4.5 Linear Momentum & Conservation
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
If an object with mass is in motion what does it have?
Linear momentum:
Linear momentum of object remains _______ unless system is _____ upon by _______ _____ force
Momentum equation :
Momentum is _____ quantity: _______ and _______
Initial direction of motion is usually assigned the ______ direction
Object with mass is in motion so has velocity, and momentum
Linear momentum is momentum of object is moving in only one dimension
Linear momentum of object remains constant unless system is acted upon by external resultant force
Momentum equation : mass x velocity p =mv
Momentum is vector quantity: magnitude and direction
Initial direction of motion is usually assigned the positive direction
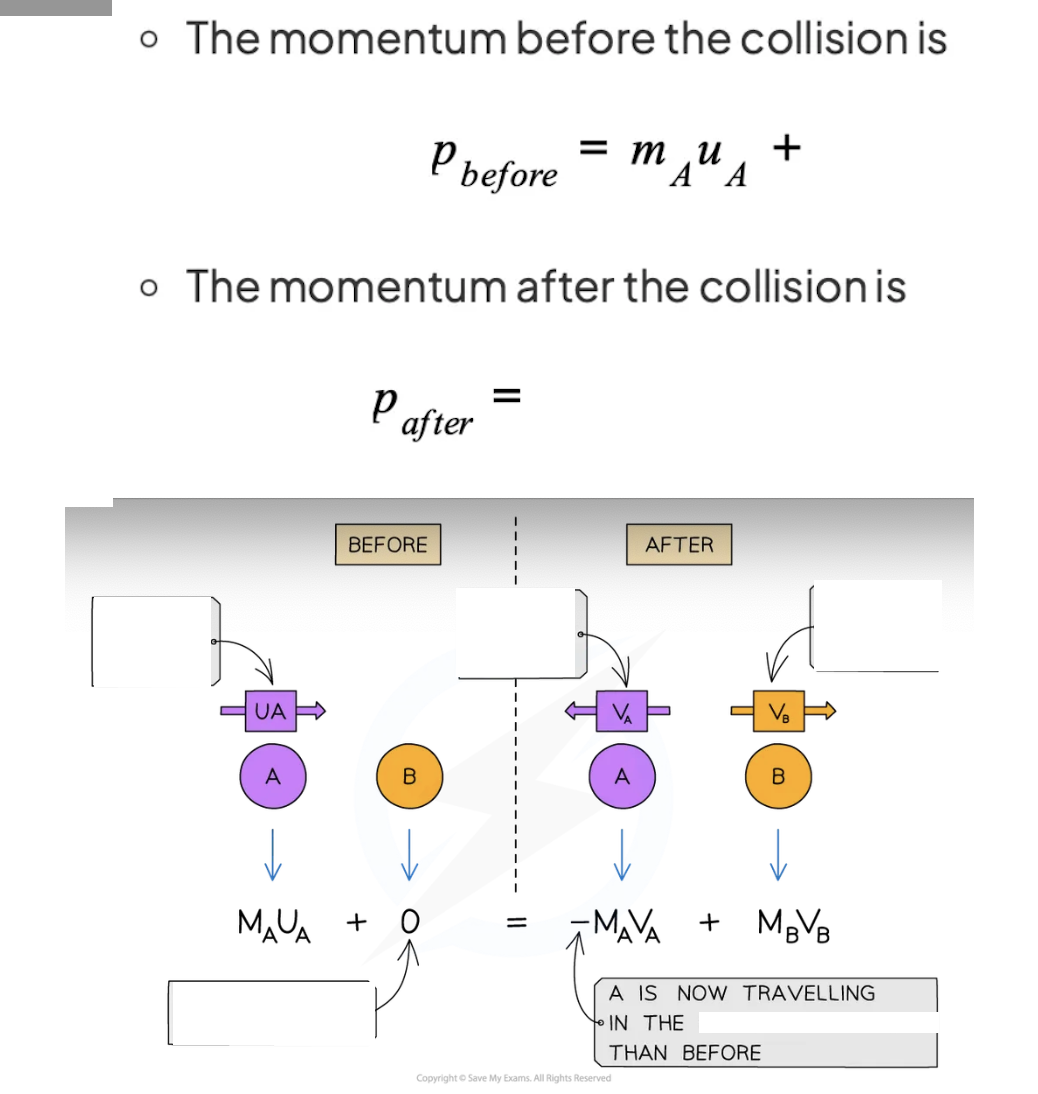
Principle of conservation of linear momentum states:
momentum _______ = momentum ______
Momentum is a vector quantity: opposing vectors…
Object collides with another object and ______, has a _________ velocity before the collision and a ________ velocity after
Principle of conservation of linear momentum states:The total momentum before a collision is equal to the total momentum after a collision, provided no external force acts
