1.3 Organization of the Brain Diagram | Quizlet
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Anatomy of the Brain
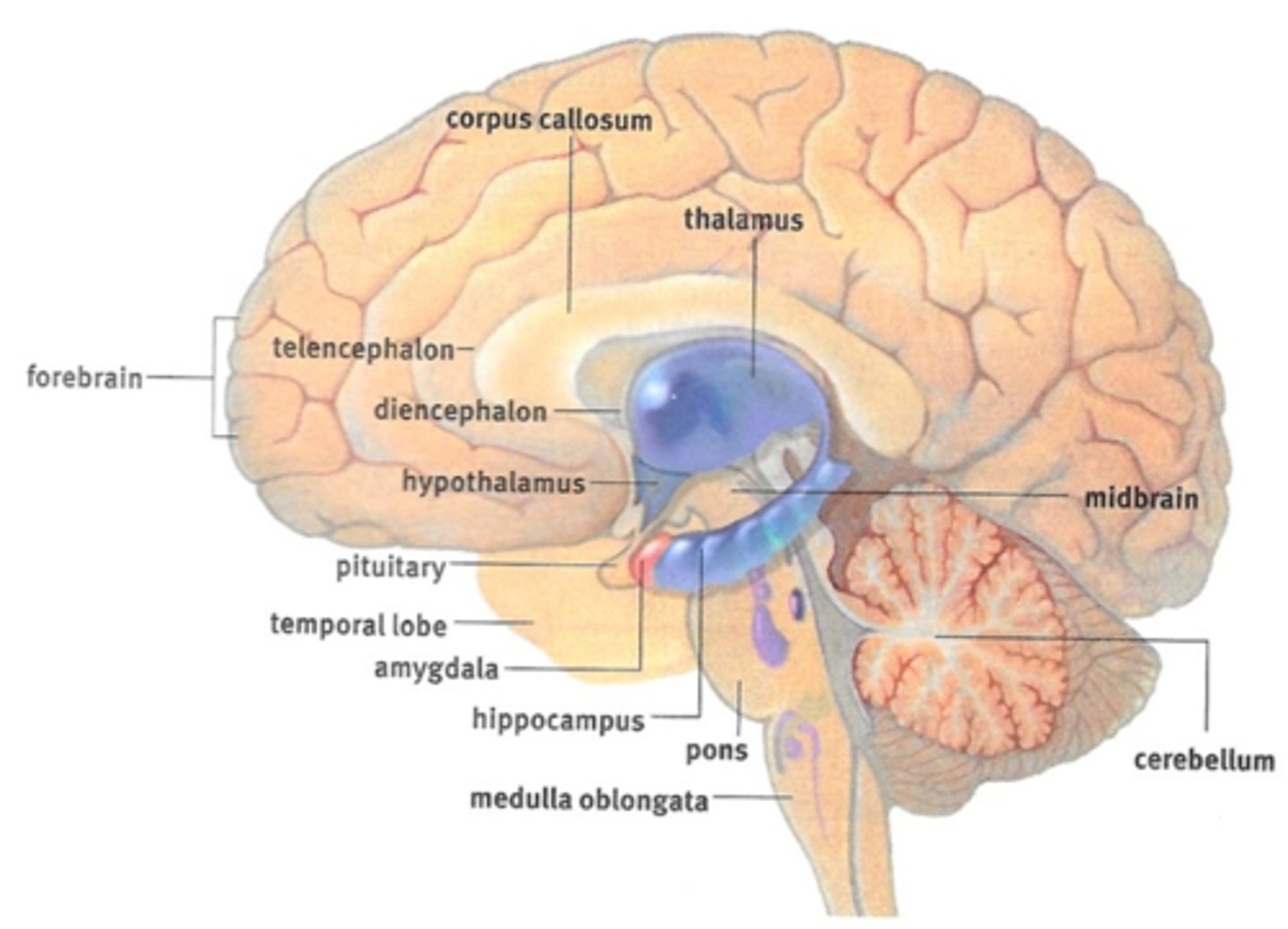
Summary of Brain Functions
