Power Diodes
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is the main function of a power diode? -
A diode allows current to flow in only one direction-from anode to cathode-while blocking current in the reverse direction.
What happens to current when a diode is forward biased? -
It conducts a large current with a small forward voltage drop.
What happens when a diode is reverse biased? -
Only a tiny leakage current flows until breakdown occurs.
What is the peak-inverse voltage (PIV) rating of a diode? -
The maximum reverse voltage the diode can withstand without breaking down.
How is power dissipation in a diode calculated? -
Power = forward voltage drop * forward current.
Why is switching time important for diodes? -
It determines how fast the diode can change from conducting to blocking; slower diodes are fine for 50-60 Hz, fast-recovery ones are used for high-frequency circuits.
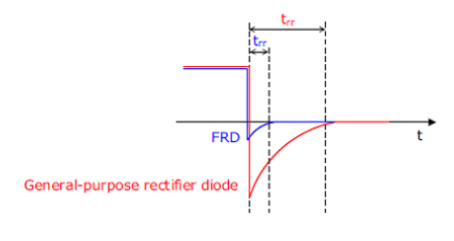
What is a fast-recovery or high-speed diode? -
A diode designed with short reverse-recovery time so it can switch quickly in high-frequency applications such as PWM circuits.
Name three key diode ratings. -
(1) Power dissipation (2) Peak inverse voltage (3) Switching time.
What is a flyback or snubber diode used for? -
It provides a path for inductive current when a switch turns off, protecting components from voltage spikes.
Give examples of diode applications in power electronics. -
Rectifiers, clamping circuits, voltage multipliers, reverse-polarity protection, spike suppression, and solar-panel bypass diodes.
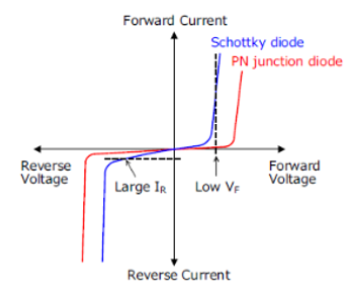
How does a Schottky diode differ from a normal silicon diode? -
It uses a metal-semiconductor junction, has lower forward voltage (approximately 0.3 V), and switches faster but handles lower reverse voltage.
Why are diodes used in rectifier circuits? -
They convert alternating current (AC) into pulsating direct current (DC) by conducting only during one half of each cycle.
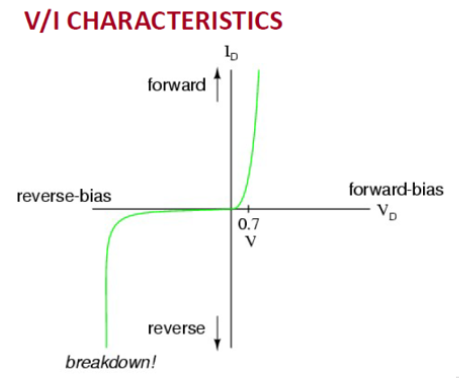
Describe the I-V characteristic curve of a diode. -
The curve has three regions: (1) In forward bias, current rises sharply once the forward voltage exceeds about 0.7 V for silicon; (2) In reverse bias, only a small leakage current flows; (3) Beyond breakdown voltage, current rises rapidly in reverse direction.
What happens at the knee of the diode I-V curve? -
It's the point where the forward voltage is high enough that the diode begins to conduct heavily, marking the transition from non-conduction to conduction.
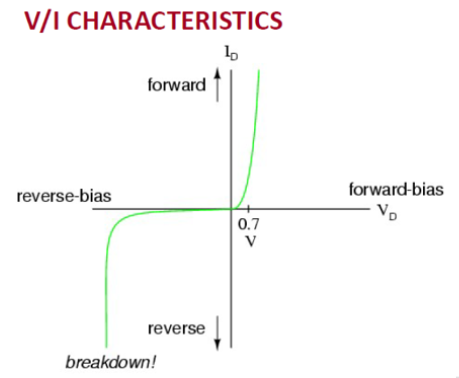
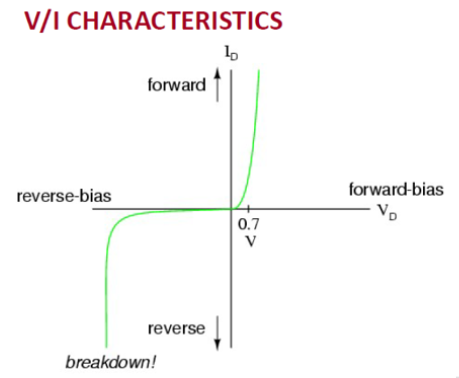
Describe how a diode behaves in forward and reverse bias on a graph. -
On a graph with voltage on the x-axis and current on the y-axis, the forward-bias region shows an exponential rise in current after the threshold; the reverse-bias region is nearly flat until breakdown.