momentum before = momentum after
Momentum is a vector quantity: opposing vectors cancel each other out, resulting in a net momentum of zero
Object collides with another object and rebounds, has a positive velocity before the collision and a negative velocity after
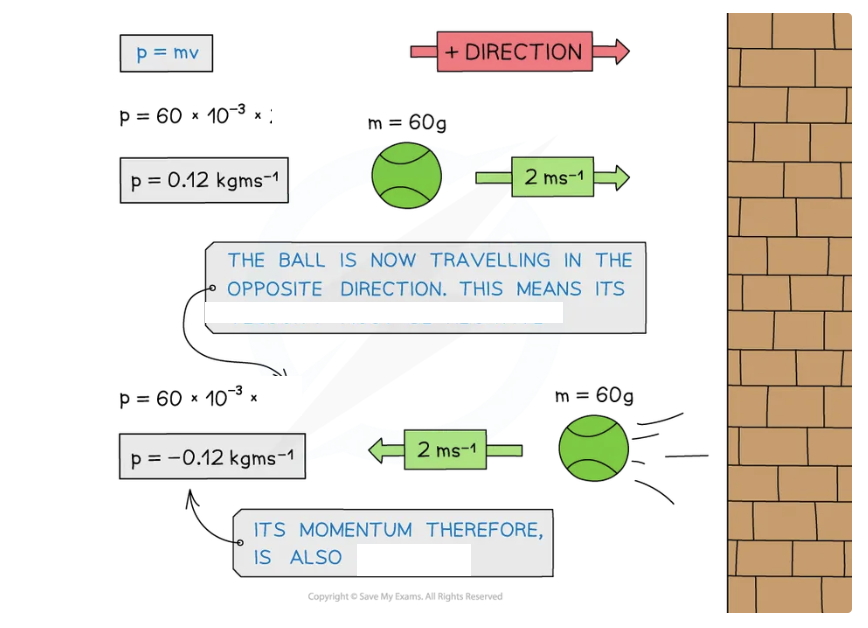
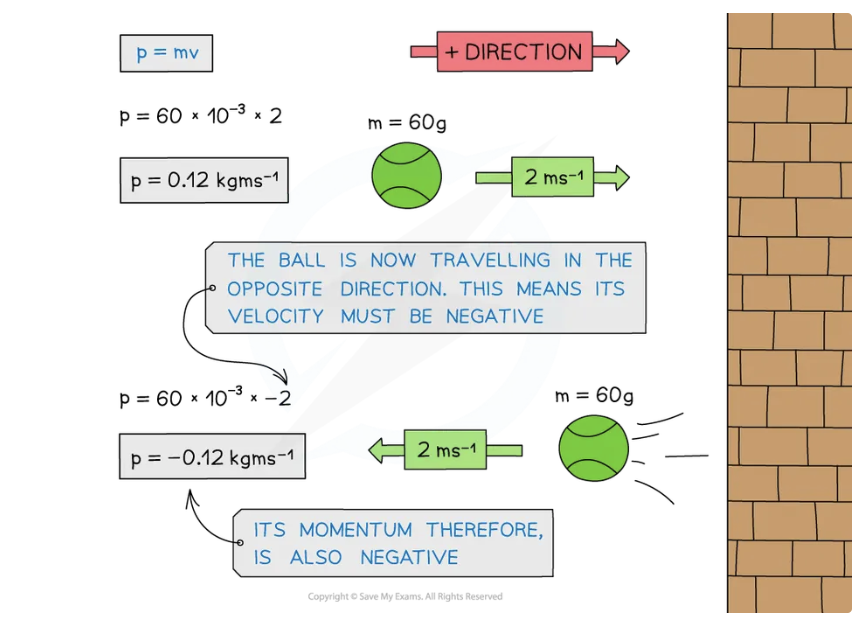
Momentum, just like energy, is _____ ______: Ball A moves with an _____ velocity of, Ball A collides with Ball B which is stationary, After the collision, both balls travel in _____ directions
Direction of initial motion Ball A as the _______ direction (to the right)
Minus sign shows Ball A travels in the ______ direction to the _____ travel
Object stationary like Ball B is before the collision has momentum of and now has a ____ velocity
Momentum, just like energy, is always conserved: Ball A moves with an initial velocity of, Ball A collides with Ball B which is stationary, After the collision, both balls travel in opposite directions
Direction of initial motion Ball A as the positive direction (to the right)
Minus sign shows Ball A travels in the opposite direction to the initial travel
