Chapter 12 Business Analytics IS-300
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
The Manager’s Job and Decision Making
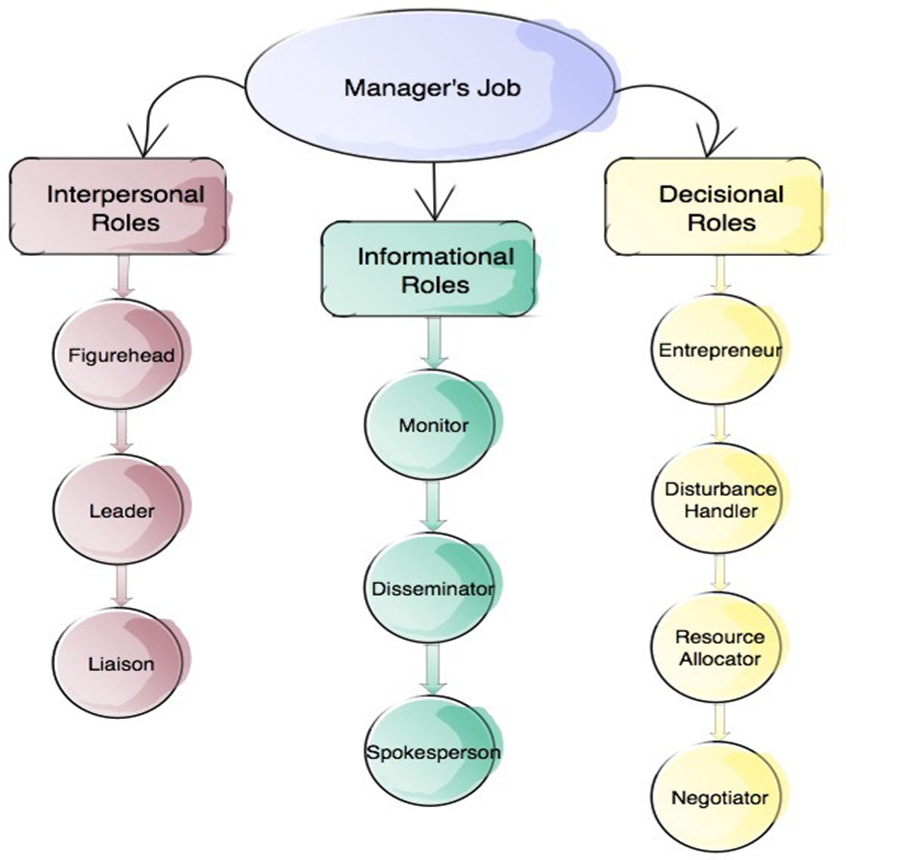
Mintzberg (1973) labelled managerial functions into three basic roles
interpersonal: leader, liaison, figurehead
informational: monitor, disseminator, spokesperson
decisional: entrepreneur, disturbance handler, resource allocator, negotiator
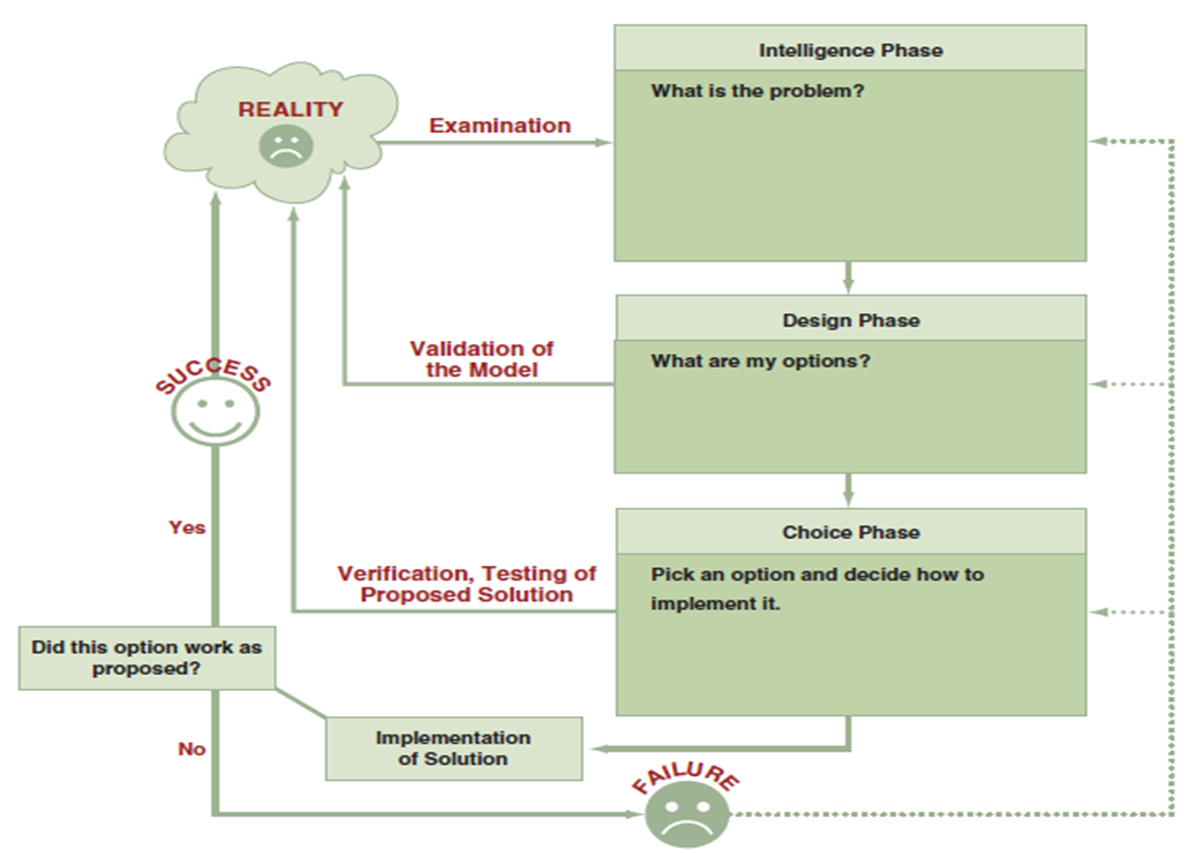
The process and phases in decision making
intelligence phase: what is the problem
design phrase: what are my options
choice phrase: pick an option and decide how to implement it
Why managers need IT support
too many alternatives to evaluate manually
time pressure for decisions
uncertainty and rapid change in environment
need for remote access, expert consultation, and group decision-making
Decision Framework
