Chapter 13: Blood, Heart, and Circulation
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
what is the circulatory system
organ system that transports molecules and other substances rapidly over long distances, between cells, tissues, and organs
what are the divisions of the cardiovascular system
cardiovascular and lymphatic
what is in the cardiovascular system
heart, vessels/vascular system, blood
heart (cardiovascular system)
pump of variable rate and strength
vessels/vascular system (cardiovascular system)
pipes of variblae diameter
interconnected system
blood (cardiovascular system)
fluid (connective tissue) of variable volume and viscosity
contains water, solutes, and cells
averages 5.5L
what is a hematocrit
a rapid assessment of blood composition. it is the percent of blood volume that is composed of red blood cells (RBCs or erythrocytes)
what is hemaglobin
in RBCs carries O2 to tissues and CO2 away from tissues
what is plasma
the fluid portion of blood, includes water, ions, proteins, nutrients, gasses, hormones, wastes, etc.
what are white blood cells
(WBCs or leukocytes) for immunity
what are platelets
cell fragments for clotting
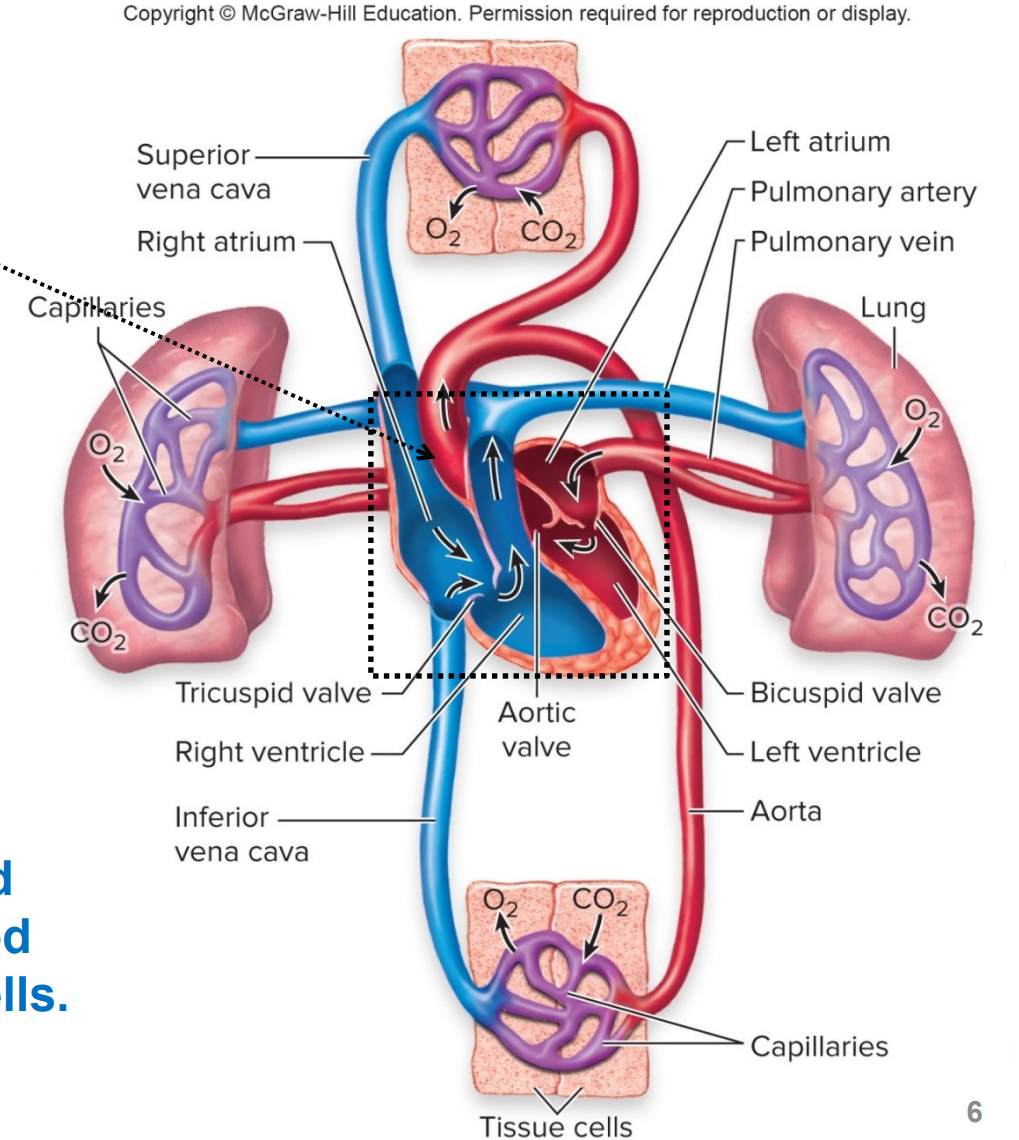
what does the red color indicate
blood is fully oxygenated due to its passing through the lungs
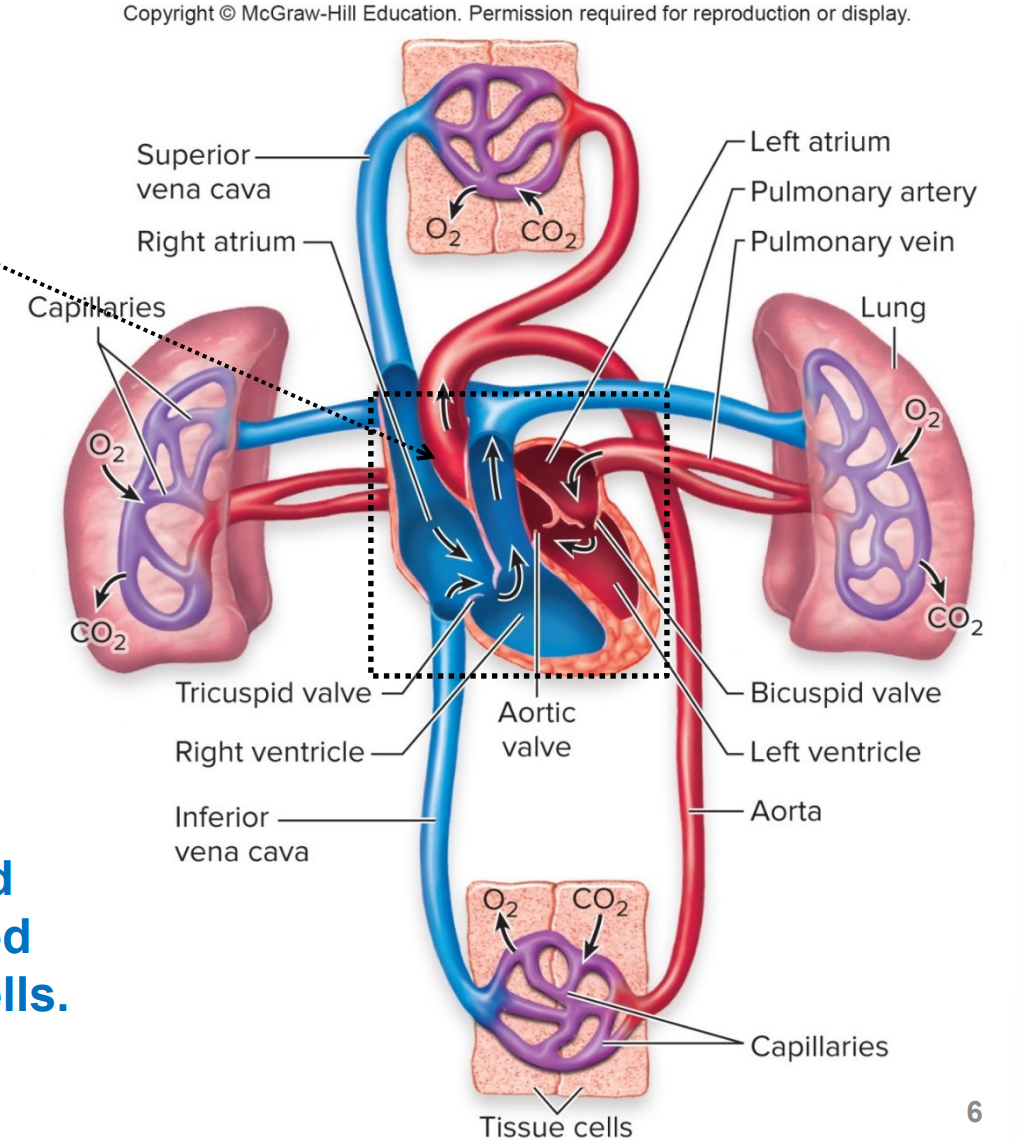
what does the blue color indicate
blood is partially oxygenated due to delivery of O2 to cells
what is the heart
it is a muscular pump that propels the blood thorugh the pulmonary (lung) circulation and systemic (other organs and tissues) circulation
what muscular organs does the heart contain
cardiac muscle and endothelial cells
what is myocardium
muscular tissue of heart
each cardiac muscle BLANK with a heart beat
contracts
what does pumping action of heart due to muscle contraction do
creates pressure to move blood quickly throughout the body
what are the right and left sides of the heart separated by
the septum
what is a ventricle
lower chamber of the heart, pumps blood into arteries
where does the right ventricle pump blood to
the lungs (via pulmonary arteries), pulmonary circulation
where does the left ventricle pump oxygenated blood to
the other tissues (via aorta), systemic circulation
what separates the two ventricles
the interventricular septum
what is the atrium
upper chamber of the heart, receives venous blood returning to heart
where does the right atrium receive blood from
the systemic circulation (via vena cava)
where does the left atrium recieve blood from
