Interior Design Illustrated: Key Concepts and Principles
1/666
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
667 Terms
Interior Design
The art of enhancing interior spaces.
Interior Space
Enclosed areas within buildings for human use.
Design Vocabulary
Terminology specific to design disciplines.
Interior Building Elements
Structural components within interior spaces.
Environmental Systems
Systems managing indoor climate and comfort.
Lighting
Use of artificial or natural light in design.
Acoustics
Study of sound behavior in interior spaces.
Finish Materials
Surface materials used for aesthetic appeal.
Furnishings
Furniture and accessories in interior design.
Bibliography
List of sources referenced in the book.
Index
Alphabetical listing of topics covered.
Preface
Introduction outlining the book's purpose.
Glossary
Definitions of terms used in the book.
Copyright
Legal protection for the book's content.
Limit of Liability
Disclaimer regarding the book's accuracy.
ISBN
International Standard Book Number for identification.
Published
Date when the book was made available.
Acid-free Paper
Paper that resists deterioration over time.
Interior Architecture
Designing interior spaces with architectural principles.
Space (Architecture)
Volume within structures designed for activities.
Interior Decoration
Enhancing interior aesthetics through furnishings.
21st Century
Current century from 2001 to 2100.
Customer Care Department
Support service for product inquiries.
Permissions Department
Handles requests for content reproduction.
Technical Support
Assistance with product-related technical issues.
Library of Congress
National library of the United States.
Printed in the USA
Indicates the book's place of printing.
Interior Design
The art of creating functional, aesthetic spaces.
Interior Space
The volume in which interior design occurs.
Design Principles
Fundamental concepts guiding design choices.
Sustainable Materials
Eco-friendly resources used in design.
Indoor Air Quality
Measurement of air cleanliness in interiors.
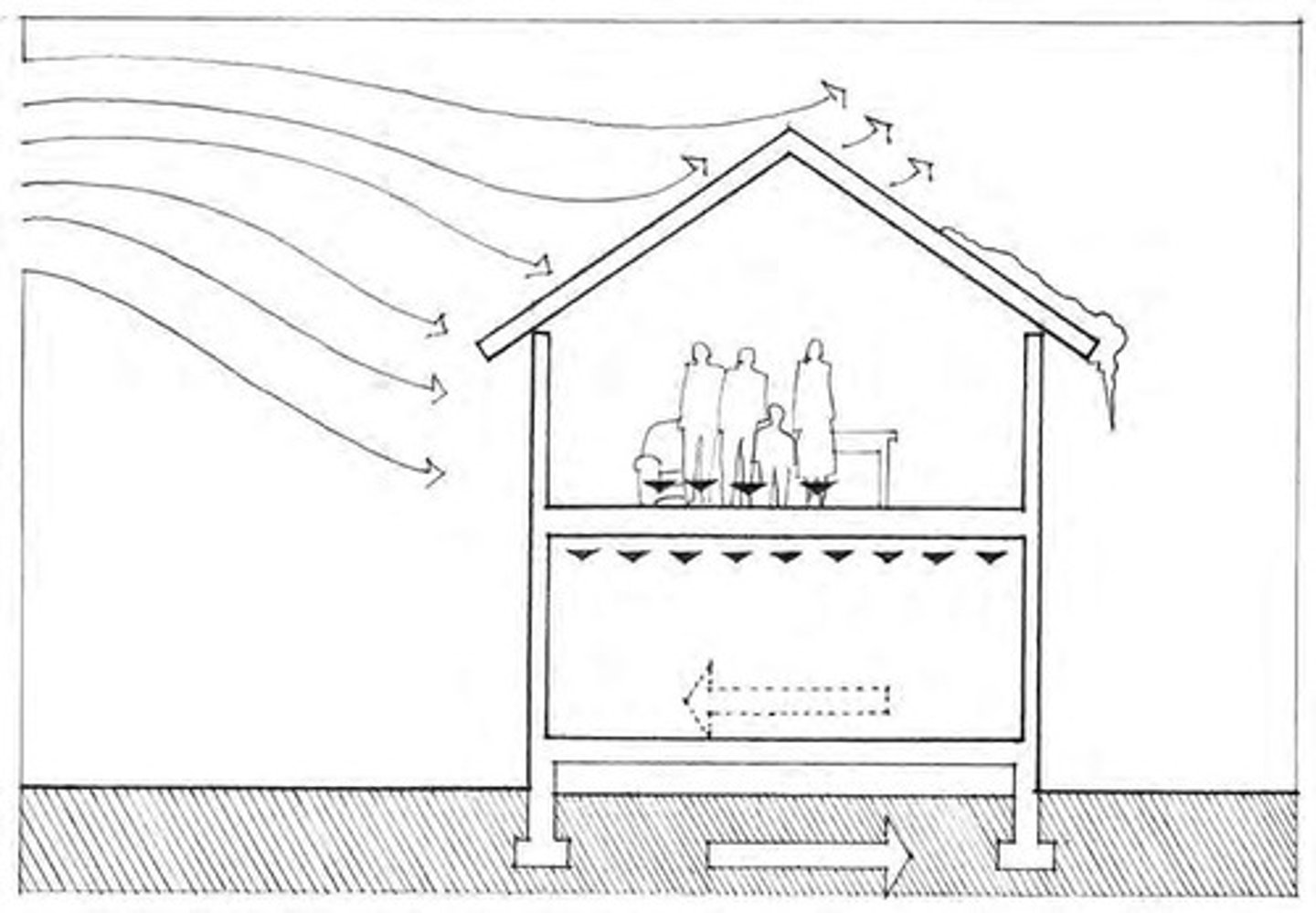
Lighting
Use of artificial and natural light in design.
Furnishings
Movable and built-in components in interiors.
Design Vocabulary
Terminology specific to visual design principles.
Environmental Systems
Systems controlling climate within interior spaces.
Finish Materials
Surface treatments modifying architectural elements.
Bariatric Design
Design accommodating larger body types.
Aging in Place
Design allowing seniors to live independently.
Visitability
Design ensuring accessibility for all visitors.
International Code Council (ICC)
Organization setting building safety standards.
Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
