APBio Unit 1-5
1/303
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
304 Terms
Macromolecules
Molecules composed of thousands of atoms: the four main classes being carbohydrates, lipids, prteins, and nucleic acids
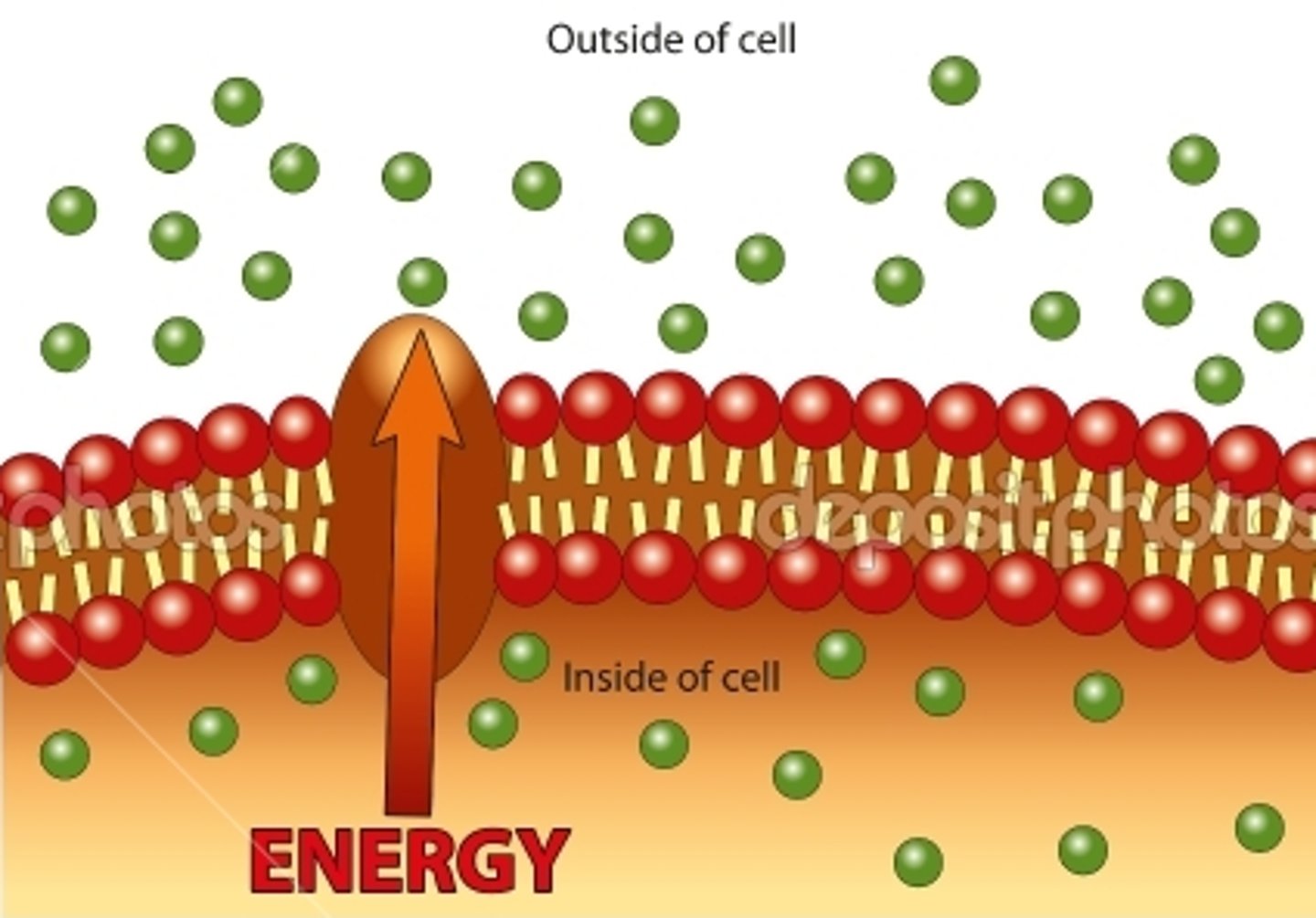
Active transport
Movement of molecules against a gradient from a region of low concentration to high concentration; requires energy (ATP)
(e.g., Na+/K+ pumps)
Polymer
Chainlike molecules, consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds.
