Visceral & Special senses
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
183 Terms
Where are the cell bodies of PARA fibers carried in CN III?
Accessory oculomotor nuc. (Edinger Westphal)
(In periaqueductal grey of midbrain)
Pre PARA fibers from CN III go into the orbit & synapse in the ___ ganglion
Ciliary
The ciliary ganglion contains cell bodies of ___ _______
Post PARA
What muscle is innervated by post PARA of CN III that constricts the pupil?
Sphincter pupilae
T/F: The greater petrosal n. carries only Post SYMP fibers
FALSE → Pre SYMP
T/F: The Greater petrosal n. leaves the facial n. at the geniculate gang, but does NOT synapse there
True
Where does the Greater petrosal n. synapse after going through the pterygoid canal?
Pterygopalatine ganglion (Post Symp)
Where are the cell bodies of Pre Para found for CN IX?
Inferior salivary nuc.
What fibers does the Lesser petrosal n. carry?
ONLY Pre PARA
Where does the Lesser petrosal n. synapse w/ post. PARA cell bodies
Otic gang.
Where are the cell bodies of pre PARA for CN X
Dorsal nuc. of Vagus
Post PARA from CN X have what effect when they innervate the heart?
Constrict coronary vessels
What nerve is the sup. 1/3 of the esophagus supplied by?
Recurrent laryngeal n.
What are Pre PARA from CN X carried in to reach the stomach?
Ant. & Post. vagal trunks
What type of fiber carries nociceptors to the appendix?
Post PARA CN X (pathway to Alimentary canal)
What are pre PARA from CN X carried in that synapse in the gallbladder, biliary tree, & pancreatic glands?
Hepatic plexus
The motor pathway to the kidneys from CN X carries what type of fibers?
Sympathetic ONLY
What type of information is within the Inferior hypogastric plexus?
Pre PARA (Pelvic splanchnic nn.)
T/F: The inferior hypogastric plexus carries PARA information ONLY
FALSE → PARA & SYMP
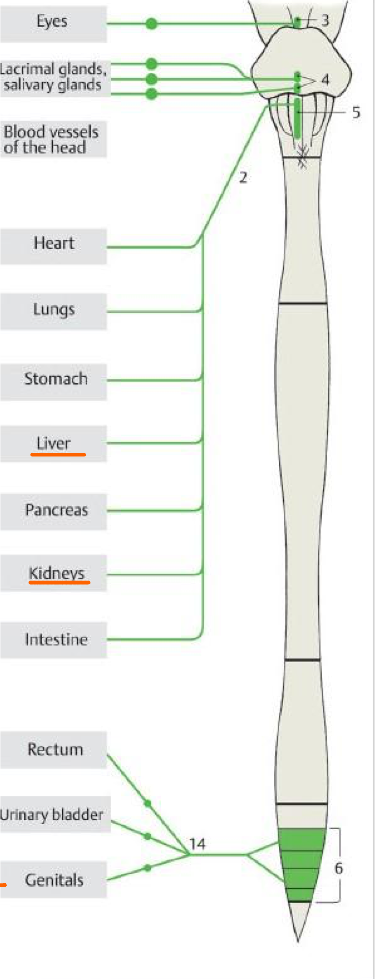
3
Accessory oculomotor nuc.
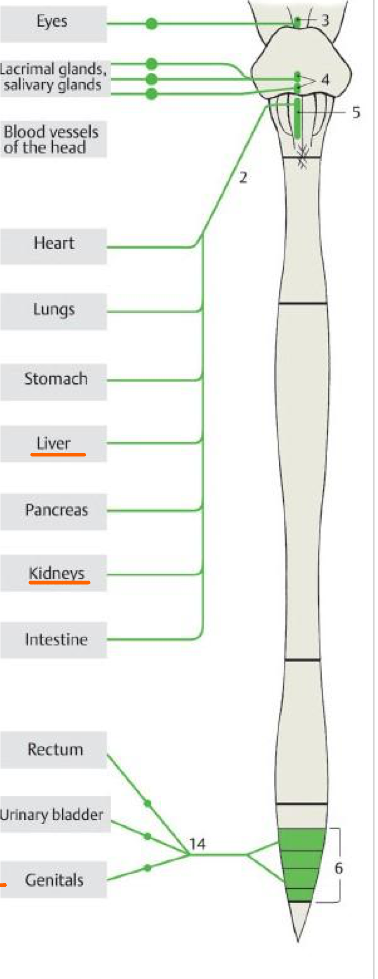
Top #4
Sup. salivary nuc.
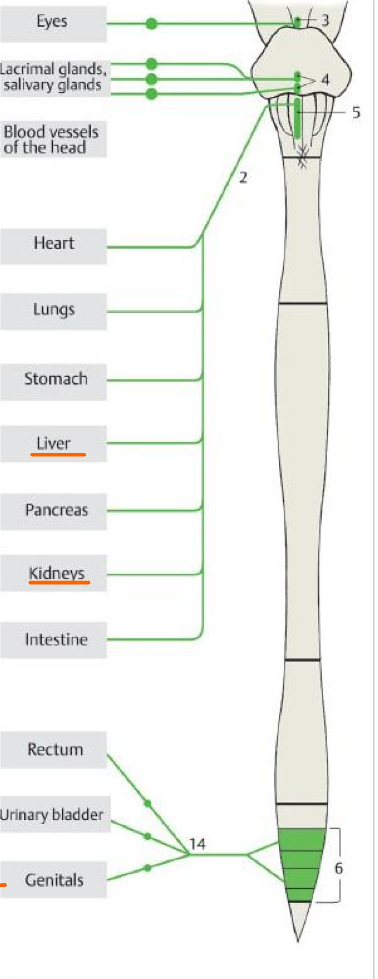
Bottom #4
Inf. salivary nuc.
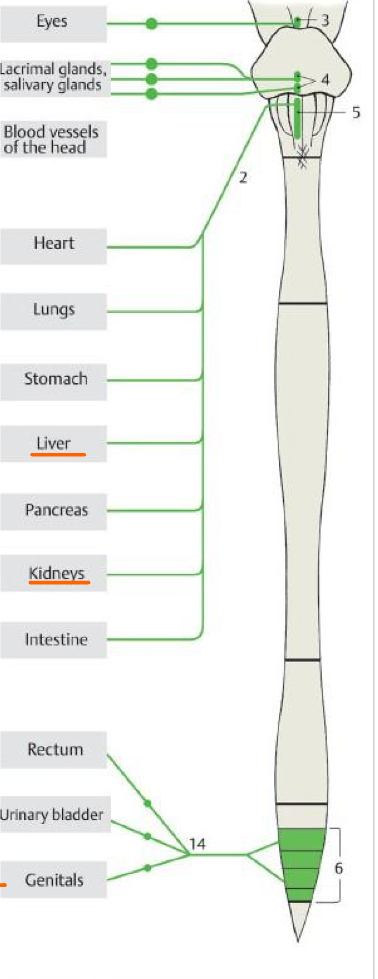
5
Post. nuc. of vagus
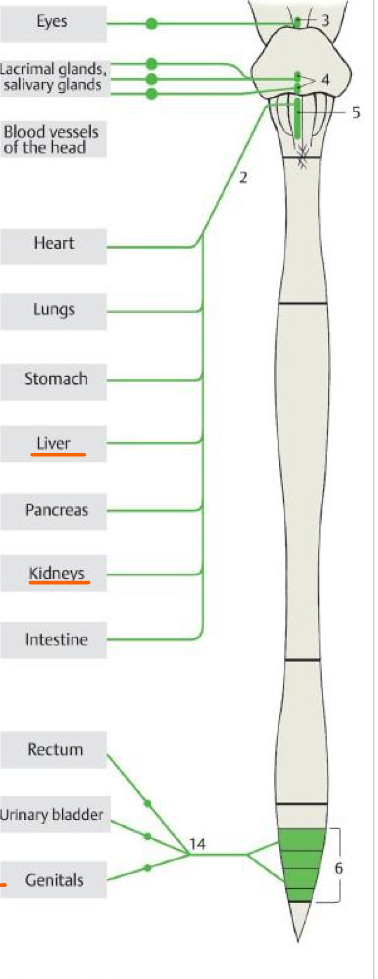
6
Lateral horn of S2,S3,S4
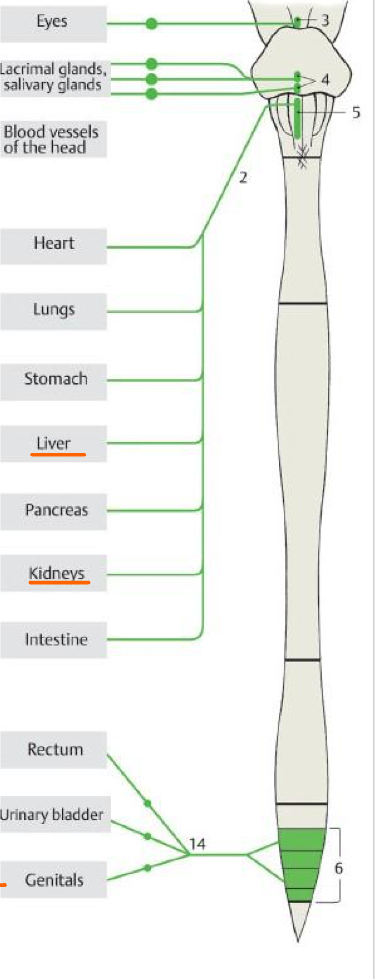
14
Pelvic splanchnic nn.
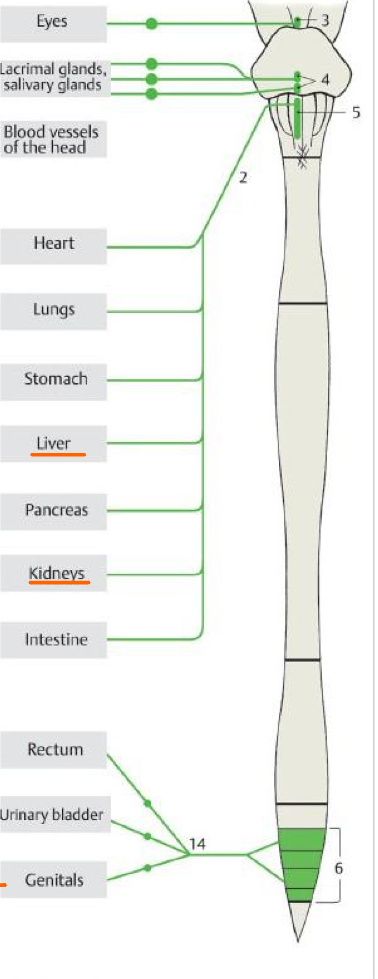
The liver, suprarenal glands, & kidneys are NOT supplied by what type of fibers?
MOTOR
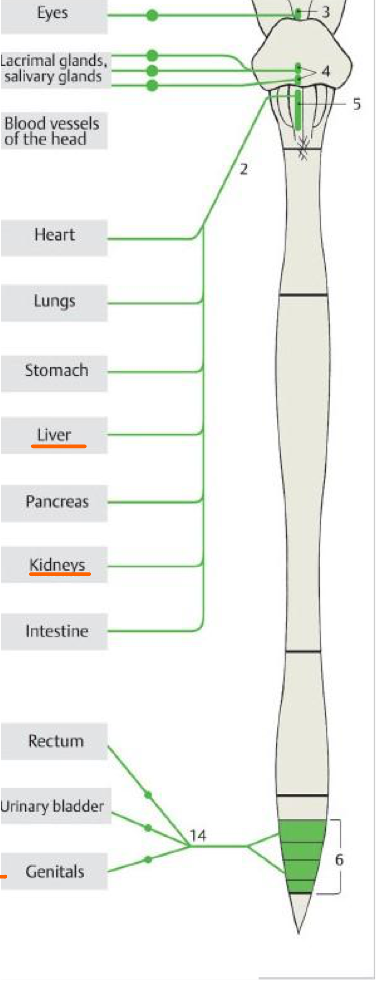
What primarily controls the uterus?
Hormonal (humeral)
T/F: ALL adjustments affect sympathetic functions
True
What segments make up the superior cervical gang.?
C2 & C3
What forms at the level of the coccyx?
Ganglion impar
Pre SYMP information to the head is carried from what cord levels?
T1 & T2
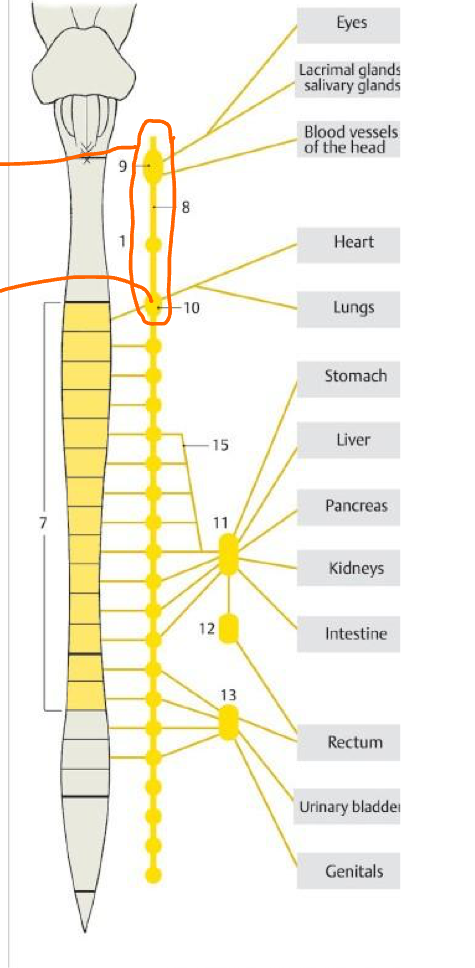
What is the circle enclosing?
Cervical SYMP gang.