Object stationary like Ball B is before the collision has momentum of 0 and now has a final velocity
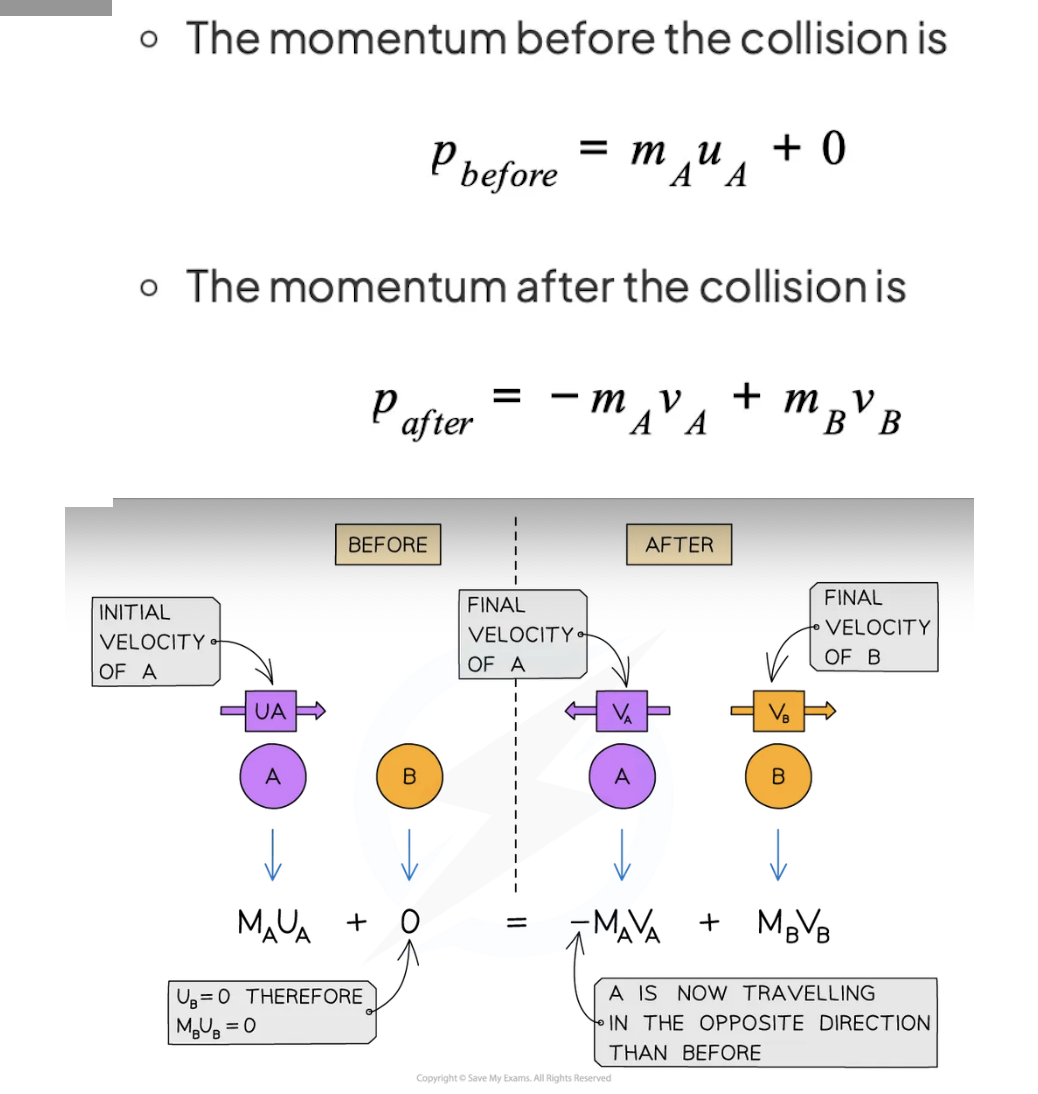
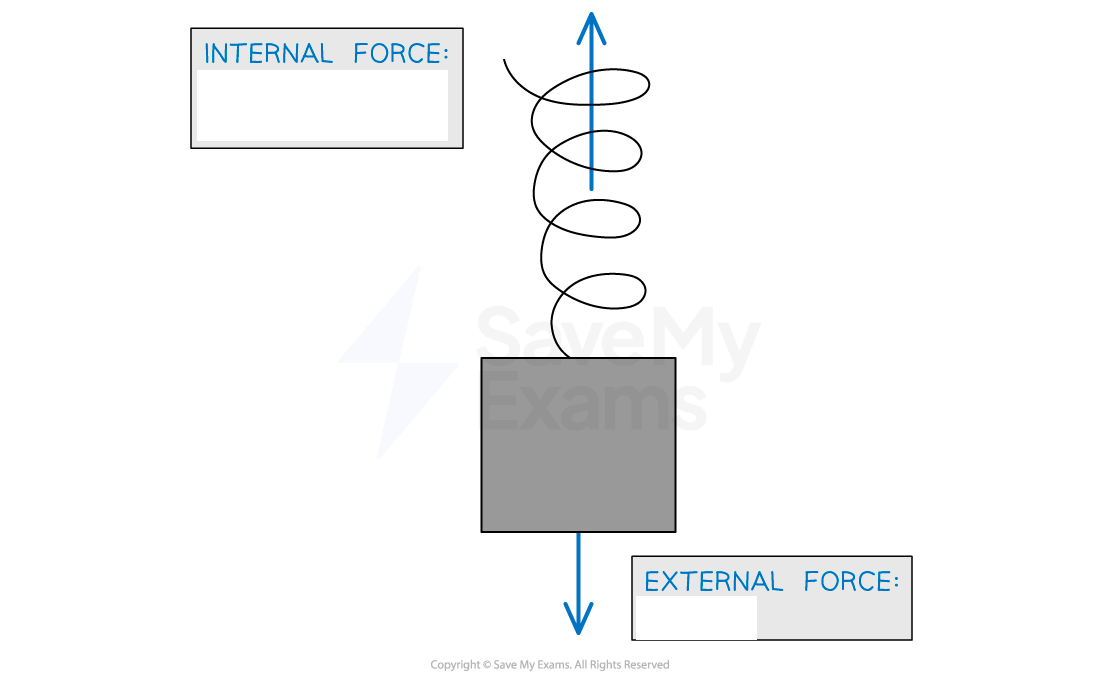
External forces:
internal forces:
Forces internal or external depend on _____ ______
Systems with no external forces is ‘_____’ or ‘______’
External forces: forces act on structure from outside e.g. friction and weight
Internal forces: forces exchanged by particles in system e.g. tension in string
Forces internal or external depend on system itself
Systems with no external forces is ‘closed’ or ‘isolated’
Swimmer diving from a boat: Diver will move forwards, and, to ______ momentum, the boat will move ______ because the momentum beforehand was _____ and no ______ forces were present to ______ the _____ of the diver or the boat
Swimmer diving from a boat: Diver will move forwards, and, to conserve momentum, the boat will move backwards because the momentum beforehand was zero and no external forces were present to affect the motion of the diver or the boat
Force: ___ of _______ of momentum on a body
Change in momentum:
Equations:
Force and momentum ______ quantities ______ and _____
Resultant force: Force equal to ….