Carrier Protein
An integral membrane protein that undergoes a conformational change to move a molecule from one side of the membrane to another.
Monomer
Make up polymers: connected by covalent bonds.
Cell wall
Found in plant cells and not animal cells, an additional layer of protection and rigidity
Dehydration Synthesis
(Condensation Reaction): Covalent bonds which connect monomers have distinct functions: One monomer provides a hydroxyle group and the other provides a hydrogen, creating water (as a biproduct) and a bond between the monomers.
Central Vacuoles
Found in plant cells, for large storage of food and water
Hydrolysis
Adding water to reverse dehydration synthesis, so the polymer recieves a hydrogen atom and a hydroxyl group
Channel Protein
type of cell membrane protein used in passive transport (specifically facilitated diffusion)
Carbohydrates
A macromolecule made up of C, H and O, with a 2:1 ratio between the hydrogen and oxygen.
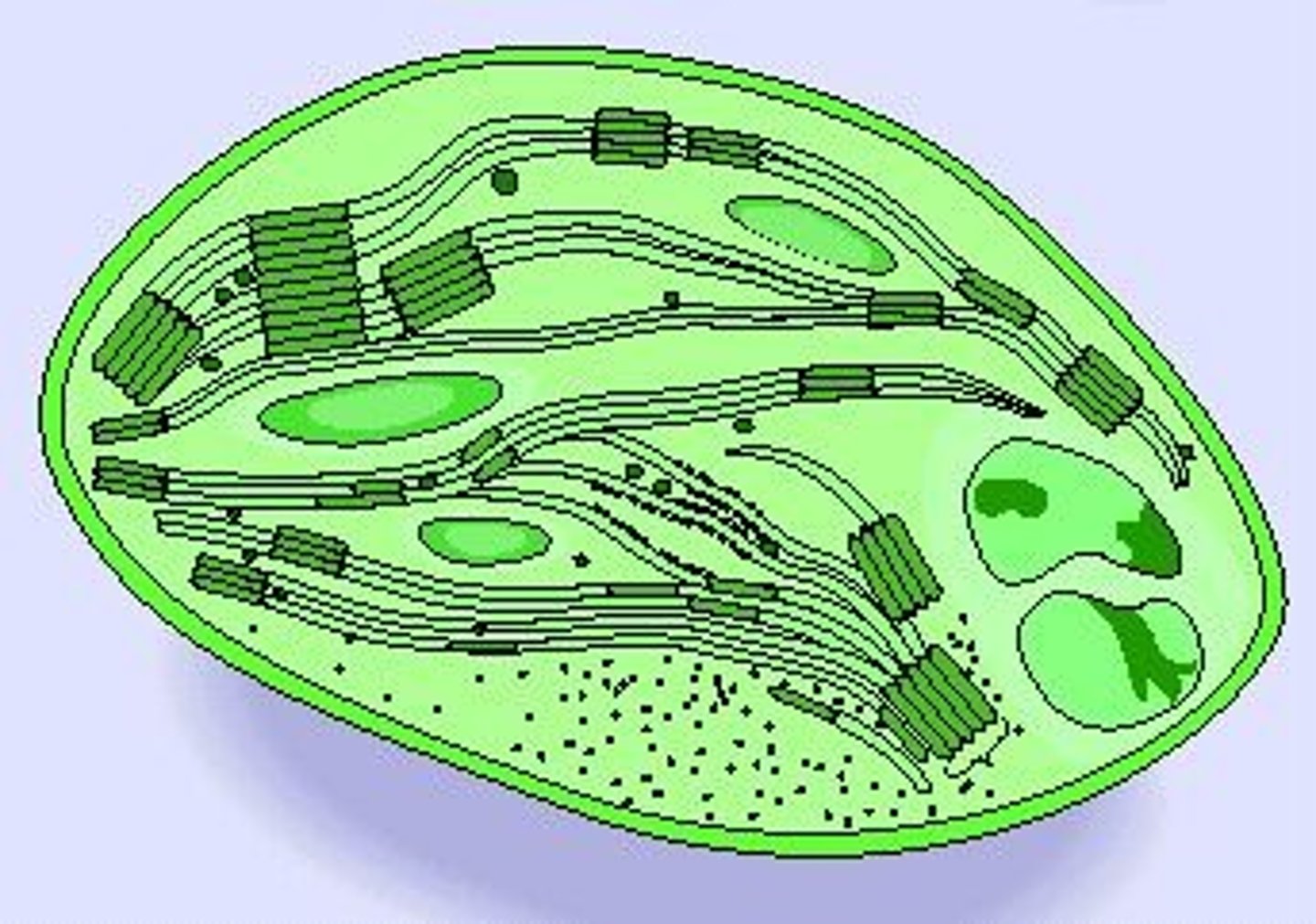
Chloroplast
Site of photosynthesis
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars with 1 ring: Provides immediate energy, classified by the amount of carbons
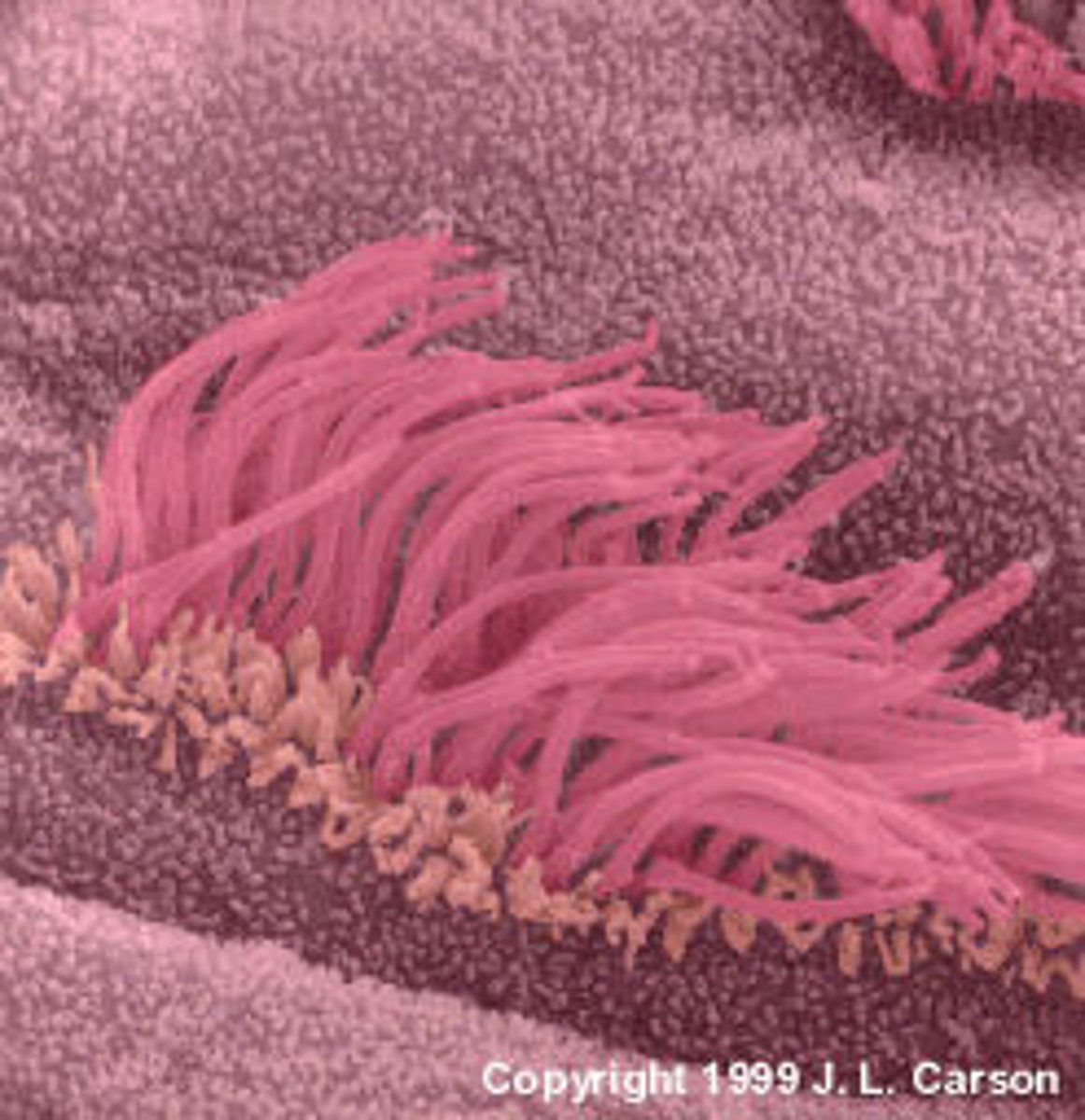
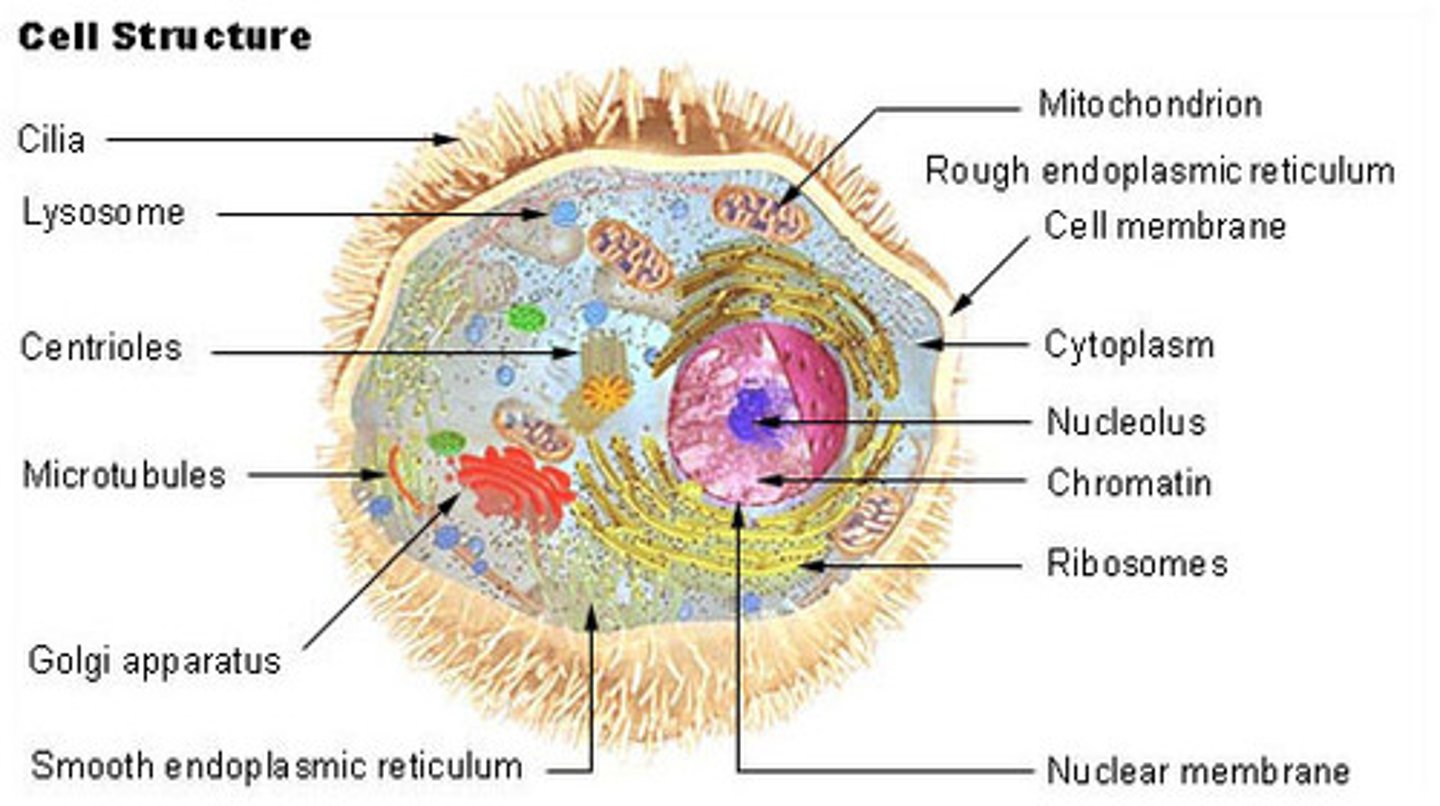
Cilia
