Sport psychology 2
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is a group
Two or more people sharing an identity and working towards a common goal
What is social loafing
Loss of individual effort in a group due to lack of motivation
Factors affecting cohesive team
Environmental factors such as location contributes to team cohesion by creating common environment
Style of.leadership as it affects relationship with members
Personal factors - motivation and personalities
The extent to which players towards a shared goal
Cooperation between team members
Size of group as that can lead to social loafing
What is the ringlemann effect
The decrease in contribution of individuals as group size increases- athletes believe others will compensate for their efforts
What is Steiners group productivity theory
Actual productivity = potential productivity - losses due to faulty processes
What is social loafing theory
Loss of individual effort in a group due to lack of motivation
What is Weinburgs cohesion theory
Task cohesion - how committed teammates are to achieving pre - determined goal
Social cohesion - how much team members enjoy being together
What is Carrons conceptual model of cohesion
4 factors affecting a cohesive team
Environmental (group size, time, facilities, age)
Personal (motivation, personality, ability)
Leadership (behaviour, personality, relationship to the group)
Team factors (nature of task, team ability)
What is Tuckman’s Theory (group development)
Forming (lack clarity)
Storming (problem solving)
Norming (clarity of purpose)
Performing (motivation and pride)
What is a goal
An object or aim for an individual
What is Goal setting
The system of specifying long term performance targets and short term objectives and methods to achieve these
What are the SMART(ER) targets
Specific - should be specific to what athlete is trying to achieve
Measurable - the goal is measurable allowing progress to be determined
Achievable - is it possible to achieve your goal in the circumstances
Recorded - The goal is measured and tracked
Time bound - should be a time that goal should be completed in
Evaluate - athlete should see if goal should be adjusted
Realistic - goal must be achieved but still challenging
What are the types of goals
Short term, medium term, long term which can be used for microcycles, mesocycles, and macro cycles
