Geography #12-13: Urban Settlements & Urbanization
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Case Study: New York & Cape Town, pg. 75-84
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
What is urbanization?
An increase in the proportion of people living in towns and cities.
What is a market town?
A settlement originally serving as a place for farmers to buy and sell goods.
What is a port?
A settlement located on coasts, rivers, and lakes for the movement of goods and people.
What is an Industrial Town?
A settlement where raw materials are processed into manufactured goods, normally in factories.
What is a Tourist Resort?
A settlement where many tourists visit on their holidays, normally in an attractive coastal or mountain location.
What is a Residential settlement?
A settlement mainly made up of housing and a few shops, where the majority of residents live but do not work.
What defines a Commercial settlement?
A settlement that contains a large number of businesses.
What is a Cultural/Religious settlement?
A settlement that attracts people for educational or religious reasons.
What is the land in urban areas used for ?
Leisure & Recreation, Residential, Transport, Business & Commerce, Industry
What are the 4 types of urban settlements?
Town, Cities, Conurbation, Megalopolis
What is a town?
A rural settlement with better resources, development, and infrastructure than a village.
What differentiates a town from a village?
The major difference is the availability of resources, with towns having more basic facilities.
How does a city compare to a town?
Cities are larger in size and population, with greater economic functions and better transportation, quality of life, and education.
What is conurbation?
A large area of urban settlement formed by the merging of towns or cities that were initially separate.
What is a megalopolis?
A megalopolis is a super urban combination of various cities and defined as the “great city.”
What is an urban settlement model?
A simplified representation of how land is used in a city or town. It explains the patterns of different land uses such as residential, industrial, and commercial areas, and how they are organized within a city.
What are the 3 models that explain the organization of urban land use?
The Burgess Model, Hoyt Model, and Multiple Nuclei Model
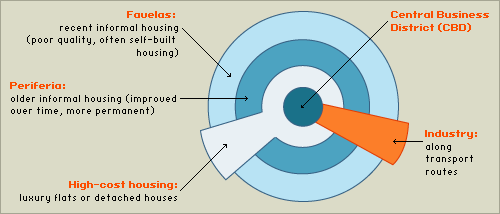
What are the differences in the structure of the land use between major settlements in a LEDC and a MEDC.
In LEDC, the high-class residentials are closer to the CBD, and the industry overlaps the high-cost housing. The quality of housing decreases as you move out from the CBD as many people are forced to live in shanty towns on the edge of the city.
In MEDC, that would never happen: high-class residents are placed on the very outer part of the ring as they do not wish to live close to the CBD or industries because of traffic, noise, and pollution.
What is the Central Business District (CBD)?
It is the city centre where most businesses and commerce is located.

What are the characteristics of a Central Business District (CBD)?
They have high/multi-story buildings, expensive land values, department stores or specialist shop (jewellers), shopping malls and pedestrian precincts, cultural/historical buildings, museums and castles, offices, finance, banks, administration, town hall (business sector), and bus and railway stations.
Why is the CBD located in the centre?
Because its a central location for road/railways to converge, the most accessible location for workers, and accessible to most people for shops and businesses.
Why does the CBD have these characteristics?
It has high/multi-story buildings as land in the CBD is very expensive, so buildings are built upwards to maximize space and profits.
It has expensive land values as it is in the centre of the city, the space is limited and the demand for land is very high, which increases its value. This is why there are only businesses that can afford high rents (like offices, finance, banks, administration) can operate here.
CBDs often developed first; the original core of the settlement, so they include cultural/historical buildings such as museums, churches and castles. They're also the seat of local or national government offices, since it's a central location.
The CBD is mainly for commercial activities like department stores or specialist shop (jewellers), shopping malls, banking, and offices, not for factories or homes, as people live elsewhere and commute.
They are pedestrian precincts and bus and railway stations to reduce traffic and pollution and to support the large number of people coming in daily.
What are some of the changes in a MEDC Central Business District (CBD)?
Pedestrianisation, Urban Renewal & Regeneration, Improved Public Transport Links, Growth of Shopping Centres / Malls. More Green Spaces & Street Furniture, Gentrification & New Housing, and Skyscrapers and High-Rise Developments
What is genetrification?