Appendage that protrude from eukaryotic cells for movement
Disaccharides
Double sugars with 2 rings
Concentration Gradient
difference in concentration of a substance on two sides of a membrane
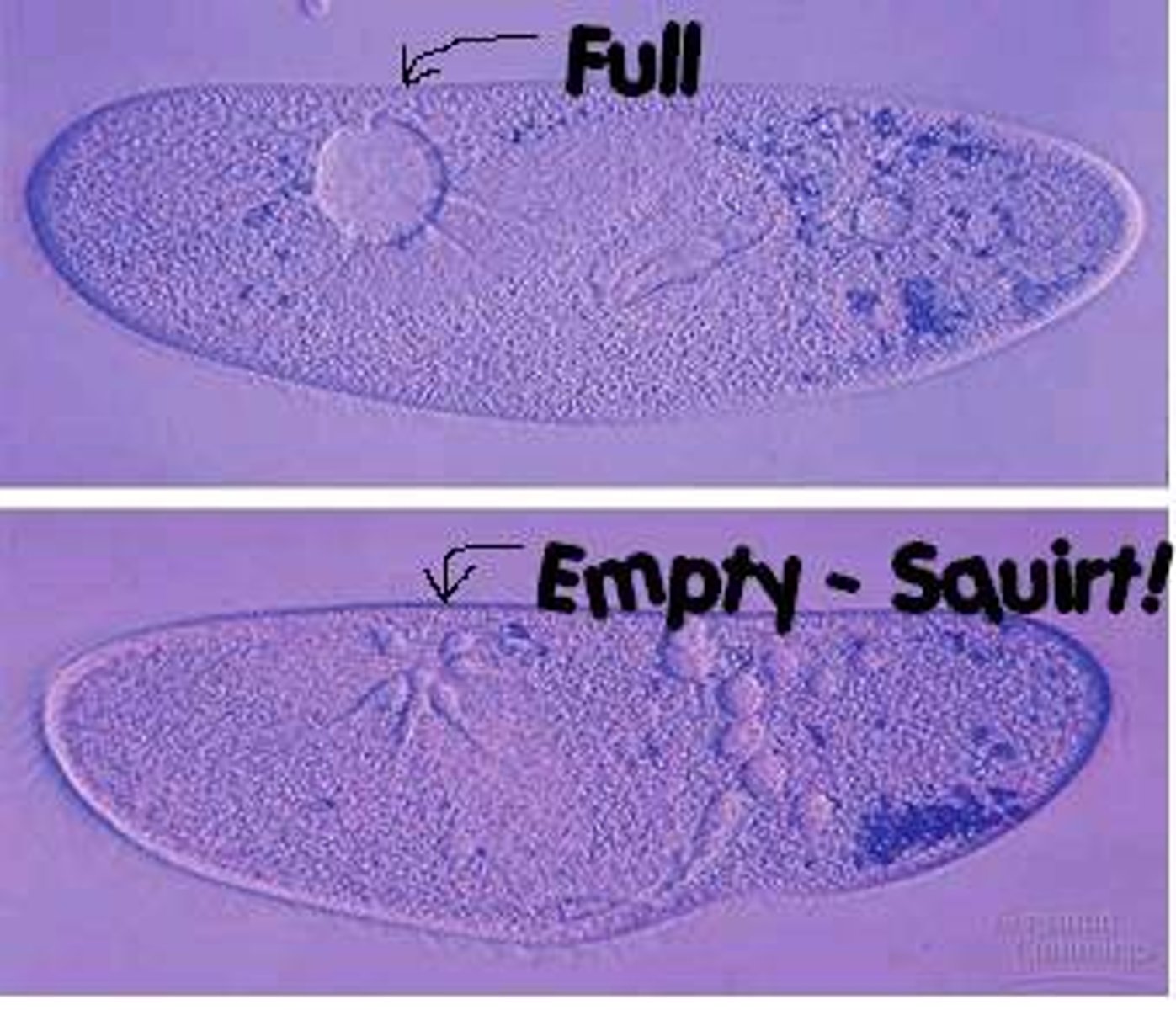
Contractile Vacuole
Found in freshwater organisms, pump out excess water that diffuses inward because organisms in a hypotonic environment
Polysaccharides