Law ensuring accessibility for individuals with disabilities.
Visual Art
Art form focusing on aesthetics in design.
Three-Dimensional Design
Design considering height, width, and depth.
Architectural Space
Physical space defined by building structures.
Design Patterns
Arrangements of elements in a cohesive manner.
Functional Qualities
Usability aspects of interior spaces.
Structural Qualities
Physical integrity and support of spaces.
Aesthetic Qualities
Visual appeal and beauty of interiors.
Computer Technology
Digital tools enhancing design processes.
Illustrations
Visual representations conveying design concepts.
Design Relationships
Connections between elements affecting overall design.
Diagrams
Simplified drawings demonstrating design principles.
Space
Inherently formless area defined by relationships.
Architectural Space
Defined by geometric elements like point and plane.
Column
Marks a point in space, visible in 3D.
Two Columns
Define a spatial membrane for passage.
Columns and Beam
Delineate edges of a transparent plane.
Wall
Opaque plane separating portions of space.
Floor
Defines a field of space with boundaries.
Roof
Provides shelter for the space beneath.
Exterior Space
Designer's response to functional and contextual conditions.
Building Form
Architecture's response to site and environmental factors.
Merging with Site
Building integrates seamlessly with its surroundings.
Dominating Site
Building stands out prominently against its context.
Surrounding Space
Building captures a portion of exterior space.
Defining an Edge
Building marks a boundary of exterior space.
Exterior Walls
Interface between interior and exterior environments.
Thin Walls
Transparent, merging inside and outside spaces.
Thick Walls
Heavy, isolating controlled interior from exterior.
Windows and Doorways
Openings that transition between spaces.
Spatial Transitions
Spaces mediating between outside and inside.
Visitability
Designing homes for accessibility for mobility impairments.
Interior Space
Defined by bounding floor, wall, and ceiling.
Shelter and Enclosure
Perception created by enclosing architectural elements.
Architectural Elements
Define physical limits of rooms and spaces.
Amorphous Space
Undefined area before elements are introduced.
Geometric Elements
Fundamental shapes used to articulate space.
Building Scale
Proportions of a building relative to its context.
Sustainable Design
Design minimizing environmental impact and resource use.
Technical Aspects
Structural and construction requirements in design.
Expressive Qualities
Aesthetic characteristics influencing architectural image.
Entrances
Mark transitions between different spaces.
Spatial Qualities
Characteristics of space including light and proportion.
