Chapter 11: Product, Branding, and Packaging Decisions
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Chapter 11 Notes
Mercedes billion dollar mistake:
- Garbage in garbage out
- Worn way tread and everything they modeled goofed up and they lost championship, sponsors, drivers
- Don't model on false things
Flavor Fave
- Flav's fried chicken (clinton iowa) (old long-john silver)
- Next to kfc and steal their identity (white and red)
- so many kids couldn't afford child support so had a bunch of businesses
- flavor love (love island)
Sonic Branding:
- Little jingles, bleeps, tactics, everything that make it easy to buy and remember brands and spend more money
- like the little noise it makes when you tap your card
Brand loyalty
- younger is better
- people more loyal to retailers
- convenience is huge
Uncrustable / Trader Joe's:
- trader joes is copying uncrustable and being sued for it
Types of Consumer Products
- Specialty
- Shopping
- Convenience
- Unsought
Consumer products:
- products and services used by people for their personal use.
- Marketers further classify these products by the way they are used and how they are purchased.
Specialty
- products/services for which customers express such a strong preference that they will expend considerable effort to search for the best suppliers.
Shopping
- products or services for which consumers will spend a fair amount of time comparing alternatives such as furniture, apparel, fragrances, appliances, and travel.
Convenience
- products or services for which the consumer is not willing to expend any effort to evaluate prior to purchase.
Unsought
- products or services that consumers either do not normally think of buying or do not know about.
Specialty Consumer products
- products/services for which customers express such a strong preference that they will expend considerable effort to search for the best suppliers.
Shopping Consumer products
- products or services for which consumers will spend a fair amount of time comparing alternatives such as furniture, apparel, fragrances, appliances, and travel.
Convenience Consumer products
- products or services for which the consumer is not willing to expend any effort to evaluate prior to purchase.
Unsought Consumer products
- products or services that consumers either do not normally think of buying or do not know about.
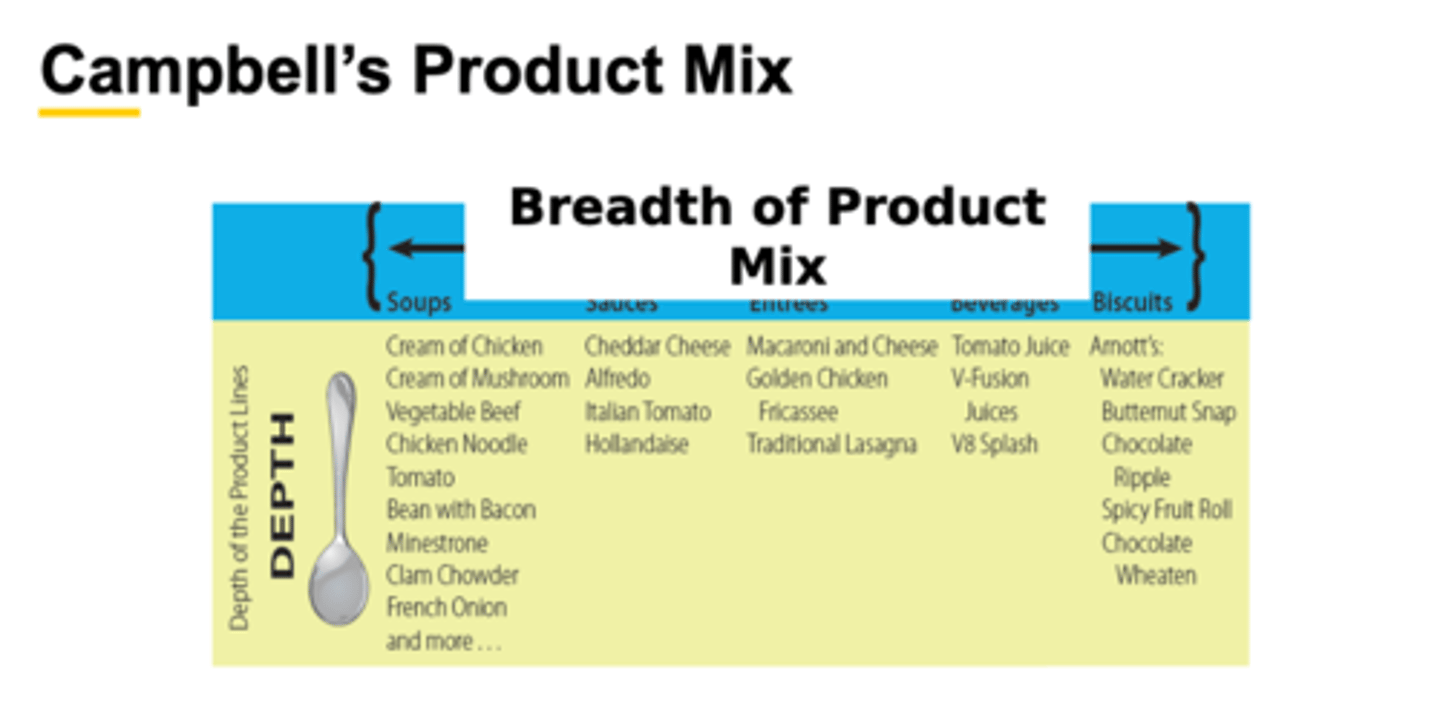
Breadth of Product Mix
- the number of different product lines a company offers
- A product line is a group of closely related products that either function in a similar manner, are sold to the same customer groups, or are marketed through the same outlets.