Polymers, with many rings, joined by glucosidic linkages. Acts as an energy storage macromolecule, building materials for cells or whole organisms
Maltose
A disaccharide formed by joining the two glucose molecules: found in malt sugar
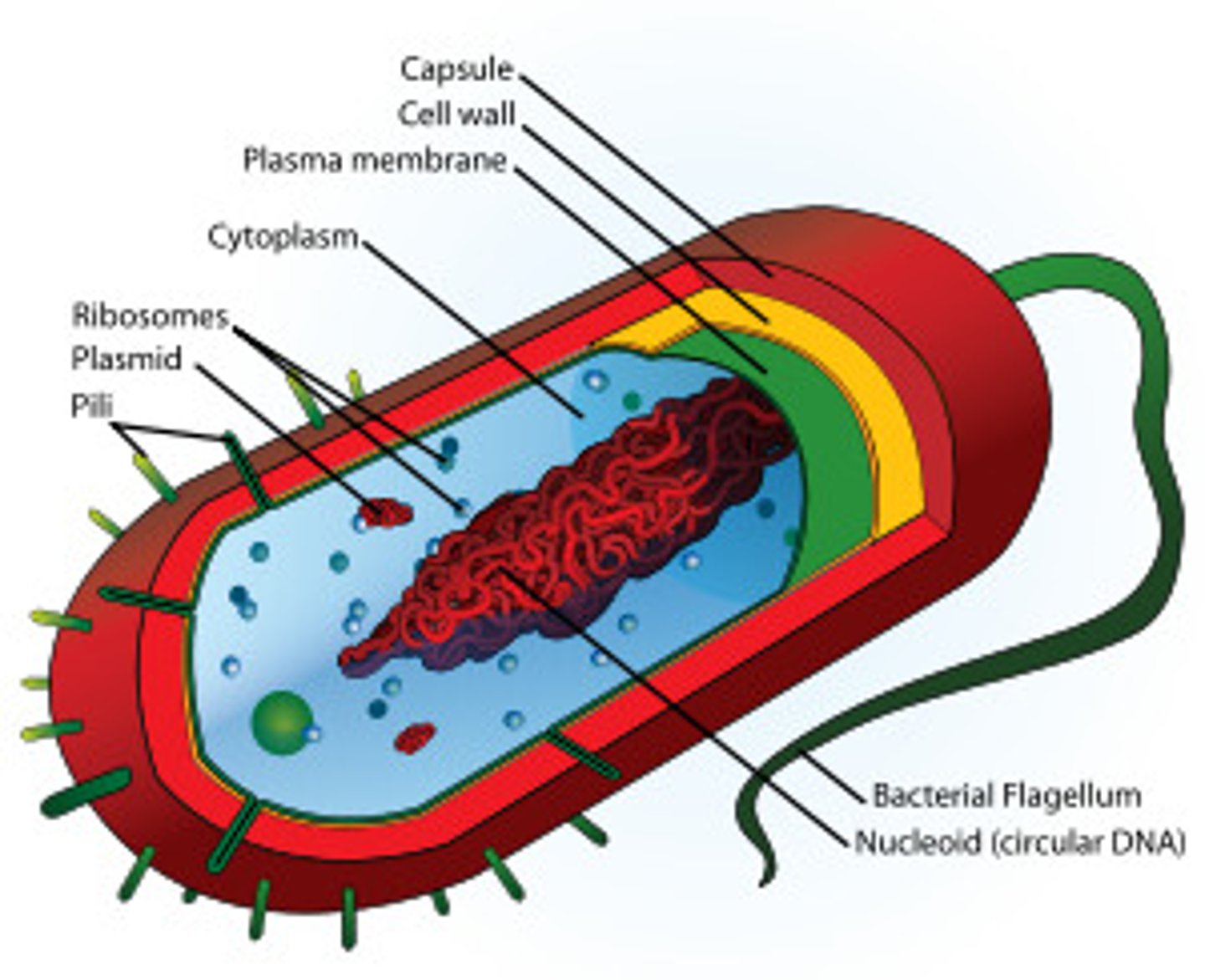
Prokaryotes
Cells with no nuclear or internal membranes
Sucrose
A disaccharide formed by joining glucose and fructose, major form of sugars in plants: found in table sugar
Eukaryotes
