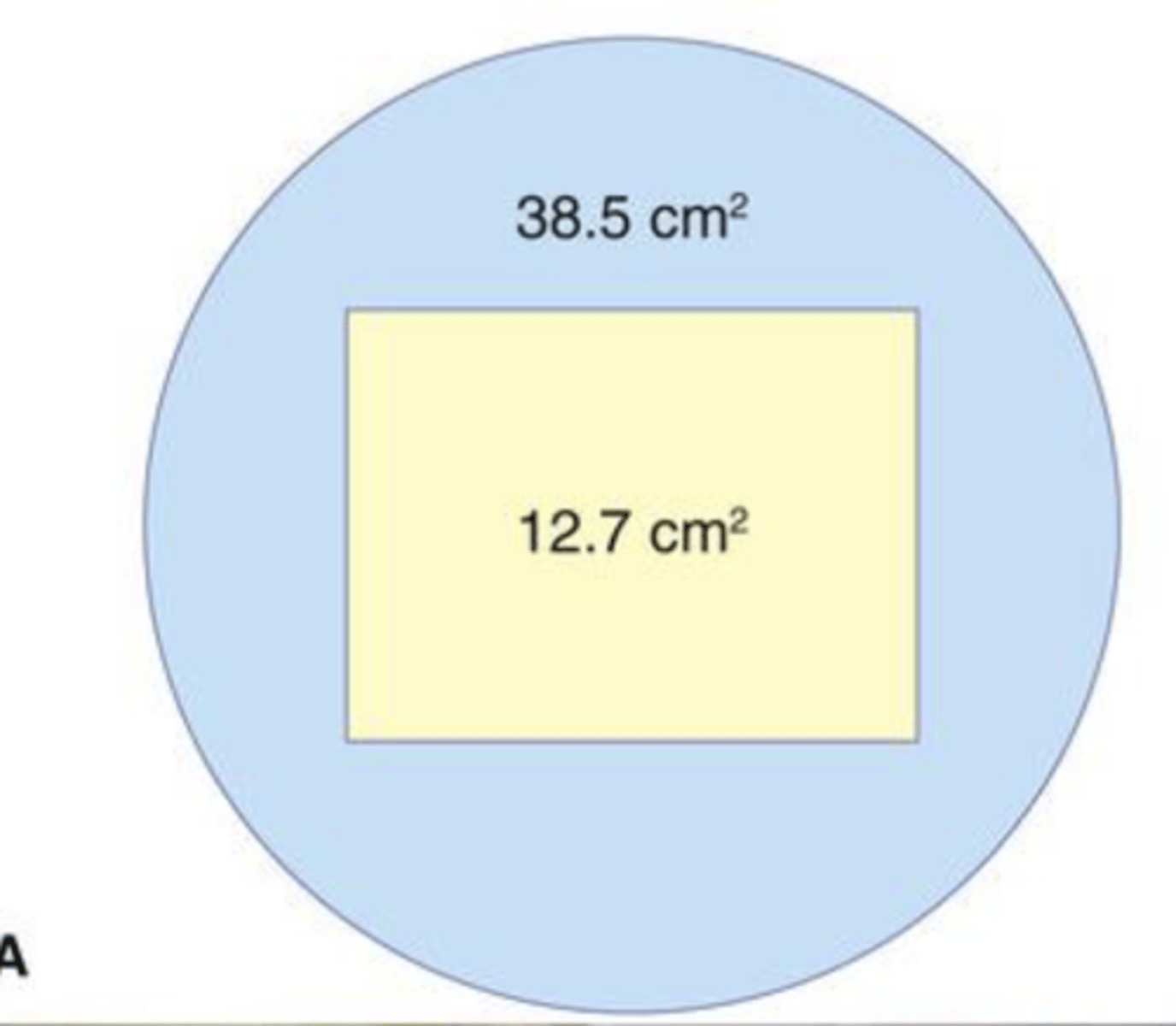
Rectangular collimation
the area of patients skin surface exposed by 50% to 65% over round
Dose Limit (NCRP: National Council on Radiation Protection)
is there a limit?
no
ALARA____________________________________________
(As Low As Reasonably Achievable)
ALADA _________________________________________
(As Low As Diagnostically Acceptable),
Pregnant or potentially pregnant patient
• Follow the same principle of _______________, ADA selection criteria for dental radiographs
• Estimated fetal dose from dentomaxilofacial radiography is ________________ fold lower than the threshold dose for deterministic effects on embryo and fetus.
ALARA, 42,000
Dosimeter
The ADA recommends who should wear a dosimeter
• the workers who may receive an annual dose greater than 1 mSv should wear personal dosimeters to monitor their exposure levels.
• Pregnant dental personnel operating x-ray machine, regardless of anticipated exposure levels.
The requirement to use personnel dosimeters is specified by ____________________________________
state and national regulations
• In US, the code of federal regulations requires that personnel likely to receive more than _______ of the annual dose limit be monitored.