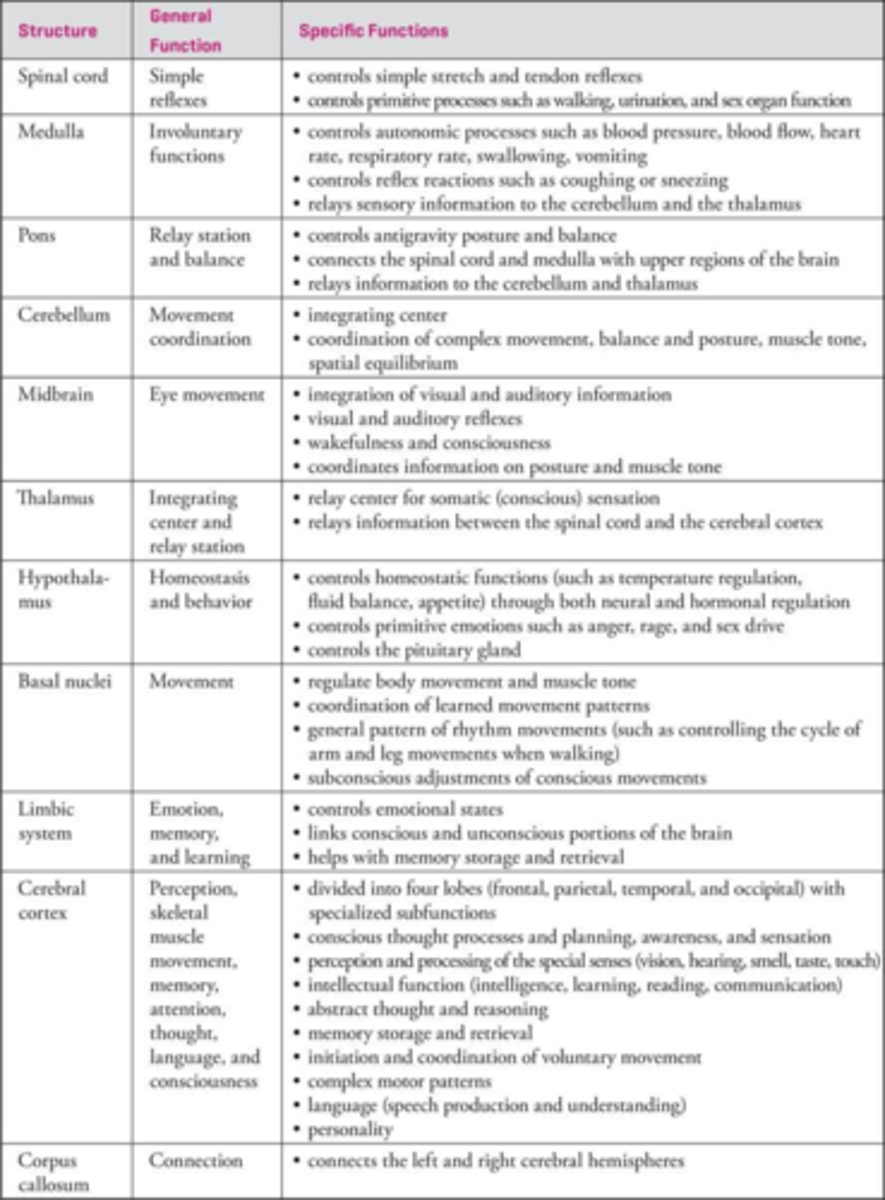
Petty Medical Residents Test Death, Melts My Soul
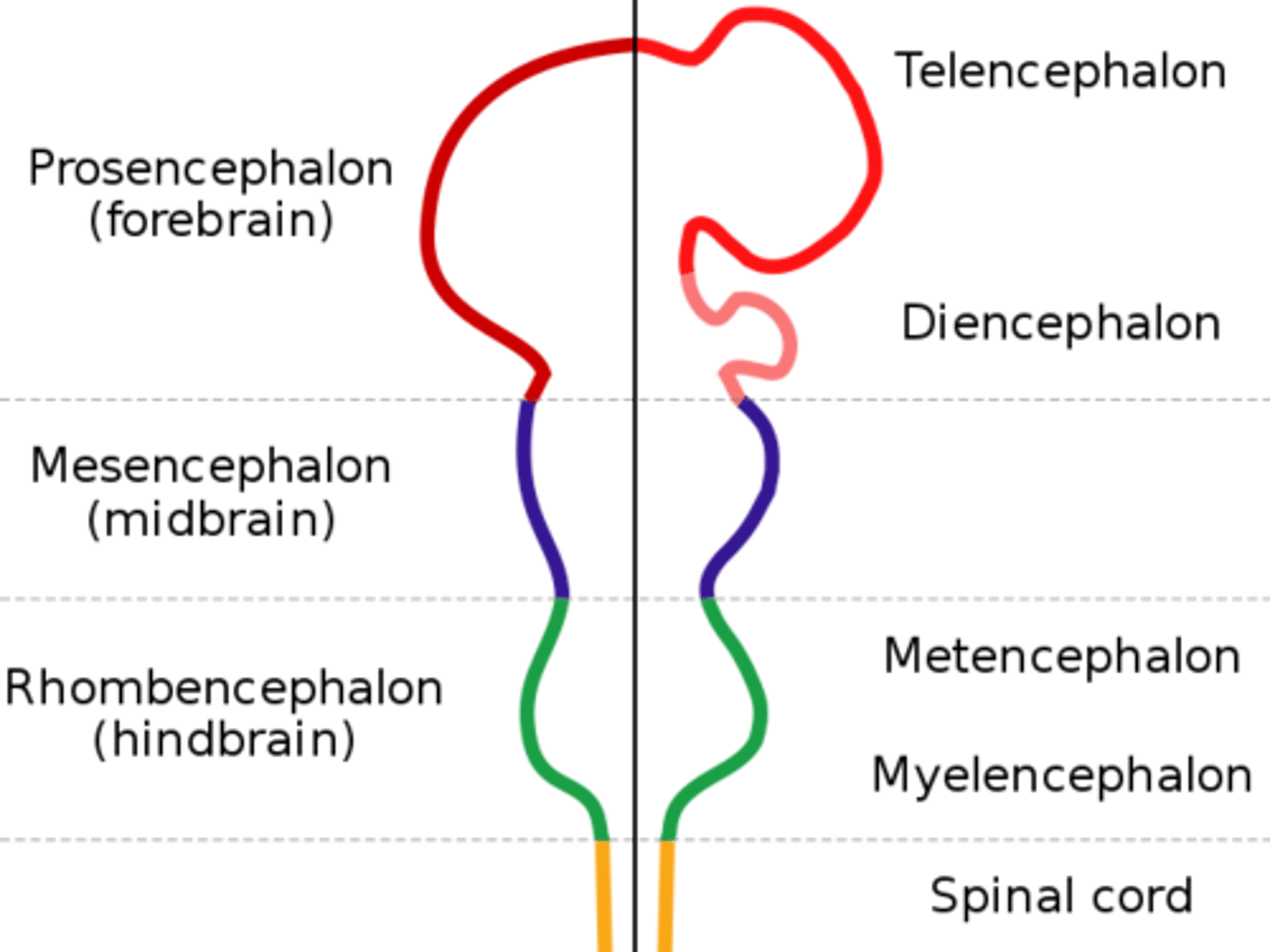
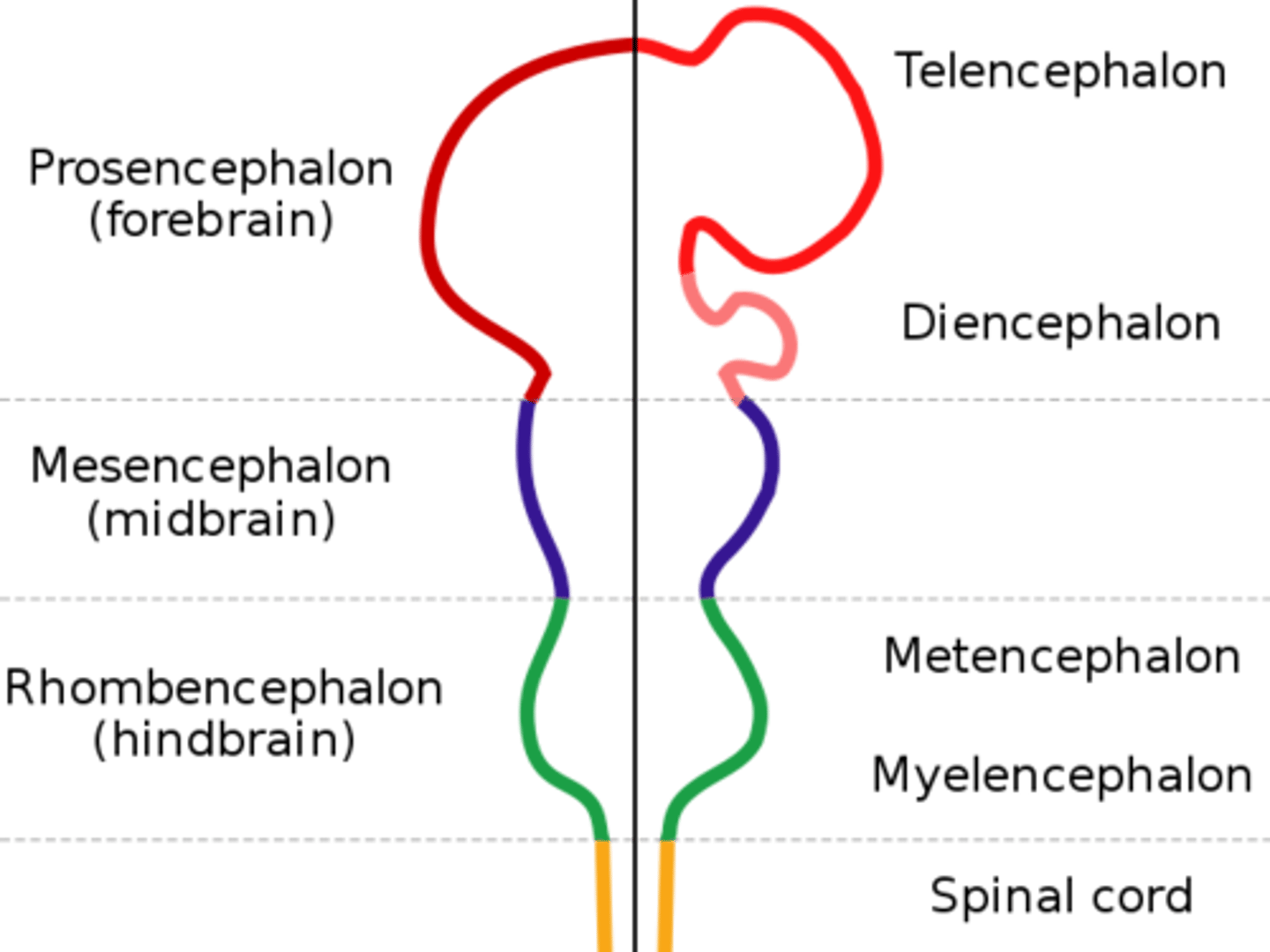
Subdivisions of the embryonic brain mnemonic.
