CS november mock
1/198
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
199 Terms
object-oriented programming
a programming paradigm that uses objects, that have thier own attributes and methods
objects interact with each other
processing is done by objects
Class
a blueprint for an object
defines attributes and methods that capture the charecteristics of the object
Constructor
a method which allows new objects in the class to be created, runs automatically
Abstraction
removing unecessary details that do not contribute to the overall problem
*The London underground is a good example of abstraction
Encapsulation
All data and methods of each objects are wrapped up into a single entity
Involves hiding the implementation of an object from the rest of the application
*Necessary as Client code is not meant to change values of an objects atrributes
Private vs public
*By default an objects methods and attributes are public - They can be directly accessed by the client
*a double underscore is used to indicate it's attributes and methods are private, This is an example of encapsulation - can only be accessed by methods of the object itself
Instantiation
a statement for creating an object belonging to a particuclar class
Inheritance
Inheritance is when a child class (or subclass) inherits the attributes and methods from the parent class (or superclass)
*The functionality of the child class can be changed by adding additional methods or changing pre-existing methods inherited from the parent class (This is known as overriding)
*based on a "is a" relationship
Polymorphism
redefining a class method defined in a superclass, using the same method name it is altered to behave differently through overriding
Overiding
where a method in the subclass takes precedence over the method with the same name in the base class
Class diagram
A way of representing the relationship between classes
*Hierarchal in structure - superclass at top with subclasses beneath
*inheritance is represented using arrows
*defines data type and whether they are protected, private or public
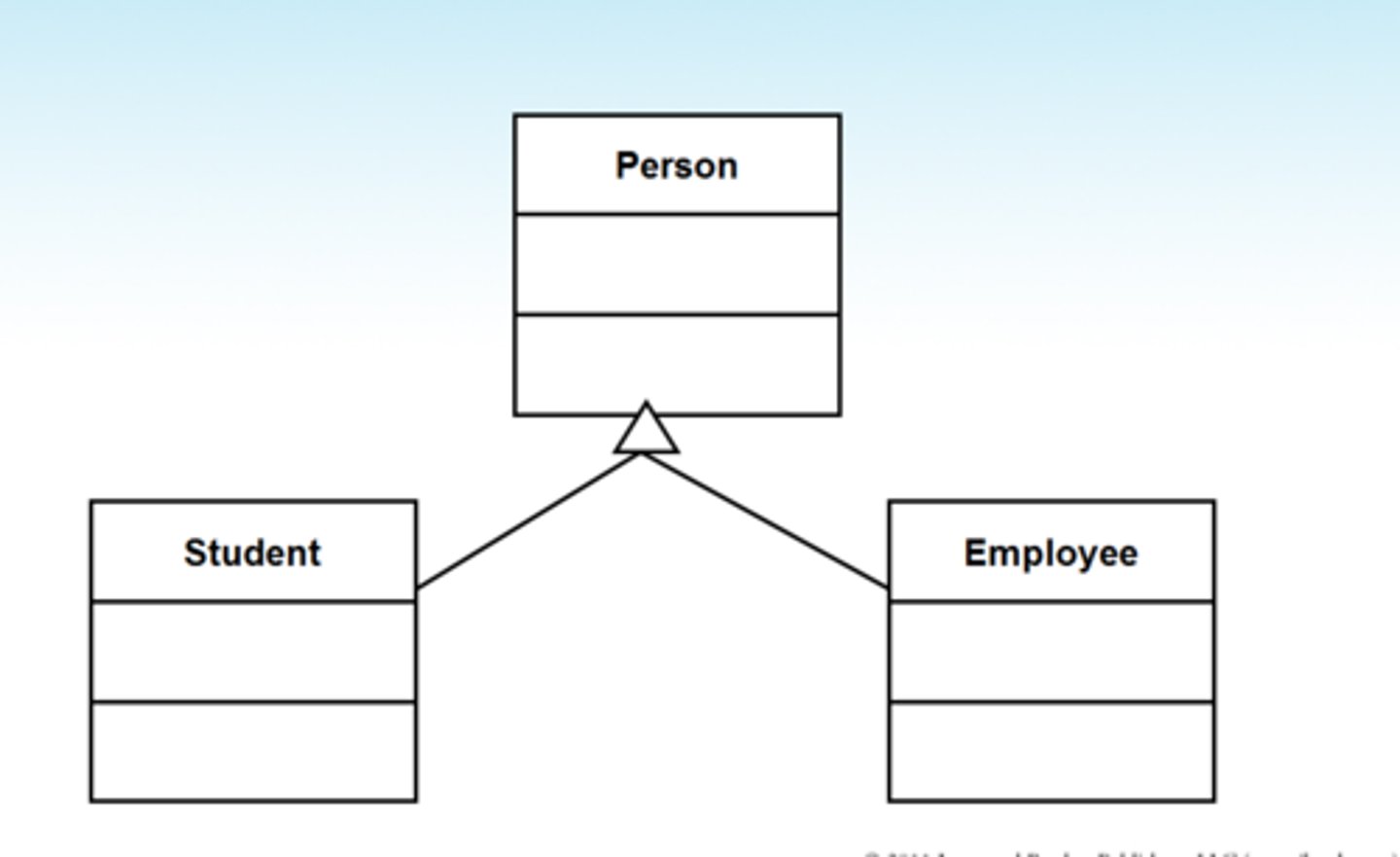
Public, Private and Protected (Class diagrams)
Public methods are represented using a "+"
- visible to all classes
private methods are represented using a "-"
- Can only be used in that class
Protected methods are represented using "#"
- can be used by subclasses of the class
Association
*Is a "has a" relationship between two classes, meaning they can be created and deleted independantly
*Is a method of creating new objects that contain existing objects, based on the way which objects are related
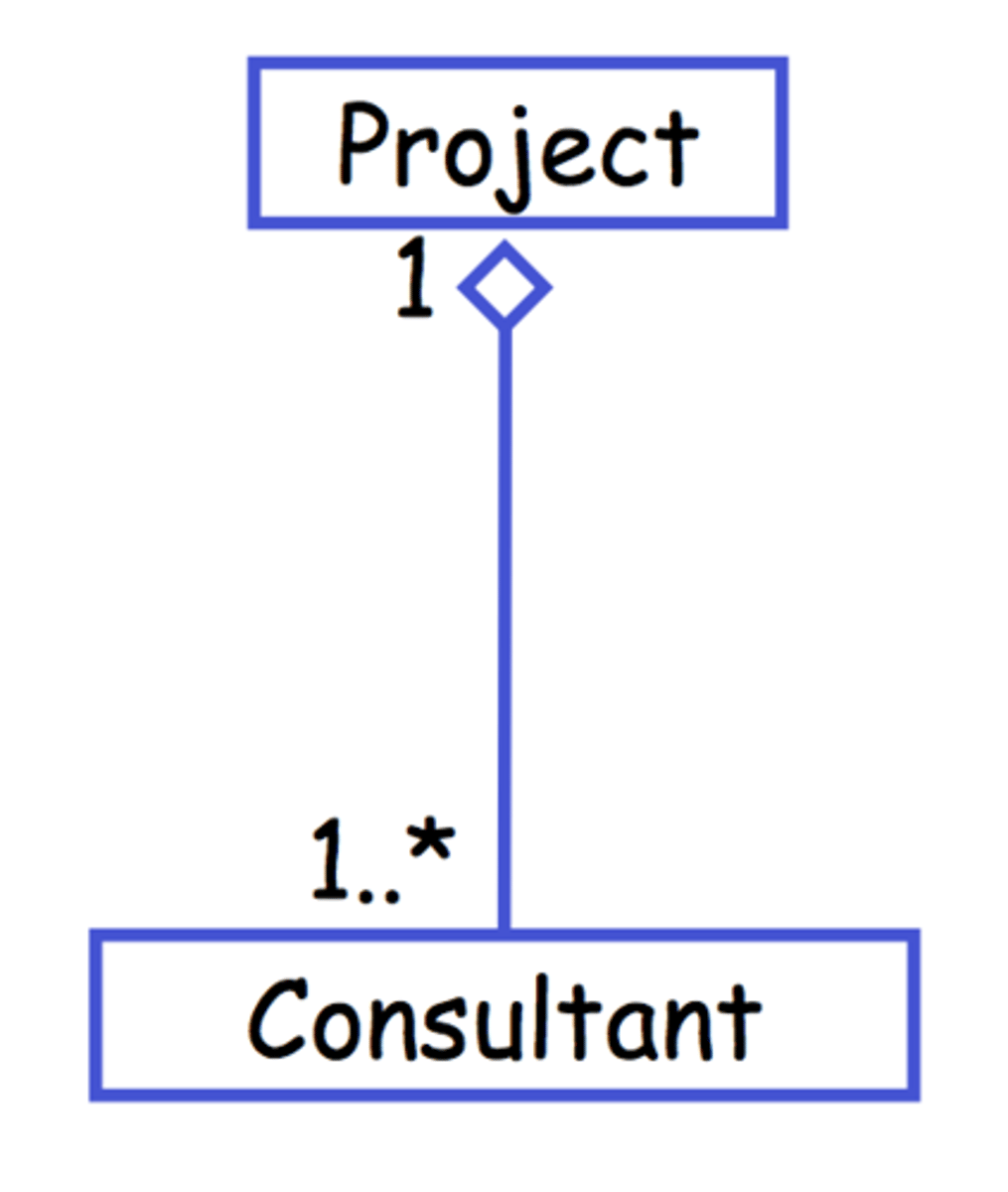
Association Composition
Creating an object that contains other objects, and will cease to exist if the containing object is destroyed