When run down terraced housing is bought by investors and improved into luxury apartments or townhouses appeal to young professionals who like to live near to the CBD for work and entertainment.
Why has gentrification and new housing become a change in the CBD (MEDC)?
To bring people back into city centres, reduce commuting, and make better use of land.
Why has skyscrapers & high-rise developments become a change in the CBD (MEDC)?
More tall office blocks have been constructed in CBDs because land is expensive, so companies build upwards to make the most of limited space.
Why has pedestrianisation become a change in the CBD (MEDC)?
Many CBD streets have been closed to traffic and made pedestrian-only zones to reduce congestion, lower pollution, and make shopping areas safer and more attractive for people on foot.
Why has Improved Public Transport Links become a change in the CBD (MEDC)?
More bus lanes, metro extensions, park-and-ride schemes, and cycle lanes have been introduced to encourage people to leave their cars at home, carpool, reduce congestion, and help people get in and out of the CBD more easily.
Why has more greenery become a change in the CBD (MEDC)?
More trees, benches, flower beds, and small public parks have been added to improve quality of life, create pleasant spaces for workers and shoppers, and make the area feel less crowded and concrete-heavy.
What is an urban sprawl?
When a city expands outwards over the surrounding countryside, often in an unplanned and uncontrolled way.
As a city grows, it land use changes. For example, Farmland can turn into..?
Housing estates to support a growing population and allow people to commute to work and not live in a crowdy, noisy area.
As a city grows, it land use changes. For example, old industrial areas can turn into..?
Shopping Malls/Apartements for regeneration, gentrification, and modern use of land.
As a city grows, it land use changes. For example, warehouses can turn into..?
Offices or hotels due to it being more profitable and in demand.
As a city grows, it land use changes. For example, parks/greenfield sites can turn into..?
Roads or new suburbs due to pressure to expand and develop.
What are some of the effects on rapid urban growth or urbanization?
Housing Shortages leading to growth of slums/shanty towns, traffic congestion from cars from long commutes and not enough roads/public transport, pressure on services, loss of green space as farmland and forests are cleared, and high land prices as there is high competition for property.
What are the effects of urban sprawl?
Loss of agricultural land, more car use leading to air & noise pollution, providing services is costly as its more expensive to provide electricity, water, roads over a large spread-out area, and causes environmental damage.
What probelms do urban areas cause?
Pollution, inequality, housing issues, traffic congestion, and conflicts over land use change.
What different types of pollution do urban areas cause?
Air Pollution from cars, factories, burning waste that releases carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxide, Noise Pollution from road traffic, people, weather and music which can cause mental stress, anger issues, & sleep deprivation, Water Pollution as rivers & lakes get polluted from sewage, waste dumping, or chemicals, & Visual Pollution as there can be ugly or overcrowded buildings, billboards, graffiti, litter making the environment unpleasant to live in.
What is inequality?
Extreme differences between poverty and wealth, as well as in people’s well being and access to things like jobs, housing, and education.
How does urban areas create inequality?
When there is unequal access to housing, jobs, and services. Wealthy areas have better schools, healthcare, transport, and job opportunities, while poorer areas like slums or inner cities may lack clean water, sanitation, and reliable services. High land prices force the poor into overcrowded housing far from the city centre, limiting their access to work and education. Poor transport and planning worsen this gap. In some cities, gentrification or development of inner city areas pushes out low-income residents, leading to land use conflicts. These inequalities are often caused by rapid urban growth, poor planning, and unequal investment.
Where may inequalities occur?
Housing Provisions, Access to Services, Access to open land, & Safety and Security
How do urban areas cause Housing Issues?
When many migrants move from rural areas, there are not enough houses or not enough affordable housing leading to slums, homelessness, overcrowding, or shanty towns. These houses may lack clean water, electricity, sanitation and happen when cities grow too fast for planning to keep up.
What are shanty towns, squatter settlement, slum, and favelas?
They are areas of housing built by people themselves out of material they can find, often around the LEDC cities. They are often illegally built and can have no sanitation, water, or electricity connection.