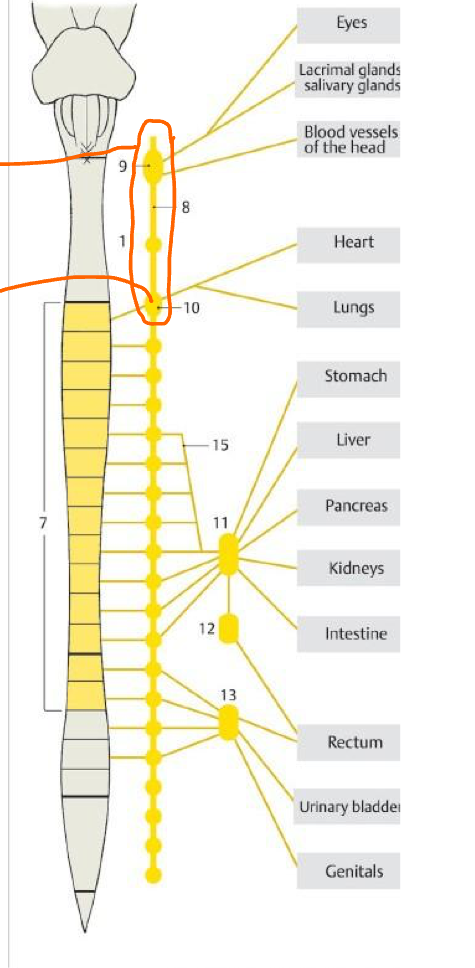
10
Stellate gang.
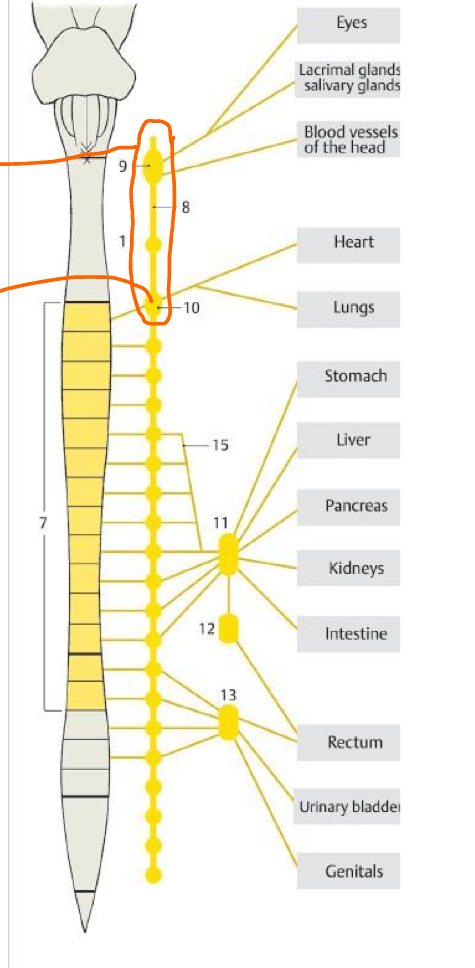
15
Greater splanchnic n.
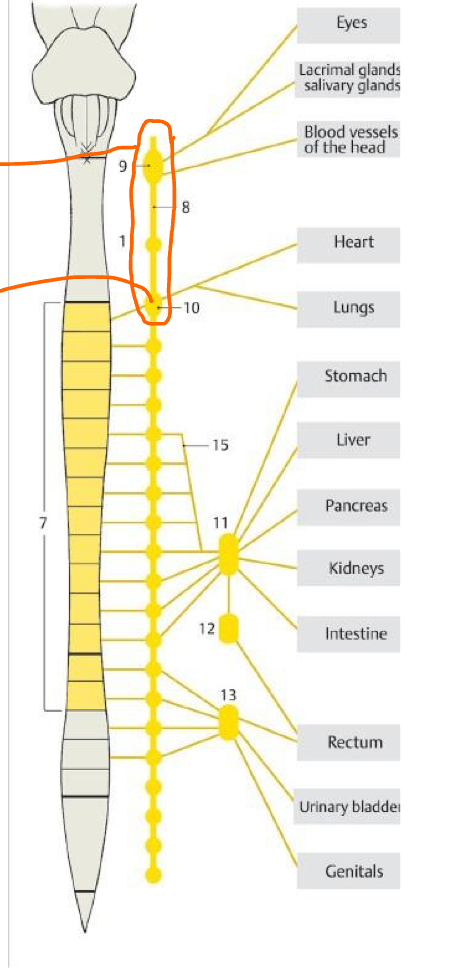
11 & 12
Celiac plexus (Pre & Post symp)
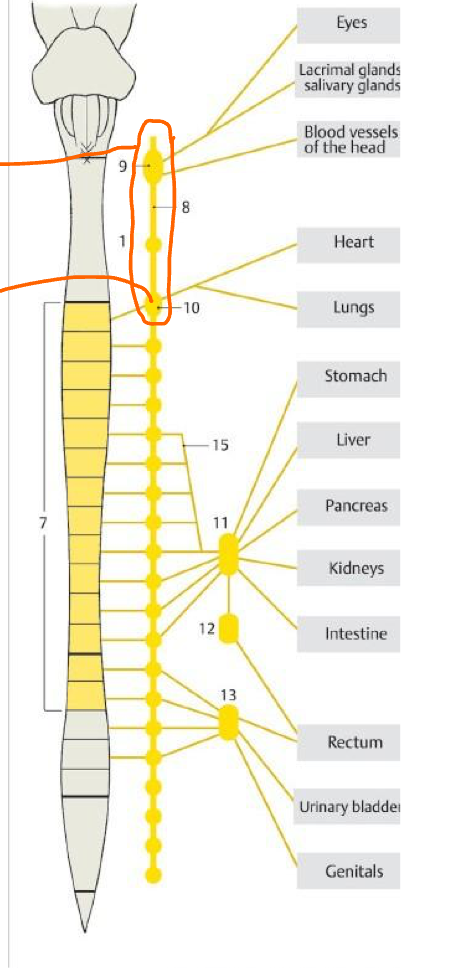
13
Inf. hypogastric plexus (pre & post symp)
Where does Pre SYMP info from T1-T4 cord levels innervate?
Heart
What levels of the sympathetic trunk brings SYMP info to the lungs?
T2-T4
What effect does SYMP from T2-T4 have?
Bronchodilate in the lungs
What cord levels bring Pre SYMP information to the abdominal viscera?
T5-T12
What level is the superior cervical gang. located?
C2/C3
80% of the time __ fuses with __ to form a stellate ganglion
Inferior cervical gang
T1 ganglion
What branch of the inferior cervical gang. sends branches to the subclavian a.?
Anterior branch
How many SYMP gang. are found in the lumbar trunk?
4
What is the largest prevertebral plexus?
Celiac plexus
What nerves contribute to the tympanic plexus & is presumed to be the structure that was affected with the adjustment Harvey Lillard received?
Caroticotympanic nn.
What is between L4 & S1 levels and includes sup hypogastric/inf mesenteric
Celiac plexus
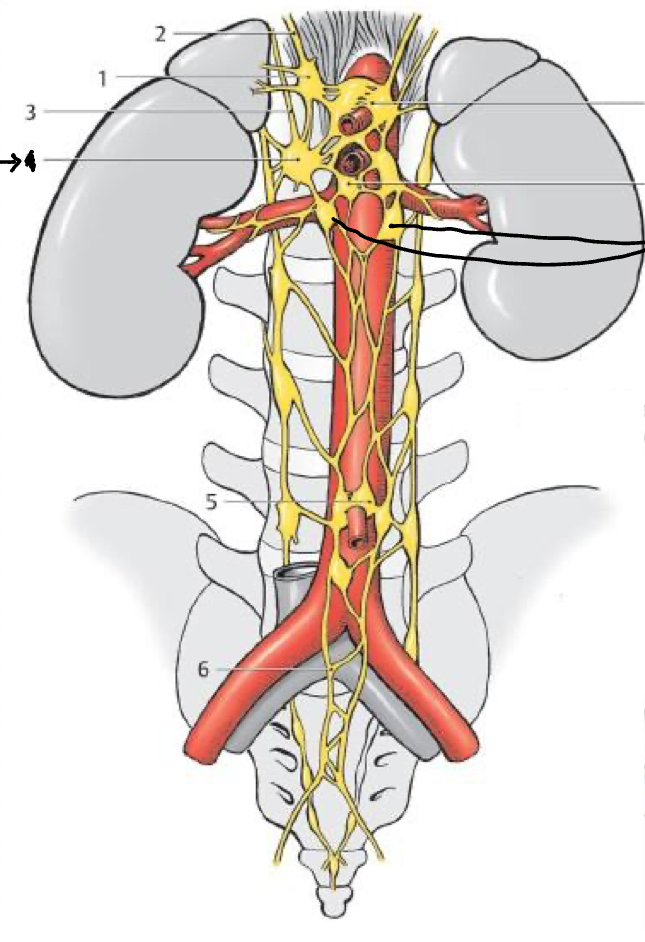
1
Celiac gang.
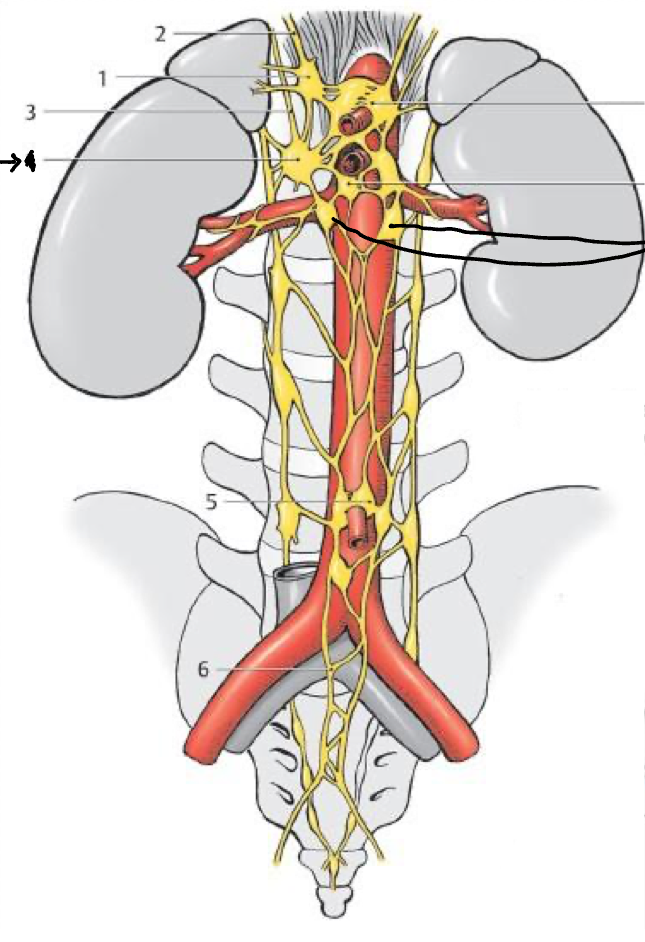
2
Phrenic plexus
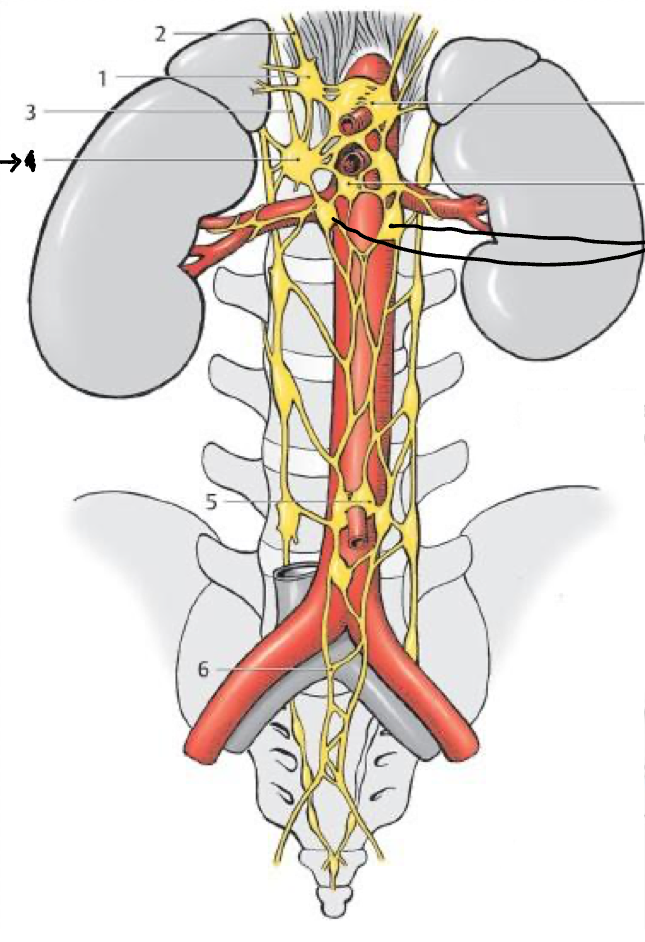
5
Inf. mesenteric gang
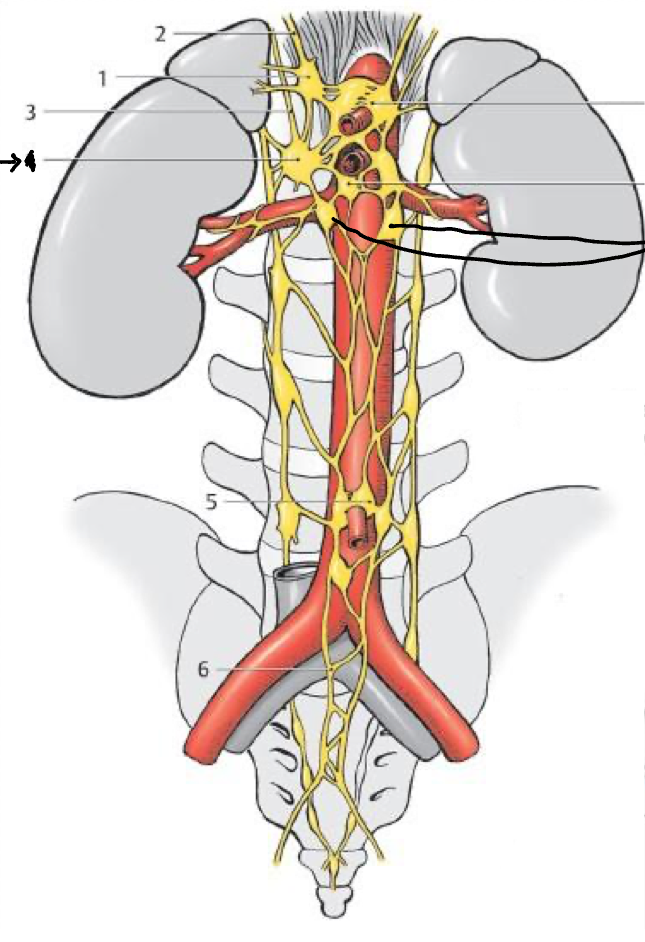
4
Sup. mesenteric gang
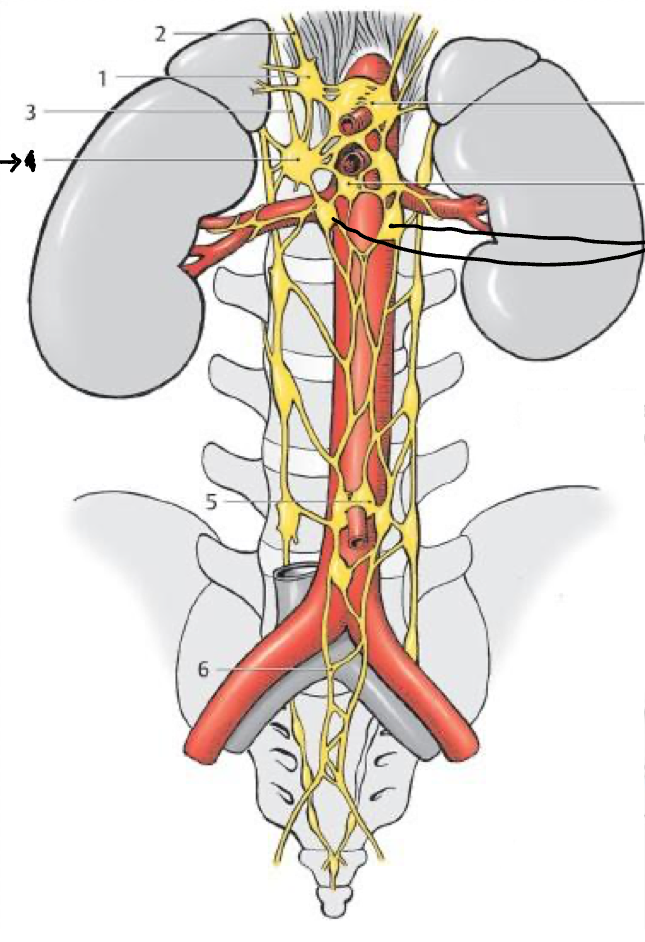
What structure is the bold lines pointing to?