Meninges
Pia mater, arachnoid mater, dura mater.
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Shock absorber secreted by specialized cells that line the ventricles.
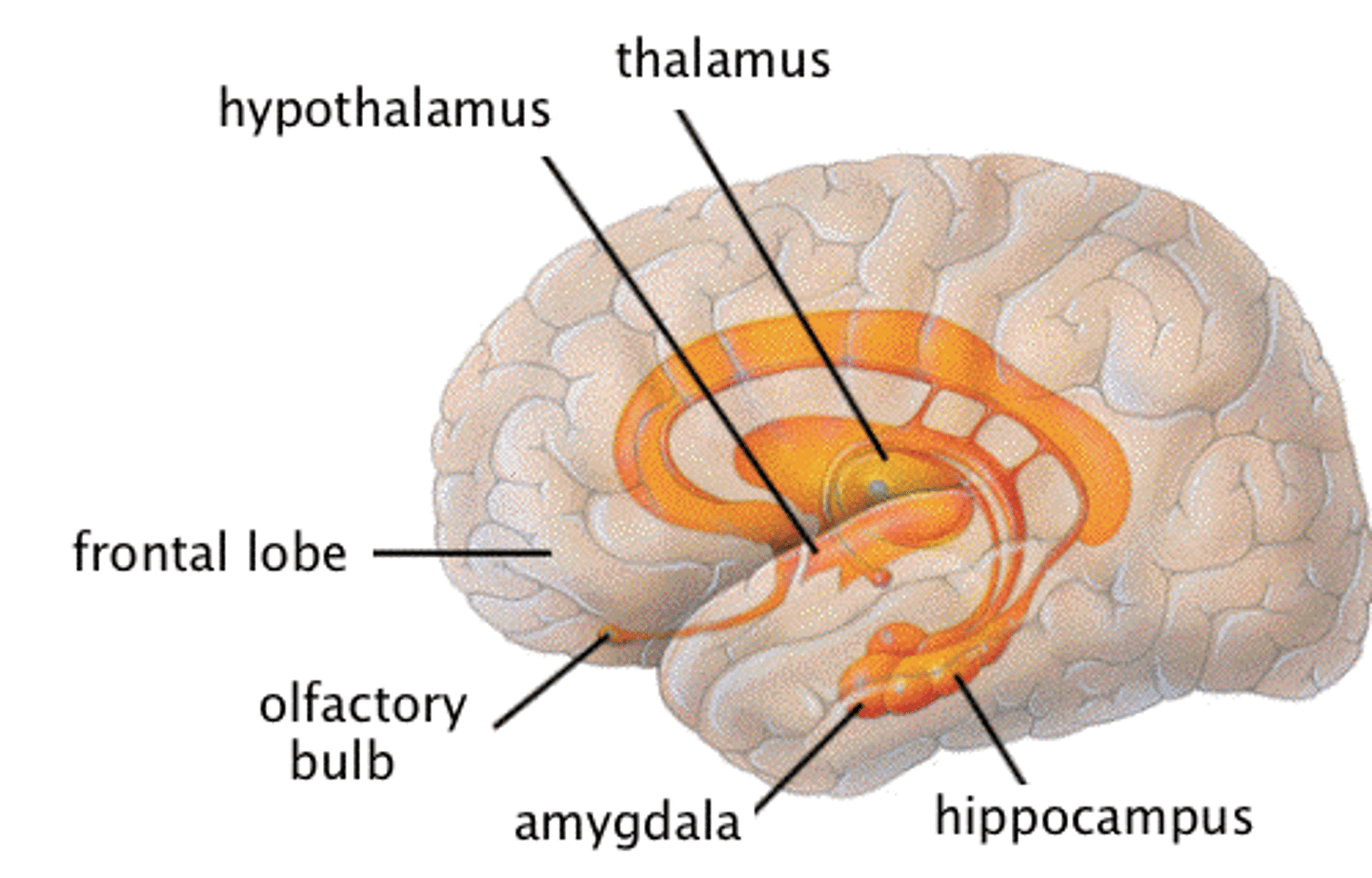
Limbic System
A group of neural structures associated with emotion and memory.
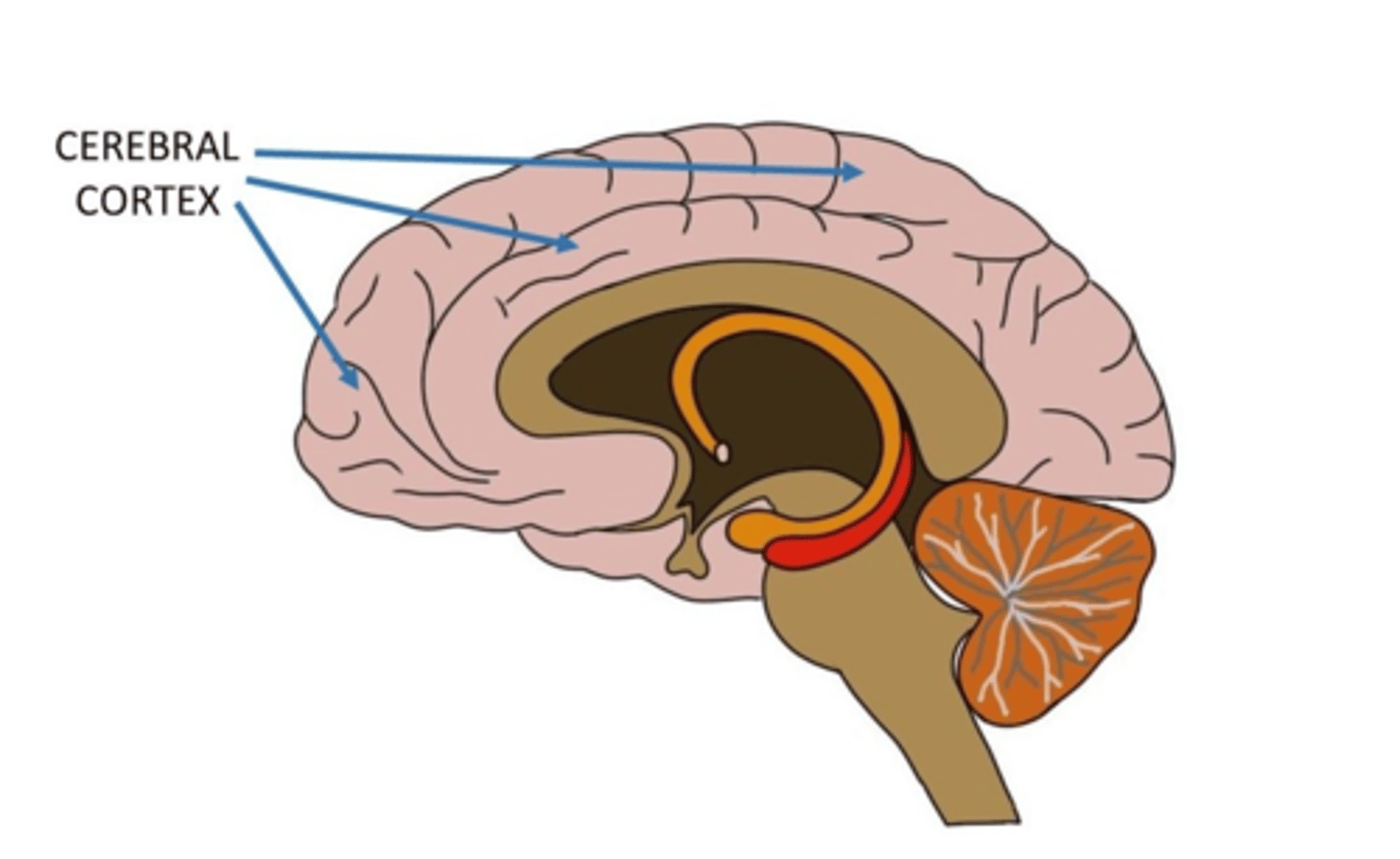
Cerebral Cortex
Outer covering of the cerebral hemispheres.
