Cancer & Treatment Part 0.5 (copy)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What is cancer
"Cancer is a disease where control of cell growth is lost, leading to a solid mass of cells called a malignant tumor, unlike benign tumors."
What are the current treatment modalities for cancer
Surgery removes visible tumors
Radiotherapy destroys fast-dividing cells
Chemotherapy targets proliferating cells,
Hormone therapy inhibits hormone-dependent cancers
Targeted therapy blocks specific pathways
Immunotherapy enhances the immune system's cancer-fighting ability.
Why do primary tumors become life-threatening
"Primary tumors obstruct vessels and organs, but death most often results from metastasis, spreading to other body sites, making surgery impossible."
What are hematological cancers
"Hematological cancers, like leukemias, involve a buildup of large numbers of white blood cells in the blood, distinct from solid tumors."
What is a tumor or neoplasm
"A tumor (neoplasm) is an abnormal tissue mass resulting from neoplasia, where deficient growth control mechanisms lead to uncontrolled cell proliferation."
What is a sarcoma
"Sarcoma refers to tumors in mesodermal tissues, including connective tissue, bone, and muscle, such as osteosarcoma (bone cancer)."
What is a carcinoma
"Carcinoma refers to tumors of epithelial tissues, like mucous membranes and glands, including cancers of the breast, ovary, lung, and pancreas."
How do normal cells appear histologically
"Normal cells have a large cytoplasm surrounding a darker, clear nucleus with a fairly round border in clusters."
How do cancer cells appear histologically
"Cancer cells have irregular nuclear borders and a nucleus that occupies most of the cytosol, contrasting with normal cells."
How do cancer cells resemble their origin in early tumor growth
"In early tumor growth, cancer cells often resemble their original tissue but lose this appearance and function as growth progresses."
How do normal adult tissues maintain cell numbers
"Normal tissues maintain steady cell numbers; some (e.g., liver) have little proliferation or loss, while others (e.g., bone marrow) balance fast division with cell loss."
What causes tumor growth in cancer
"Tumor growth results from an increased proliferation rate outpacing normal control, causing cells to pile up due to lost growth suppression."
How do tumors sustain growth in later stages
"Tumors secrete factors to attract blood vessels (vascularization) for nutrients, with outer cells accessing oxygen and the hypoxic core signaling necrosis."
What transforms a normal cell into a cancer cell
"A normal cell transforms into a cancer cell by losing growth control, forming a primary tumor that can metastasize into secondary tumors."
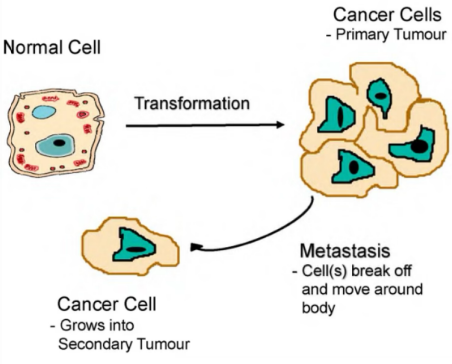
What is metastasis
"Metastasis is the spread of solid tumor cells to new body sites, forming secondary cancerous growths."
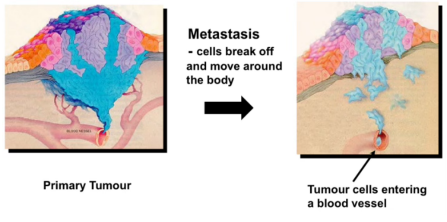
How do tumor cells penetrate lymphatic and blood vessels
"Tumor cells penetrate lymphatic vessels to reach lymph nodes or directly invade weak-walled capillaries for systemic spread."
How do tumors spread across body cavities
"Tumors spread across body cavities (e.g., ovary to stomach) from one organ to another."
Why is metastasis deadly
"Most cancer deaths result from metastatic spread to vital organs, with tumors infiltrating tissue and causing pain by affecting nerve endings."
What is the cancer stem cell (CSC) hypothesis
"The CSC hypothesis states that a tumor contains multipotent, tumorigenic cancer stem cells capable of self-renewal and differentiation, reconstituting tumor heterogeneity."
Where have cancer stem cells been identified
"Cancer stem cells were first isolated in acute myeloid leukemia and later characterized in solid tumors of the breast, brain, lungs, liver, prostate, pancreas, ovaries, kidneys, and colon."
What markers identify cancer stem cells in head and neck cancer
"In head and neck cancer, cancer stem cells show high aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) activity and CD44 expression."
How do cancer stem cells contribute to treatment resistance
"Cancer stem cells' slow proliferation and high ABC transporter expression allow them to evade treatments targeting fast-dividing cells and pump out cytotoxic agents."
How does cisplatin affect cancer stem cells
"Cisplatin enhances Bmi-1 expression, a self-renewal regulator, enabling cancer stem cell accumulation via symmetrical division."
Why are cancer stem cells linked to relapse
"Cancer stem cells resist chemotherapy and radiotherapy, remaining dormant for years before causing tumor regrowth, explaining relapse after remission."
How do cancer stem cells originate according to the hypothesis
"A stem cell transforms into a malignant cancer stem cell via oncogenic mutation, generating a tumor with differentiated cells and a limited CSC population."
Why does the heart rarely develop cancer
"The heart muscle rarely develops cancer (though its lining can form sarcomas), possibly due to its critical role and evolutionary protection against such mutations."
What age group is most affected by new cancer diagnoses
"Most new cancer diagnoses (65-70%) occur in people aged 60 and older."
What are the top four most common cancers in the UK (2017)
"The top four cancers in the UK (2017) include breast, prostate, lung, and bowel cancers, with high incidence rates."
How do incidence and deadliness differ among common cancers
"Breast and prostate cancers lead in incidence but are less deadly; lung and bowel cancers rank higher in mortality; pancreatic (mid-tier incidence) and liver (low incidence) are among the deadliest."
What are key environmental causes of cancer
"Environmental factors (carcinogens in diet and surroundings) and occupational factors (4-6%) contribute, with lifestyle/diet accounting for 30-35% of cancers."
How have social behaviors changed to reduce cancer risk
"Reductions in cigarette use, public smoking bans (e.g., 2014 car ban with children), healthier diets, more exercise, and stricter workplace safety rules aim to lower cancer rates."
What are the leading preventable cancer risk factors (2019)
"Tobacco was the top preventable risk factor in 2019, but recent studies show obesity has surpassed it due to rising incidence and declining tobacco use."
What are the main challenges in treating cancer
"Challenges include over 200 cancer types, late diagnosis (e.g., pancreatic), metastasis, evolving aggressive tumor cells, similarity to healthy cells, and shared drug targets with healthy cells."
How successful is testicular cancer treatment
"Testicular cancer has a 98% ten-year survival rate with early detection, aided by effective platinum-based chemotherapy."
What cancers have seen treatment progress
"Significant progress has been made in treating testicular cancer, malignant melanoma, breast cancer, and certain lung cancer subsets."
Why is cancer treatment progress slow
"Progress is slow due to insufficient research investment and lack of innovation, with profit-driven tweaks to existing drugs to maintain patent control rather than new mechanisms."