Organic Chemistry II Exam 1: Chapter 16 "Reactions of Aromatic Compounds"
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
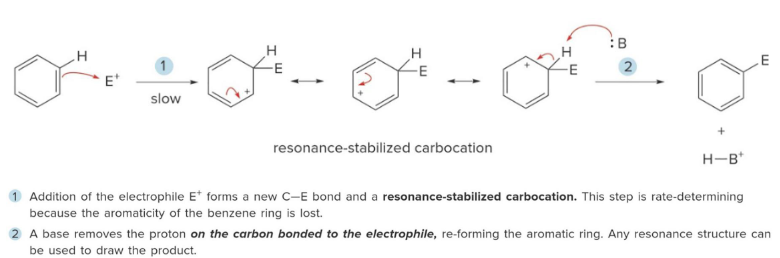
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
The addition of an electrophile, E+, to form a resonance stabled carbocation, followed by deprotonation with a base.
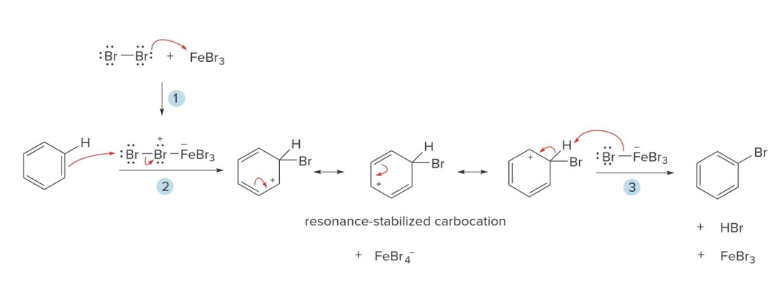
Halogenation
In this reaction, benzene reacts with Cl2 or Br2 in the presence of a Lewis Acid Catalyst (FeCl3, FeBr3) to create an aryl halide
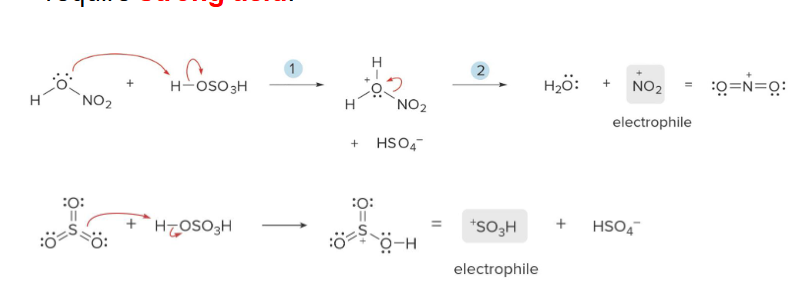
acid
In Nitration and Sulfonation, generating the electrophile requires a strong _____
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation
In this reaction, the treatment of benzene with an alkyl halide and a lewis acid forms an alkyl benzene
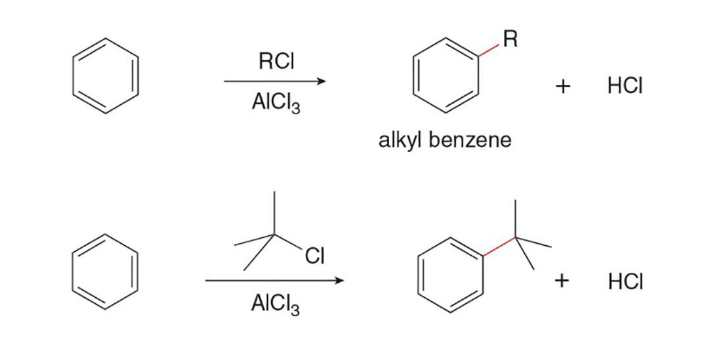
T
Vinyl Halides and Aryl Halides do not react in Friedel-Crafts Alkylation (T/F)

most
In Friedel Craft’s reactions, rearrangement occurs to create the (most/least) stable cation attachment to the main ring
Friedel Crafts Acylation
In this type of reaction, a benzene ring is treated with an acid chloride (RCOCl) and AlCl3 to form a ketone
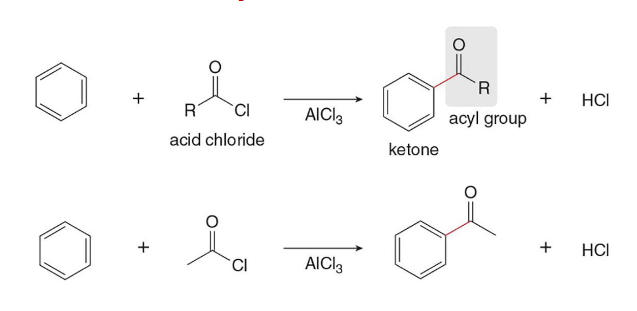
E (must be sp3)
What is the product of the following reaction?