_______ direction is the direction of initial motion:
Force on an object will be negative if the force ________ its initial velocity:
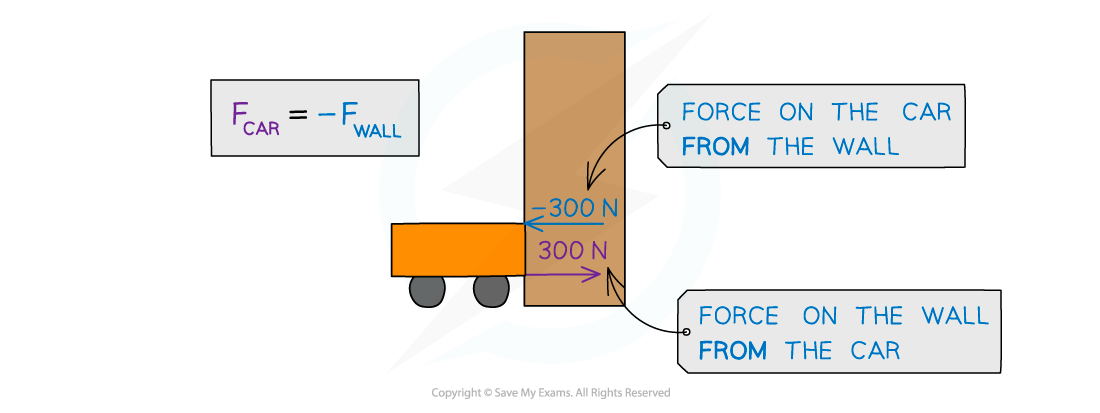
________ force exerted by object it has collided with and the forces will be of ______ _______ and ________ in ________, Newton's Third _____
Force: rate of change of momentum on a body
Change in momentum: final momentum - initial momentum
Equations: F = ∆p/∆t. ∆p = pfinal - pbefore
Force and momentum vector quantities magnitude and direction
Resultant force: Force equal to rate of change of momentum
Positive direction is the direction of initial motion:
Force on an object will be negative if the force opposes its initial velocity:
Opposing force exerted by object it has collided with and the forces will be of equal magnitude and opposite in direction, Newton's Third Law
Impulse and an example:
Impulse equation
Why is hard to measure magnitude of impulse force?
impulse: External resultant force acts on object for very short time and changes the object's motion.Example: Kicking a ball, Catching a ball, collision between two objects
Impulse product of force applied and the time for which it acts:
impulse = F ∆t
Force acting for short time, very difficult to directly measure magnitude of force/time for which it acts so is measured indirectly
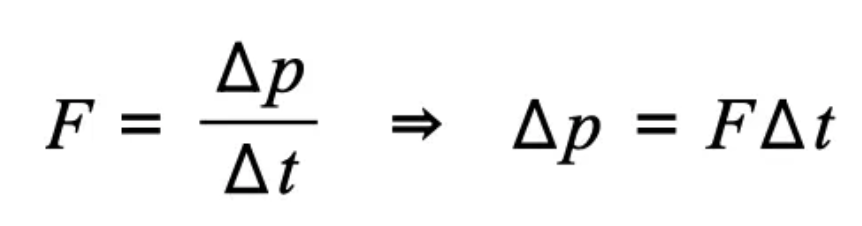
Newtons' second law (momentum):
Change in momentum is equal to ______
How do you measure impulse?