How do urban areas cause traffic congestion?
As city grows, more people arrive with vehicles, and because there are not enough roads leading to them get busy especially during peak commuting times (morning & early evening). This causes longer travel times, road rage, higher fuel use and worsens air & noise pollution.
How do urban areas cause conflict over land use?
It happens when different groups want to use the same land for different things. This occurs more in the rural urban fringe. As locals want to preserve a park, but a company wants to build a mall, residents want affordable homes but the government sells land for luxury apartments, or a river area is needed for flood control, but factories want to build there.

What are some possible solutions to fix the issue of pollution?
There can be an increase in public transport; expanding buses and trains to reduce car use and air pollution. Carpool to reduce the number of cars coming in and out of the city. Make and enforce strict laws on factories and vehicles that pollute and fine them. Make green spaces and create parks and tree-lined streets to clean the air and improve appearance.
What are some possible solutions to fix the issue of housing issues?
Site-and-service schemes provide new or cleared sites with basic services for people to buy at low cost, with low-cost loans to buy materials to make their homes, make high-rise developments and build upwards in cities to fit more people on less land, and completely remove squatter areas and rebuild them into suitable homes.
What are some possible solutions to fix the issue of inequality in the city?
Improving slums with clean water, sanitation, and electricity, have the government support people in poorer areas and invest in schools, clinics, and job training, and make affordable housing schemes by encouraging building low-cost homes to reduce informal settlements.
What are some possible solutions to fix the issue of traffic congestion in the city?
Investing in public transport such as trains, metros, cycle lanes, and bus lanes, park-and-ride schemes and let commuters park outside the city and use buses in, congestion charges and make people pay to drive in busy areas (like London), make low emission zones, encourage more car-pooling so that less cars are used on the road.
What are some possible solutions to fix the issue of land use conflicts in the city?
Make zoning laws and separate areas for housing, industry, and leisure to avoid clashes. Ensure public involvement and let communities be part of planning decisions. Make mixed-use developments and combine homes, jobs, and shops in one area to reduce conflict and travel.

What are the characteristics of a CBD in LEDC?
They are small, compact, and busy. They have government offices, banks, and small high-rise buildings. As well poor infrastructure.
What are the reasons for the characteristics of an LEDC CBD?
There is lack of planning, limited investment, and historical development around transport or colonial core.
What things have changed in the LEDC CBD over time?
Modern shopping malls and office towers have started developing due to foreign investment.
What are the characteristics of the suburbs in LEDC?
Gated communities, villas with gardens, reliable utilities and services.
What are the reasons for the characteristics of an LEDC suburbs?
They are built for wealthy locals and expats, far from pollution and crime, and have better transport access.
What things have changed in the LEDC suburbs over time?
It has expanded due to the growing wealthy class and an increased demand for secure housing.
What are the characteristics of the slums in LEDC?
It is overcrowded, poor housing, basic or services, informal settlements, bad living conditions, illegally built and have no sanitation, water, or electricity connection.
Why does an LEDC slum have these characteristics?
Rural to urban migration has caused housing shortages as there is too many people and not enough or expensive homes, forcing people out and living in slums as the land is cheap and unregulated. There is limited government support to provide people with better living conditions.
In the LEDC, how have the slums changed over time?
In some areas, slums have been upgraded thanks to government assistance and have been provide with better infrastructure and services such as sanitation, water, and electricity while others have been cleared for commercial use or roads.
What are the characteristics of an Industrial Area in a LEDC?
Scattered industries near the outskirts of the city or near rivers, poor waste disposal causing water pollution, and informal work.
Why does an LEDC Industrial Area have these characteristics?
Land is cheaper on the outskirts and there are fewer regulations. Close to informal settlements such as slums where they can get away with paying migrants for cheap.
In the LEDC, how has the Industrial Area changed over time?
Formal industrial parks have developed with the help of foreign investments. (ex. SEZs in India).

In the LEDC, what are the characteristics of the rural-urban fringe?
Rapidly expanding, mix of land uses, poor infrastructure, and contains informal settlements, such as slums.
What are the reasons that the LEDC rural urban fringe has these characteristics?
