7L10 DNA Damage & Repair
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
mutation
nonsense, missense, silent, frameshift
in-frame deletion
delete a multiple of 3 so no shift frame, but still bad
example: UUC in CFTR causes cystic fibrosis
DNA damage
spontaneous, environmental, carcinogenic
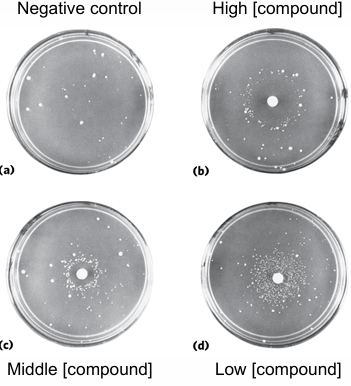
Ames Test
determines if compound is a mutagen,
uses salmonella typhimurium with inactive histidine biosynthetic pathway;
if a cell grows, it must’ve mutated to allow it to grow in the deadly medium
mutagens v carcinogens
cause change in DNA sequences;
cause cancer
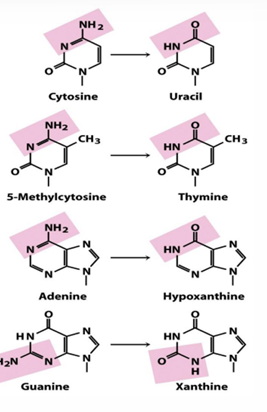
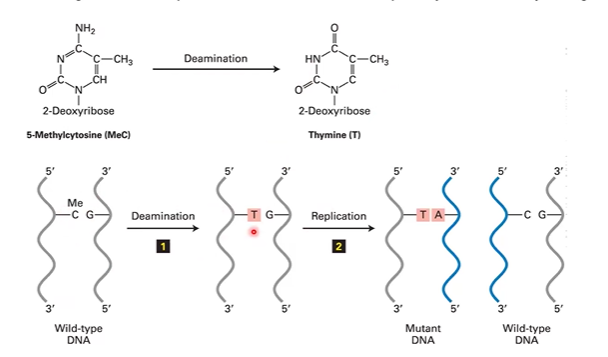
deamination
C > U, 5MC > Thymine, Adenine > HypoX, G > X
deaminating chemicals
sodium nitrate and nitrite
cured meats, tobacco, pesticides, leafy veggies
most common DNA damage
single strand breaks, depurination
how does a mutation become cancer
when repair systems replace it wrongly
5MCs are found in
CpG islands, hypermethylation silences genes. have lots of mutations, c an be accidentally activated
oxidation
cellular respiration makes ROS that insert themself into genes
ROS
reactive oxygen species,
free radical hydroxide > G or T
sometimes C or A
sometimes single strand breaks
depurination
removes base from nucleotide, forms abasic site
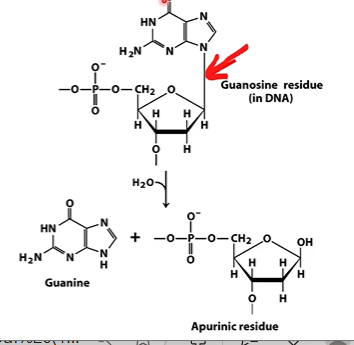
abasic site
site with no base;
apurinic site AP site
alkylation
agents covalently modify bases in DNA
spontaneous SAM of G > 7MG
like sulfur gas
distorts double helix
sulfur mustard
inserts itself between DNA strands, links them together so they cant transcribe
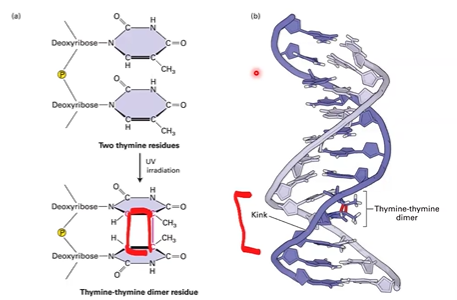
thymine dimers
from uv radiation
forms cyclobutane ring, distorts DNA structure
DNA strand breaks
PDE bond broken
ionizing radiation
single strand, double strand (may be staggered)
damaged bases prevent DNA ligase
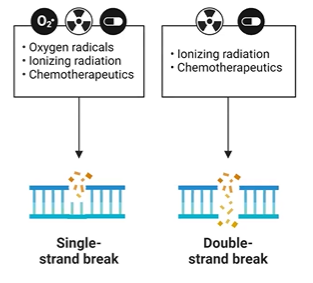
ionizing radiation
high energy, breaks covalent bonds;
cosmic rays, x rays, radioactive materials
repair systems
all cells have multiple:
mismatch repair, base-excision repair, NT-excision repair, direct repair
cancer is from accumulation of mutations
DNA repair pathway
Recognition of the lesion.