Example:
- Campbell Product Lines: Soups, Sauces Frozen Entrees, Beverages, Biscuits
Campbell's Product Mix
1. All of Campbell's products constitute its product mix. Each product in the product mix may require a separate marketing strategy.
2. In some cases, product lines and mixes share some marketing strategy components.
3. Advertising economies:
-product lines provide economies of scale in advertising.
4. Package uniformity:
- packages in the product line may have a common look but maintain their individual identities.
5. Standardized components:
- reductions in manufacturing and inventory costs.
6. Efficient sales and distribution:
- a product line enables a full range of choices to customers, and as a result, better distribution and retail coverage.
7. Equivalent quality:
- all products in a line are perceived as having similar quality.
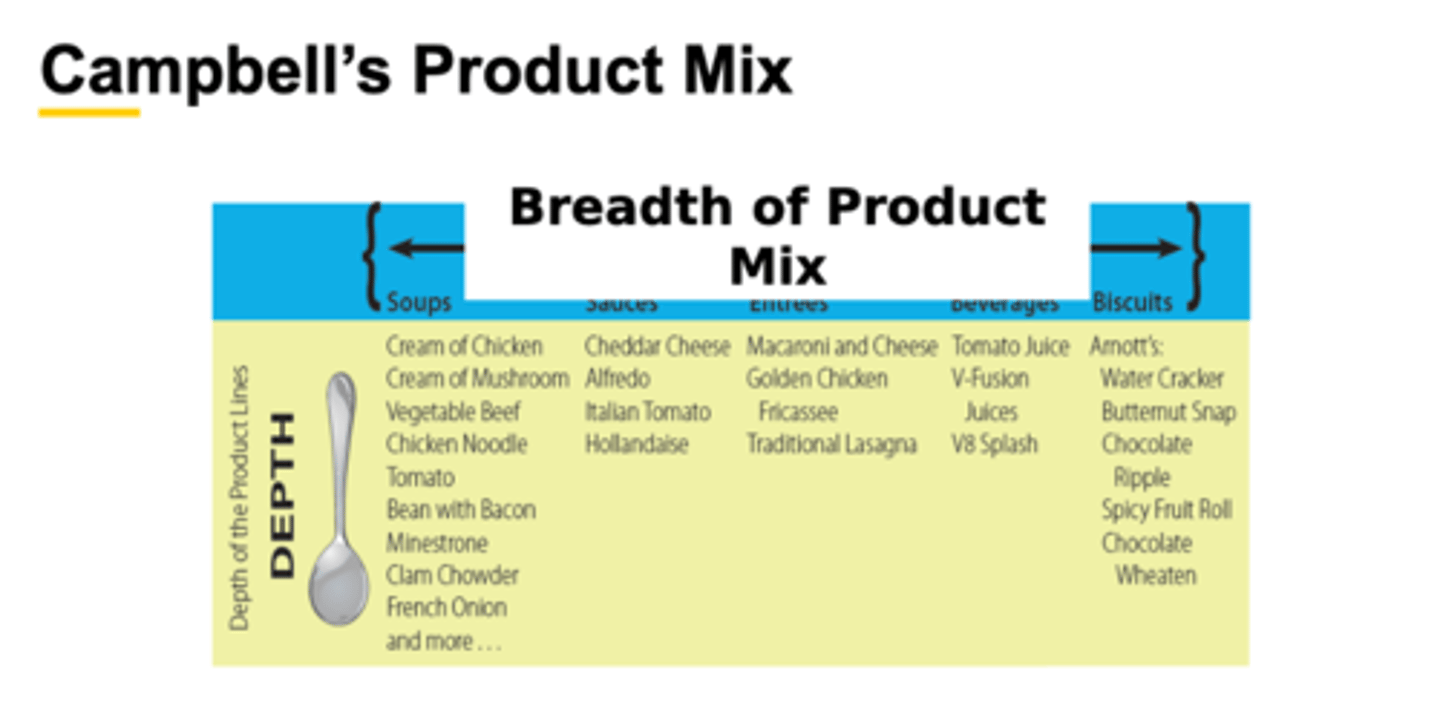
Depth of Product Mix
- the number of variations or options available within a single product line. These variations can be based on features such as size, flavor, color, or model
Example:
- Soup: Cream of Chicken, Tomato, French Onion, etc.