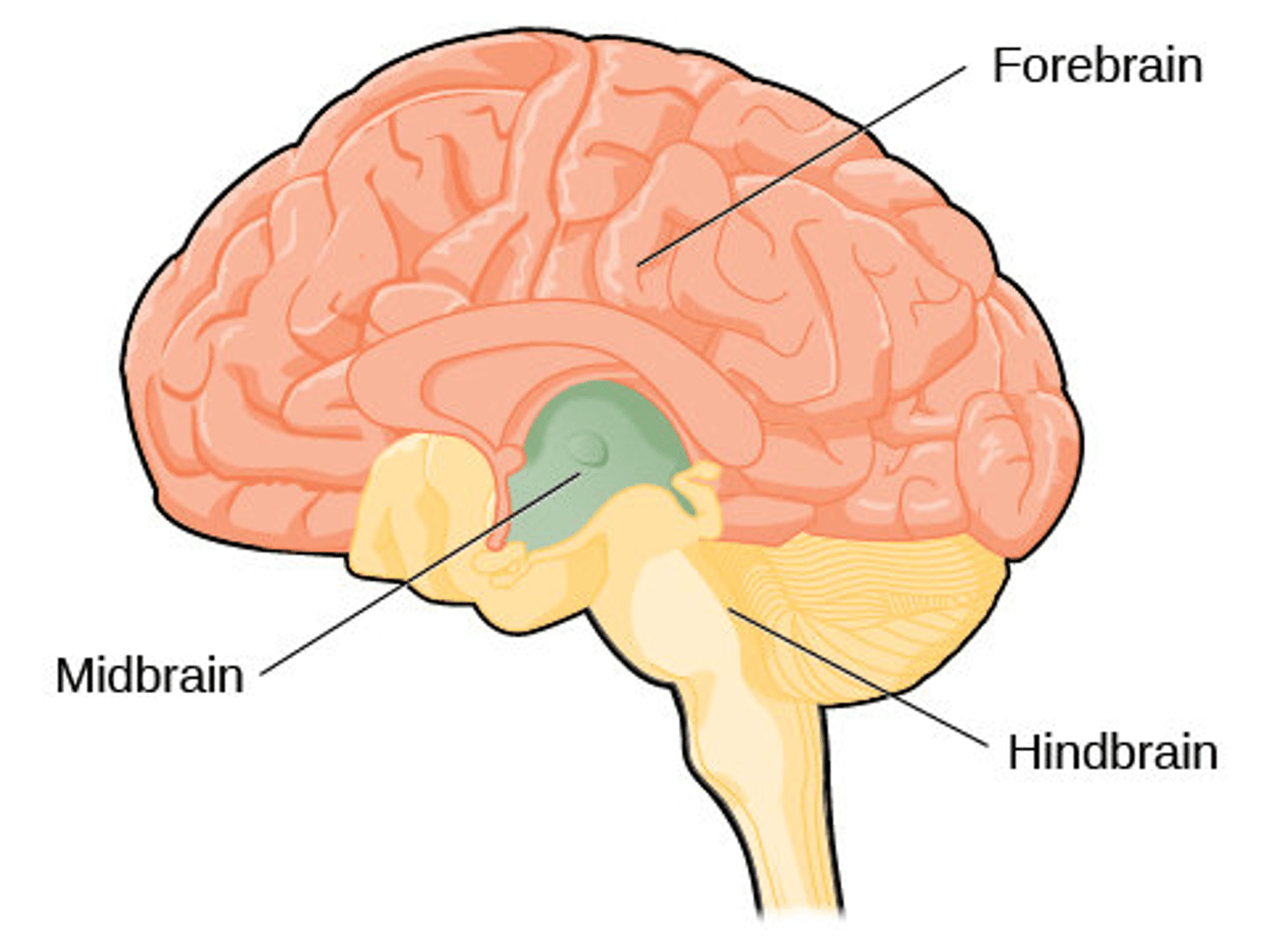
Hindbrain Location
Coronal plane where the brain meets the spinal cord.