Impulse ______ quantity with both a ______ and ________
Impulse is always in ________ of the _______ force
Small force acting over a _______ time has same effect as large force acting over a ______ time
Newtons' second law (momentum): The resultant force on an object is equal to its rate of change of momentum
Change in momentum is equal to impulse
change in momentum can be used to measure impulse indirectly
Impulse vector quantity with both a magnitude and direction
Impulse is always in direction of the resultant force
Small force acting over a long time has same effect as large force acting over a short time
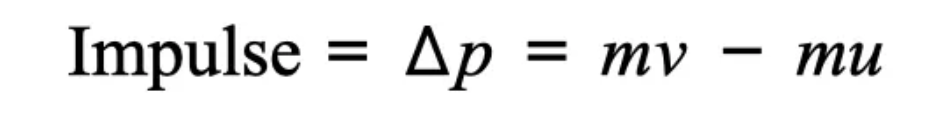
Examples of impulses:
Water droplets splatter/roll off umbrella as ______ ______ in ________
Hailstones _______ mass so bounce back off umbrella, as ______ change in momentum so impulse of umbrella applies on hail stones ______ the impulse the umbrella applies on the raindrops
_____ force required hold umbrella upright in hail compared to rain
Water droplets splatter/roll off umbrella as ______ ______ in ________
Hailstones larger mass so bounce back off umbrella, as greater change in momentum so impulse of umbrella applies on hail stones greater the impulse the umbrella applies on the raindrops
More force required hold umbrella upright in hail compared to rain
Impulse used: ______ the time over which the _____ in momentum occurs, _______ the force experienced by the person
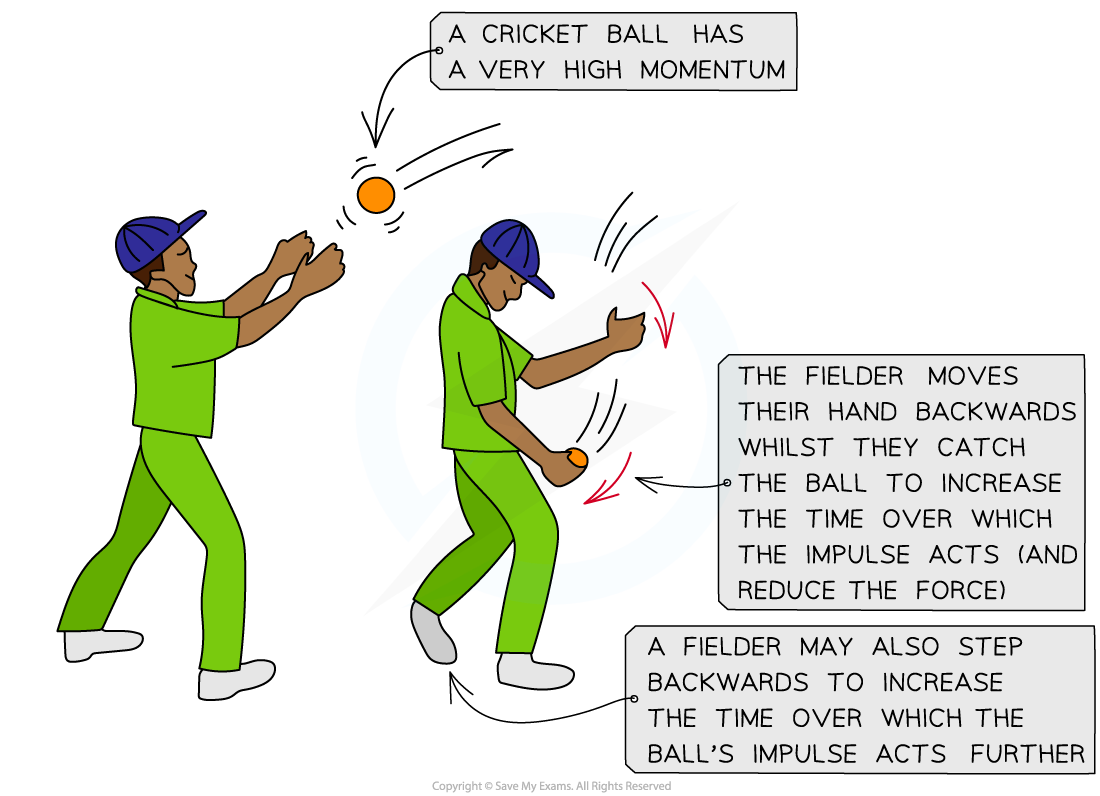
Cricket ball travels very high ______ so high _______
Fielder catches ball, the ball exerts a _______ on their hands
Impulse used: Increasing the time over which the change in momentum occurs, reduces the force experienced by the person
Cricket ball travels very high speeds so high momentum
Fielder catches ball, the ball exerts a force on their hands carry on
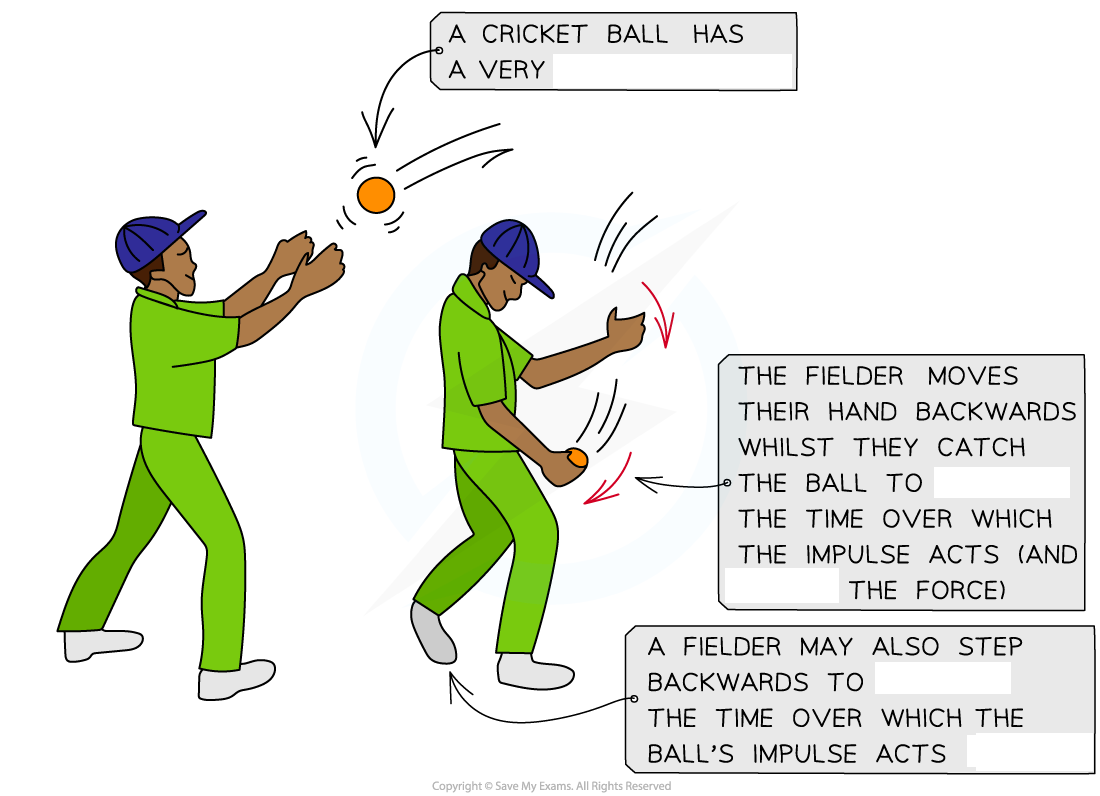
Fielder catches ball, the ball ______ a force on their hands