Aorticorenal gang.
What structures make up the fibrous tunic?
Sclera & cornea
What is the transition between the sclera & cornea called?
Limbus
What is the primary refractory structure?
Cornea
What causes an astigmatism?
Irregularity in the shape of the cornea
What is the thickest layer of the cornea?
Substantia propria
What part of the vascular tunic has a rich blood supply?
Choroid
What are the 2 muscles of the iris?
Sphincter pupillae → PARA
Dilator pupillae → SYMP
Which tunic is an outgrowth of the diencephalon?
Nervous/retina
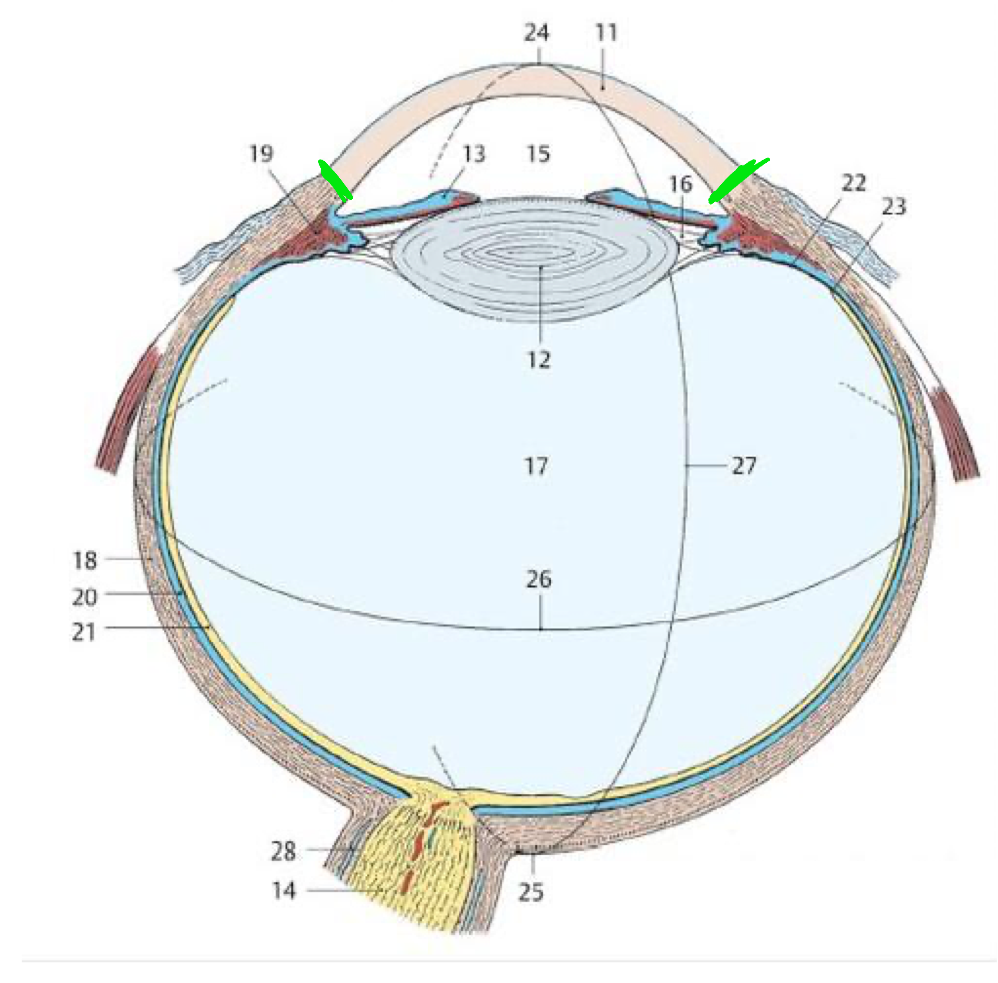
15 (TQ)
Pupil
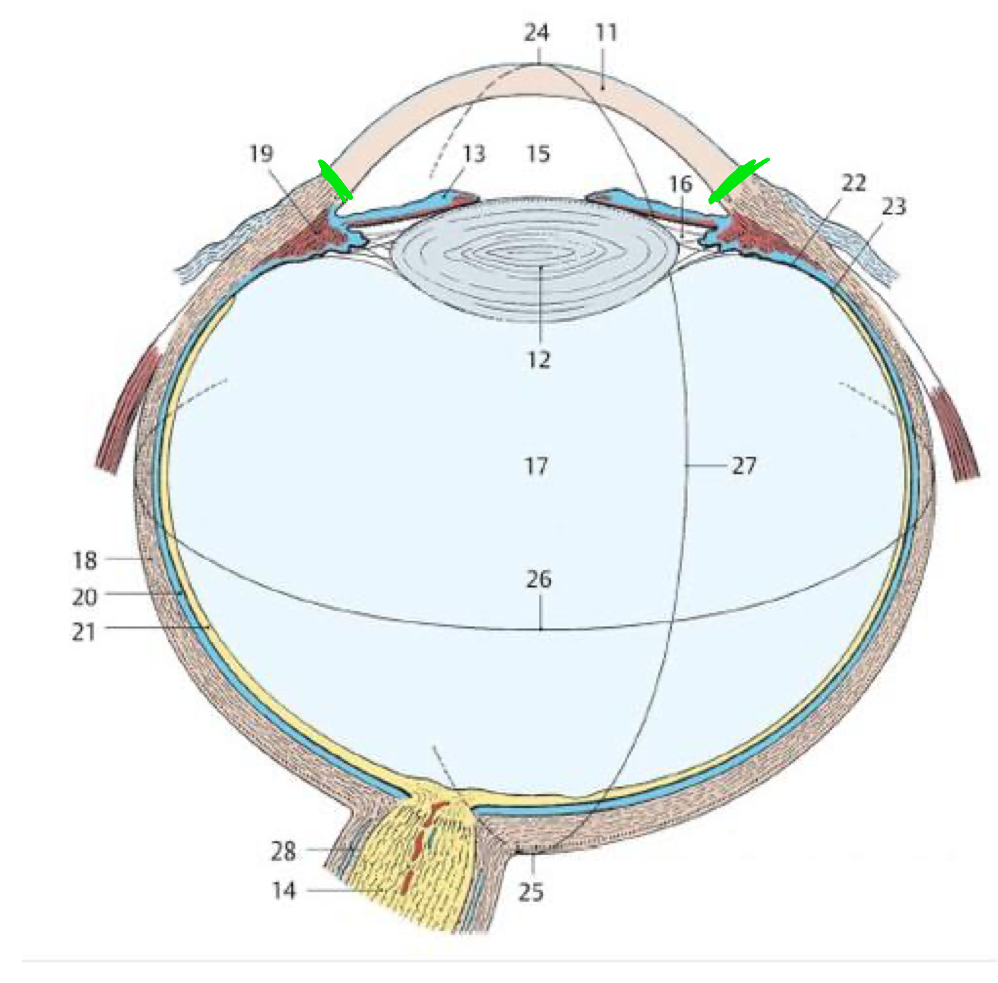