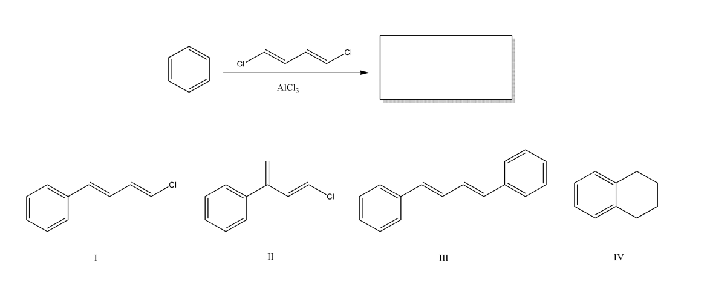
I and II
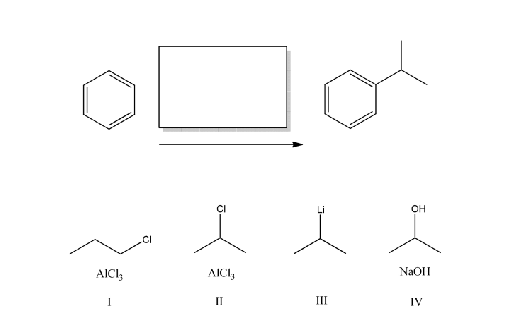
Which reagents will best complete the following reaction
electronegative
Atoms more __________ than carbon (N, O, and X) pull electrons away from carbon and thus exhibit an electron withdrawing effect (+). This is a deactivator that makes the reaction slower
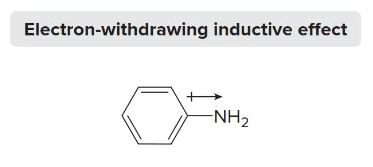
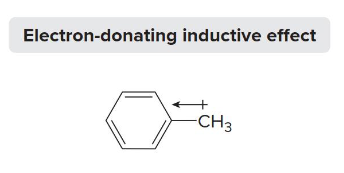
alkyl groups
Polarizable _______ donate electrons easily, thus exhibiting an electron donating inductive effect (-). This is an activator that makes a reaction faster.
T
(T/F) Induction and Resonance have opposite effects. Induction withdraws electron density, while Resonance donates electron density and stabilizes the molecule
resonance
When a neutral O or N atom is bonded to a benzene ring, the (resonance/induction) effect dominates and the net effect is electron donating
induction
When a halogen X is bonded to a benzene ring, the (resonance/induction) effect dominates, and the net effect is electron withdrawal
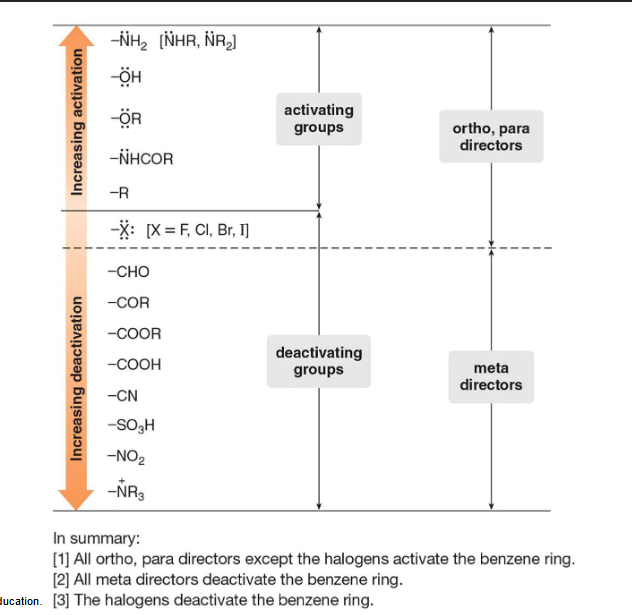
Ortho, Para
OH, CH3, and NH2 are what kind of directors?
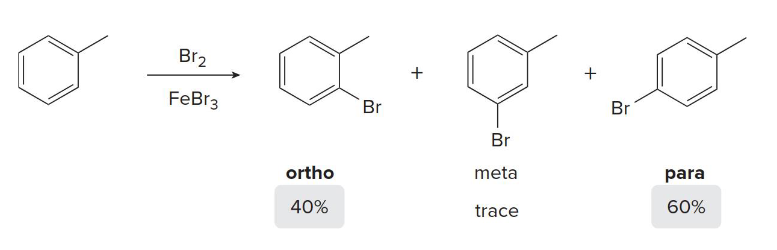
Meta
NO2, COOH, CN, and SO3H are what kind of director?