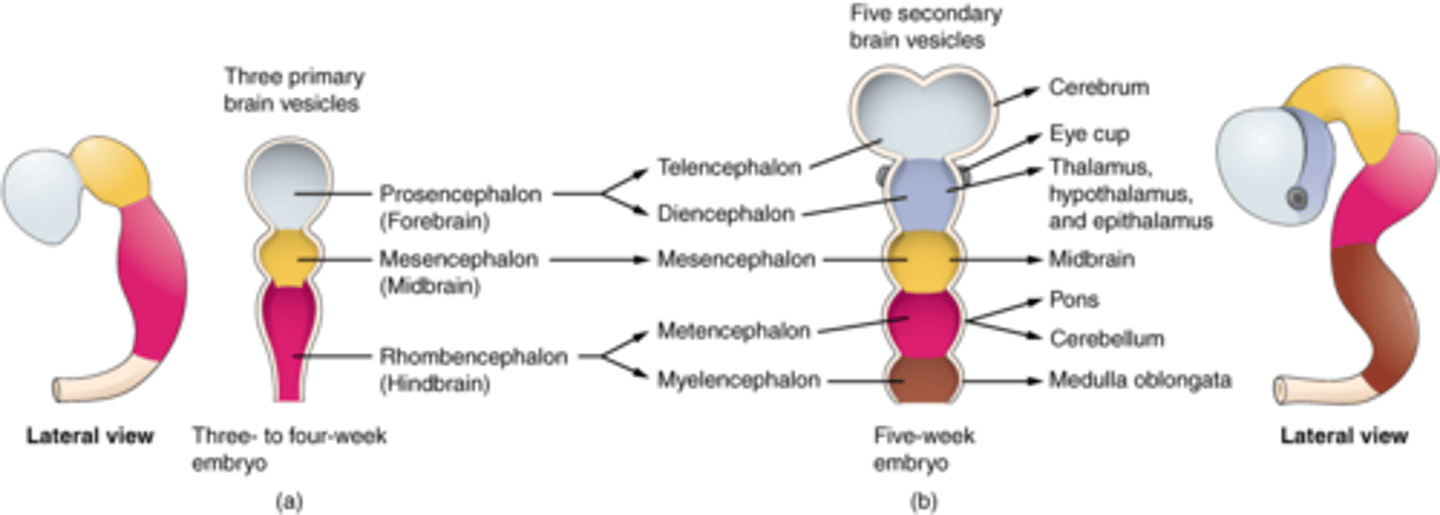
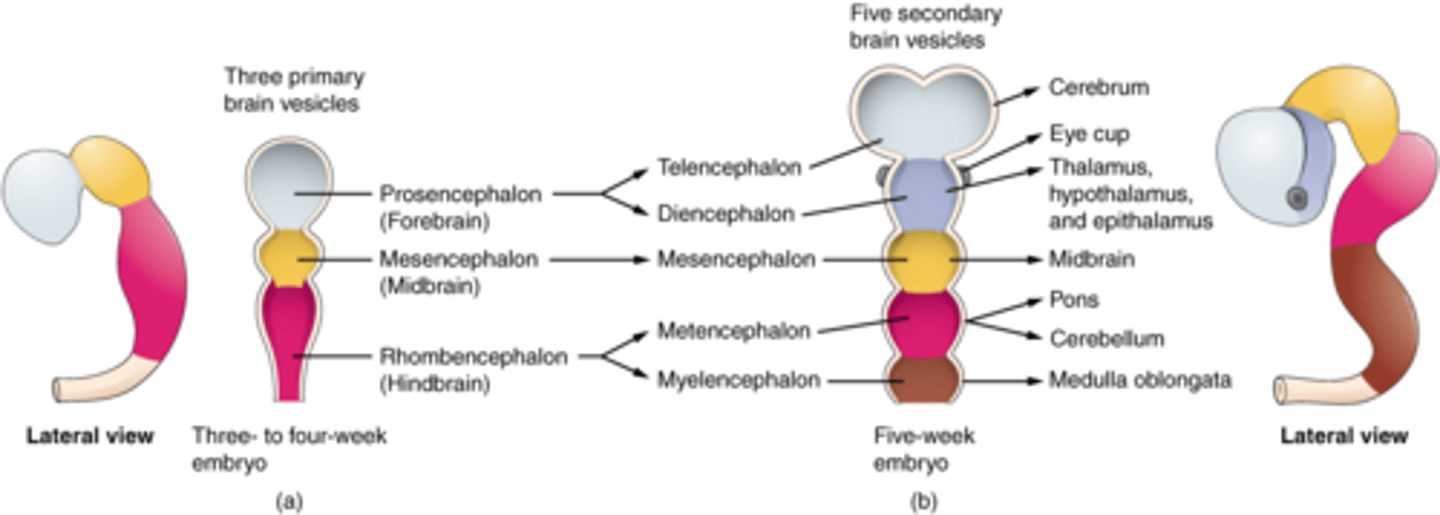
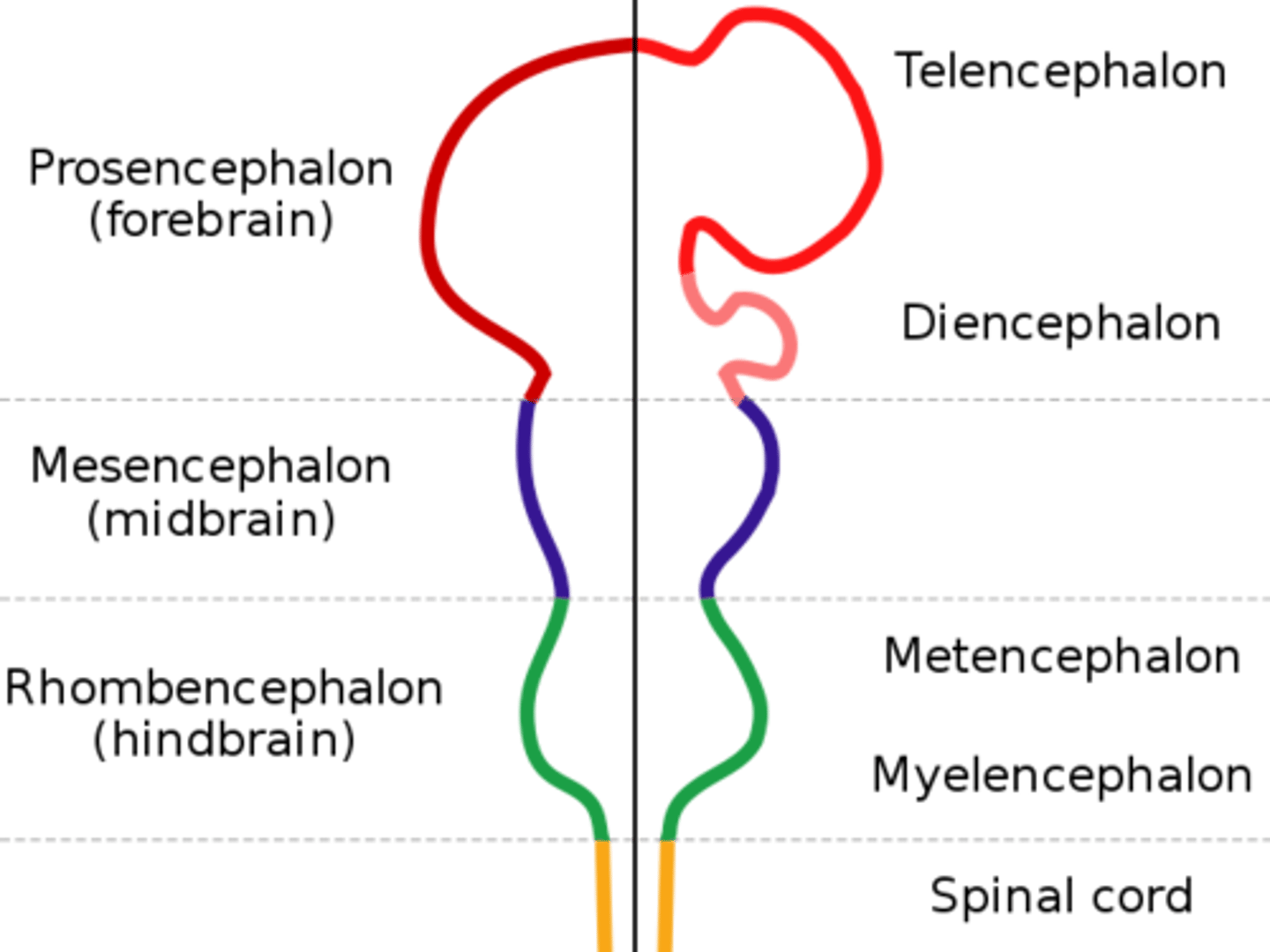
Rhomboencephalon
Hindbrain name. Divides to form the metencephalon and the myelencephalon.
Hindbrain Function
Controls balance, motor coordination, breathing, digestion, sleeping and awakeness.
Metencephalon and Myelencephalon
These are what the rhombencephalon divides to form.