12 (TQ)
Lens
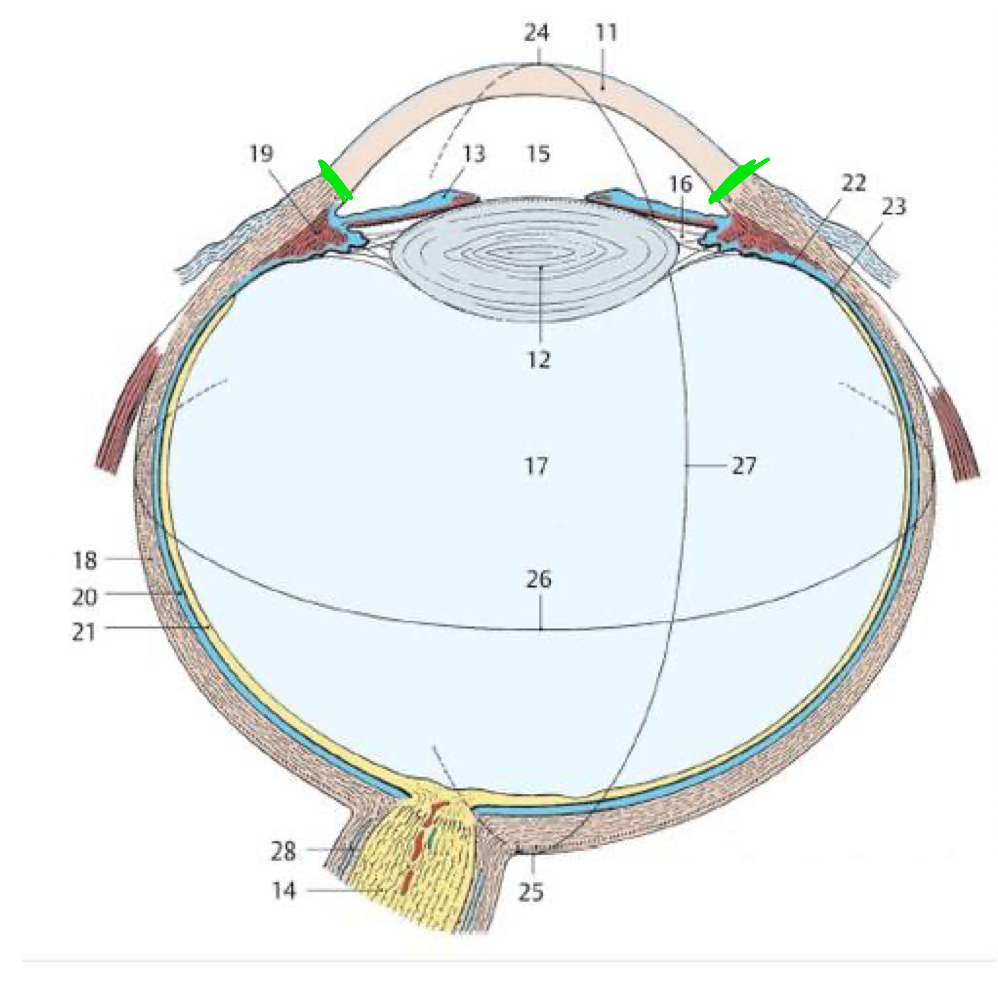
21
Retina
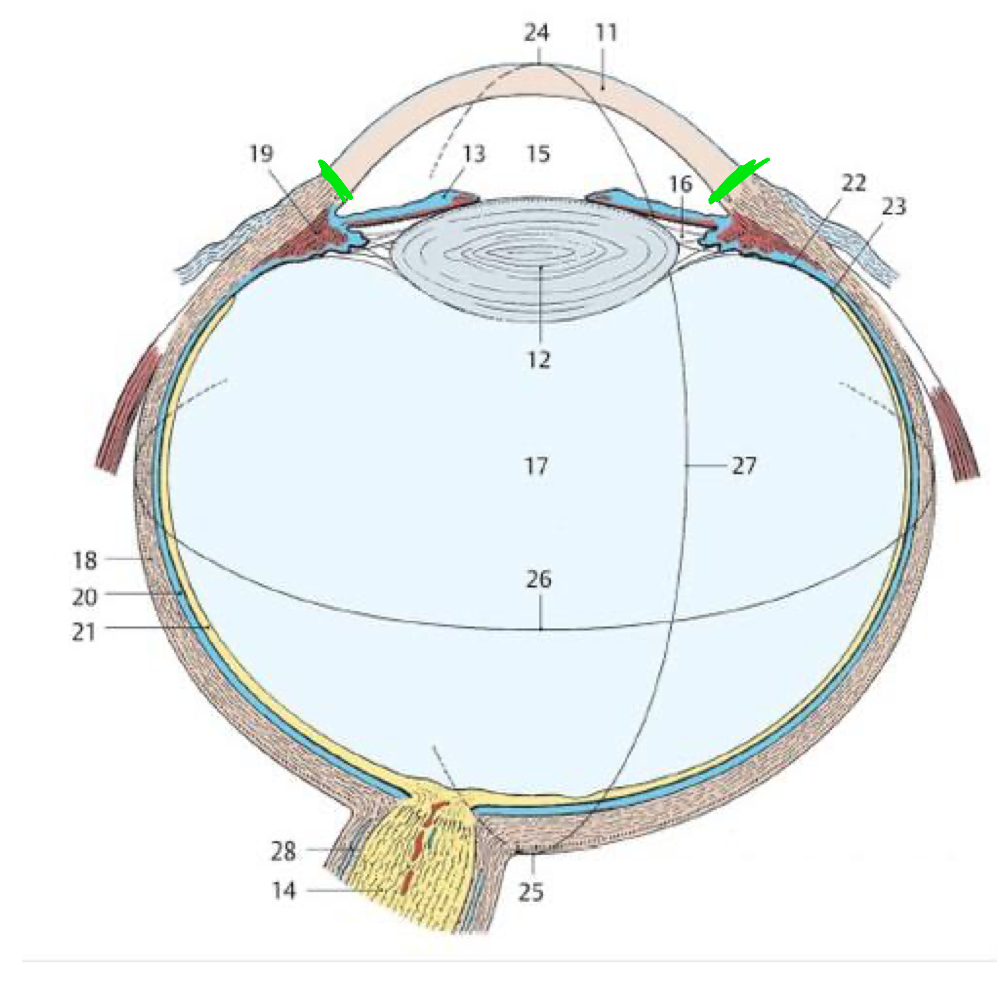
18
Fibrous tunic
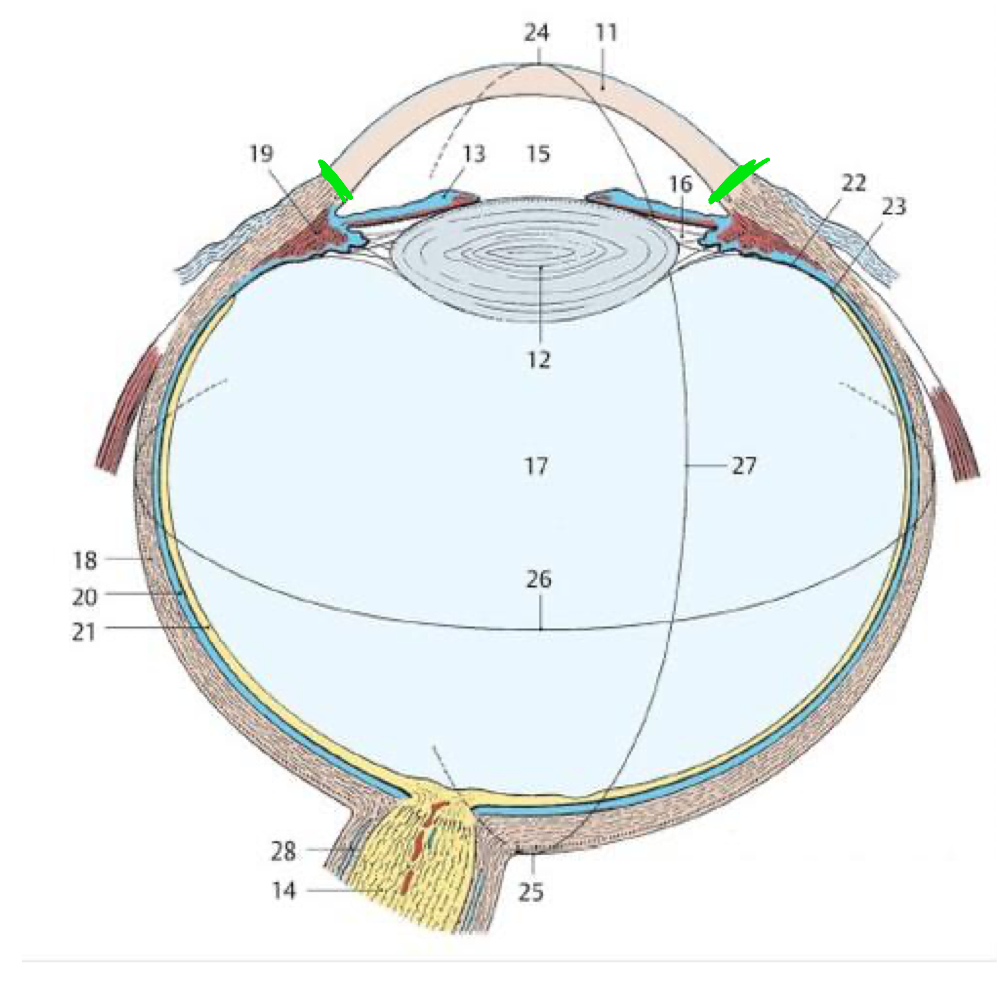
20
Vascular tunic
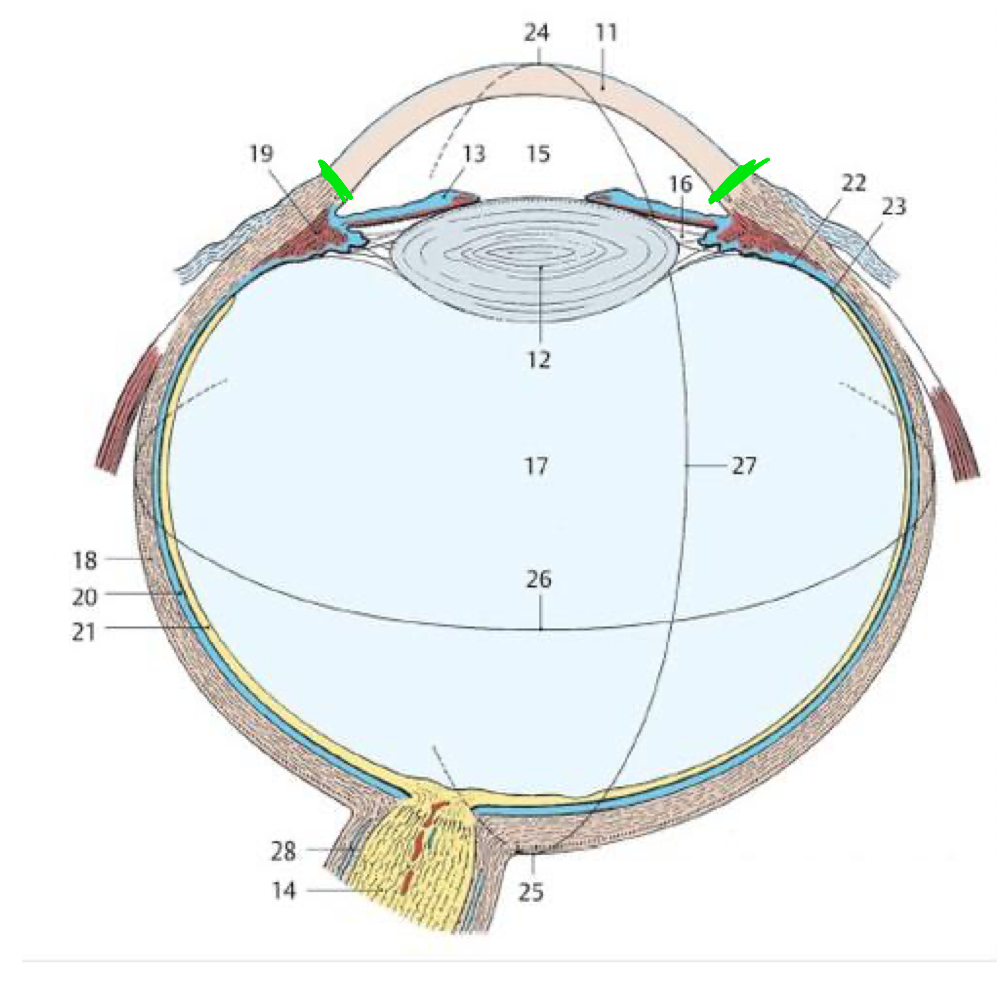
19
Ciliary body
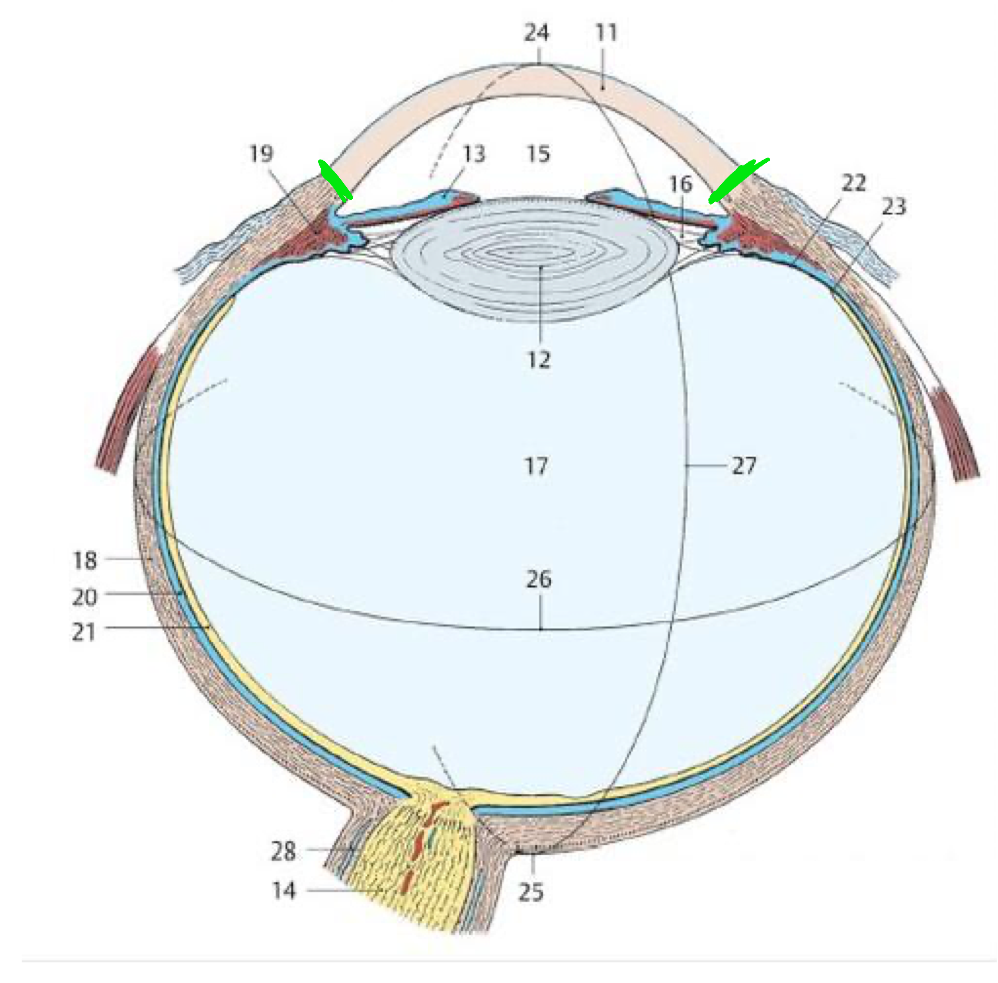
11
Cornea
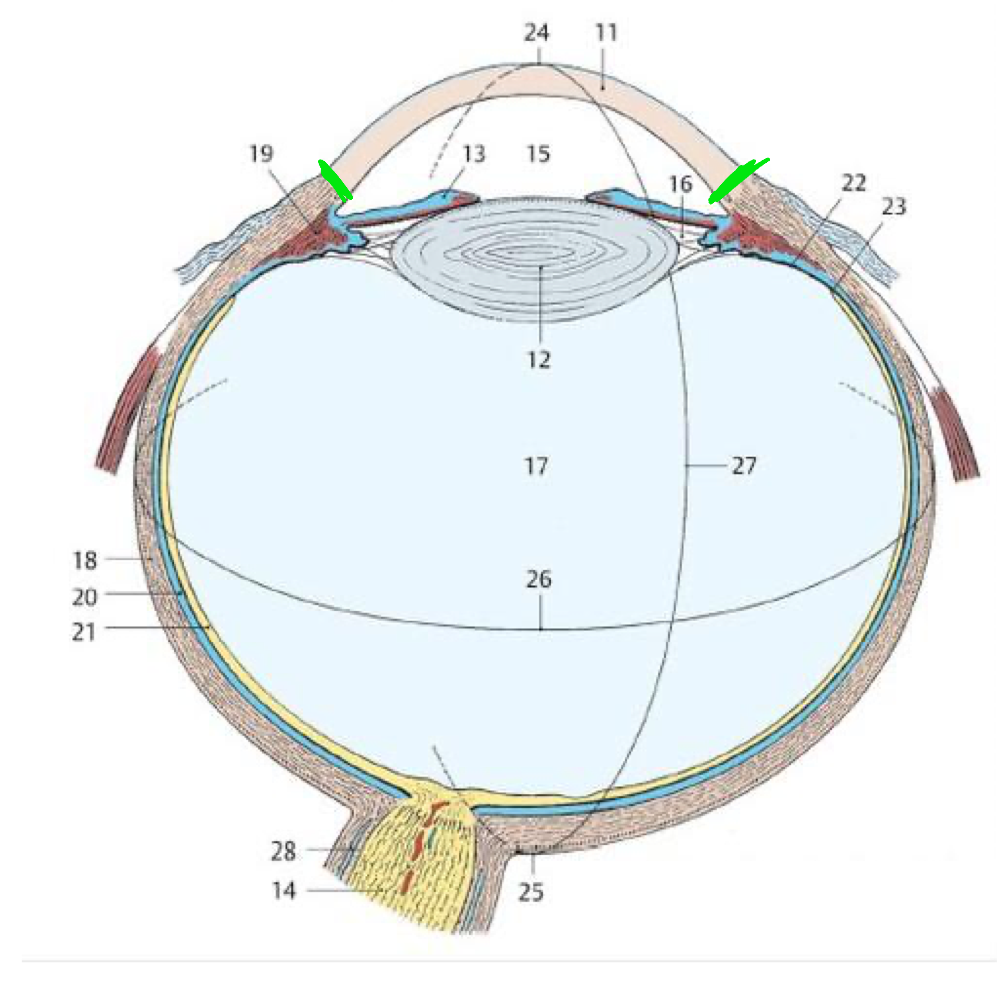
Green lines
Limbus
What fills the ant. segment of the eye and what is it secreted by?
Aqueous humor
Ciliary processes
What is the flow of aqueous humor?
Post. chamber → through pupil → ant. chamber → leaves via sclera venous sinus
What is it called when there is a loss of resiliency of the lens?