- Sauce: cheddar cheese, alfredo, Hollandaise, etc.
Campbell's Product Mix
1. All of Campbell's products constitute its product mix. Each product in the product mix may require a separate marketing strategy.
2. In some cases, product lines and mixes share some marketing strategy components.
3. Advertising economies:
-product lines provide economies of scale in advertising.
4. Package uniformity:
- packages in the product line may have a common look but maintain their individual identities.
5. Standardized components:
- reductions in manufacturing and inventory costs.
6. Efficient sales and distribution:
- a product line enables a full range of choices to customers, and as a result, better distribution and retail coverage.
7. Equivalent quality:
- all products in a line are perceived as having similar quality.
Branding
"A brand is the set of expectations, memories, stories and relationships that, taken together, account for a consumer's decision to choose one product or service over another." - Seth Godinin
- Firms institute a variety of brand-related strategies to create and manage key brand assets. The decisions surrounding these strategies are mentioned on this slide.
Branding:
- Increases awareness and provides a way to differentiate from competitors
Value of Branding for the Customer and the Firm:
- Facilitate Purchases
- Establish Loyalty
- Protect from competition price competition
- Assets
- Affect market value
Branding Strategies:
- Whether to use manufacturer brands or retailer/store brands.
- How to name brands and product lines.
- Whether or not to extend the brand name to other products and markets.
- Should the brand name be used with another firm or licensed to another firm?
- Whether or not the brand should be repositioned.
Branding Strategies:
- Whether to use manufacturer brands or retailer/store brands.
- How to name brands and product lines.
- Whether or not to extend the brand name to other products and markets.
- Should the brand name be used with another firm or licensed to another firm?
- Whether or not the brand should be repositioned.
Value of Branding for the Customer and the Firm:
- Facilitate Purchases
- Establish Loyalty
- Protect from competition price competition
- Assets
- Affect market value
Dimensions of Brands
What Makes a Brand:
- Brand Name
- URLs
- Logos and Symbols
- Characters
- Slogans
- Jingles or Sounds
Brand Name
- The spoken component of branding, it can describe the product or service characteristics and/or be composed of words invented or derived from colloquial or contemporary language.
- Examples include Comfort Inn (suggests product characteristics), Apple (no association with the product), or Zillow.com (invented term).
URLs
- Locations of pages on the Internet, which often substitute for the firm's name, such as Toyota ( www.toyota.com)
Logos and Symbols
- Visual branding elements that stand for corporate names or trademarks. Symbols are logos without words.
- Examples include the McDonald's arches.
Characters
- Brand symbols that could be human, animal, or animated.
- Examples include Tony the Tiger, the Energizer Bunny, and Rice Krispies' Snap, Crackle, and Pop.
Slogans
- Short phrases used to describe the brand or persuade consumers about some characteristics of the brand.
- Examples include State Farm's "Like A Good Neighbor" and Dunkin's "America Runs on Dunkin'."
Jingles or Sounds
- Audio messages about the brand that are composed of words or distinctive music.
- An example is Intel's four-note sound signature that accompanies the Intel Inside slogan.