Structured: routine, repetitive (e.g., payroll)
Semi-structured: mix of standard & judgment (e.g., loan approval)
Unstructured: Novel, complex (e.g,. entering new markets)
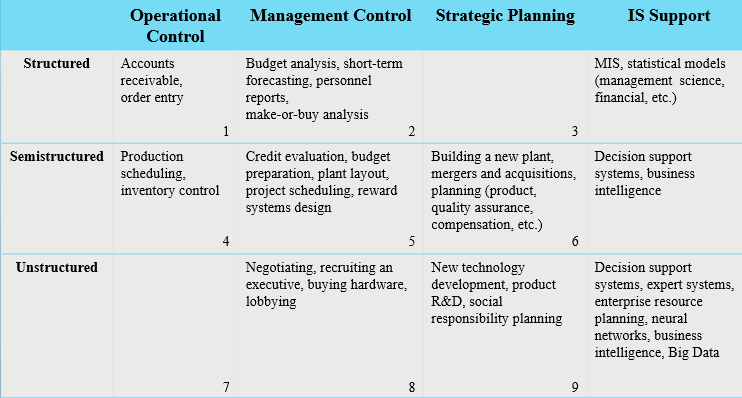
Nature of Decisions - Three broad categories of managerial decisions
Operational Control: executing specific tasks efficiently and effectively
Management Control: acquiring and use resources efficiently in accomplishing organizational goals
Strategic Planning: the long-range goal and policies for growth and resource allocation
Business Analytics
the process of developing actionable decisions or recommendations for actions based on insights generated from historical data
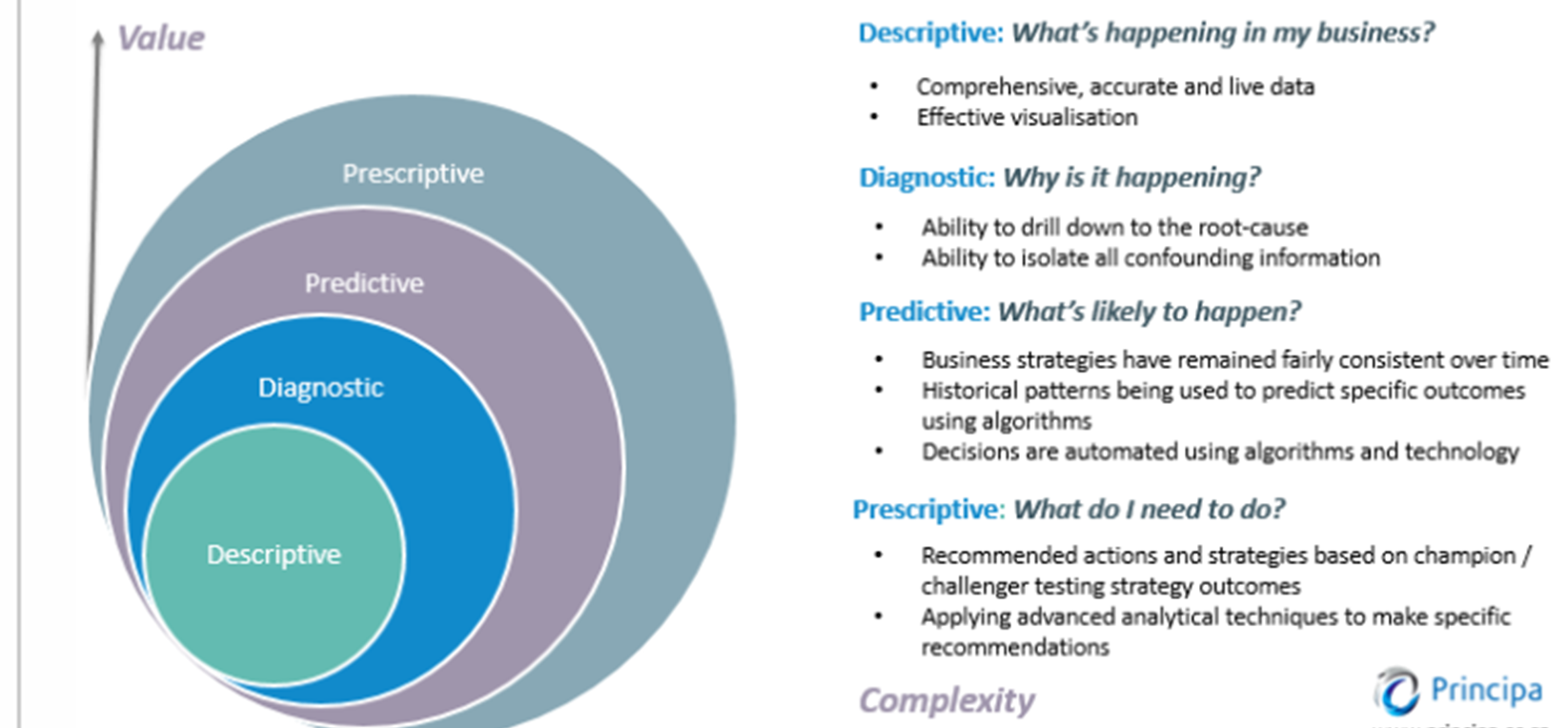
4 Types of Data Analytics
Descriptive Analytics: What’s happening in my business
Diagnostic Analytics: Why is it happening
Predictive: What’s likely to happen
Prescriptive: What do I need to do
Descriptive Analytics
def: analyzes past data, present in dashboards/reports to identify patterns and anomalies
tools: OLAP, DSS, Data Mining
Example:
Coca-cola: uses sales data to refine marketing
Amex analyzes transaction data for customer segmentation
Cardlytics: tracks consumer buying behaviors
Predictive Analytics
def: forecasts future outcomes using patters, trends, and statistical models
tools: data mining, variety of statistical procedures such as regression, multiple regression, and logistic regression
example:
COVID-19: Predicted infection trends and healthcare needs
Amazon: Product recommendations
Netflix: Content suggestions
UPS: Optimized delivery routes
Case Study: Target
predicted teen pregnancy based on purchase behavior —> marketing opportunities
Prescriptive Analytics
def: recommends actions and shows likely outcomes.