Presbyopia

14
Iris
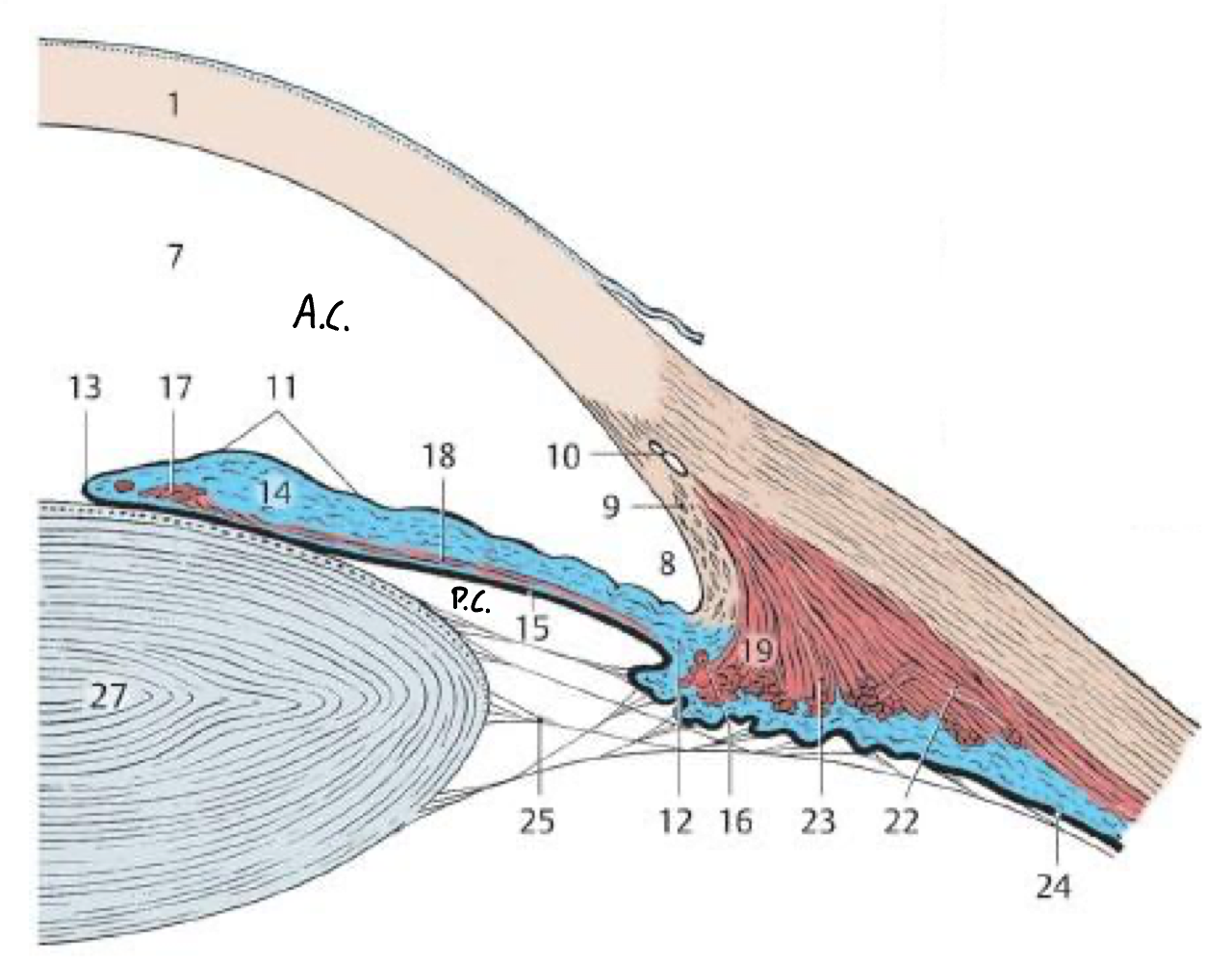
7
Anterior chamber
18
Dilator pupillae
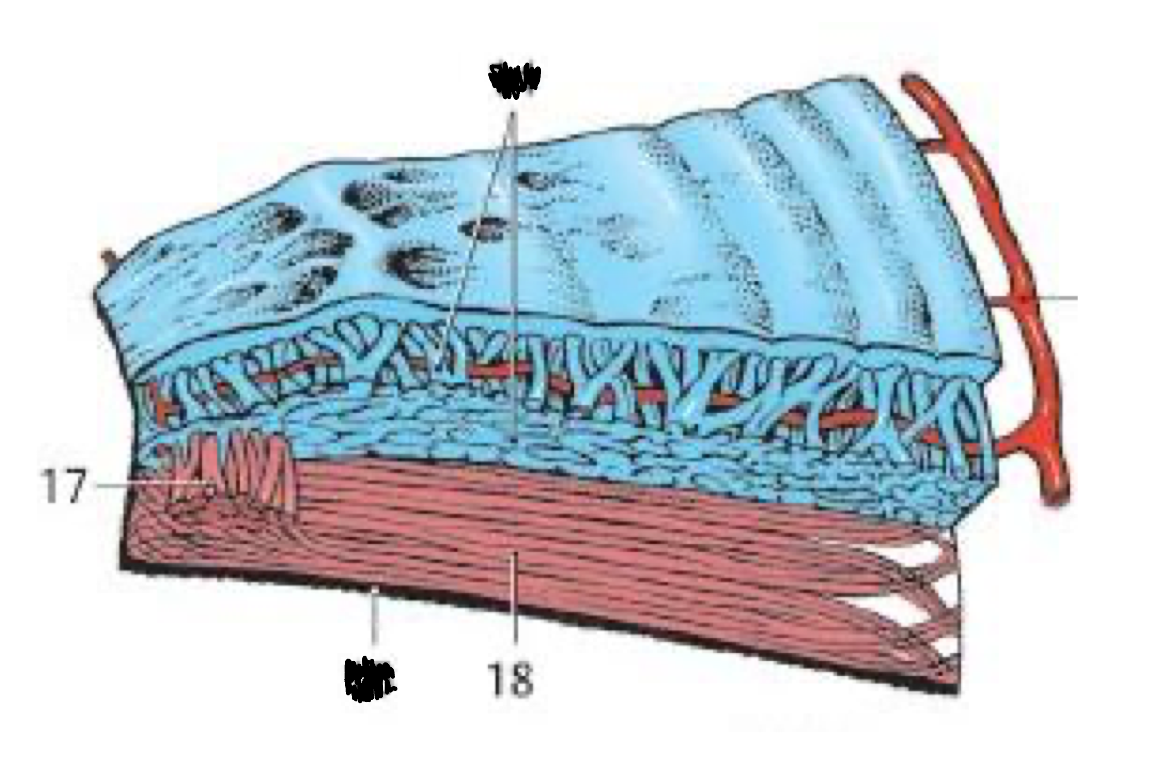
17
Sphincter pupillae
What structure is associated with glaucoma?
Aqueous humor

11
Pigmented layer
17
Rods & cones (receptors)
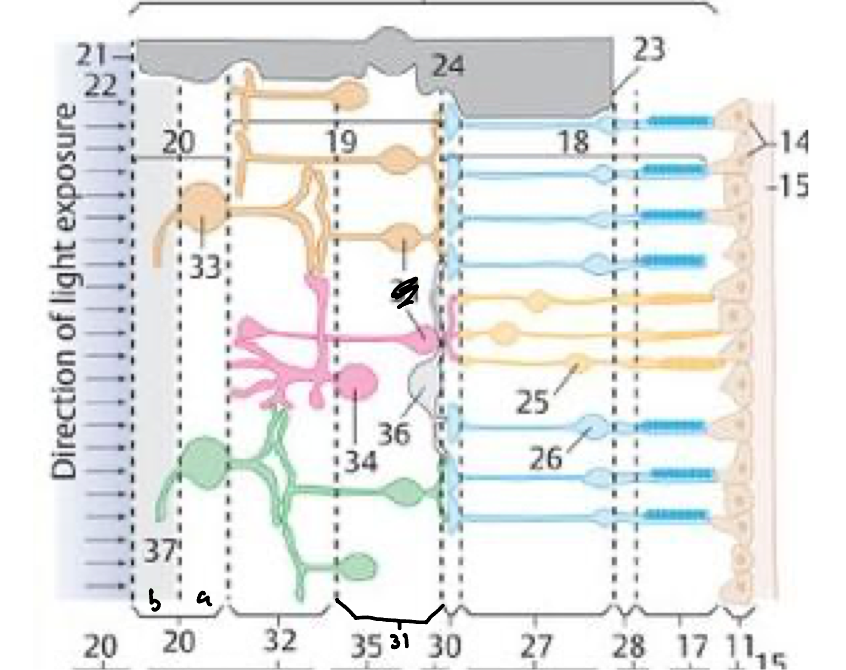
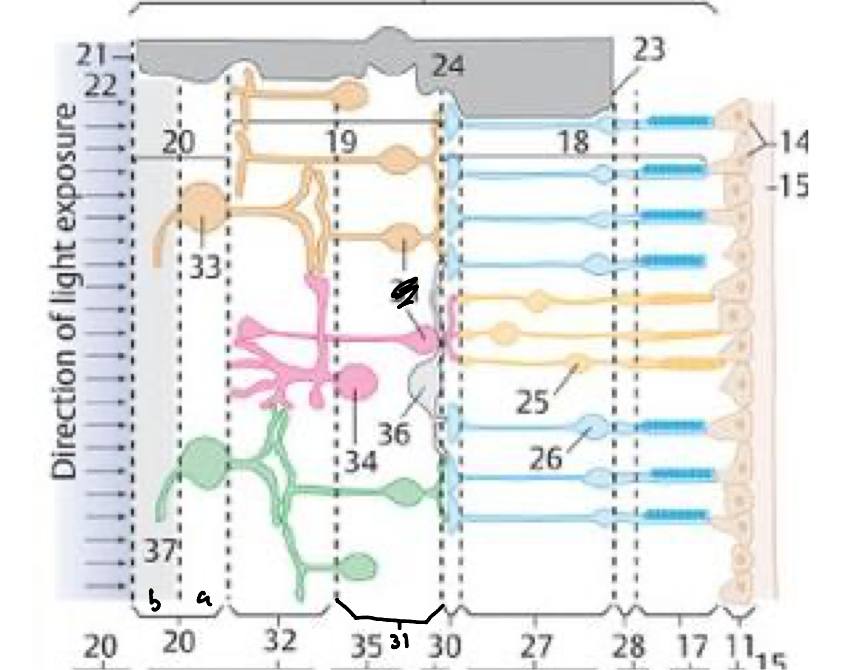
28
External limiting membrane