Interior Design
Enhancement of architectural space through layout and furnishings.
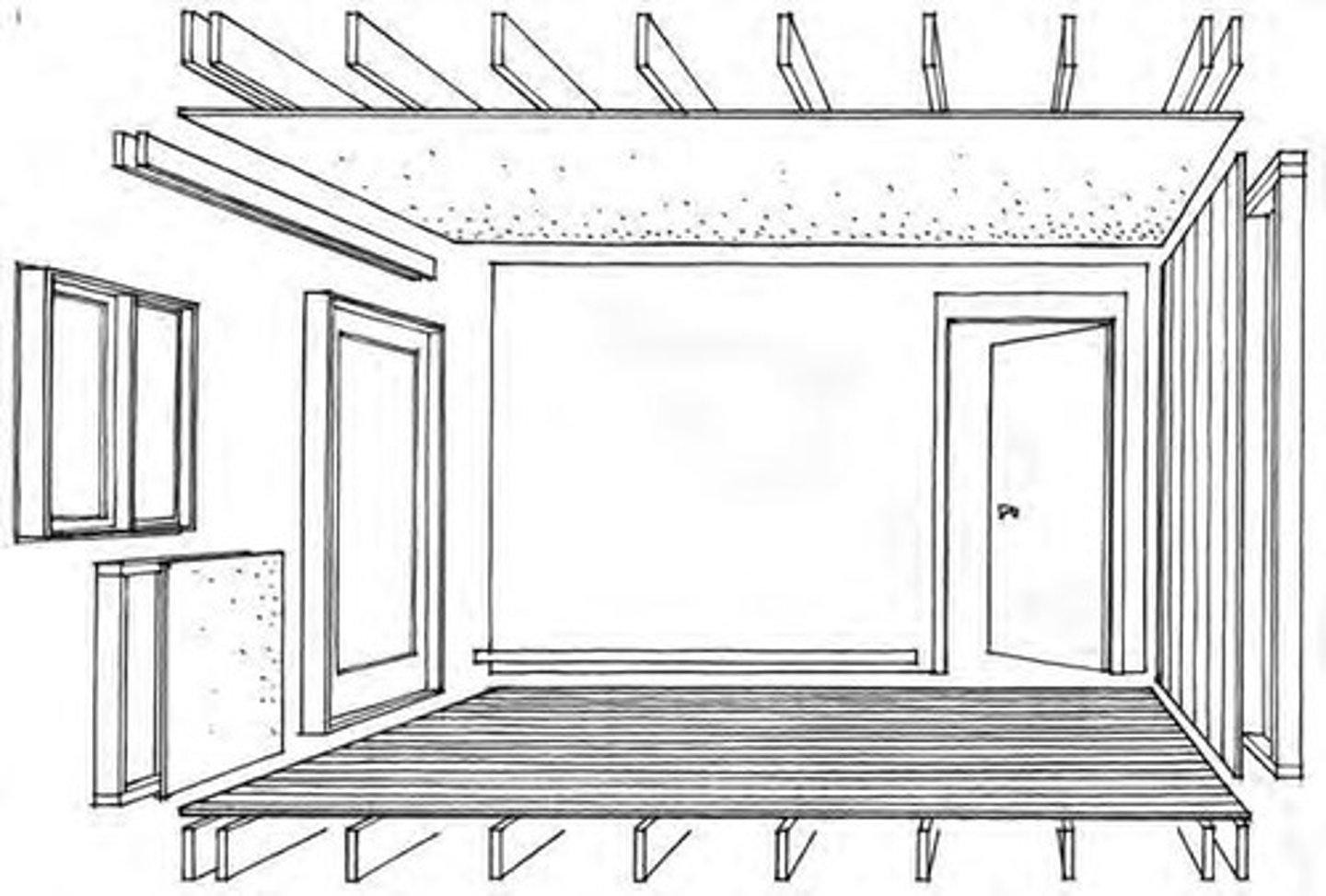
Superstructure
Vertical extension of foundation, includes columns and beams.
Foundation System
Substructure anchoring building to the ground.
Dead Loads
Static vertical load from structural components.
Live Loads
Movable load from occupants and equipment.
Dynamic Loads
Loading from wind and earthquakes.
Building Envelope
Exterior elements protecting interior from environment.
