Ap bio: ecology
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Photoperiodism
A plant's response to seasonal changes in length of night and day
- flower bloom according to amount of uninterrupted darkness
Tropism
A growth response of a plant toward or away from a stimulus
Gravitropism
A growth response to gravity
- negative: growing up, away from the pull of gravity
Auxins
Hormones involved in plant-cell elongation, shoot and bud growth, and rooting.
- promote growth on one side of the plant
- tip of plant
Gibberellins
A class of related plant hormones that stimulate growth in the stem and leaves, trigger the germination of seeds and breaking of bud dormancy, and stimulate fruit development.
cytokinins
promote cell division, leaf enlargement, slow aging of leaves
ethylene
plant hormone that stimulates fruits to ripen
abscisic acid
inhibits cell growth, helps close stomata
biosphere
part of Earth in which life exists including land, water, and air or atmosphere
ecosystem
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.
community
All the different populations that live together in an area and interact with each other
simpson’s diversity index
used to measure biodiversity of a habitat
the higher the index value, the more diverse a community is
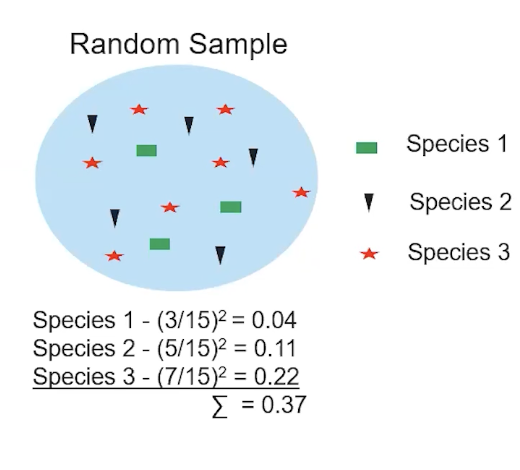
1 - sum(n/N)²
trophic cascade
negative effect the removal of or decrease in a key species has on other trophic levels