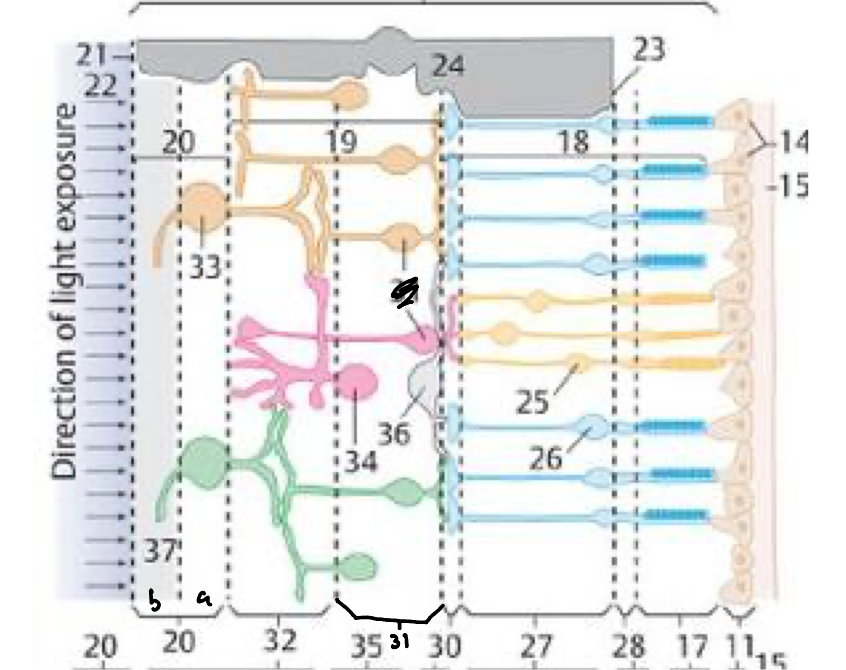
27
Outer nuclear layer
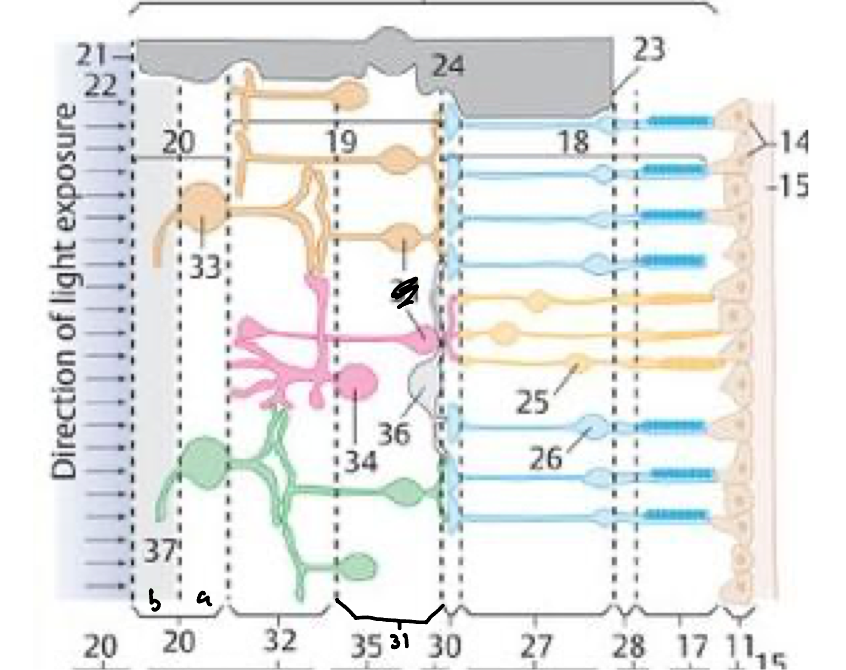
30
Outer plexiform layer
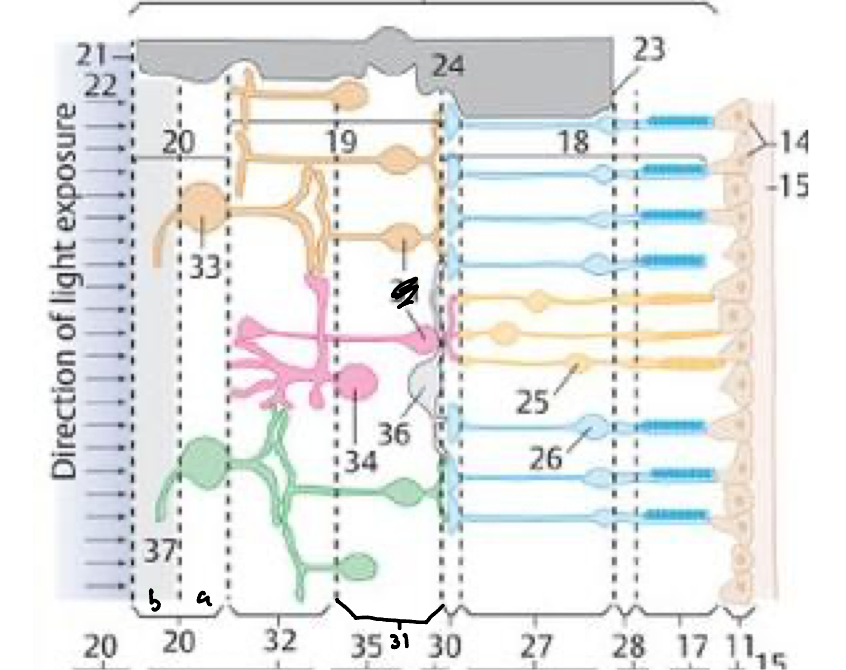
31
Inner nuclear layer
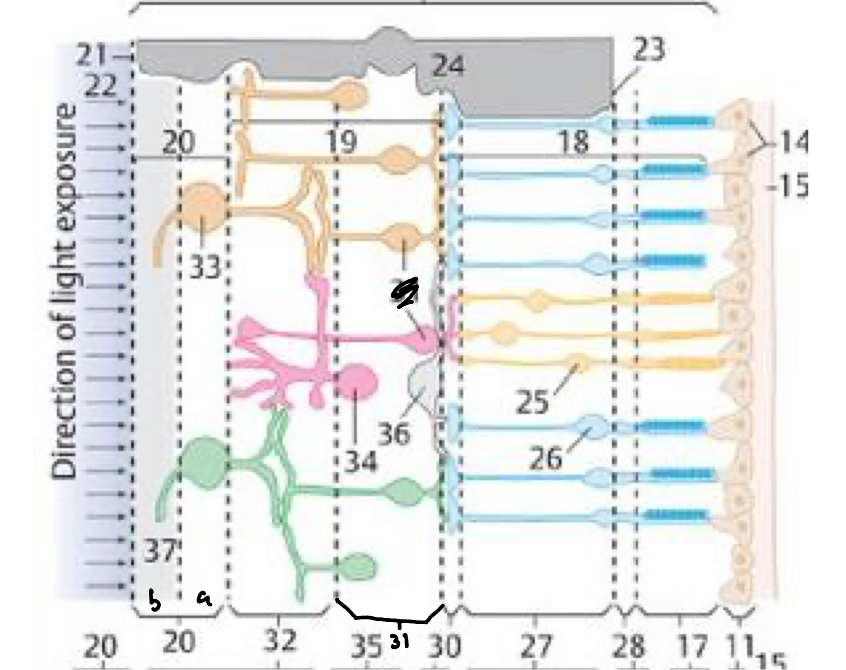
32
Inner plexiform layer
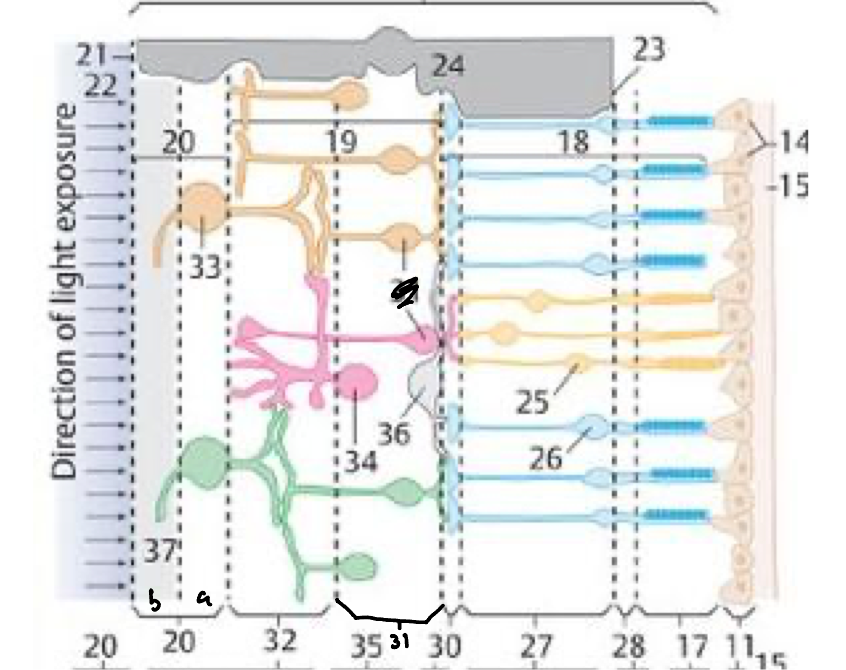
20a
Ganglion cell layer
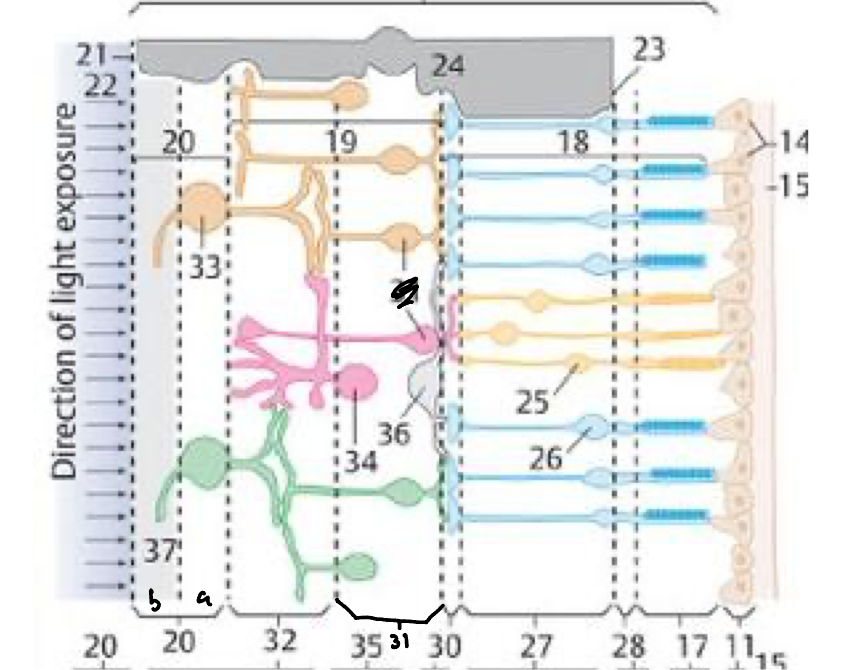
