AP Micro - Unit 3
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
inputs v outputs
inputs - 4 factors of production, what is needed
outputs - what we are producing
short run
fixed plant size (land, factory, etc.)
variable usage
variable output
long run
variable plant size (more land, more factories, etc.)
entry and exit (new companies can come, go)
letters
T = total
A = average
M = marginal
P = product (means price when alone)
C = cost
F = fixed (does not change as output changes, taxes, fees, etc.)
V = variable (wages, utility costs, etc.)
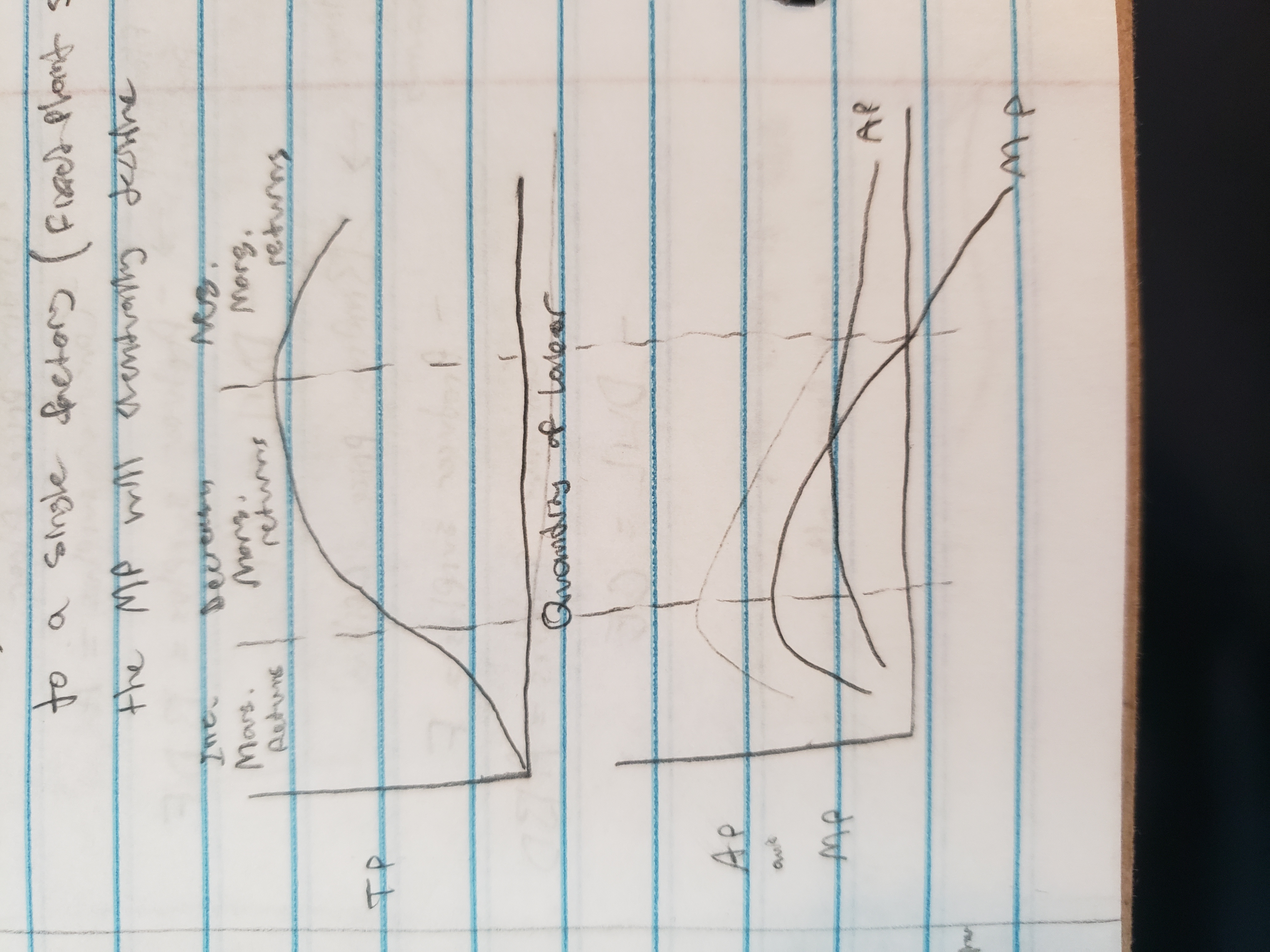
MP = change in TP / change in input
AP = TP / number of inputs
Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns
As more of a variable resource is added to a fixed resource, at some point, the MP of the variable resource will decline
ex, as we add more workers to a single factory (fixed plant), the MP will eventually decline
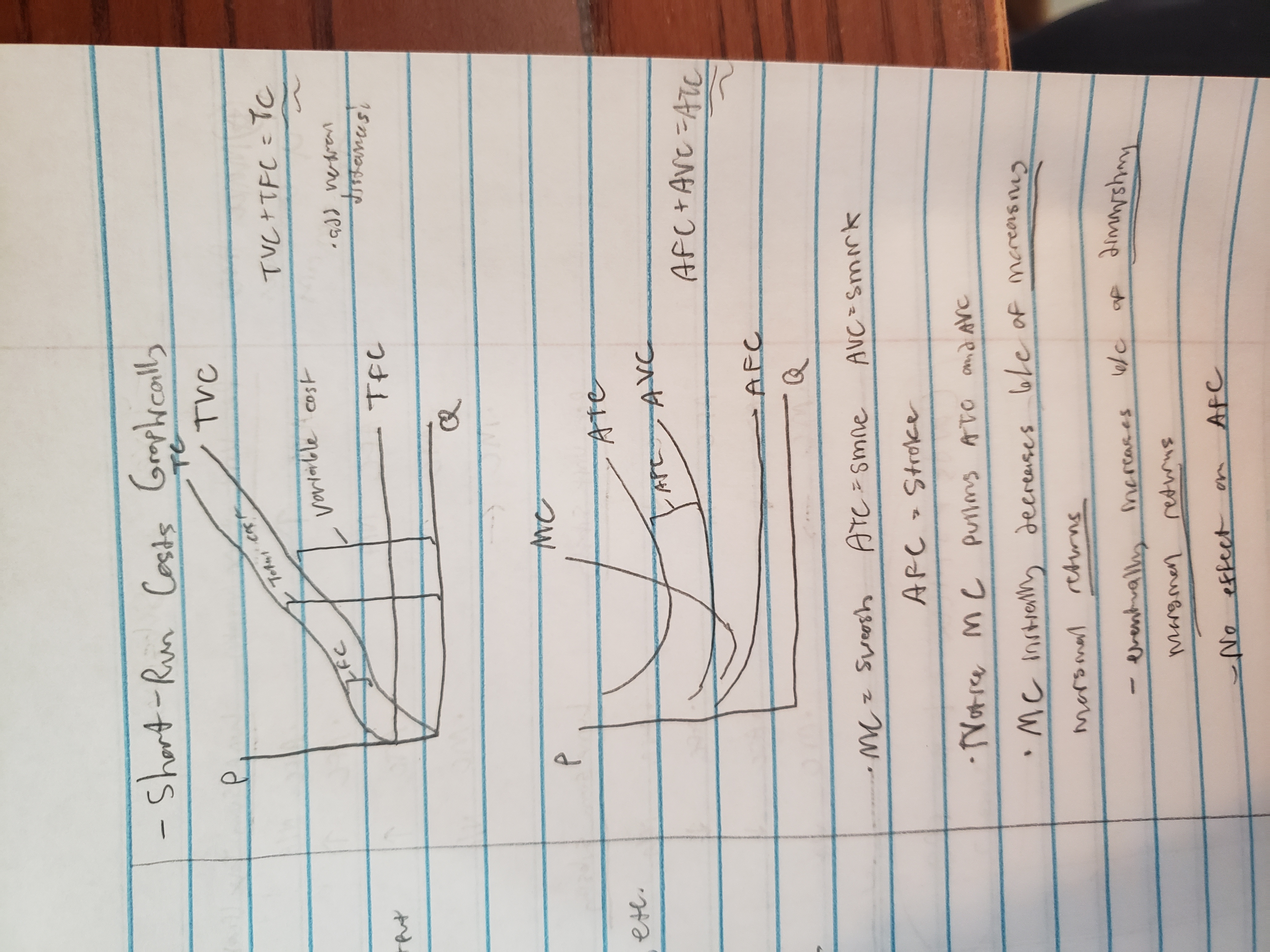
Fixed costs
TFC
average fixed costs = TFC / Q
Variable costs
TVC
AVC = TVC / Q
Total cost
TC = TFC + TVC
ATC = TC / Q
marginal cost (MC)
MC = change in TC / change in Q or change in TVC / change in Q
fixed costs do not affect MC
effect of MP on AP
if MP < AP, AP decreases
if MP > AP, AP increases
MC also controls AVC and ATC the same way
short run costs graphically
determinants of cost curves