niche partitioning
decrease in competition over limited resources between two similar species because each species is accessing the resource in different ways
population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area
biomes
a broad, regional type of ecosystem characterized by distinctive climate and soil conditions and a distinctive kind of biological community adapted to those conditions.
- tundra, taiga, temperate deciduous forest, grasslands, deserts, tropical rainforests
carbon cycle
The organic circulation of carbon from the atmosphere into organisms and back again
producers
Organisms that make their own food
gross productivity
the total gain in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time
net productivity
the gain in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time that remains after deductions due to respiration
consumers
An organism that obtains energy and nutrients by feeding on other organisms or their remains.
- macromolecules --> smaller monomers
primary consumers
animals that feed on producers; ex. herbivores
secondary consumers
carnivores/omnivores that eat herbivores
tertiary consumers
carnivores that eat other carnivores
keystone species
A species that influences the survival of many other species in an ecosystem
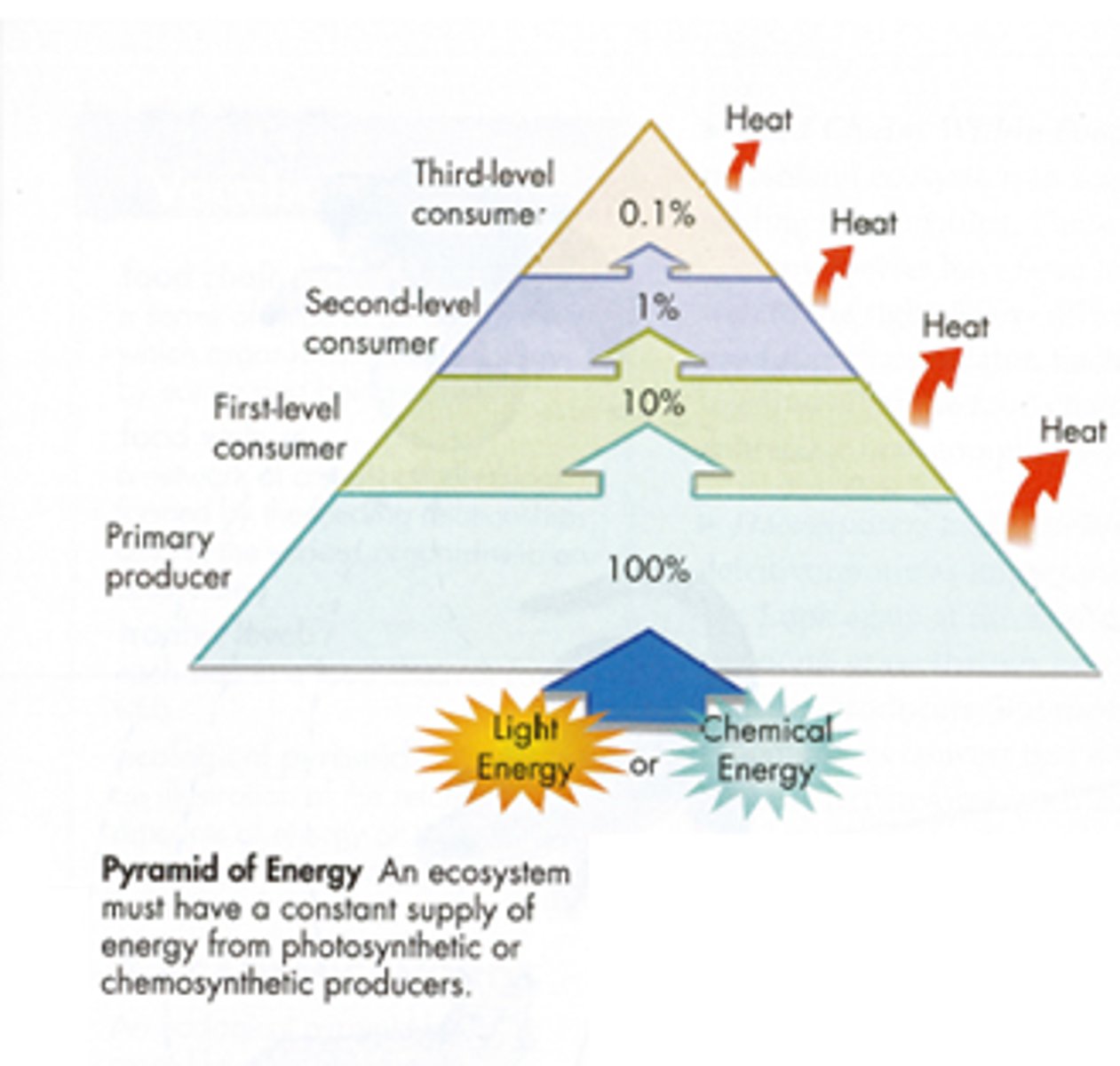
10% rule
Only 10% of the total energy produced at each trophic level is available to the next level. The amount of energy passed up to the levels of the food pyramid reduces as you go up.