20b
Nerve fiber layer
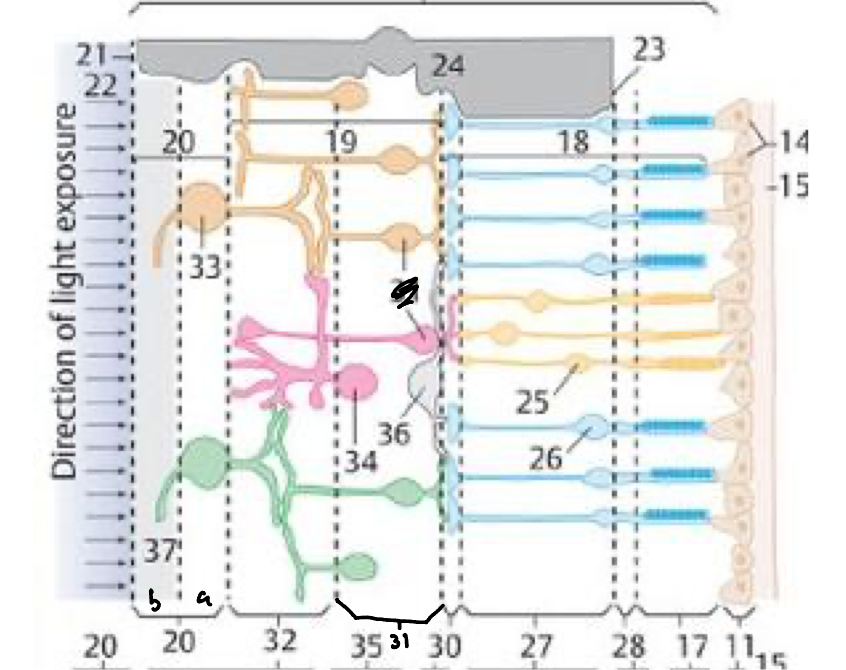
21
Internal limiting membrane
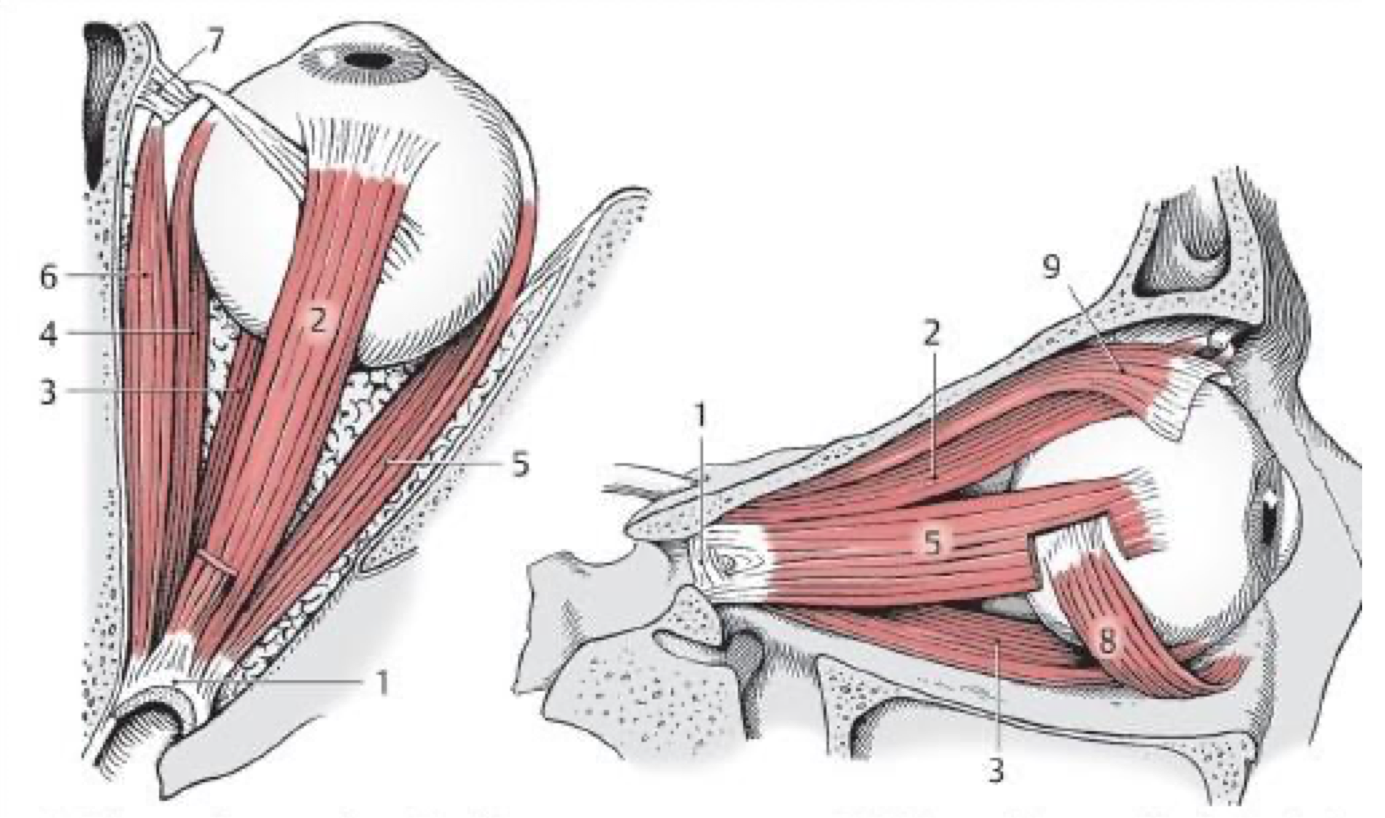
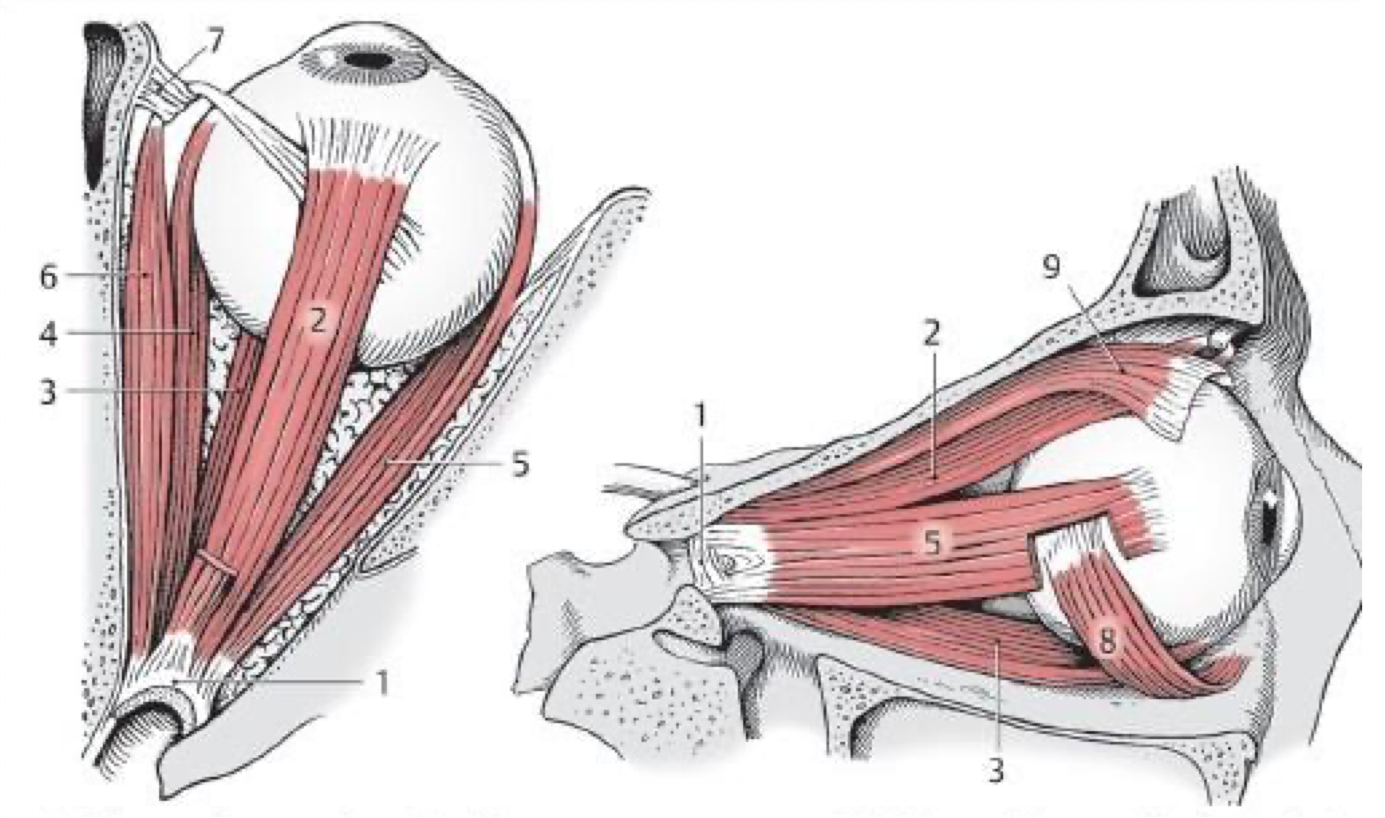
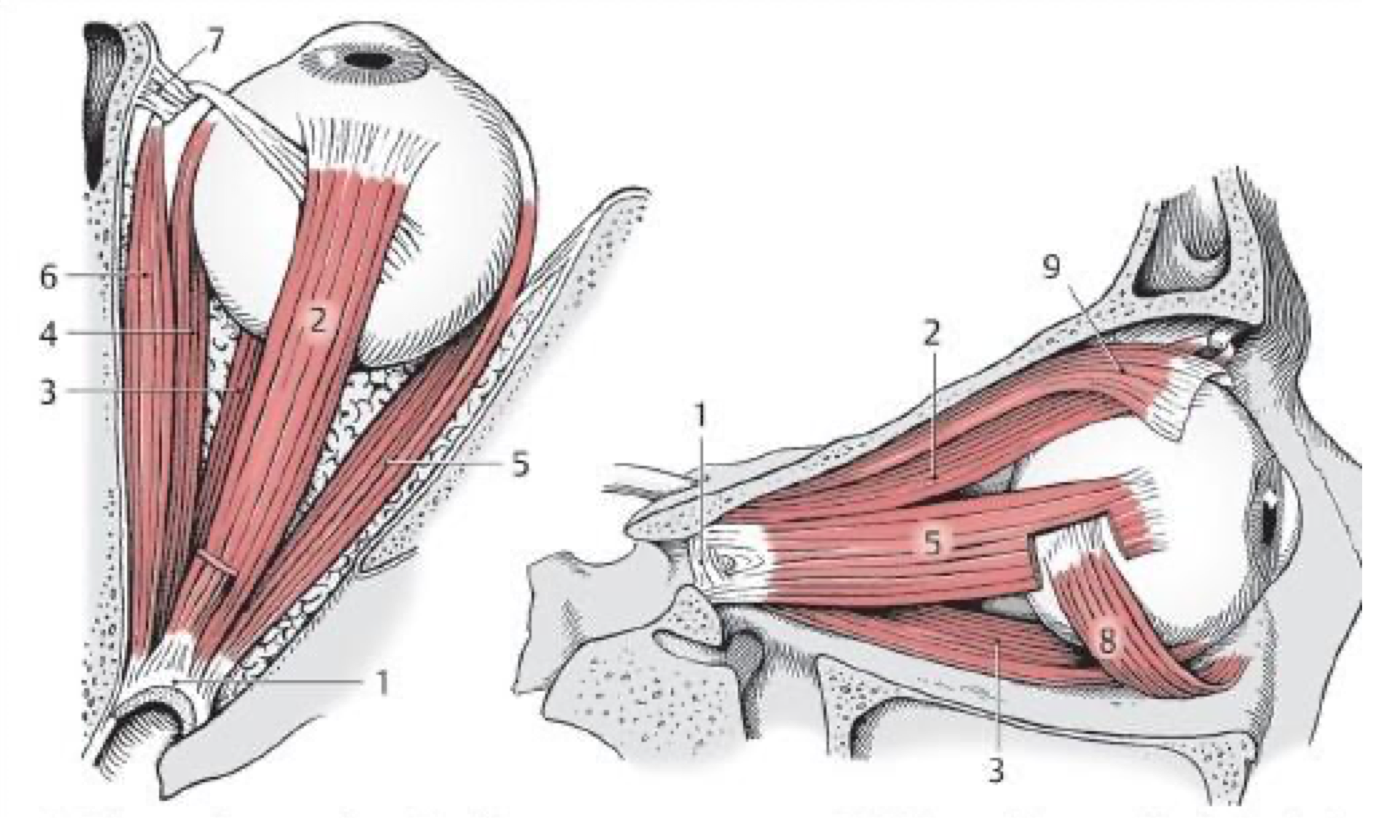
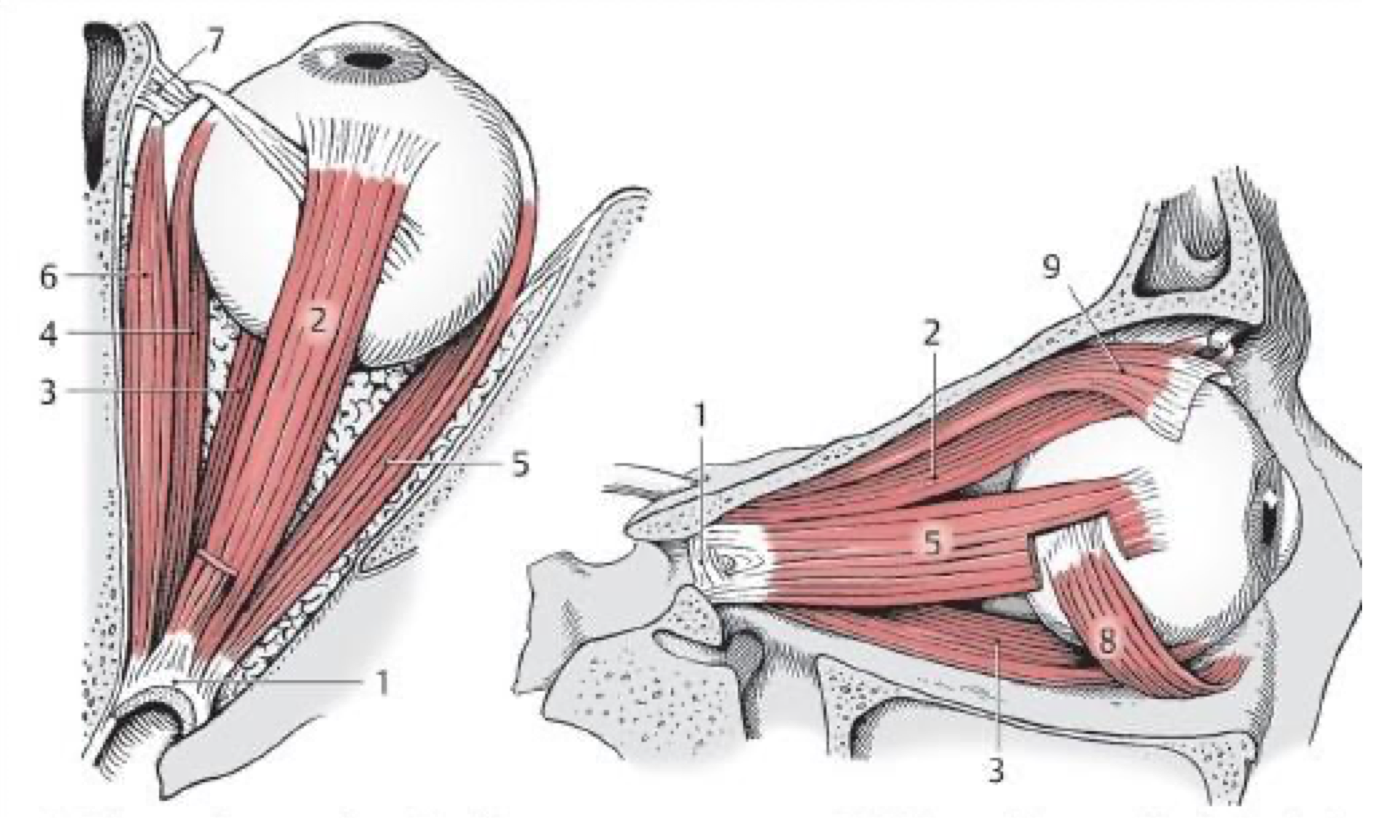
2
Superior rectus m.
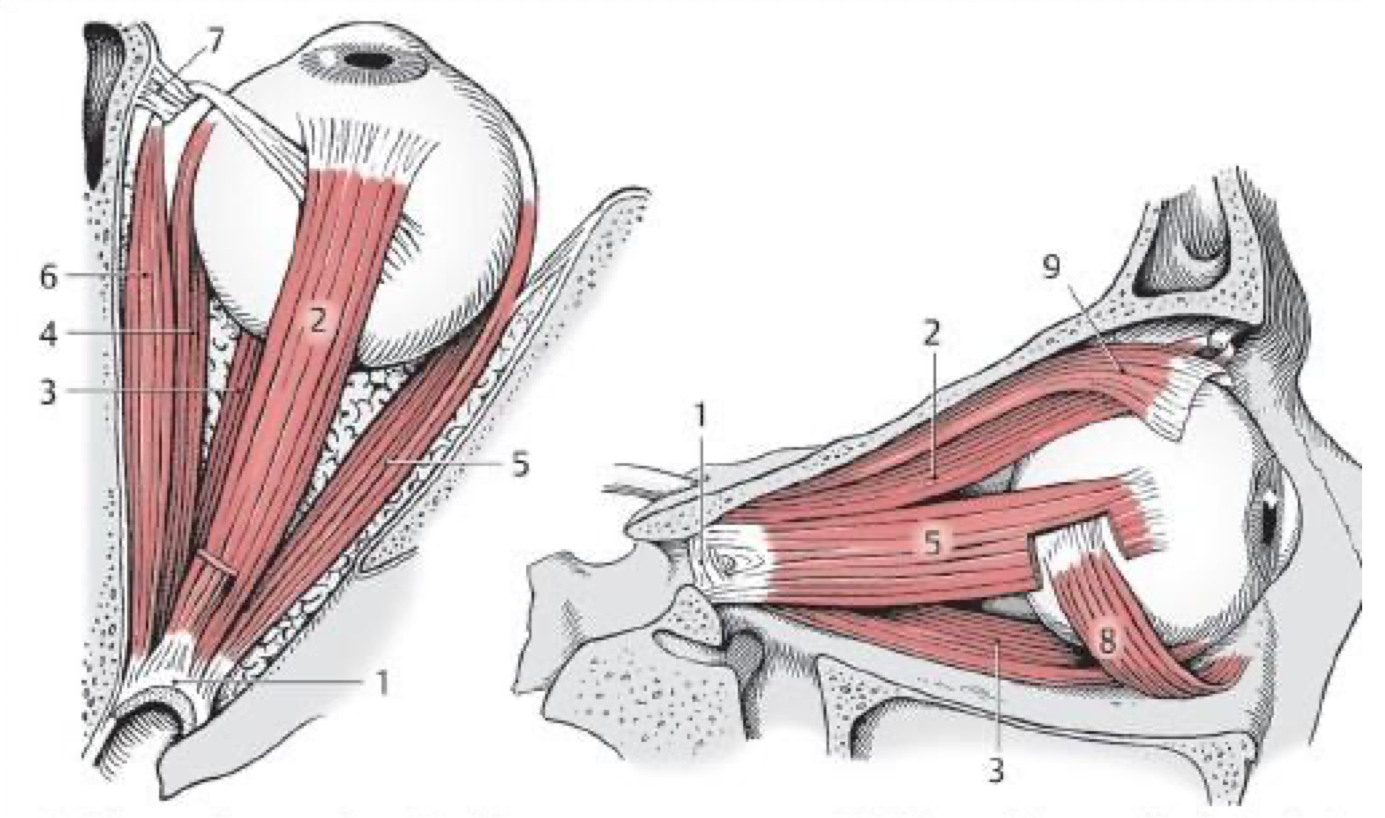
3
Inferior rectus m.
4
Medial rectus m.