tools: statistical procedures—optimization, simulation, decision trees
example:
P&G: Optimized inventory & supply chains
IBM Watson: Personalized healthcare treatments
AirBnB: pricing strategies for rentals
Google: self-driving car decision-making
Descriptive Analytics Vs. Predictive Analytics Vs. Prescriptive Analytics
| Descriptive Analysis | Predictive Analysis | Prescriptive Analysis |
Summary | What happened? | What’s going to happen? | What should happen? |
Function | It uses data mining and data aggregation to discover historical data. | It looks at historical data and analyzes past data trends to predict what could happen. | It takes the conclusions gleaned from descriptive and predictive analysis and recommends the best future course of action. |
Pros | It’s easy to employ in daily operations. Little experience is needed. | It’s a valuable forecasting tool. | It offers critical insights into making the best, most informed decisions. |
Cons | It offers a limited view and doesn't go beyond the data’s surface. | It needs lots of historical data to work. It will never be 100% accurate. | It requires a lot of past data and often cannot account for all possible variables. |
Decision Support Systems (DSS)
Sensitivity Analysis: Effect of change in inputs
What-If Analysis: Predicts impacts of hypothetical scenarios
Goal-seeking Analysis: works backward from a desired output
Data Mining
def: process of discovering patterns in large data sets involving methods at the intersection of artificial intelligence, machine learnings, statistics, and database management systems
2 basic operations:
identifying previously unknown patterns (descriptive analytics)
predicting trends and behaviors (predictive analytics )
Data Mining techniques
Associate Rule Learning (if a customer buys bread, they are 80% likely to also buy butter)
Classification: assigns data to categories (e.g. spam folder)
Clustering: groups similar data points (e.g. customer segmentation)
Regression: predicts numeric values
Anomaly Detection: identifies unusual behavior (e.g fraud detection)
Sequential Patterns: discovers recurring events
Prediction
Decision trees
Decision rules
Artificial Neural Networks: detect complex patterns
Direct Marketing
can benefit from several data mining techniques: including not limited to: cluster analysis, regression analysis, classification, and decision trees
Customer Churn
identifies which customers may be leaving you
can learn why and/or try to retain them by
artificial neural networks & decision trees techniques can help companies identify customers who are likely to churn then take proactive action to retain them
Data Mining Deviation Analysis
DM techniques can help identify fraudulent transactions by studying credit cards or various behaviors as a previous transaction history data set
Neural Networks
utilize geo-spatiality to provide immediate information on crimes to enhance law enforcement decision making
can predict specific types of crime using location and time information and predict a crime’s location when given the crime and time of day
The Capabilities of Dashboards
Drill down
CSF’s
KPI’s
Status access
Trend analysis
Exception reporting
Geographic Information System (GIS)
def: a computer-based system for capturing, integrating, manipulating, and displaying data using digitized maps. Its most distinguishing characteristic is that every record or digital object has an identified geographical location
ex: Children’s National Health Center: enabled clinic to identify hotspots where burn injuries were occurring on a Map, ex, the Hispanic community, a prevention program could be developed and tailored to reduce the risk