Enclosure System
Defines interior space with walls and ceilings.
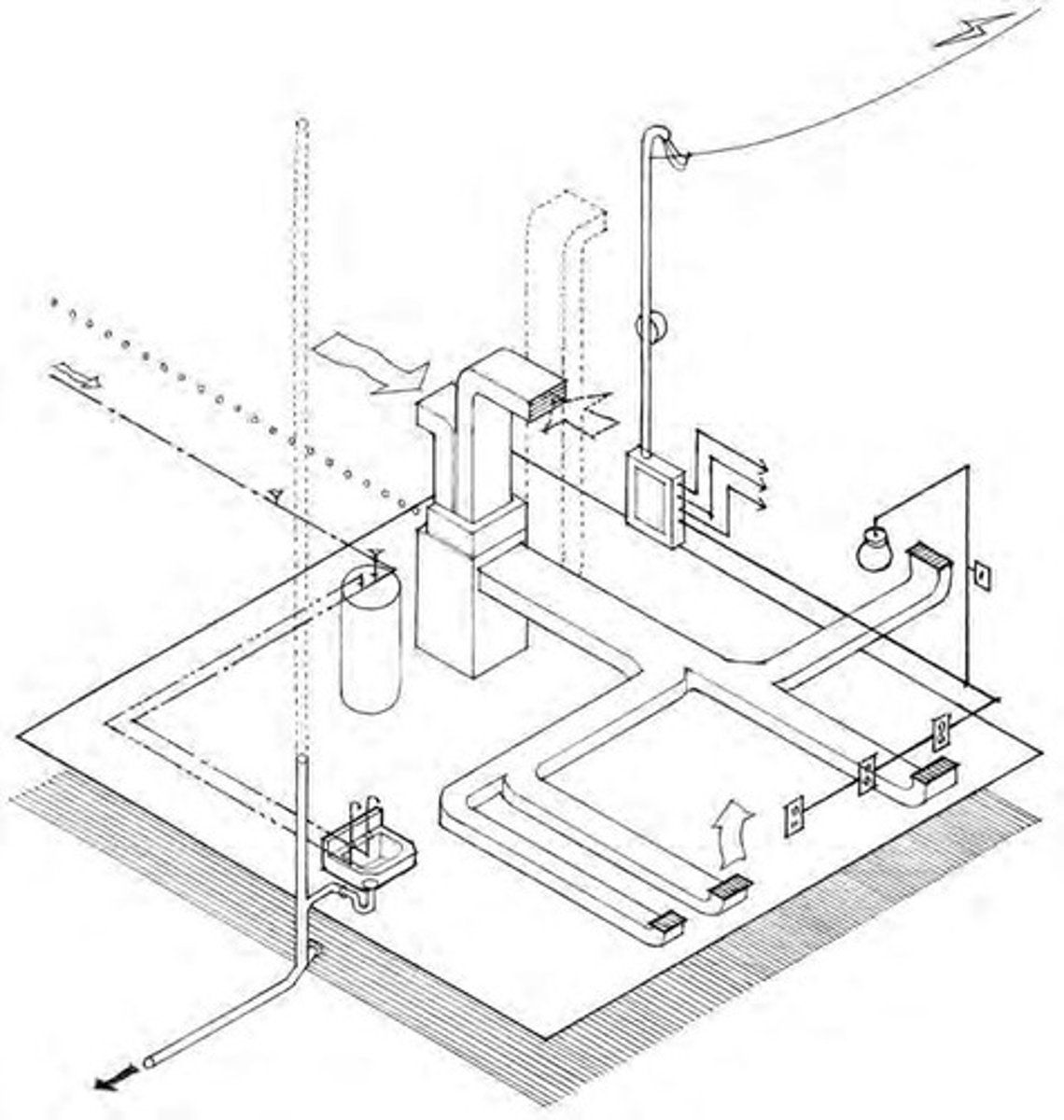
Building Services
Systems providing essential services like HVAC and plumbing.
Mechanical Systems
Provide heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning.
Plumbing Systems
Supply water and dispose of waste.
Electrical Systems
Control and distribute power for various needs.
Structural Systems
Physical systems supporting building loads.
Columns
Vertical supports in the superstructure.
Beams
Horizontal supports transferring loads to columns.
Bearing Walls
Walls that support loads from above.