Sonic Branding:
- Little jingles, bleeps, tactics, everything that make it easy to buy and remember brands and spend more money
- like the little noise it makes when you tap your card
Sonic Branding:
- Little jingles, bleeps, tactics, everything that make it easy to buy and remember brands and spend more money
- like the little noise it makes when you tap your card
Brand Name
- The spoken component of branding, it can describe the product or service characteristics and/or be composed of words invented or derived from colloquial or contemporary language.
- Examples include Comfort Inn (suggests product characteristics), Apple (no association with the product), or Zillow.com (invented term).
URLs
- Locations of pages on the Internet, which often substitute for the firm's name, such as Toyota ( www.toyota.com)
Logos and Symbols
- Visual branding elements that stand for corporate names or trademarks. Symbols are logos without words.
- Examples include the McDonald's arches.
Characters
- Brand symbols that could be human, animal, or animated.
- Examples include Tony the Tiger, the Energizer Bunny, and Rice Krispies' Snap, Crackle, and Pop.
Slogans
- Short phrases used to describe the brand or persuade consumers about some characteristics of the brand.
- Examples include State Farm's "Like A Good Neighbor" and Dunkin's "America Runs on Dunkin'."
Jingles or Sounds
- Audio messages about the brand that are composed of words or distinctive music.
- An example is Intel's four-note sound signature that accompanies the Intel Inside slogan.
Private Label Brands / Retail Store Brand
- Brand developed and marketed by a retailer and available only from the retailer.
- Unlike Europe, where store brands such as Tesco (U.K. grocery chain) were extremely popular, in the United States, few store brands had achieved such status and were often considered inferior to manufacturer or national brands.
- Today, many store brands are well established, such as Kirkland, Charter Club, and Trader Joe's store brand.
Manufacturer or National Brands:
- Kraft, Nike, Coca-Cola
Retailer/Store brands (Private Label brands):
- Kroger, Costco, Trader Joe's
Brand extension:
- Same brand name in different product line.
- When a company uses the same brand name for a new product in a different product line (e.g., Ferrari apparel),
Example:
- Ferrari has licensed its brand name to manufacturer-related apparel that appeals to those who can't afford the automobile.
Line Extension
- Same brand name within the same product line.
Example:
- Ferrari has licensed its brand name to manufacturer-related apparel that appeals to those who can't afford the automobile.
Co-branding
- Marketing two or more brands together.
- Can enhance perceptions of quality through links between brands.
Example:
- Yum! Brands combines two or more of its restaurant chains (A&W, KFC, Long John Silver's, Pizza Hunt, and Taco Bell) into one store space.
Brand Licensing
- A contractual arrangement between firms, whereby one firm allows another to use its brand name, logo, symbols, or characters in exchange for a negotiated fee.
- common for toys, apparel, and entertainment products
Example:
- The NBA team, the New Orleans Pelicans (licensor), provides the right to use its brand to apparel manufacturers (licensee) in return for royalty payments.
Brand Repositioning
- refers to a strategy in which marketers change a brand's focus to target new markets or realign the brand's core emphasis with changing market preferences.
- Change a brand's focus.
- Can improve the brand's fit with its target segment.
- Can boost the vitality of old brands.
- Not without costs and risks.
Example:
- Adding Value 11.2 An Abbreviation No More: Weight Watchers Rebrands as Simply WW highlights the rebranding efforts of Weight Watchers, including a name change that shortened the firm's official moniker to simply WW.
Primary vs. Secondary Packaging
- Although often overlooked as a marketing tool, packaging helps determine the success of a product.
- In some instances, such as Coca-Cola or Aunt Jemima Maple Syrup, the package has become synonymous with the brand.
Packaging:
- An important brand element that has more tangible or physical benefits than other brand elements have.
- Primary vs. Secondary package
- What packaging do you as a consumer find useful?
- Packages come in different types and offer a variety of benefits to consumers, manufacturers, and retailers.
The primary package:
- is the package the consumer uses, such as the toothpaste tube.
- From the primary package, consumers typically seek convenience in terms of storage, use, and consumption.
The secondary package:
- is the wrapper or exterior carton that contains the primary package and provides the UPC label used by retail scanners.
- Consumers can use the secondary package to find additional product information that may not be available on the primary package.
Key Roles of Packaging:
- Attracts the consumers' attention.
- Enables products to stand out from their competitors.
- Allows the same product to appeal to different markets with different sizes.
- A recent development is sustainable packaging.