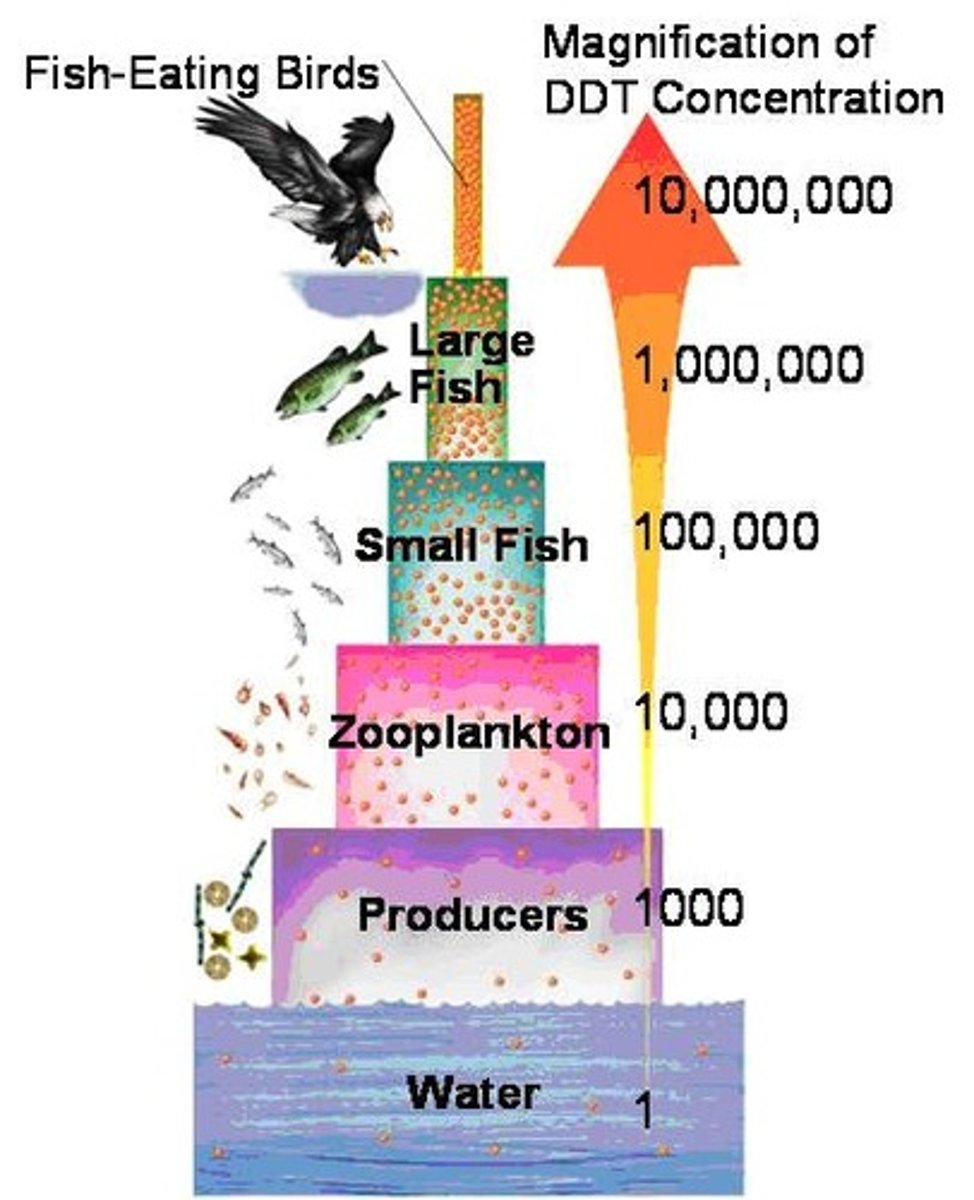
bioaccumulation
The accumulation of a substance, such as a toxic chemical, in various tissues of a living organism.
- animal who eats prey with a high concentration of toxin dies
biomagnification
accumulation of pollutants at successive levels of the food chain
population ecology
The study of populations in relation to the environment, including environmental influences on population density and distribution, age structure, and variations in population size.
population growth
births - deaths / N
density independent factors
limiting factor that affects all populations in similar ways, regardless of population size
- natural disasters
density dependent factors
factor that limits a population more as population density increases
- resources
r strategists
species that grow exponentially when environmental conditions allow them to reproduce
k strategists
species where organisms tend to reproduce later in life, have a smaller number of offspring, and are long living
- due to their lack of competition
ecological succession
series of gradual changes that occur in a community following a disturbance
primary succession
An ecological succession that begins in an area where no biotic community previously existed
pioneer organisms
The first to colonize a barren environment in primary ecological succession.