Stopping ball with _____ momentum ________ will exert ______ force on their hands as the ______ in momentum (impulse) acts over _____ period of time creating a _____ force on the fielder's hands and could cause ______ injury
Fielder moves hands _____ when catch the ball, which ________ the time for the change in momentum to occur so there is ______ force exerted on the fielder's hands and therefore, less chance of injury
Fielder catches ball, the ball exerts a force on their hands
Stopping ball with high momentum abruptly will exert large force on their hands as the change in momentum (impulse) acts over short period of time creating a large force on the fielder's hands and could cause serious injury
Fielder moves hands back when catch the ball, which increases the time for the change in momentum to occur so there is less force exerted on the fielder's hands and therefore, less chance of injury
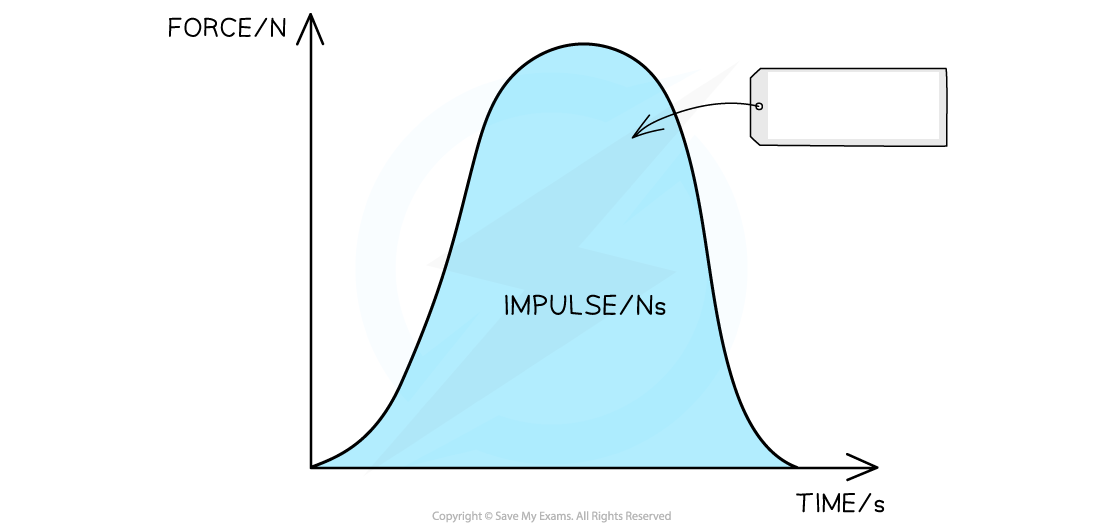
Area under the force-time graph is equal to the ________
Impulse =
Impulse is always equal: _____ force/______ period of _____/ large force over a small period of time
Graph is curve, area found by ______ the squares underneath
Graph is straight lines, split graph into sections, the total area is the ______ of the areas of each section
Area under the force-time graph is equal to the impulse
Impulse = Force × Change in time
Impulse is always equal: small force/long period of time/ large force over a small period of time
Graph is curve, area found by counting the squares underneath
Graph is straight lines, split graph into sections, the total area is the sum of the areas of each section.

How is impact forces reduced?
How is impact force reduced in sports - football?
After a strong kick the _______ from the foot is _____ to the ball so creates a ____ ______ and the ball has as _____ ____
Why do we bubble wrap packages and what does it help to do?