Realistic and aspirational goals - what is possible for you to achieve, what would be your dream to achieve
outcome goals, performance goals process goals - did you win/lose, did you perform well, did you have improvements in technique
Subjective goals, objective goals - going out and trying your best, or having a goal based on your performance
What is attribution
Process of giving reasons for behaviour and assigning causes of events
What is learned helplessness
Mental state that is caused by failure and lack of success
What is attribution re- training
The coach changing an individuals perception on failure so it doesn’t impact future performance
What is weiners attribution theory
2 dimensions:
Locus of causality (internal + external) - something to do with the performer + something to do with an outside source
Locus of stability (stable + unstable)
Something that is unchangeable
Something that is changeable
Internal stable - refers to ability of performer
External stable - refers to task difficulty
Internal unstable - refers to the effort of the performer
External unstable - refers to Luck
What is self confidence
The level of trust an individual has in their own ability
What is self efficacy
Confidence in specific situations
What is self concept -
The way an individual views themselves based on perception of actions and how others see them
what is the humanist approach of self concept
Perceived self - view you have on yourself
Ideal self - what you wish you were really like
Self esteem/ self worth - how much value you place on yourself
What is vealeys model of sport specific confidence
Self confidence trait (SC- trait) = consistent personality trait, how confident you are in your abilities in general
Self confidence state (SC - state) how confident you feel in that situation right then
Competitive orientation - expectation of success, opportunity to achieve a performance goal
3 factors that improve self efficacy
Personality -introvert/extrovert, type a/ b personality, state/trait anxiety
Situation - task difficulty, weather, luck, audience, importance of event
History - previous performance success, stage of learning: cognitive, associative, autonomous, experience as a performer
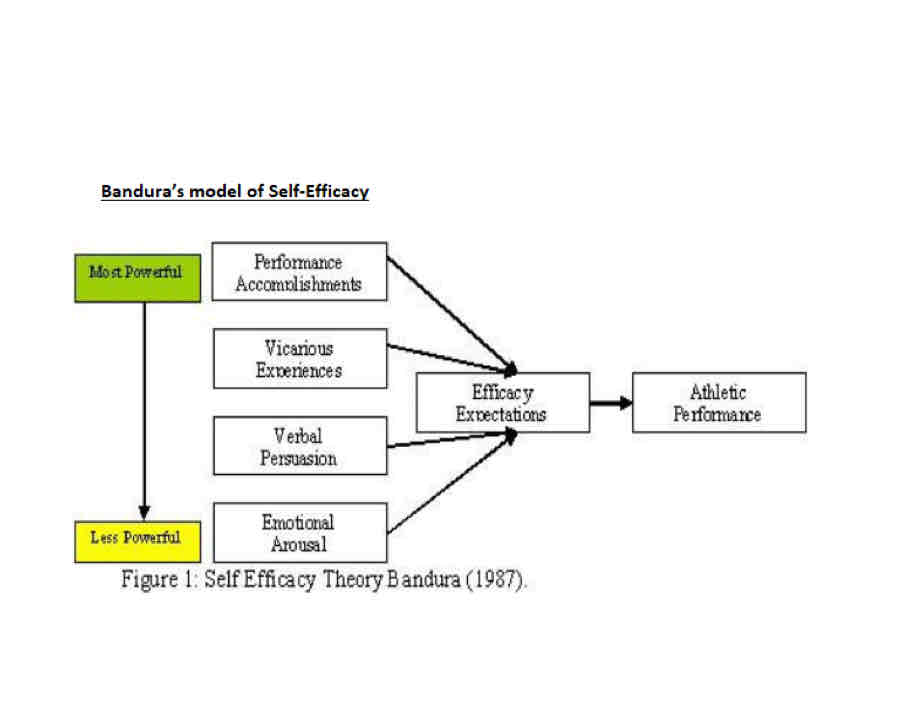
4 main factors of banduras model of self efficacy
Past experiences/performance accomplishments - success leads to high levels of confidence
Vicarious experiences - watching others perform a task increases confidence