Unplanned urban sprawl, low land value, and weak regulations.
In the LEDC, what changes in the rural urban fringe has happened over time?
Informal housing, farming and even slums have grown more. Some improvement has been made through the help of NGO or government projects.
What are the characteristics of the suburbs in MEDC?
They are large detached residential areas located on the outskirts of the city, garages and bigger space, good schools, private gardens, and roads are not as straight as it is often in cul-de-sacs or wide avenues.
In the MEDC, why do the suburbs have these characteristics?
The wealthier population prefers quiet, safe, green areas away from the noisy, polluted city. They have good accessibility by car/train making it easy to commute to and from work in the city/town.
In the MEDC, what has changed in the suburbs?
There has been more gentrification and rising property prices. Sometimes it replaces low-income housing.
What are the characteristics of the slums in a MEDC?
Semi-detached or terraced houses, near the CBD/work, mix of public/private housing, and very packed (high density of people)

Why did the MEDC slums have these characteristics?
They were located close to employment areas such as factories as there was little public/private transport, being close made it easier to go to work & affordable housing for the working class was needed as they had just moved from rural areas.
In the MEDC, how have the slums changed over time?
They have been upgraded through regeneration schemes or gentrified, especially near CBD to attract new young workers and to also provide locals with better living conditions.
What are the characteristics of the MEDC Industrial Area?
They are modern, well-planned, they are located on the outskirts of the city/town, often located in industrial parks with good road access.
What are the reasons the MEDC Industrial Area has these characteristics?
There is cheaper land on the outskirts, access to ring roads, strict pollution laws.
In the MEDC, how has the Industrial Zone changed over time?
Deindustrialization led to old factories being converted into housing or commercial spaces.
What are the characteristics of the rural-urban fringe?
Much further from the CBD, often beyond the edge of the city on the other side of green space. It has new housing estates, business parks, and out-of-town shopping centres.
Why does the MEDC rural-urban fringe have these characteristics?
The price of land is cheaper, there’s more space, an increase in demand for larger homes, and has good transport links.
In the MEDC, what changes have been made in the rural urban fringe?
Urban sprawl controlled by greenbelts; increasing suburban development.
How does urban rapid growth happen?
When large numbers of people move from rural areas to cities, mainly in LEDCs and NICs. It is driven by a mix of physical, economic, and social factors.
How do physical factors cause urban rapid growth?
Natural disasters like droughts, floods, or poor soil makes farming and overall living conditions difficult in rural areas. In contrast, cities often have more stable conditions and access to clean water and healthcare.
How do economic factors cause urban rapid growth?
Cities offer more educational and job opportunities in factories, services, or construction. People leave rural areas due to poverty, lack of mechanized farming jobs, and low incomes to support their themselves or their familuy.
How do social factors cause urban rapid growth?
Urban areas have better education, hospitals, electricity, and entertainment. Rural areas often lack basic services such as eletricity or water, causing rural depopulation.
How does urban growth impact rural areas?
The population declines as young people migrate to cities, leaving behind an ageing population and labor shortages. Services like schools and clinics may close due to low demand of doctors, nurses, and teachers. Farmland can be abandoned, and local economies suffer.
How does urban growth impact urban areas?
It leads to overcrowding, pressure on housing, traffic congestion, unemployment, and pollution (air, water, visual, noise). The natural environment is damaged through deforestation, loss of green space, and water contamination. Cities may struggle to provide clean water, sanitation, waste disposal, and electricity. This results in the growth of squatter settlements (or shanty towns), which are illegal, overcrowded, poorly built areas found on the outskirts of cities, often without basic services like clean water, sewage systems, or electricity.
What are some possible solutions to reduce the negative impacts of urbanization?
Governments & Organizations can upgrade squatter settlements by improving housing and infrastructure (e.g., sanitation, water pipes). Build affordable housing closer to employment areas. Improve public transport to reduce congestion and air pollution. Create green belts to protect the natural environment from urban sprawl. Encourage rural development (e.g., better schools, roads, jobs) to slow rural-urban migration. Enforce better urban planning and zoning to avoid overcrowding and manage land use efficiently.