Productivity
Specialization
Division of Labor
Tech
Input Prices
Taxes / Subsidies
Shifting Cost Curves
Higher costs will increase AVC and MC shifts left
MC curves = supply curves for a company (which is why they shift left and right like one)
effect of per unit tax on AVC, AFC, ATC, MC
AVC increases
AFC (n/a)
ATC increases
MC shifts left
effect of per unit subsidy on AVC, AFC, ATC, MC
AVC decrease
AFC (n/a)
ATC decrease
MC shifts right
effect of lump sum tax on AVC, AFC, ATC, MC
AVC (n/a)
AFC increase
ATC increase
MC (n/a)
effect of lump sum subsidy on AVC, AFC, ATC, MC
AVC (n/a)
AFC decrease
ATC decrease
MC (n/a)
long-run production costs
in the long run, all costs can change! No distinction between VC and FC
P v. Q graph is a single, slightly U shaped LRATC curve (long run avg. total cost)
zones on a LRATC (and when will you see scale and return)
econ of scale: growing businesses, efficient
Increasing output decreases LRATC
vs. increasing returns to scale, doubling input more than doubles output
Constant returns to scale: doubling input doubles output
diseconomies of scale: losing efficiency, doubling input less than doubles output
“scale” = long run, “return” = short run
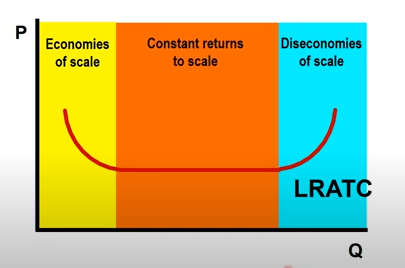
minimum efficient scale (MES)
Lowest output where costs are minimized
Larger output = industry more concentrated (fewer firms)