Excision of the lesion.
Resynthesis of the DNA.
Ligation of loose ends
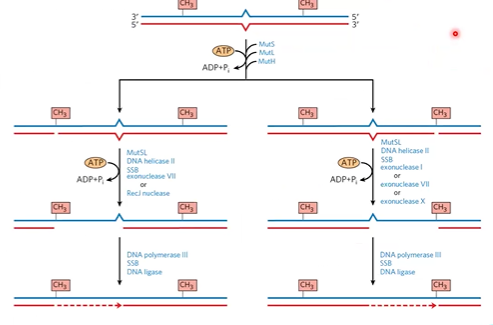
mismatch repair
follows replication fork and checks work right after replication (hemi methylated DNA)
MutL-MutS complex recognizes mismatch, binds, recruits MutH
MutH identifies methylated sites in parental DNA, binds, and uses methylation status to make ss break in new strand
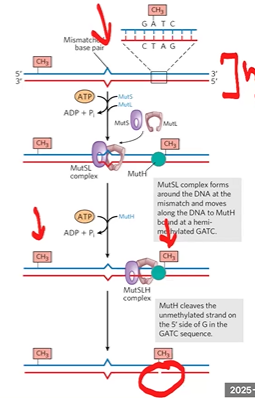
removal of mismatch
exonuclease digests from nick through mismatch
DNA pol 3 fills gap
DNA ligase seals the nick
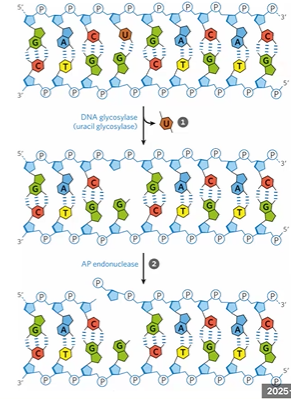
base excision repair
detects damage bases, depurination, and ss breaks
DNA glycosylase cleaves bond to AP site
AP Endonuclease repairs with single strand break
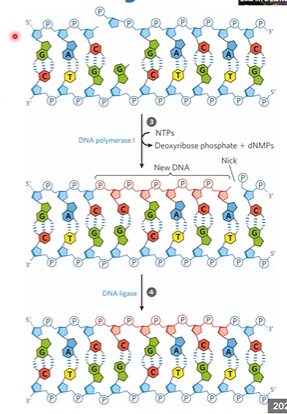
DNA pol 1 makes new DNA
DNA ligase seals it
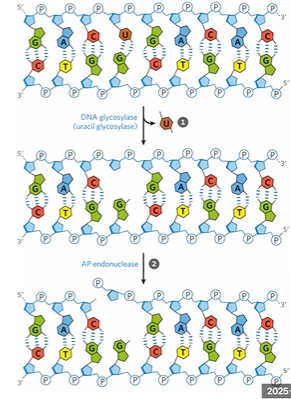
DNA glycosylase
cleaves glycosidic bond making AP abasic site
AP endonuclease
breaks PDE bond to help remove damage
DNA pol 1
has 5>3 exonuclease, high fidelity, replaces the damage
DNA ligase seals it
nucleotide excision repair
done if the entire nucleotide is problematic (causes DNA distortion)
is coupled with transcription
detection by excinuclease
helicase excises damaged DNA leaves gap
DNA pol 1 / DNA pol E fills gap
DNA ligase seals nick
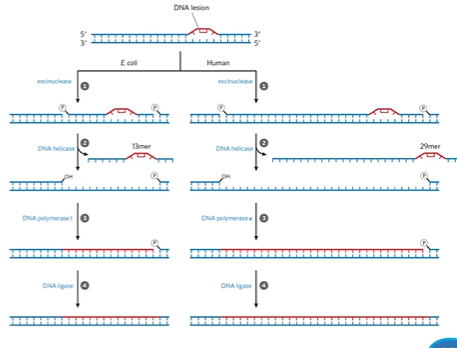
excinuclease
Hlyzes 2 PDE bonds on either side of distortion
UvrABC excinuclease prokaryotes