*represented by a filled in diamond

Aggregation Association
Creating an object that contains other objects, which can continue to exist even if the containing object is destroyed
*represented by a diamond that is not filled in
OOP three design principles
*Favour composition over inheritance
- Allows greater flexibility
- Composition is less rigid than inheritance relationships
*Encapsulate what varies
- if something varies it should be put into it's own class
- done in order to reduce testing and aid in maintanence
*Program to interfaces not implementation
- Focusing design on what code is doing, not how
- To solve this we can program and interface, which is a collection of abstract methods
- Remember an interface is purely a declaration of capability, there is no actual implementation of code
Adavantages of three principles
*Forces designers to go through an extensive planning, phase which makes for better designs with less weaknesses
*through Encapsulation classes can contain all the data and procedures needed
*Once an object is created, knowledge of how it's methods are implemented is necessary for programming
Recursion
Is a function that calls itself while running
Characteristics of recursion
*Stopping condition (base) must be included - means routine will not call itself when a condition is met and will "unwind"
*For input values other than the stopping condition, the routine must call itself
*The stopping condition must be reached under a finite number of calls

Recursion stack overflow
Every time a subroutine is called, the return address (the line after CALL statement) is put on the call Stack
*Even with a Stopping Condition, The recursive routine can be called a limited number of times before it will overflow the maximum memory capacity of the stack
State reasons why many programmers follow the design principle ‘favour composition over inheritance.’
If using inheritance, there can be unintended side-effects for the derived classes if a method in the base class is altered.
Composition is more flexible as if a new class is developed it can easily be used instead of the class that is currently used in the composition
Describe the relationships aggregation and composition, making it clear what the difference between the two is
Composition and aggregation are both ‘has a’ relationships - when an object contains another object
With composition if the containing object is destroyed so are the objects it contains, this is not the case with aggregation
Explain the circumstances when it would be more appropriate to use an adjacency matrix instead of an adjacency list
when the graph is more dense
when you have to change edges more often
Adding an item to a circular queue