on a graph, intersection between yellow and orange zones, or where it firsts hits minimum
explicit v. implicit costs
explicit = monetary payments to others
implicit = opportunity costs to owner, forgone salary, self-owned resources (PC, own car, own room)
forgone interest on static (one-time) payments / savings
accounting profit
TR - explicit costs
economic profit
TR - economic costs
economic costs = explicit + implicit
always smaller than accounting profit
normal profit
implicit costs (what you could have had) (what you would have normally had)
short run profit maximization
MR = MC rule
MR = extra revenue from selling one more unit = P (for now)
only works if you choose to produce
applies to all market models
mr = mc rule on a table
find row where MR is closest to MC, and/or where profit is the highest
mr = mc rule on a graph
MR = D = AR = P line
Study all images, know how to draw these graphs. Minimum of ATC and AVC should intersect with MC line
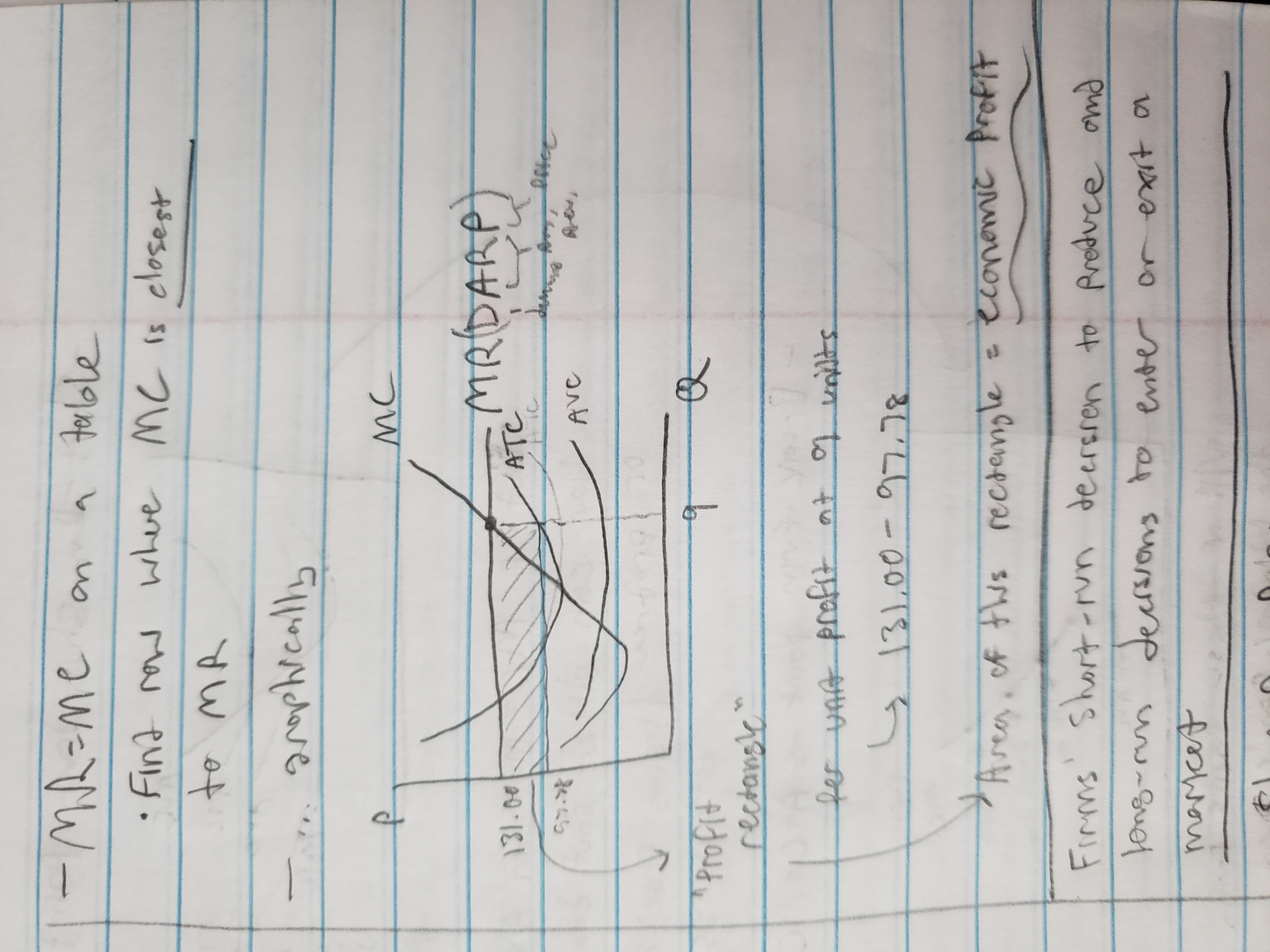
loss minimization position

short run shut-down point and break-even point
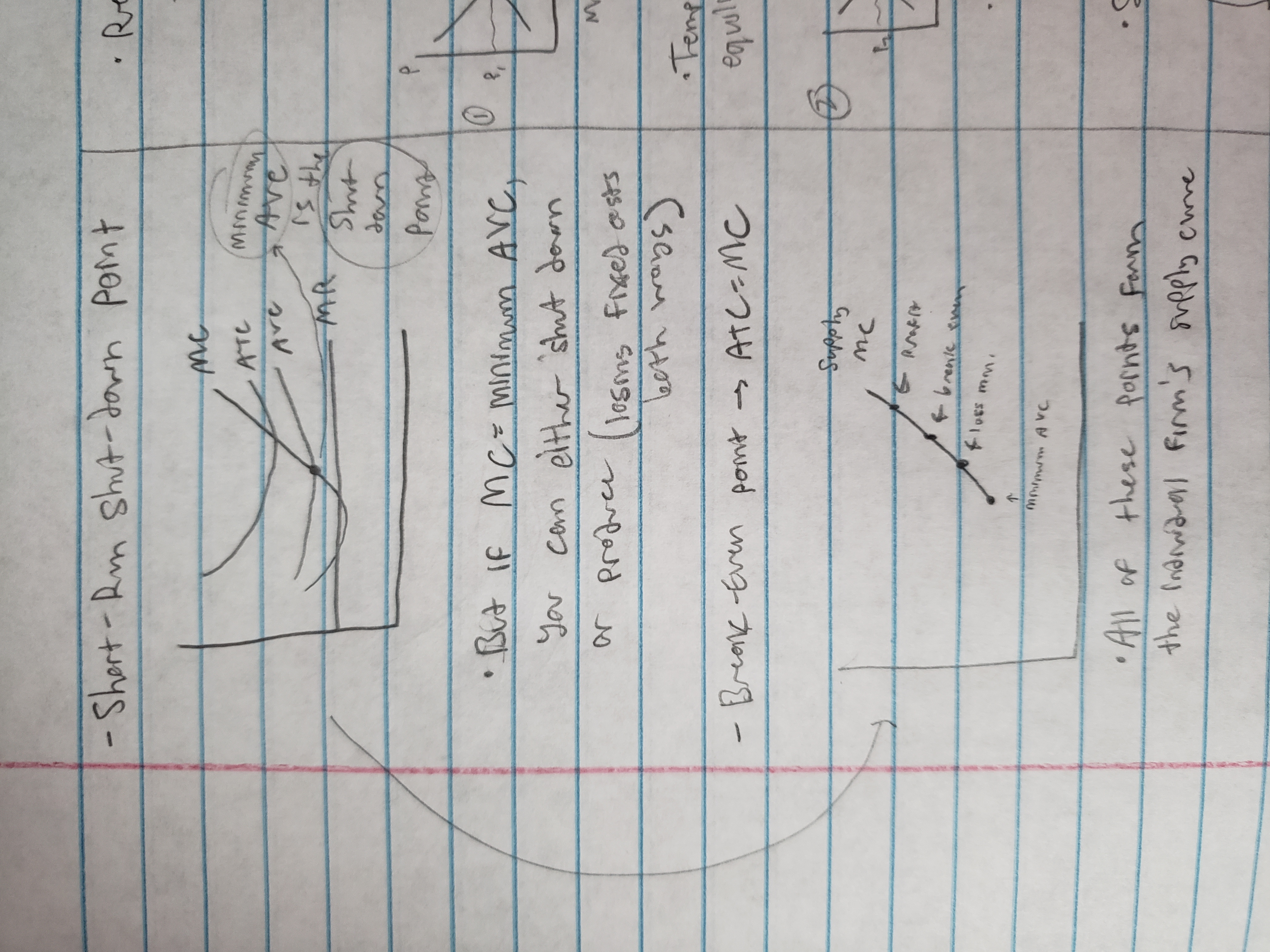
side-by-side graphs (and why)
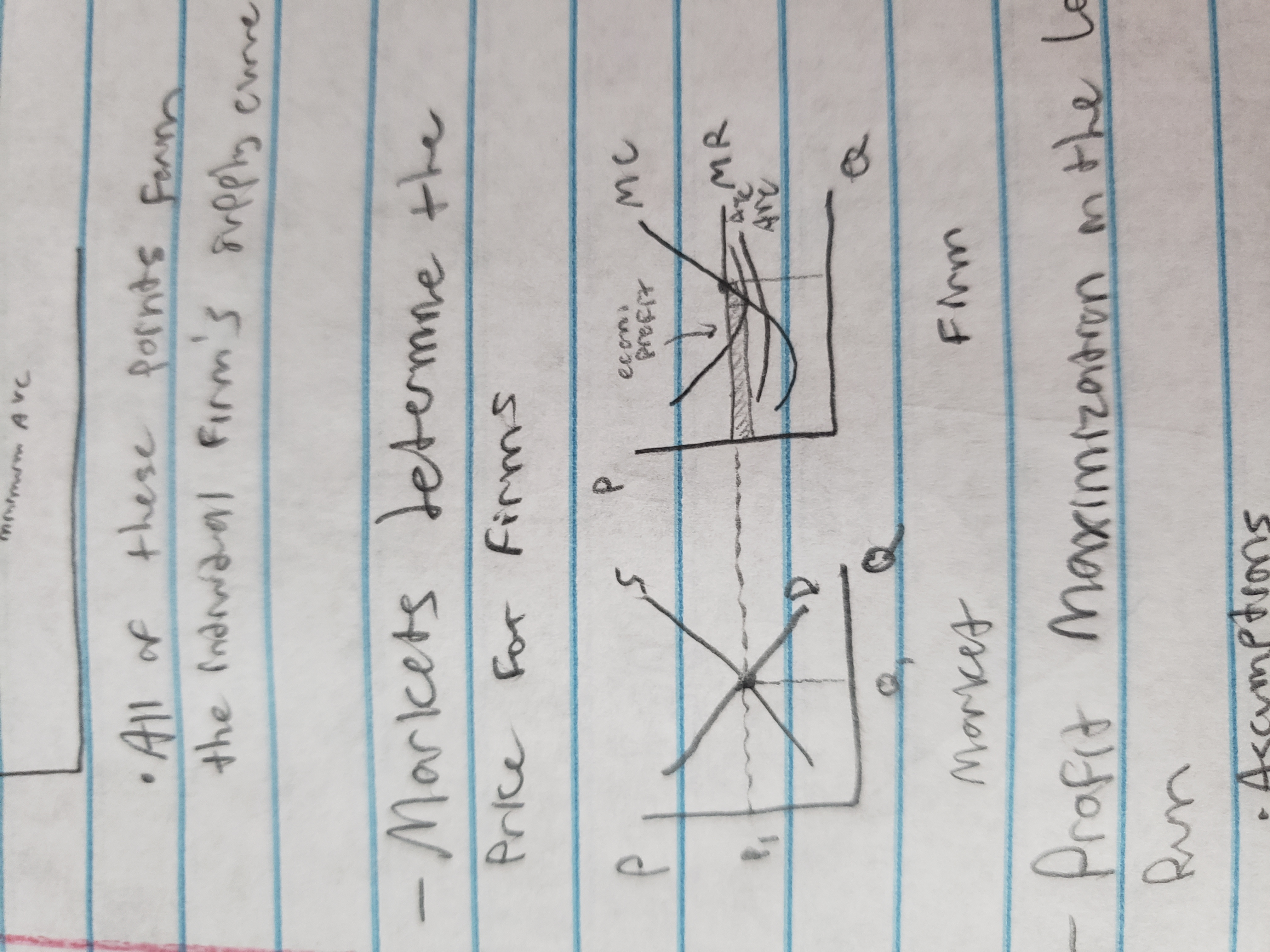
profit maximization in the long-run
Assumptions
Entry/exit only (profit = entry, loss = exit)
Identical firms and costs
Constant-Cost industry (input prices unaffected by entry/exit)