Verbal persuasion - encouragement from coach/ other develops confidence
Optimal arousal - correct level of arousal builds confidence
What is leadership
Behavioural process influencing individuals and groups towards goals
Effective leader qualities
Good communication
Motivation
Enthusiasm
Being good at sport or having good knowledge of the sport
Clear vision of goal needed to be achieved
What are emergent leaders
What are prescribed leaders
Emergent = leaders that come from within the team, they are skilful and selected by the team
Prescribed = leaders that are appointed by an external source
Advantages and disadvantages of an emergent leader
Advantage = can win hearts and minds of teammates
Disadvantage = may have friendships in team group which can affect judgement
Advantage and disadvantage of prescribed leaders
Advantage = could add creativity, carry more authority and power
Disadvantages- not work on friendships, this might delay decision making
What are the three leadership styles
autocratic - are task orientated and are dictatorial. They make most of the decisions and tend to be demanding and commanding, they show little interest in individuals of the group.
Democratic - person orientated and value views of others in the group, tend to share decisions and show interest of individuals in the group.
Laissez faire - makes very few decisions and gives little feedback allowing members to do as they wish
3 theories of how leaders are created
Trait theory
Social learning theory
interactionalist approach
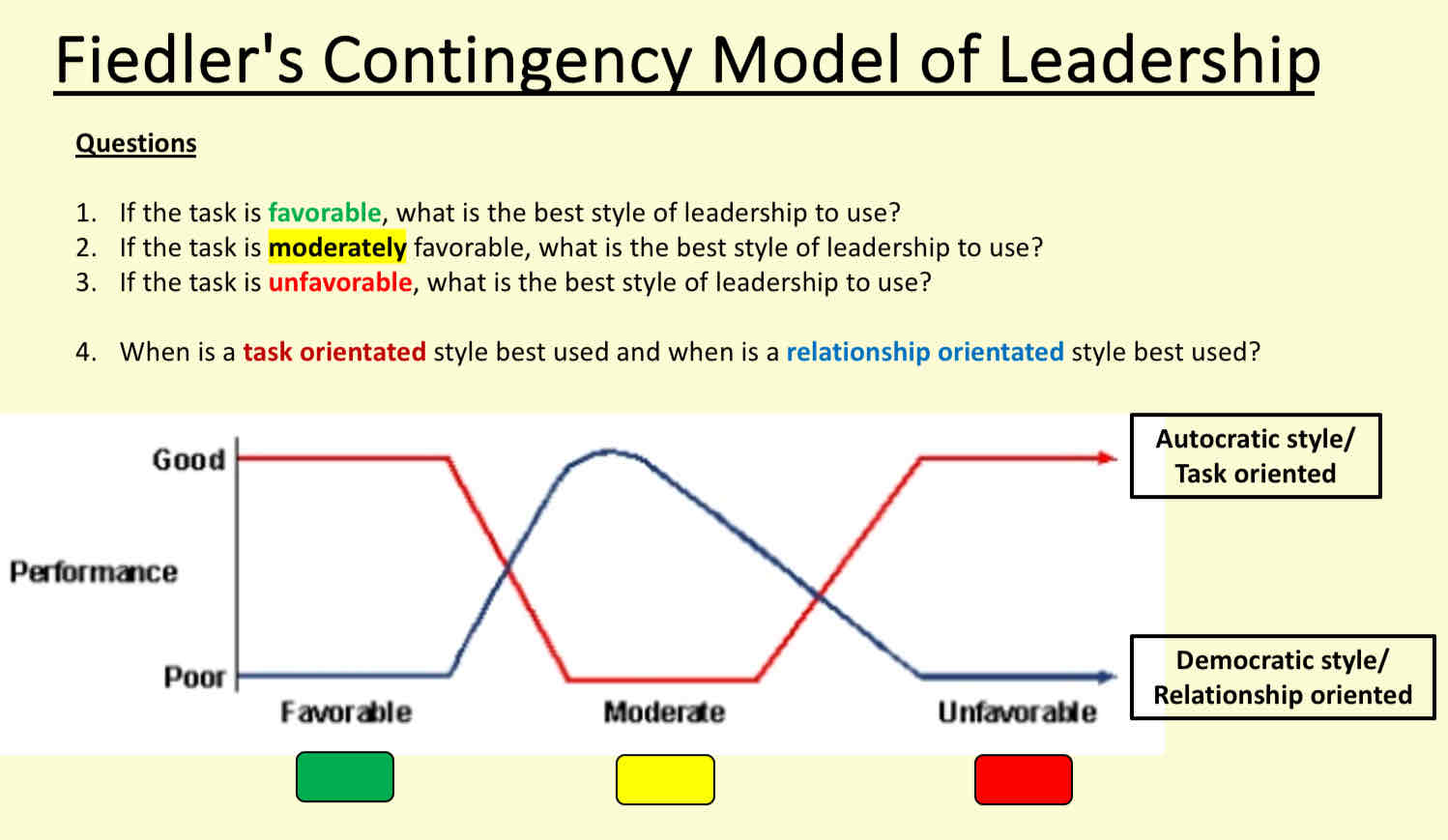
What is Fielders contingency model of leadership
Involves task orientated (autocratic leader) and person orientated (democratic leader)
If favourableness is high or low then a task orientated leader is required. Eg: highly unfavourable situation, bus is stuck in traffic and team are late for a sports competition a task orientated leader is to sort out team quickly. Eg: highly favourable - team has arrived early in competition task orientated leader is required to go through tactics and strategies
If favourableness is moderate a person orientated leader is required , team is on time might be missing a few players a person orientated leader tells people they have to play in less preferred positions but still trying to keep them happy.
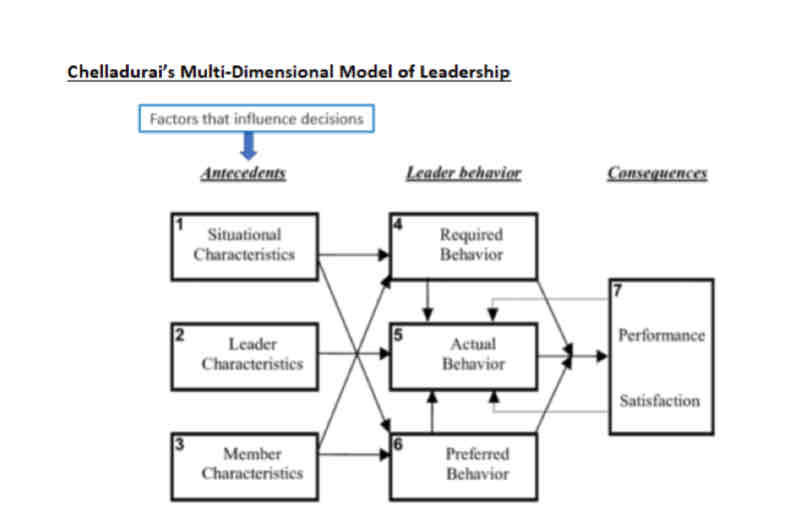
What is Chelladurai’s Multi - Dimensional model of leadership