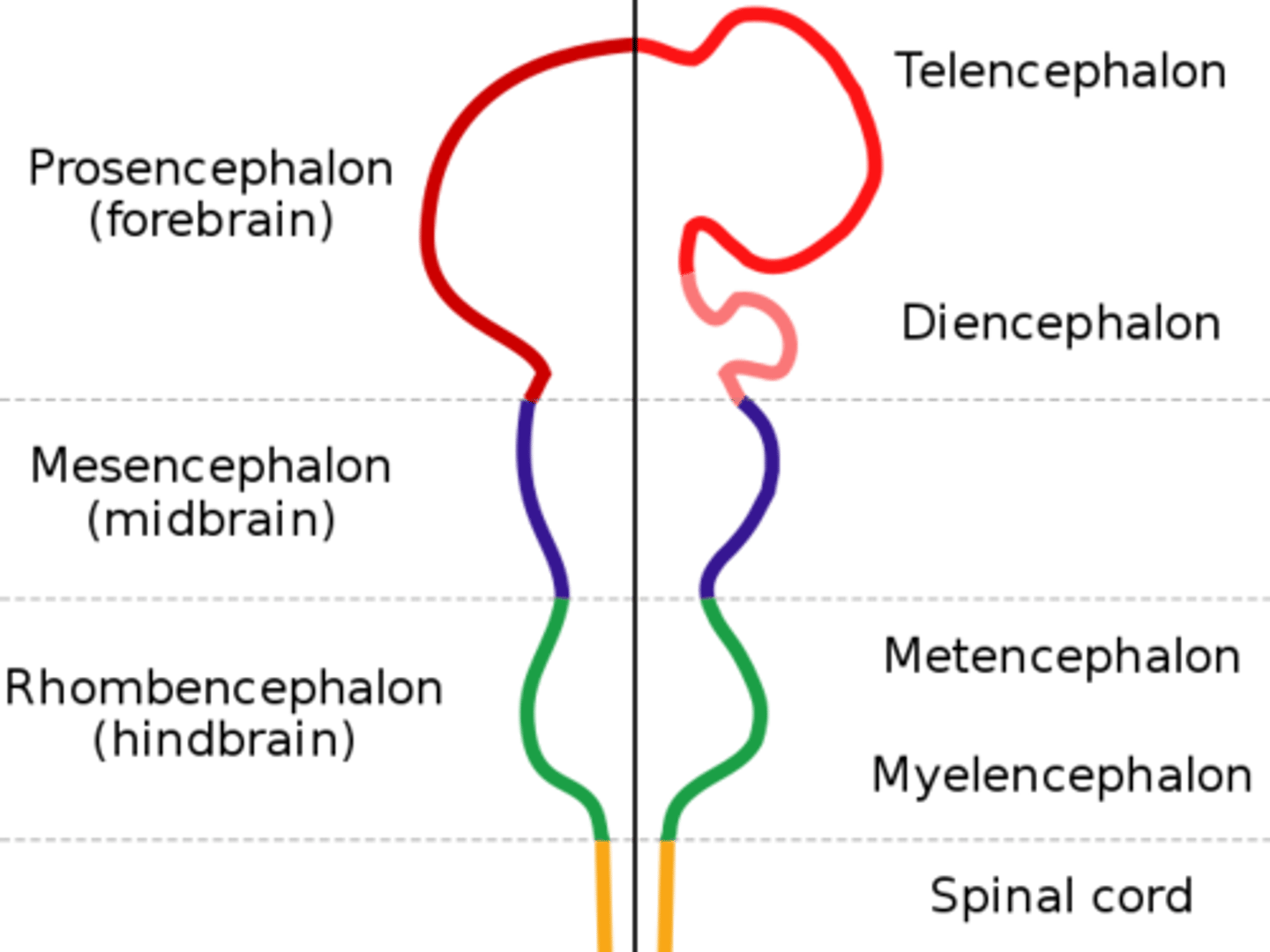
Myelencephalon
Becomes the medulla oblongata. Derived from the rhombencephalon.
Medulla Oblongata
The structure formed from the myelencephalon.
TERM
Medulla Oblongata Function
DEFINITION
Breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
Metencephalon
Becomes the pons and cerebellum. Derived from the rhombencephalon.
Pons and Cerebellum
Structures formed from the metencephalon.
TERM
Pons
DEFINITION
Contains sensory and motor pathways between the cortex and the medulla.
TERM
Cerebellum
DEFINITION
Part of the brain that controls coordination. Alcohol is known to decrease its function.
TERM
Mesencephalon
DEFINITION
Midbrain name. Does not divide, just remains the mesencephalon.
Midbrain Function
Receives sensory and motor information from the rest of the body. Associated with involuntary functions.
Superior Colliculus
Part of the midbrain, receives visual sensory input.
Inferior Colliculus
Part of the midbrain, receives sensory information from the auditory system.
TERM
Prosencephalon
DEFINITION
Forebrain name. Divides to form the telencephalon and diencephalon.
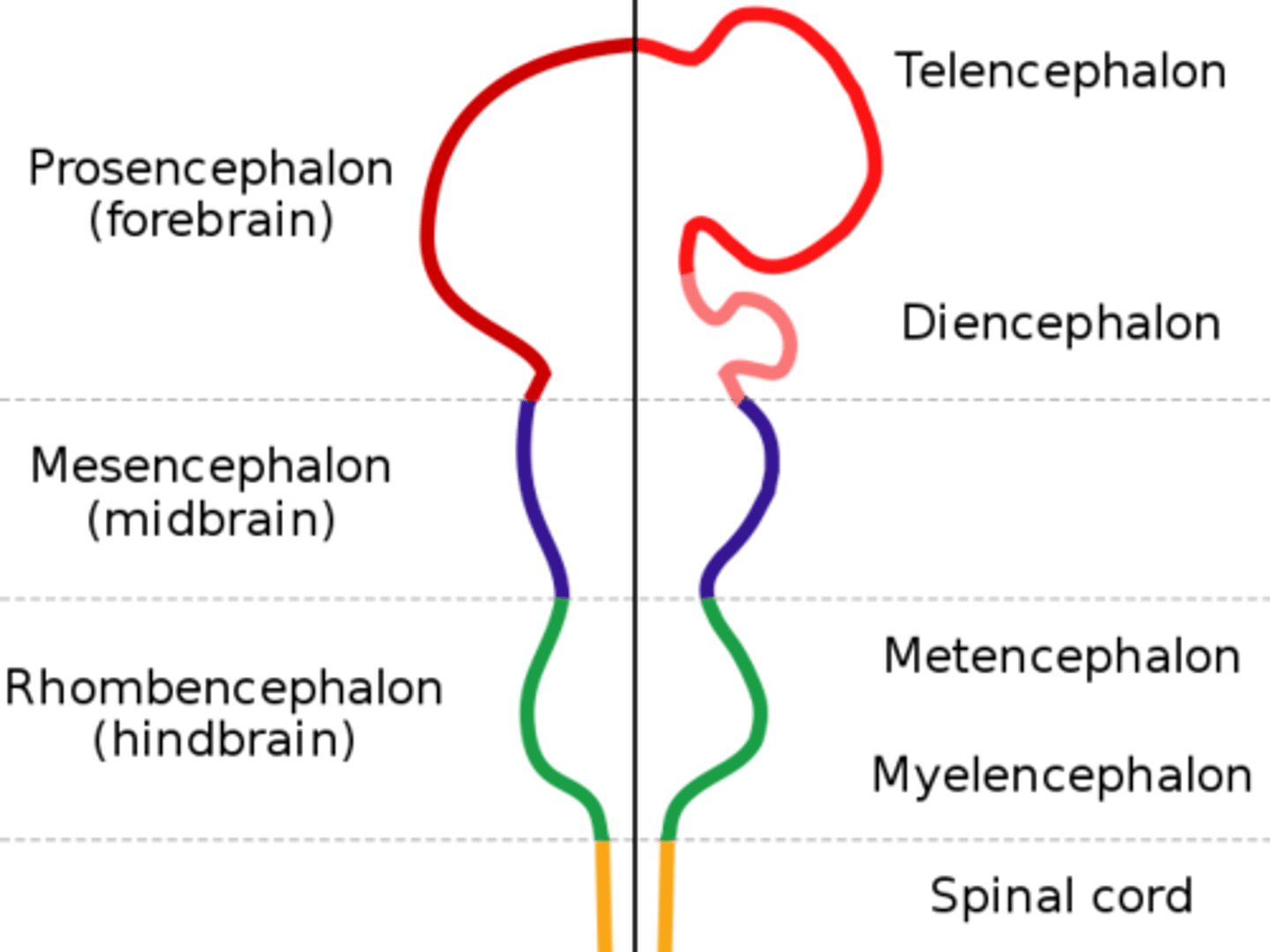
Forebrain Function
Complex perceptual, cognitive, and behavioral processes. Associated with emotion and memory.