XP excinuclease eukaryotes, has XPA-XPG
NER helicase
prokaryotes = UvrD helicase
eukaryotes = TF2H
non-homologous end joining
predominant mechanism in G0 and G1 for ds break
error prone repair (introduces mutations)
Ku70/80 complex binds loose ends
PKcs bridges broken ends with other factors
micro-homology (sticky ends)
exonuclease removes bases
DNA pol mu and lamda add bases (error prone terminal transferases)
artemis endonuclease removes overhanging flaps
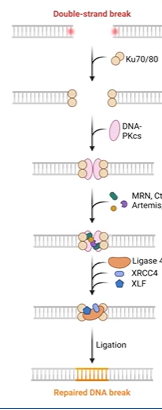
error prone terminal transferases
no template, just add random bases to repair DNA break
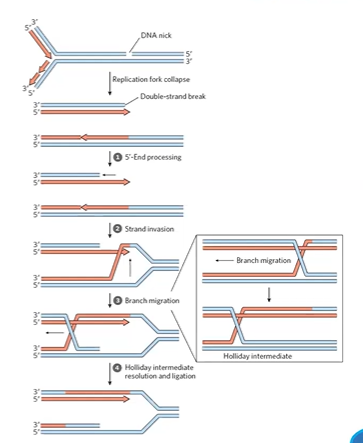
homologous recombination
no errors, repairs ds breaks, only in S or G2 phases
on broken chromosome, grab its partner and use the partner as template
BRCA genes involved
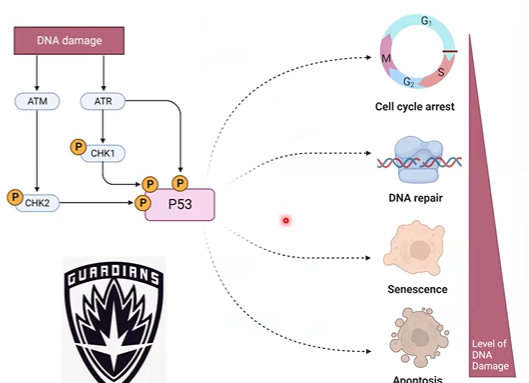
p53
activates genes involved in cell-cycle arrest, DNA repair, and apoptosis
“guardian of the genome”
kinases Plate where DNA damage, inc stability
mmr v ber v ner v nhej v hr
mmr = mismatch/small insertion. immediate. detects dna distortion, removes and remakes one strand
ber = small base damage (deam, ox, alkyl). dna glycosylase removes, ap endoN cuts backbone, DNA poly and ligase fix
ner = bulky lesions (dimers). cuts nucleotides, DNA poly and ligase fill gap
nhej = ds breaks in G1. Ku70/80 bind ends, bring near, ligase together (makes error)
hr = ds breaks in G2/S. sister chromatid is used as template