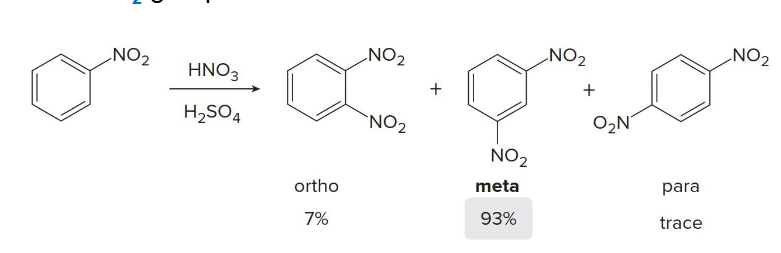
Acknowledged
Acknowledge the chart
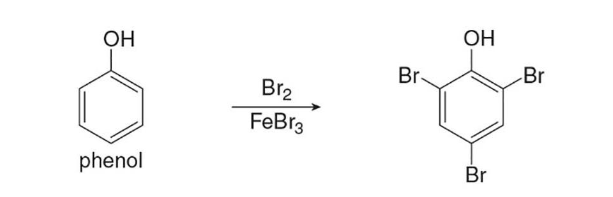
polyhalogenation
Benzene rings activated by strong electron donating groups (OH, ortho-para directors) undergo _____________ when treated with a halogen. Monohalogenation only occurs without an added catalyst
electron rich
Benzene rings deactivated by strong electron withdrawing groups (NO2, SO3H, any meta director, also NH2) are not (electron rich/electron deficient) enough to undergo Friedel Crafts reactions
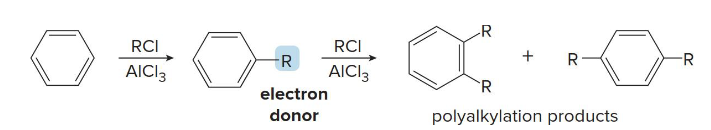
Polyalkylation
Since R groups are electron donators, treatment of benzene with alkyl halide and AlCl3 causes the benzene to be more reactive and causes further substitution, called this
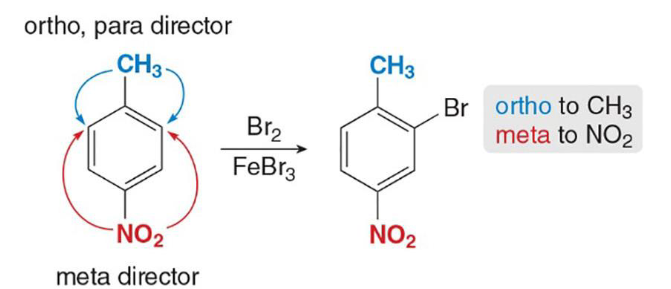
reinforcing
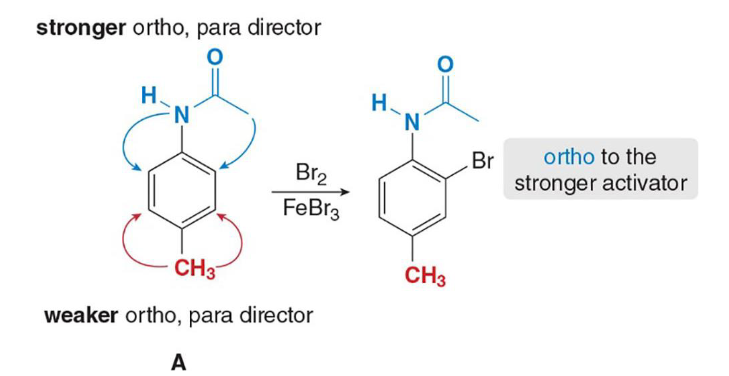
This is an example of (reinforcing/opposing) directing effects
Opposing
This is an example of (reinforcing/opposing) directing effects
Meta
No substitution can occur between two _____ substituents because of crowding (steric limitations)
Ortho/Para
With two para substituents as the goal for the reaction, which group must be added to the benzene first?