the pulmonary circulation (via pulmonary veins)
what are the atrium and ventricle separated by
connective tissue, fibrous skeleton
what is pulmonary circulation
circuit thorugh which partially oxygenated blood travels from the right ventricle of the heart via the pulmonary arteries to the lungs
there, the blood picks up O2 from inspiration and releases CO2 for expiration
this oxygenated blood travels back to the left atrium of the heart and enters via the pulmonary veins
what is systemic circulation
circuit thoruhg which oxygenated blood travels from the left ventricle of the heart via the aorta thorugh the organ systems.
there, the blood delivers O2 from inspiration and picks up CO2 for expiration
this partially oxygenated blood travels back to the right atrium o f the heart and enters via the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava
what is the atrioventricular valve between
atria and ventricles
what is the tricuspid valve (3 flaps; AV valve)
between right atrium and right ventricle
bicuspid (mitral) valve (2 flaps; AV valve)
between left atrium and left ventricle
how does the AV valve open and close
due to pressure difference across it, i.e. pressure can push a valve open or force it closed
what are papillary muscles (AV valve)
limit valve movement to prevent backflow of blood into atria
what are the two semilunar valves
pulmonary and aortic valves
pulmonary valve (SL valve)
between right ventricle and pulmonary trunk (right and left pulmonary arteries)
aortic valve (SL valve)
between left ventricle and aorta
what is diastole and systole
alternating contractings and relaxtions of atria and ventricles (apprx. 0.8s)
what is systole
period of ventricular contration and blood ejection, approx 0.3s
what is diastole
period of ventricular relaxation and blood filling, approx 0.5s
what is pressure
force exerted by blood (due to heart contraction) (mm Hg)
what is blood flow
is from region of higher pressure to region of lower pressure (volume/unit time such as L/min)
what are the two heart sounds heard through
a stethoscope
what is the first heart sound you hear when using a stethoscope
soft, low-pitched “LUB”
AV valve closure, at onset of systole
what is the second heart sound you hear when using a stethoscope
louder “DUB”
SL valve closure, at onset of diastole
Order of cardiac cycle: systole (1/5)
isovolumetric contraction: pressure in ventricles increases as ventricles begin contraction, causing AV valves to close (lub)
Order of cardiac cycle: systole (2/5)