Telencephalon and Diencephalon
These are what the prosencephalon divides to form.
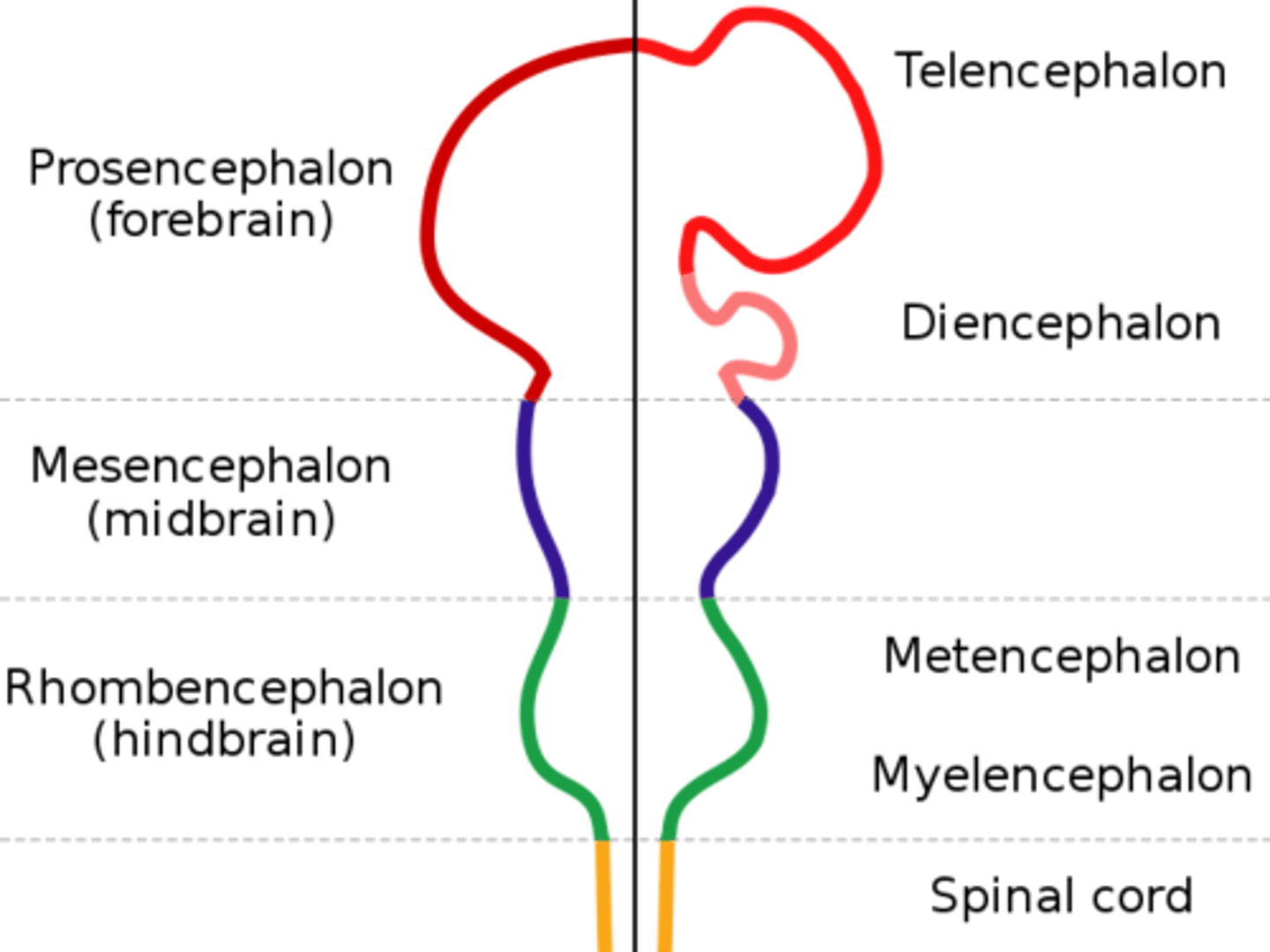
TERM
Telencephalon
DEFINITION
Forms the cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, and limbic system.
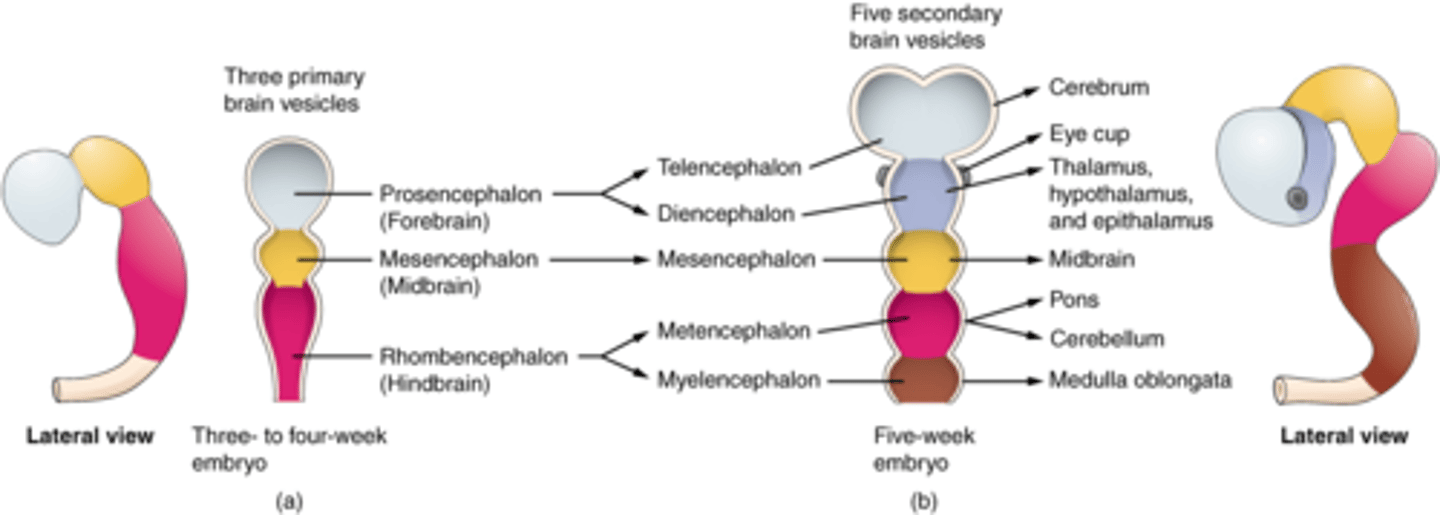
Cerebral Cortex, Basal Ganglia, Limbic System
Structures formed from the telencencephalon.