Check if queue is not full.
Compare rear pointer with max array size.
If equal, set rear pointer = 0 (or first index).
Else, increment rear pointer by 1.
Insert new item at position of rear pointer.
Removing item from circular queue
Check if the queue is not already empty.
Compare the value of the
frontpointer with the maximum size of the array.If equal, set
frontto 1 (or the first position index if one-based).Otherwise, increment
frontby one.Return/remove the item at the old
frontposition.
Describe the extra steps with adding an item to a priority queue that isn’t required with linear
Starting with the item at the rear of the queue move each item back one place in the array;
Until you (reach the start of the queue or) find an item with the same or higher priority than the item to add;
Add the new item in the position before that item;
intractable problem
a problem that can be solved but cannot be solved in polynomial time
Two advantages of normalised representation in floating point
Maximises accuracy for a given number of bits
unique representation of each number
Two reasons why Unicode was introduced as an alternative to ASCII
To enable the representation of a greater range of characters
Improved portability of documents with Unicode
Explain how majority voting works
majority voting sends the same bit in groups of 3, so that if a corruption occurs, the receiver sees they are not all the same and assumes the one it received most copies of is the correct value for the bit
Explain what is meant by a character code
a character code is a unique number to represent each character
what is a pixel
a picture element
describe how an ADC converts analogue signals to digital
The ADC takes samples of the signal at regular intervals
The amplitude of samples are measured
Each sample is assigned a binary value
digital camera
light passes through the camera lens and is refracted
to reach a grid of light sensors which measure light intensity.
the light sensors pass through
colour filters to block out any other light such as red light
passing through a red filter will block out blue light. this is
then detected by a light sensor of that colour which
generates a voltage signal to be converted to a pixel creating
the image. this conversion is done by an ADC converting the
measurement of light intensity into binary
RFID
RFID tag is a passive device which contains circuitry and an antenna
Memory on the tag stores data. The RFID reader which is an active device
sends a signal to the RFID tag which activates it. The RFID tag sends data
by radio to the RFID reader which converts the radio wave back into binary data
Barcode scanner
The user moves the barcode scanner across the barcode which flashes a light towards the barcode.