ejection of blood into aorta and pulmonary trunk occurs when ventricular pressure (120 mmHg, systolic BP) exceeds aortic pressure so that SL valves open
amount of blood ejected is the stroke volume; around 2/3 of the blood in the ventricles
Order of cardiac cycle: diastole (3/5)
isovolumetric relaxation: pressure in ventricles decreases, causing SL valves to close (dub)
aortic pressure is 80 mmHg (diastolic BP)
Order of cardiac cycle: diastole (4/5)
when pressire in ventricles falls below atrial pressure, AV valves open and there is rapid filling of the ventricles (blood in atria → ventricles)
Order of cardiac cycle: diastole (5/5)
atrial contraction delivers final amount of blood into ventricles just prior to #1 occuring again
volume of blood in ventricles at end of diastole is the end-diastolic volume (EDV)
what can the cardiac cycle be measured by
using an ECG to measure systolic and diastolic arterial BP
where does pressure and volume change during the cardiac cycle
in the left ventricle
similar changes occur in the right ventricle, but the pressures are lower
what does depolarizarion in the sinoatrial (SA) node do
initiates APs that spread to the rest of the cardiac cells, leading to contraction
what are some functions of the SA node
small group of cardiac muscles in right atrium of heart
hearts pacemaker
cells depolarize spontaneously and quickly
excitation causes contraction
APs spread through cells of atria via gap junctions, electrical synapses
what does the atrioventricular (AV) node do
carries APs from right atrium
how do APs travel to ventricles
bundle of His
slow conduction in AV node, so ventricular contraction occurs after atrial contraction has ended
what does an ECG/EKG do
detects electrical activity in the heart via electrodes on the surface of the skin
what do electrodes record (ECG/EKG)
current conducted through fluid around heart, caused by simultaneous APs in myocardial cells
what are the 3 distince ECG/EKG waves
P, QRS, and T
what is the P wave
results from the spread of atrial depolarization
what is the QRS wave
results from the spread of depolzarization into the ventricles
what is the T wave
results from repolarization of the ventricles
what is the structure of blood vessels
connective tissue, smooth muscle, and epithelial tissues
capillaries only have epithelial
what do blood vessels do
distribute blood to tissues, regulate BP
what is a closed loop (blood vessels)
blood pumped from the heard in arteries returns to the heart in veins
what do ateries branch into
arterioles, vessels between arteries and capillaries