10%
NCRP:
National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurement
ICRP:
International Commission on Radiological Protection
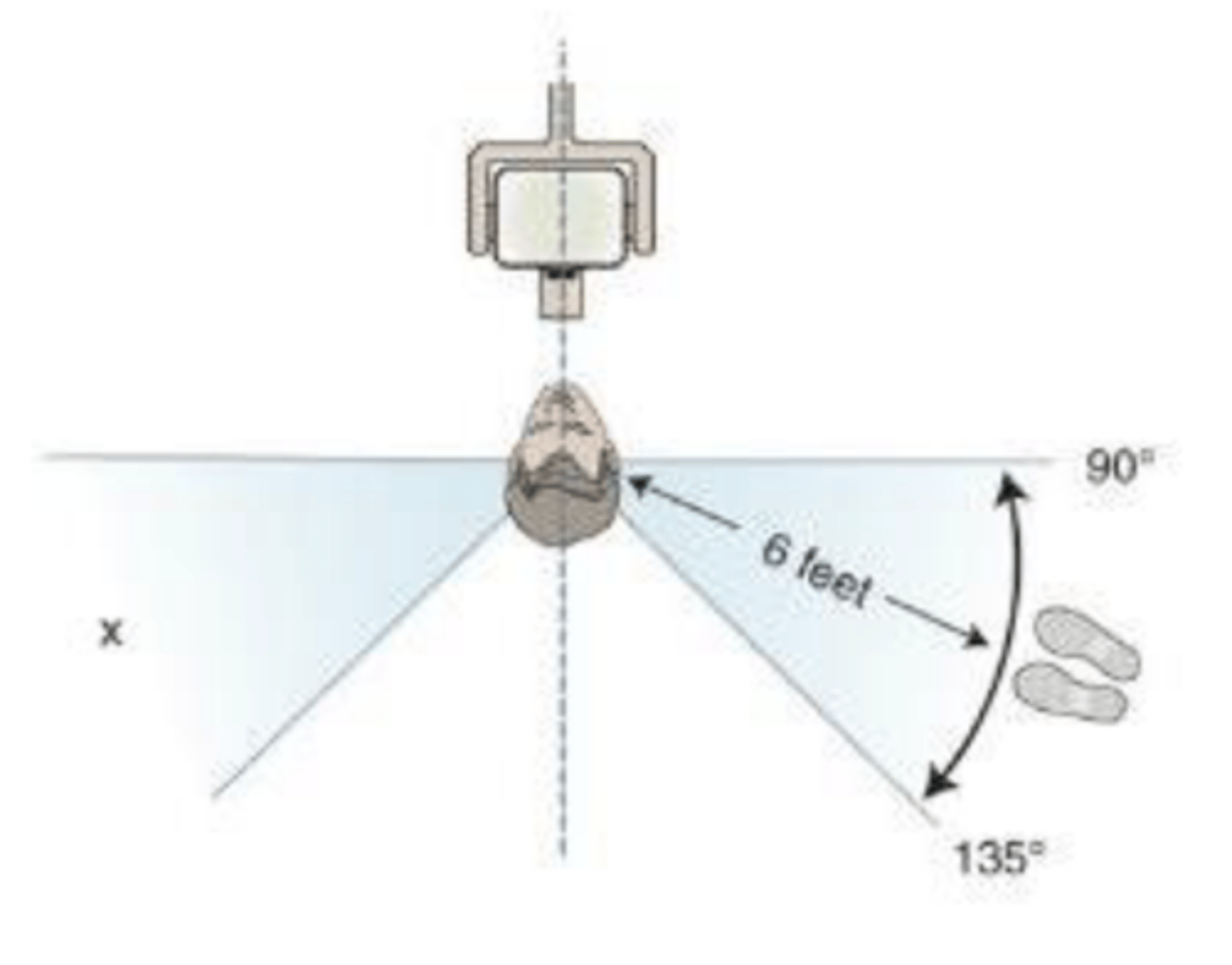
If you can't stand behind a wall, were can you stand? Minimum distance?
6 feet/2 meters
Don't stand behind or in front where there is likely to be rebounding scattered radiation
Radiographic prescription
Follow the principle of ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable)
• Least amount of radiation exposure necessary to generate diagnostically acceptable images
• Prescribe individualized radiographs only after a clinical examination
• Attempt to acquire previous radiographs from patient's previous dentist.
• Progression of caries, periodontal disease and pathology
CHILD WITH PRIMARY DENTITION (PRIOR TO ERUPTION OF FIRST PERMANENT TOOTH)
NEW PATIENT
Selected PA's/Occlusal+ BWX
CHILD WITH PRIMARY DENTITION (PRIOR TO ERUPTION OF FIRST PERMANENT TOOTH)
RECALL PATIENT
Caries High Risk
BWXevery6-12months if not visualized or probed
CHILD WITH PRIMARY DENTITION(PRIOR TO ERUPTION OF FIRST PERMANENT TOOTH)
RECALL PATIENT
Monitoring of growth and development
Clinical judgment
CHILD WITH PRIMARY DENTITION(PRIOR TO ERUPTION OF FIRST PERMANENT TOOTH)
RECALL PATIENT
Other circumstances
Clinical judgment
When is FMS first recommended?
ADOLESCENT W/ PERMANENT DENTITION (PRIOR TO ERUPTION OF THIRD MOLARS; 12~18)
New patient
ADULT DENTATE AND PARTIALLY EDENTULOUS
RECALL PATIENT
Caries Low Risk
BWX every 24-36 months
Every patient should have a FMX every 12 months T/F
False! there should not be a rule for every patient. It should depend on the patient and their risk