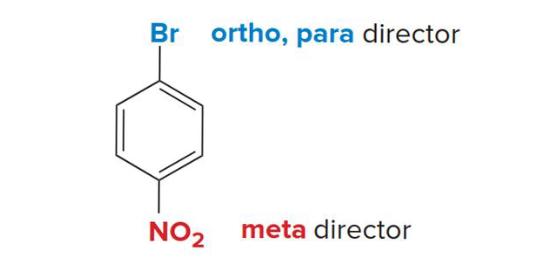
Nucleophilic aromatic subsitution
This kind of reaction results in the substitution of a halogen on a benzene ring by a nucleophile. Occurs by either addition elimination or elimination addition and creates a mixture of products (para and meta)
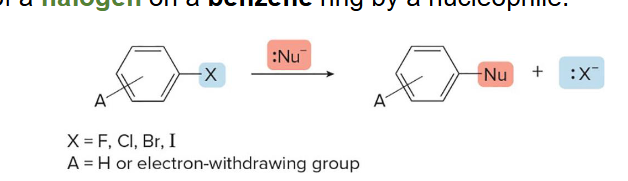
T
(T/F) In nucleophilic aromatic substitution, increasing the number of electron withdrawing groups increases the reactivity of the aryl halide, and increasing the electronegativity of the halogen also increases the reactivity of the aryl halide
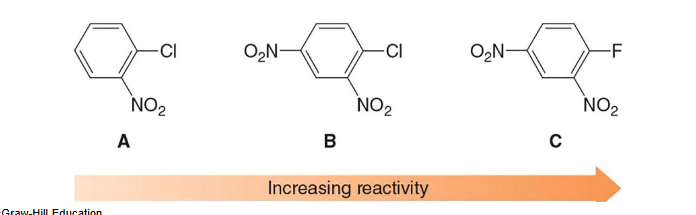
Acknowledged
Acknowledge the slide
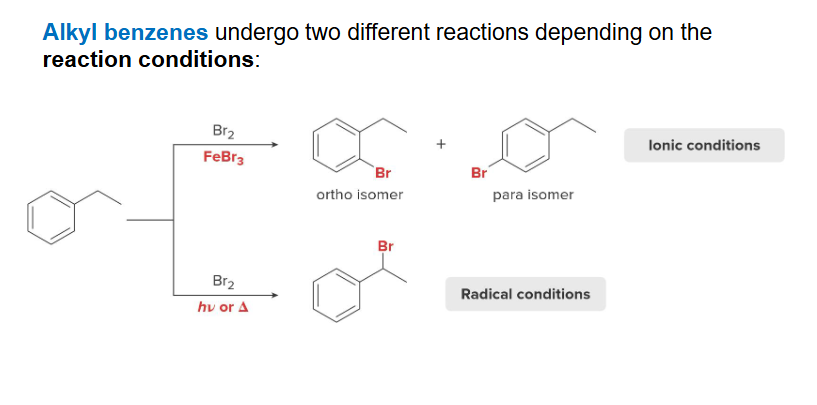
Acknowledged
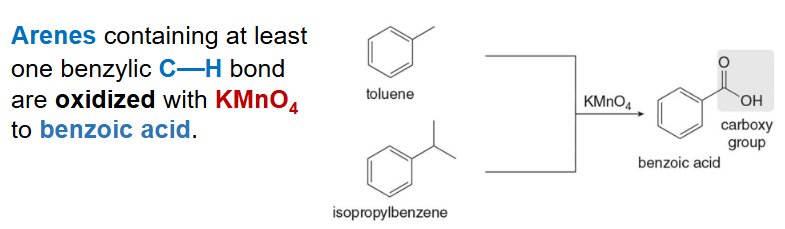
Acknowledge the slide
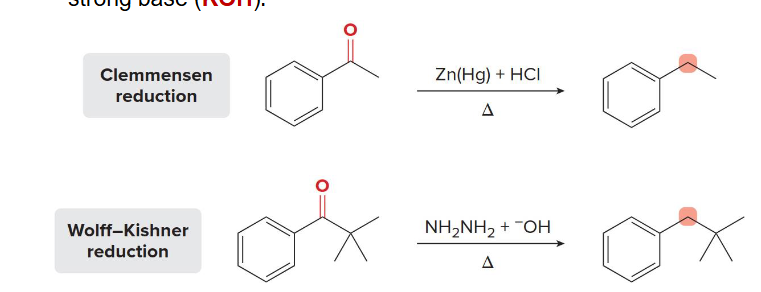
reduced
Ketones formed as products of Friedel-Crafts acylation can be _______ to alkyl benzenes by these two different methods
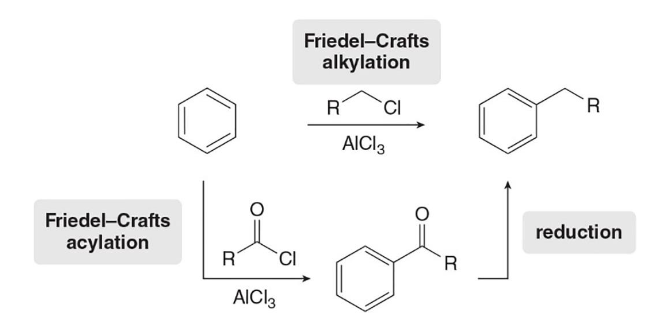
Acknowledged
Acknowledge the chart
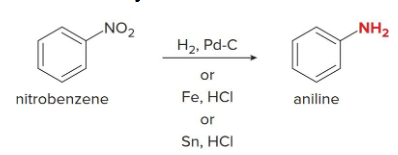
H2, Pd-C
A nitro group that has been introduced to a benzene ring by nitration of a strong acid can be reduced to an amino group (NH2) by what?