Impact forces reduced by increasing the contact time and is used in everyday life to lower the risk of injury
In football Increasing contact time is used as a advantage, so longer the contact time, the larger change in momentum
After a strong kick the momentum from the foot transferred to the ball creates a large impulse and the ball then has a higher velocity
Packaging, fragile items, uses bubble wrap packaging to reduce the impact forces that items experience in transition and helps to cushion items by increasing time over which they experience a force, which reduces the risk of damage
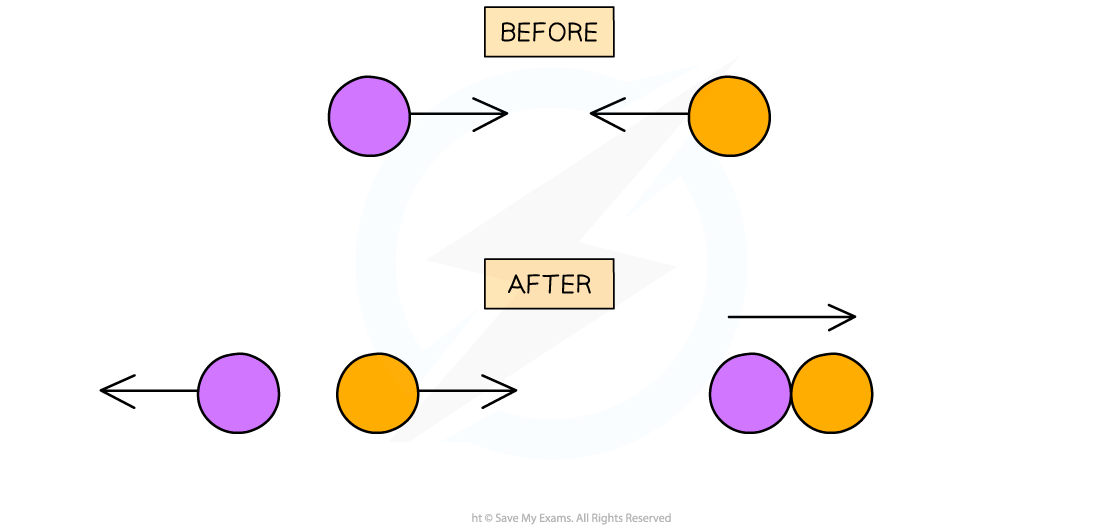
What is always and not always conserved in explosions and collisions?
What is a collision/explosion that is elastic and a collision/explosion that is inelastic?
Both collisions and explosions, momentum is always conserved and Kinetic energy not always conserved
Collision/explosion is: elastic if kinetic energy is conserved, inelastic if kinetic energy is not conserved
Collisions when objects strike against each other:
Elastic collisions where the objects colliding don’t stick together and then move in opposite directions.
Inelastic collisions where objects collide and stick together after the collision
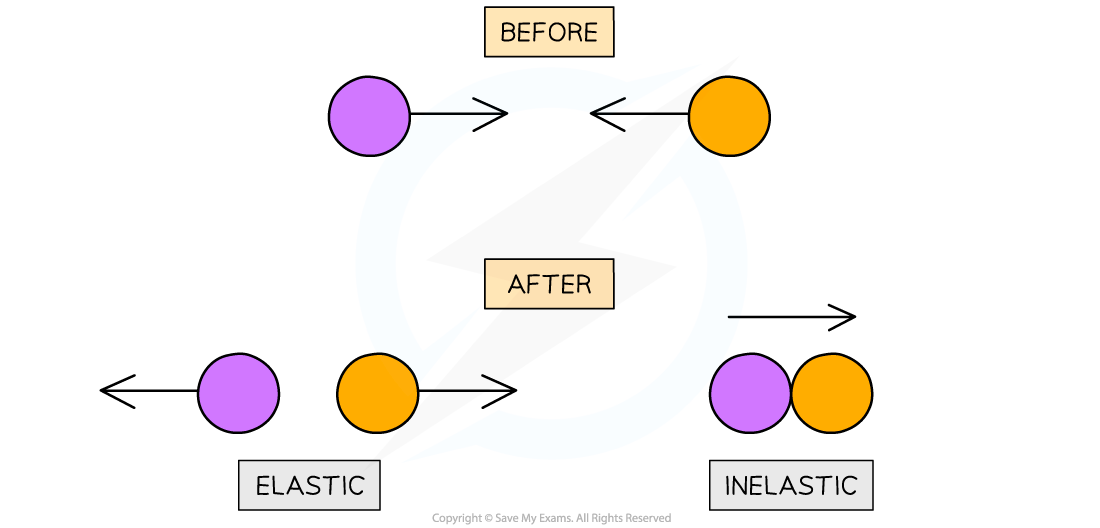
What is an explosion to with and examples?
What do you compare in elastic/inelastic collisin
Explosion is do with recoil: example, a gun recoiling after shooting a bullet or an unstable nucleus emitting an alpha particle and a daughter nucleus
Collision is elastic/inelastic, compare the kinetic energy before and after the collision. ke = 1/2mv2
How is force of impact in a collision decreased?
What is some safety features?
What are safety features designed to do?
When increasing the time what does it reduce?
Force of impact in a vehicle collision decreased by increasing the contact time over which collision occurs
Vehicles safety features: crumple zones, seat belts and airbags
Force on impact, safety features designed to absorb energy from impact increasing time taken for the change in momentum of the passenger to occur
Increased time reduces the force exerted on the passenger and reduces the risk of injury
Designing safety features:
Vehicle safety features designed to ______ _______ impact by ______ ______
Seatbelts: passengers and what are they designed, what does it reduce?
Airbags: deployed from dashboard and steering when there is a collision and what does it act as, what does it increase?
Crumple zone: what is it designed to do and how and what does it reduce?