The areas of black colour absorb the light whilst the areas of white colour reflect the light back towards the barcode scanner. Light
sensors in the barcode scanner absorb the amount of reflected light and convert it into binary.
Laser printer
A laser is shone onto the surface of the spinning disk and focussed on a spot on the spiral track. Some light is reflected back and detected by a light sensor. The amount of reflected light varies depending on whether it hits a land or a pit. Lands reflect light, while pits scatter it. The disc spins at a constant linear velocity. A transition between land and pit represents a 1, while a continuation of land or pit represents a 0.
four types of system software
utility software
translators
operating system software
library programs
Operating system software
Operating system software provides a user interface between the user and hardware and runs application programs
Utility software
Utility software is designed to help maintain the computer. Examples include disk defragmenter, virus scanner and file managers
Library programs
Library programs are collections of resources used to develop software. They include prewritten code and subroutines
define Imperative language
Instructions are executed in a programmer defined order
Imperative high level languages describe how to solve a problem
low level language
A language that is based upon the instruction set of the computer
What is an example where harvard architecture is used
digital signal processing
Explain how a SSD works
Uses NAND flash memory
data is stored using floating gate transistors
this is a type of transistor that does not lose state when power is no longer applied
cannot write individual bits
State 2 components of an SSD
NAND flash memory
Controller
Interface
Arrays
A data structure storing an ordered set of data of the same type
Boolean
Data type with two possible values (e.g., TRUE or FALSE)
Character
Data type for storing a letter, number, or special character
Data Type
Attribute determining the type of data stored in a program
Date/Time
Data type for storing date or time values
Integer
Data type for storing whole number values without decimals
Language-Defined Data Types
Primitive data types provided by a programming language
Pointer/Reference
Data type storing memory addresses of objects created at runtime
Real/Float
Data type for storing numbers with decimal or fractional parts
Records
Data structure storing related data items in fields
String
Data type for storing a sequence of alphanumeric characters or symbols
User-Defined Data Types
Custom data types designed by users for specific program needs
Assignment
Statement assigning a value to a variable consistent with its data type
Constant Declaration
Statement creating a constant in a program
Iteration
Repeating a set of statements a fixed number of times or until a condition is met
Nested Iteration
Placing iteration loops within other iteration loops
Nested Selection
Placing selection statements within other selection statements
Selection
Deciding which statements to perform based on a condition
Subroutines (Procedures/Functions)
Named code section performing a specific task in a program
Variable Declaration
Statement creating a variable defined by a name and sometimes a data type
Addition
Operator returning the sum of two numeric values
Arithmetic Operator
Operator manipulating numeric values to return a numeric result
Exponentiation
Operator raising a value to the power of another value
Integer Division
Operator dividing values to return an integer quotient
Modulo
Operator dividing values to return the remainder
Multiplication
Operator returning the product of two numeric values
Real/Float Division
Operator dividing values to return a Real/Float result
Rounding
Converts a real number to a more approximate representation by adjusting decimal places.
Subtraction
Returns the difference between two numeric values.
Truncation
Reduces the number of digits in a real number by cutting off decimals.
Relational Operators
Operators that compare values and return TRUE or FALSE.
Boolean Operators
Operators that compare boolean values and return TRUE or FALSE.
Constants
Retains the same value throughout the program run.
Variables
Used as a temporary memory container with values that can change.
Character Code
Binary representation of a character in a character set.
Concatenation
Merging two strings into a single longer string.
Length
Returns the number of characters in a string.
Position
Returns the index to locate a character in a string.
Random Number Generation
Process of generating a random number using a seed value.
Exception Handling
Dealing with exceptional events by informing users of errors.
Functions
A subroutine always returning a value, callable in an expression.
Procedures
A subroutine called by name, not required to return a value.
Parameters
Data type and characteristics passed when calling a subroutine.
Local Variables
Variables existing and usable only within a subroutine.
Global Variables
Variables declared in the main program, accessible throughout.
Stack Frames
Data collection related to an ongoing subroutine call.
Recursive Technique
A subroutine that refers to itself in its definition.
Programming Paradigms
Computation style chosen based on the problem.
Structured Programming
Programming approach based on assignment, sequence, selection, and iteration.
Aggregation
Creating an object from further objects that persist independently.
Composition
Creating an object from further objects that depend on its existence.
Encapsulation
Maintaining data integrity by restricting access to object attributes.
Inheritance
Subclasses inheriting methods and attributes from a parent class.
Instantiation
Creating an object from a class.