Results of analysis
MRDARP will end up at minimum ATC, and economic profit = 0
temporary profits, re-establishment of equilibrium (know thought process)

four market models (from most to least efficient)
Perfect competition > monopolistic comp. > oligopoly > pure monopoly
perfect competition

constant-cost industry
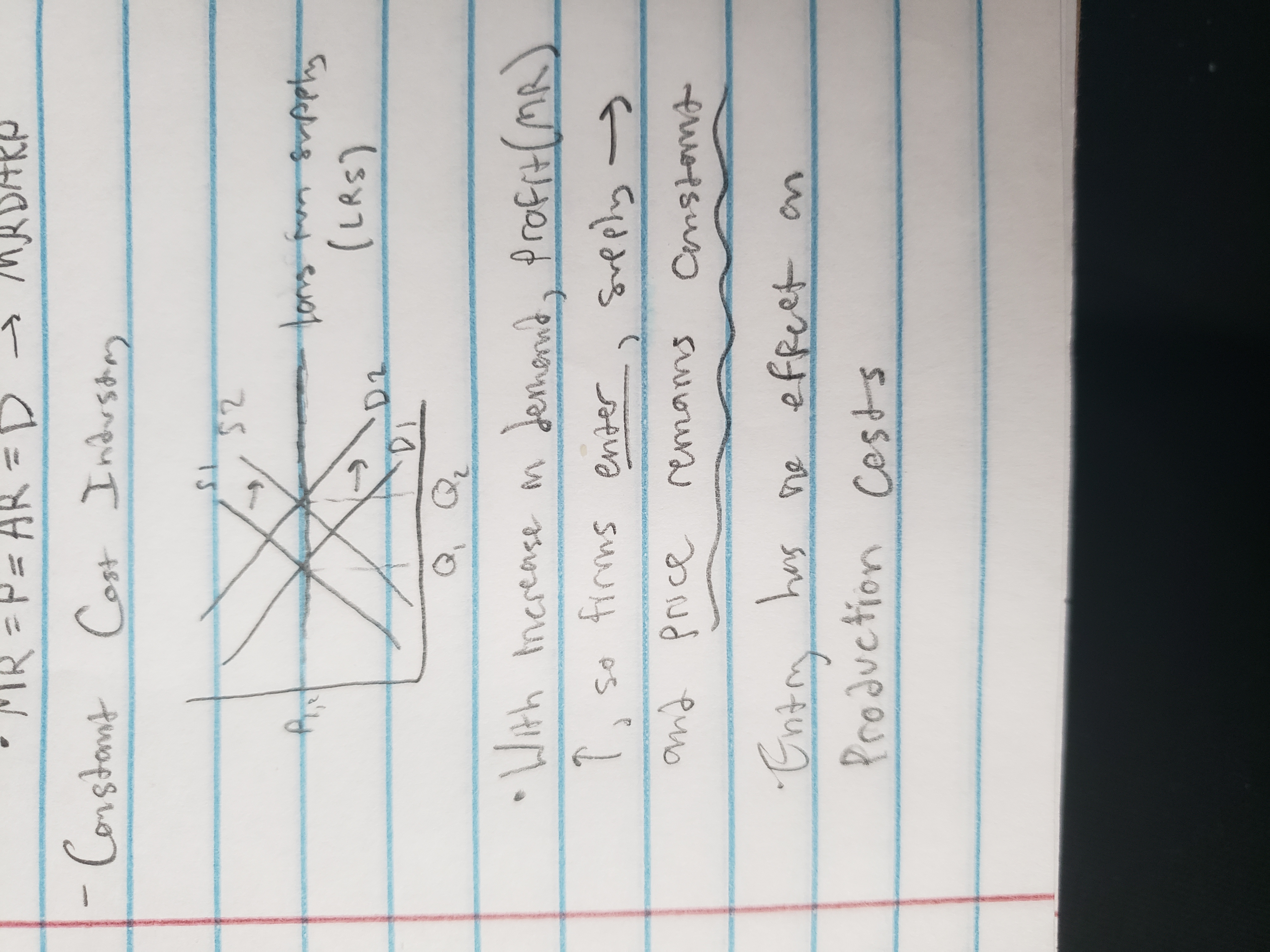
increasing cost industry

decreasing cost industry

underallocation vs. overallocation, and what guarantees efficiency
Perfect competition = productive efficiency (P = min atc, consumers getting product at lowest possible price) and allocative efficiency (P = MC, producing at the level society wants it to produce)