what are capillaries
smallest blood vessels; there is exchange of substances between cells and vessels, such as nutrients and waste
what do capillaries merge to form
venule, vessles between capillaries and veins
what do venules merge into
veins
what are arteries
have strong, thick elastic walls that resist flow
high pressure/low volume
what are veins
have weaker walls and a wider lumen and fill more easily
low pressure/high volume
act as volume reserves (54% of total volume)
what are aterioles
have the greates pressure drop
what do arterioles vessels serve as
controllers of flow into capillary beds
what does vasoconstriction of arterioles cause
(contraction of their smooth muscle layer to decrease diameter) decreases blood flow
what does vasodilation of aterioles cause
(relaxation of smooth muscle layer to increase diameter) increases blood flow
what do capillaries mediate the exchange of
substances with ISF
where are capillaries located
in every tissue except cornea
what kind of layer do capillaries have
single layer of epithelium which allows rapid exchange of substances
gas exchange (O2, CO2)
nutrient and waste exchange
cell secretions
what do veins have
greatest total blood volume and can expand with greater blood volume
what kind of pressure do veins have
low pressure, but blood flows back to the heart due to the skeletal muscle pump (skeletal muscle contraction), and the direction of flow is one-way due to venous valves in peripheral veins
what happens when muscles contract in veins
they are partially compressed → diameter reduction, venous pressure increase and increased volume of blood returning to the heart
what is coronary artery disease (CAD)
insifficient blood flow (ischemia) due to change in coronary arteries (arteries that nourish heart)
what can coronary artery disease cause
heart attack (myocardial infarcation (aka MI))
what is the primary cause of coronary artery disease
atherosclerosis in coronary arteries, which is thickeing of arterial wall with plaques that include cholesterol and fat deposits
what are some risk factors of coronary artery disease
HTN, stress, smoking, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, diabetes, high cholesterol
what what the lymphatic system transport
excess ISF that filtered out of blood vessels back to the blood
fat absorbed from the small intestine into the blood
what do lymphocytes defend against (lymphatic system)
disease-causing agents
what do lymph nodes do
filter lymph to remove pathogens before the fluid is returned to the blood