TERM
Diencephalon
DEFINITION
Forms the thalamus, hypothalamus, posterior pituitary gland, and the pineal gland.
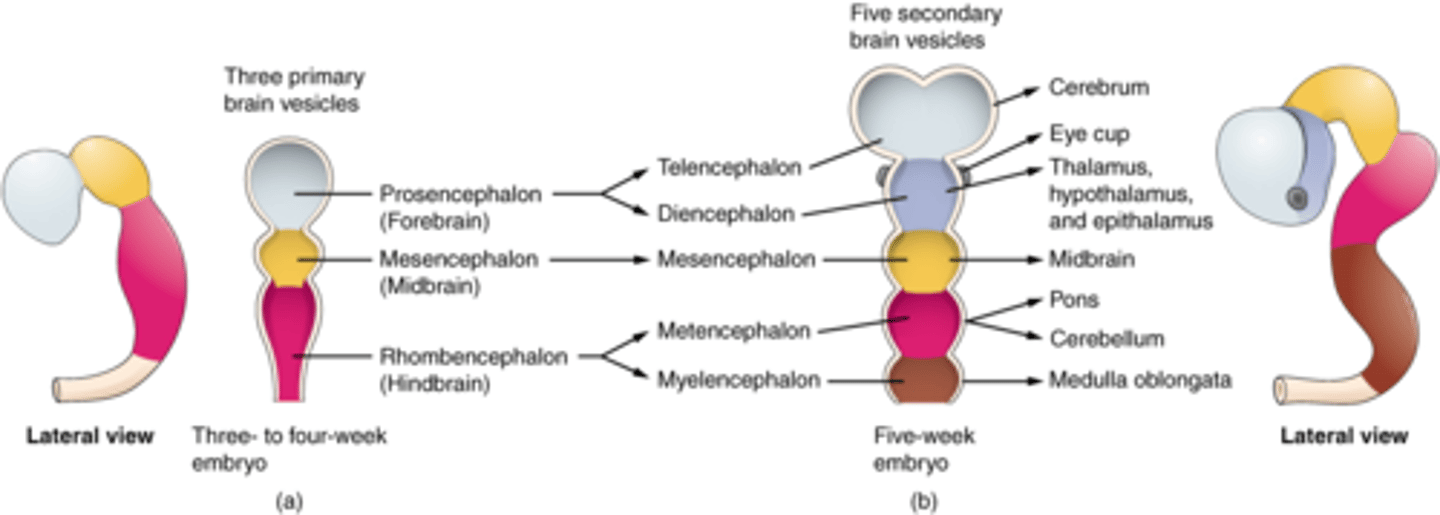
Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Posterior Pituitary Gland, Pineal Gland
Structures formed from the diencephalon.
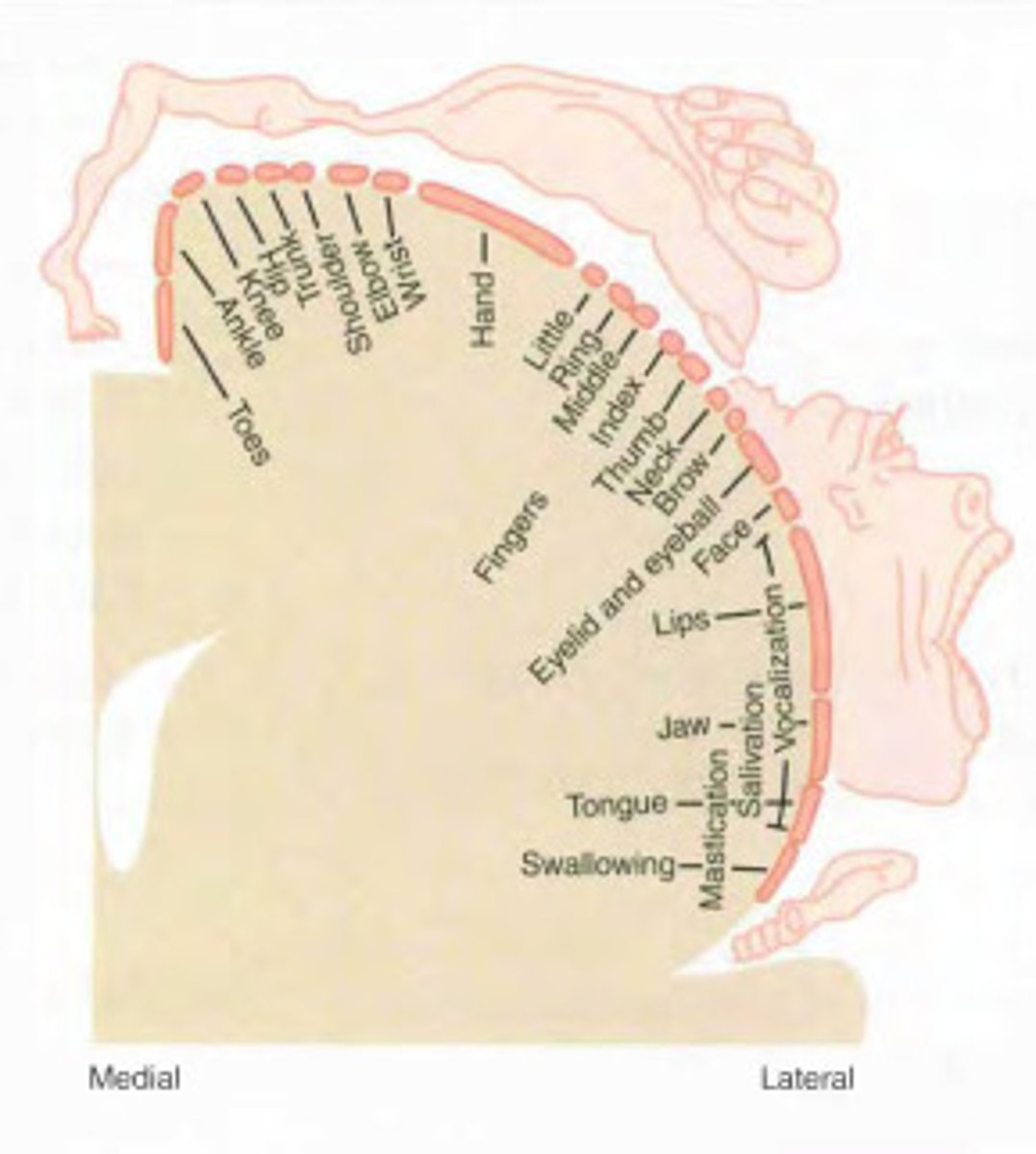
Cortical Maps
Created by stimulating parts of the brain and seeing the results.
EEG
Electroencephalogram, which is used in the research of seixures, sleep, and brain lesions.
rCBF
Regional cerebral blood flow, which detects patterns of neural activity based on increased blood flow to different parts of the brain.
PET
Positron emission tomography, in which a radioactive sugar is injected and absorbed by the body and its dispersion and uptake throughout the target tissue is imaged.
fMRI
Functional MRI, which specifically measures changes associated with blood flow.