5
Lateral rectus (CN VI)

6
Superior oblique (CN IV)
8
Inferior oblique
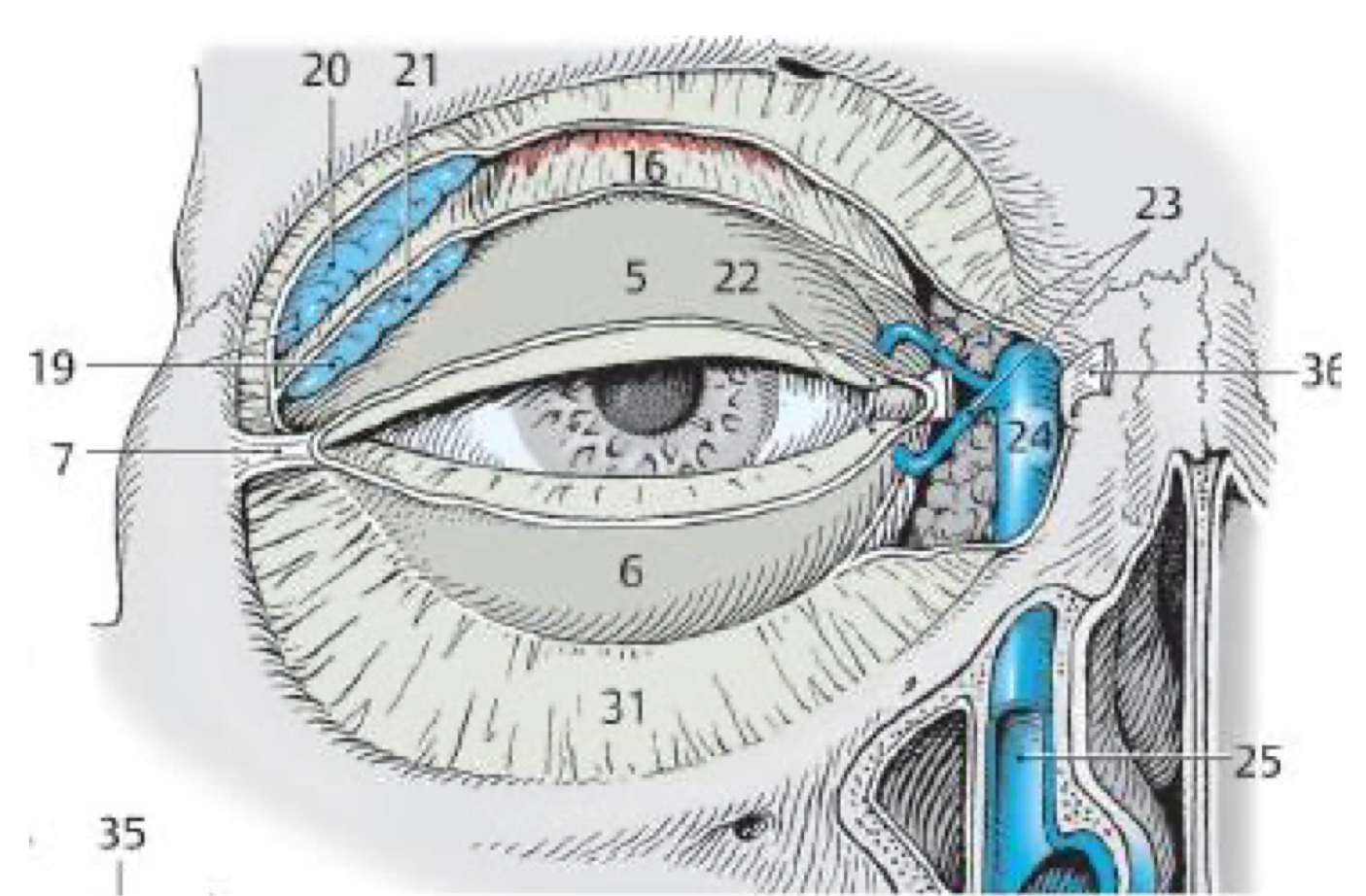
What structure is responsible for draining tears into the inferior nasal meatus?
Nasolacrimal duct
What kind of gland are the tarsal glands?
Sebaceous (oil)
20
Lacrimal gland
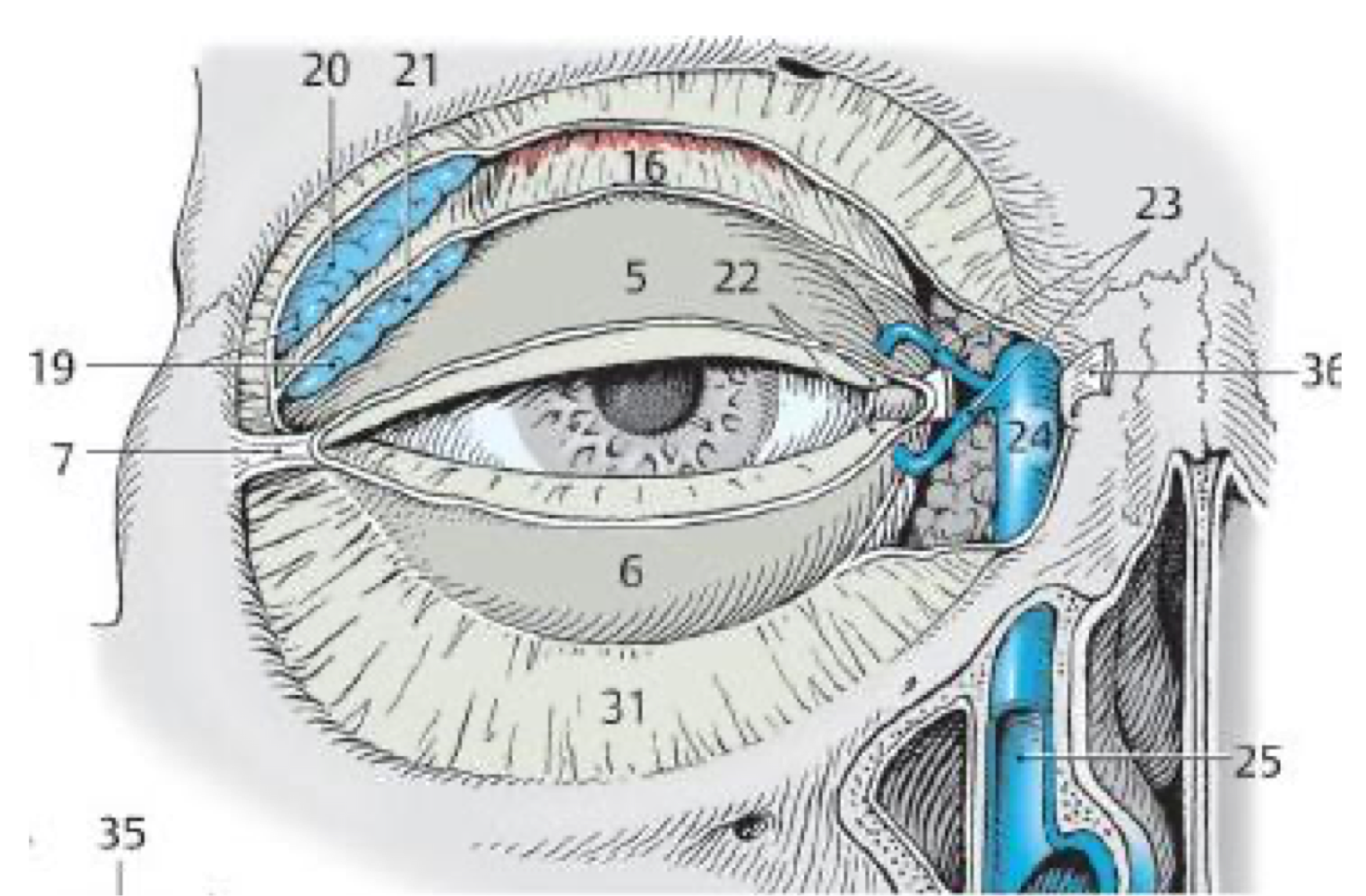
23
Lacrimal ducts
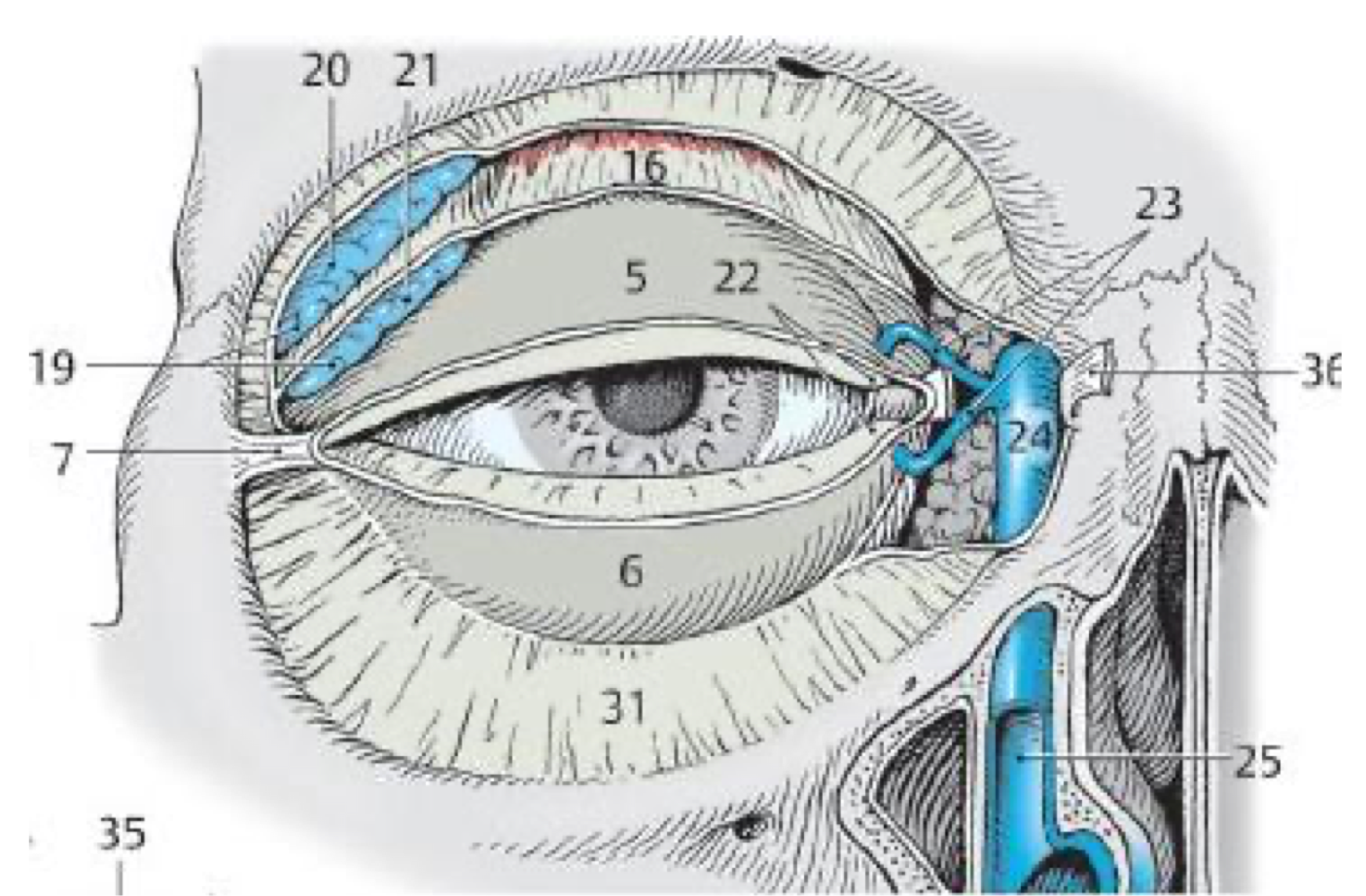
24
Lacrimal sac

25
Nasolacrimal duct
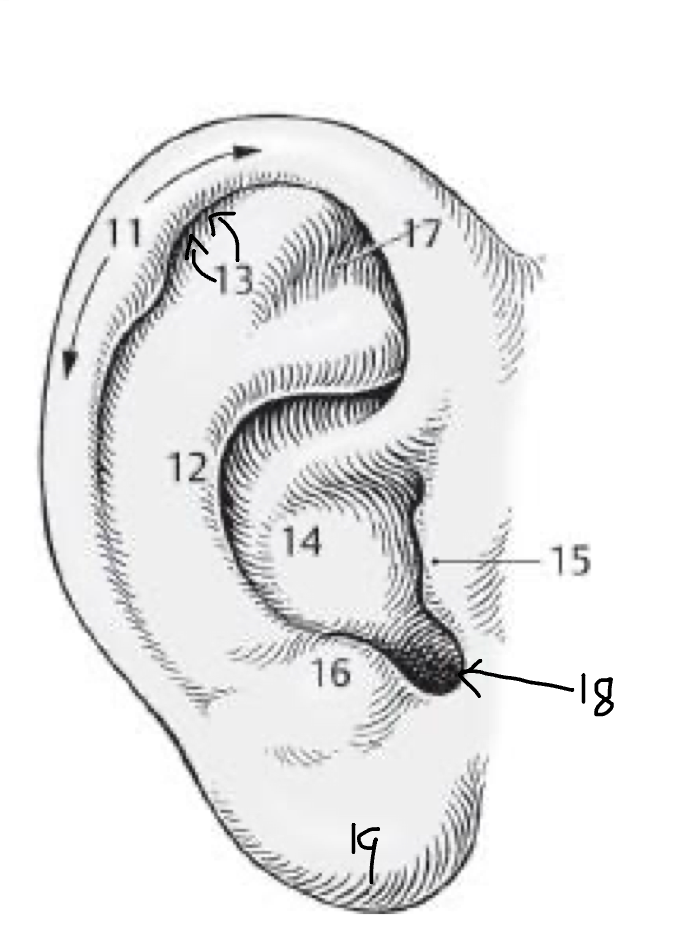
11
Helix
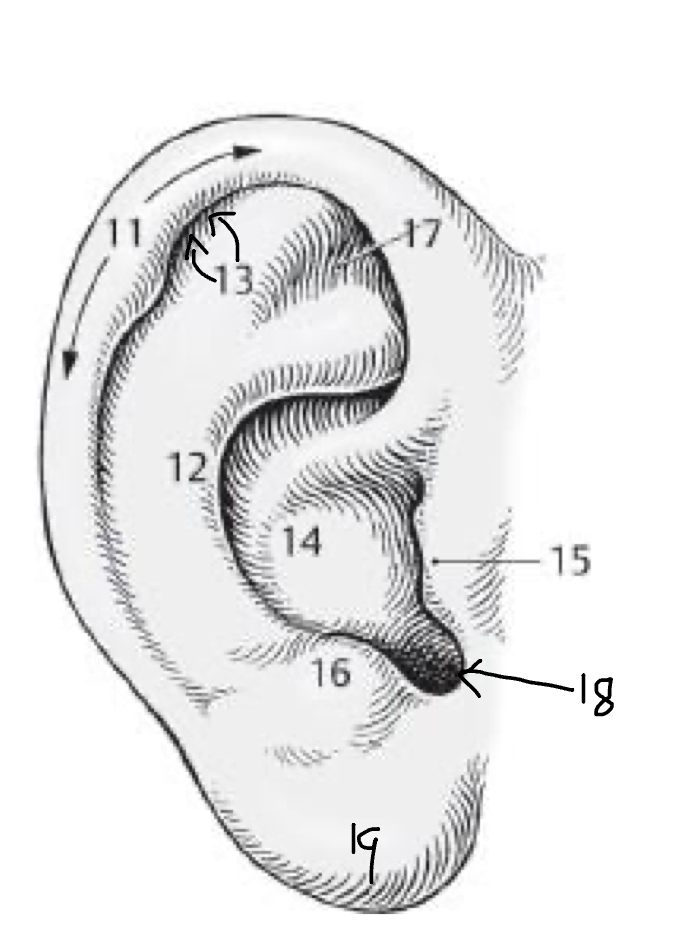
12
Antihelix