Vehicle safety features designed to absorb energy impact by changing shape
Seat belts: designed to stop passenger from colliding with interior of a vehicle by keeping them fixed to their seat in an abrupt stop
Designed to stretch slightly to increase the contact time over which passenger's momentum reaches 0 so reduces the force exerted on them during a collision
Airbags: deployed from dashboard and steering wheel when a collision occurs: acts as a soft cushion to prevent injury on the passenger when they are thrown forward upon impact
Increase contact time over which the passenger changes momentum, so reducing the force exerted on them
Crumple zones: designed into the exterior of vehicle, front and back designed to crush/crumple in a controlled in a collision
Vehicles after collision look more heavily damaged than expected, even for relatively small collisions
Crumple zones increase time which vehicle's momentum reaches 0, reducing the force on passengers
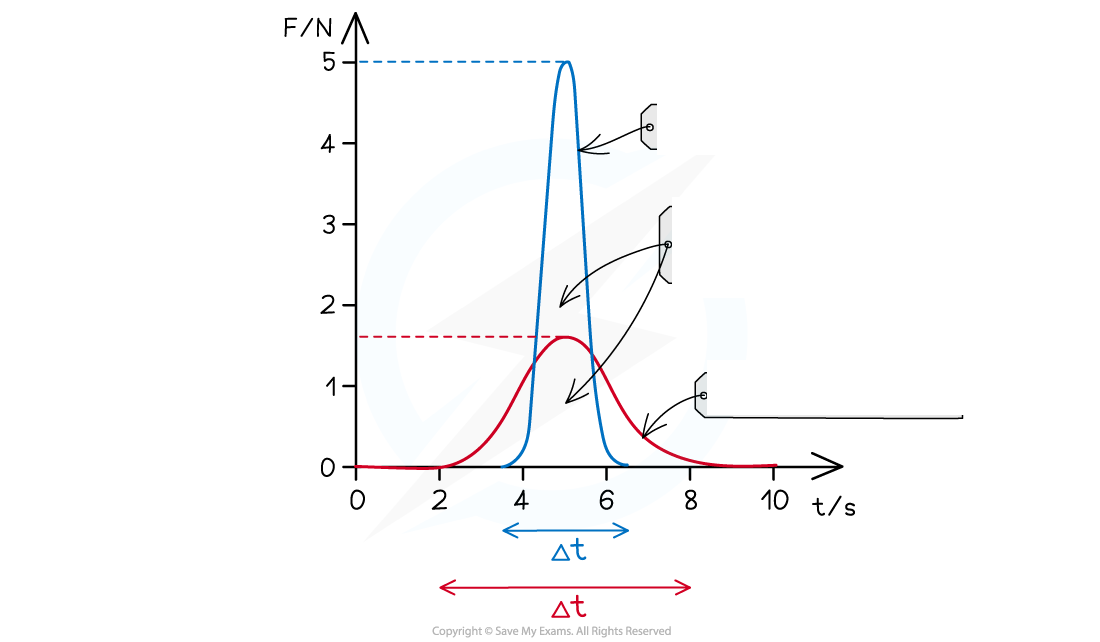
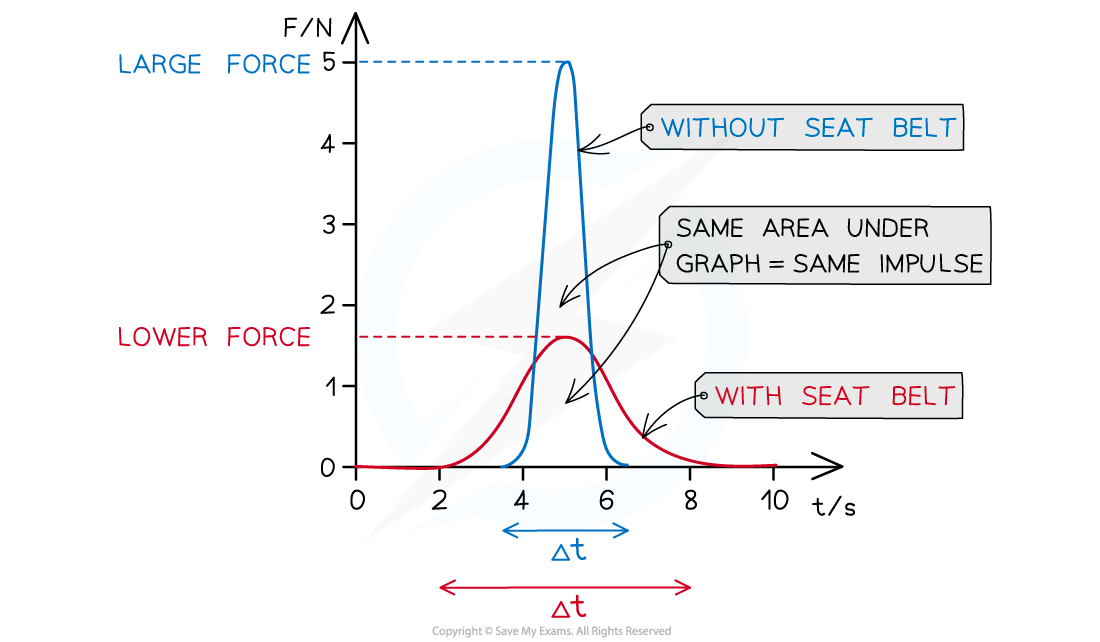
Reduced force increase in contact time is shown on force-time graph:
Same change in momentum, depends on mass and speed of vehicle, increases in contact time results in ______ in _________ force exerted on vehicle and passenger
Demonstrated by _____ _____ and ______ ___ on a force-time graph
Reduced force increase in contact time is shown on force-time graph:
Same change in momentum, depends on mass and speed of vehicle, increases in contact time results in decrease in maximum force exerted on vehicle and passenger
Demonstrated by lower peak and wider base on a force-time graph