Sere/seral stage
each phase of succession
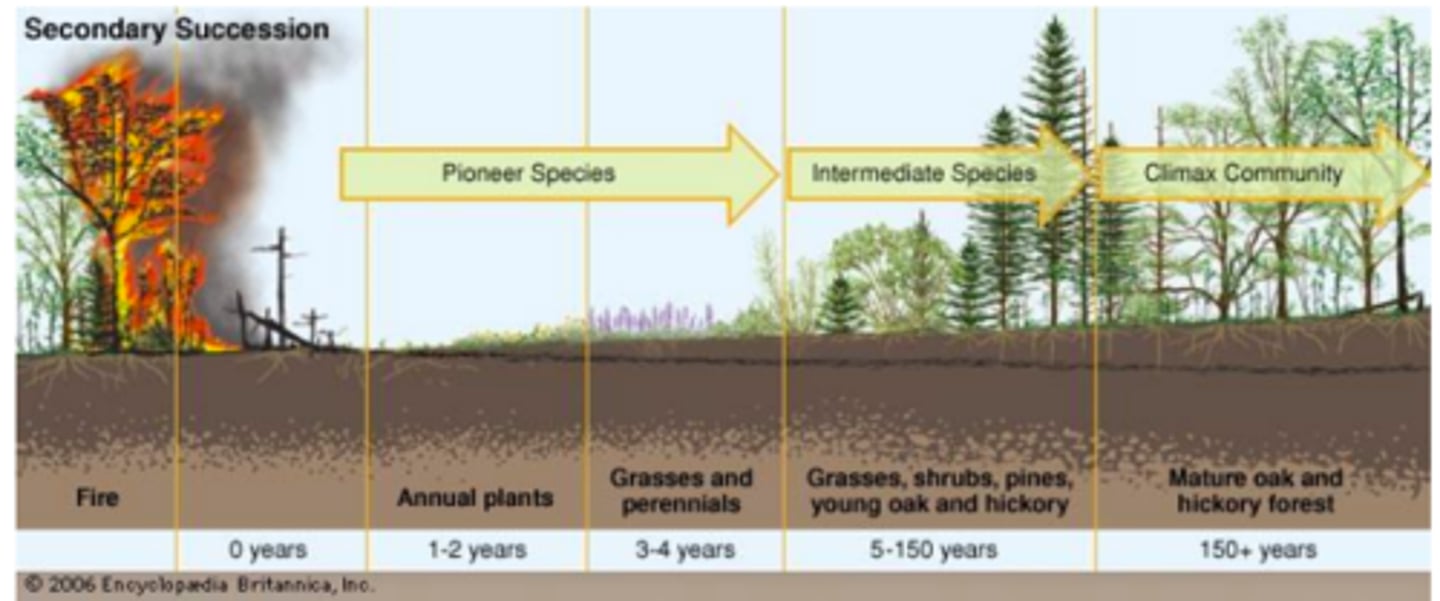
secondary succession
Succession following a disturbance that destroys a community without destroying the soil
ozone depletion
thinning of Earth's ozone layer caused by CFC's leaking into the air and reacting chemically with the ozone, breaking the ozone molocules apart
acid rain
Rain containing acids that form in the atmosphere when industrial gas emissions (especially sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides) combine with water.
desertification
Degradation of land, especially in semiarid areas, primarily because of human actions like excessive crop planting, animal grazing, and tree cutting.
DDT
A colorless odorless water-insoluble crystalline insecticide that tends to accumulate in ecosystems and has toxic effects on many vertebrates; became the most widely used pesticide from WWII to the 1950's; implicated in illnesses and environmental problem; now banned in the US.
Populations consist of:
A single specifies that:
Occupy the same general area
Rely on the same resources
Are influenced by similar environmental factors
Have a high likelihood of interacting with one another
Population density
# of individuals per unit area/volume
- can directly count # of individuals or work out an estimate based on indirect indicators or signs
clumping dispersion
Individuals "flock together" in bunches; can indicate a heterogenous environment or social interactions between individuals; most common (i.e. fish swim in schools & birds migrate in groups to avoid predation).
-usually prey, to avert predators
uniform dispersion
The pattern in which individuals are equally spaced throughout a habitat.
- territories formed based on need for resources
Random dispersion
Random spacing of individuals of the same species within an area.
- usually plants, because of the way that seeds are distributed
Demography
The scientific study of population characteristics, and what can cause growth and decline
Addition to population
births and immigration
population elimination
Occur through deaths and emigration
Two important demographic features
Age and gender ratio
Life tables
Average life expectancy of an individual
Survivorship curves
a graph that represents the distinct patterns of species survival as a function of age
Type 1 survivorship curve
low death rates during early and middle life and an increase in death rates among older age groups
- humans
type 2 survivorship curve
fairly constant death rate at all ages (small mammals and large birds)
type 3 survivorship curve
a pattern of survival over time in which there is low survivorship early in life with few individuals reaching adulthood
- sharp drop
- marine invertebrates (bivalves)