Cells with internal membranes (e.g., nucleus, organelles)
Lactose
A disaccharide formed by joining glucose and galactose. People who lack the enzyme to digest this sugar are "intolerant"
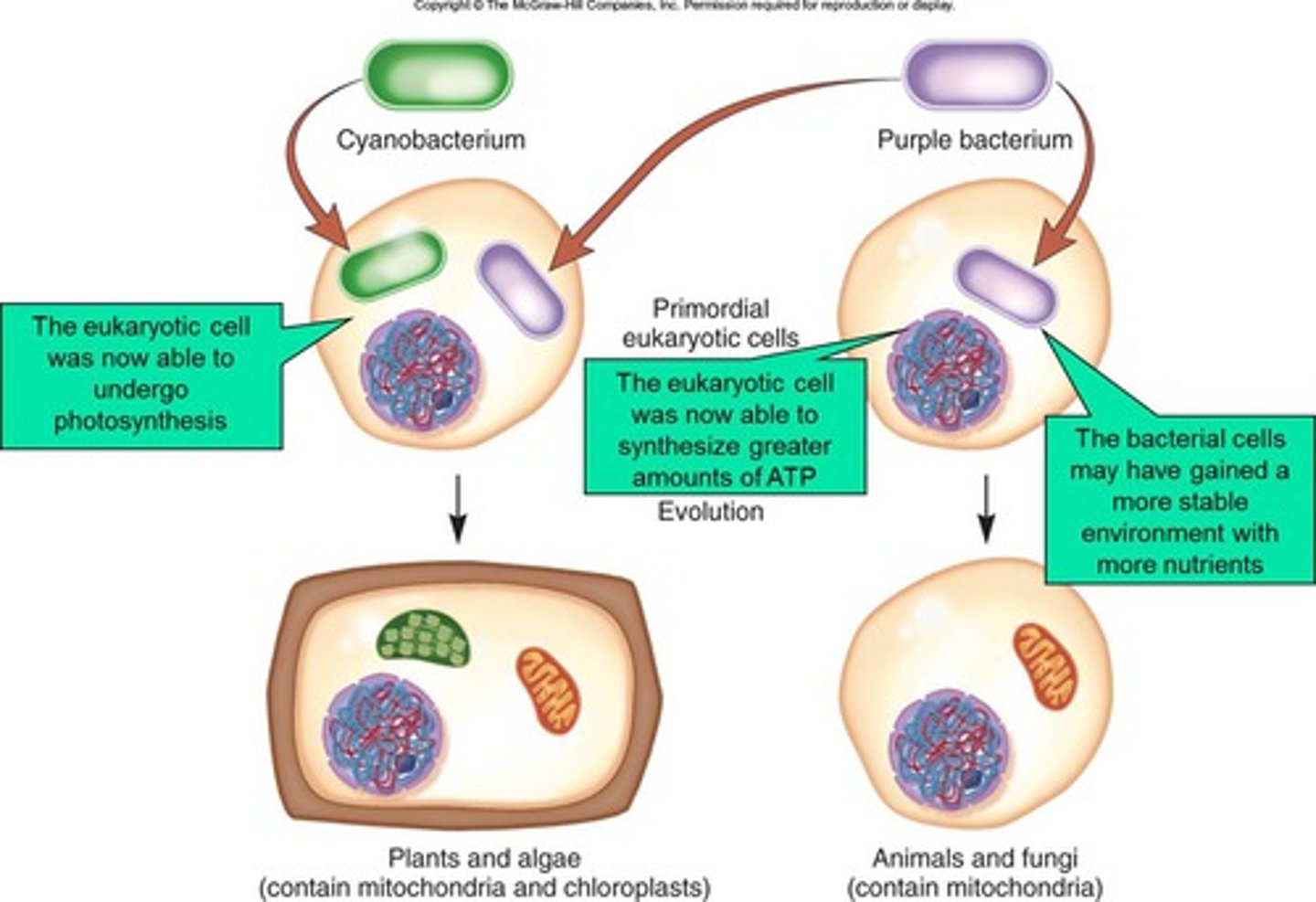
Theory of Endosymbiosis
Chloroplasts and mitochondria were formerly tiny prokaryotes that took up residence inside larger cells and formed a permanent symbiotic relationship; eukaryotes evolved from engulfing prokaryotes
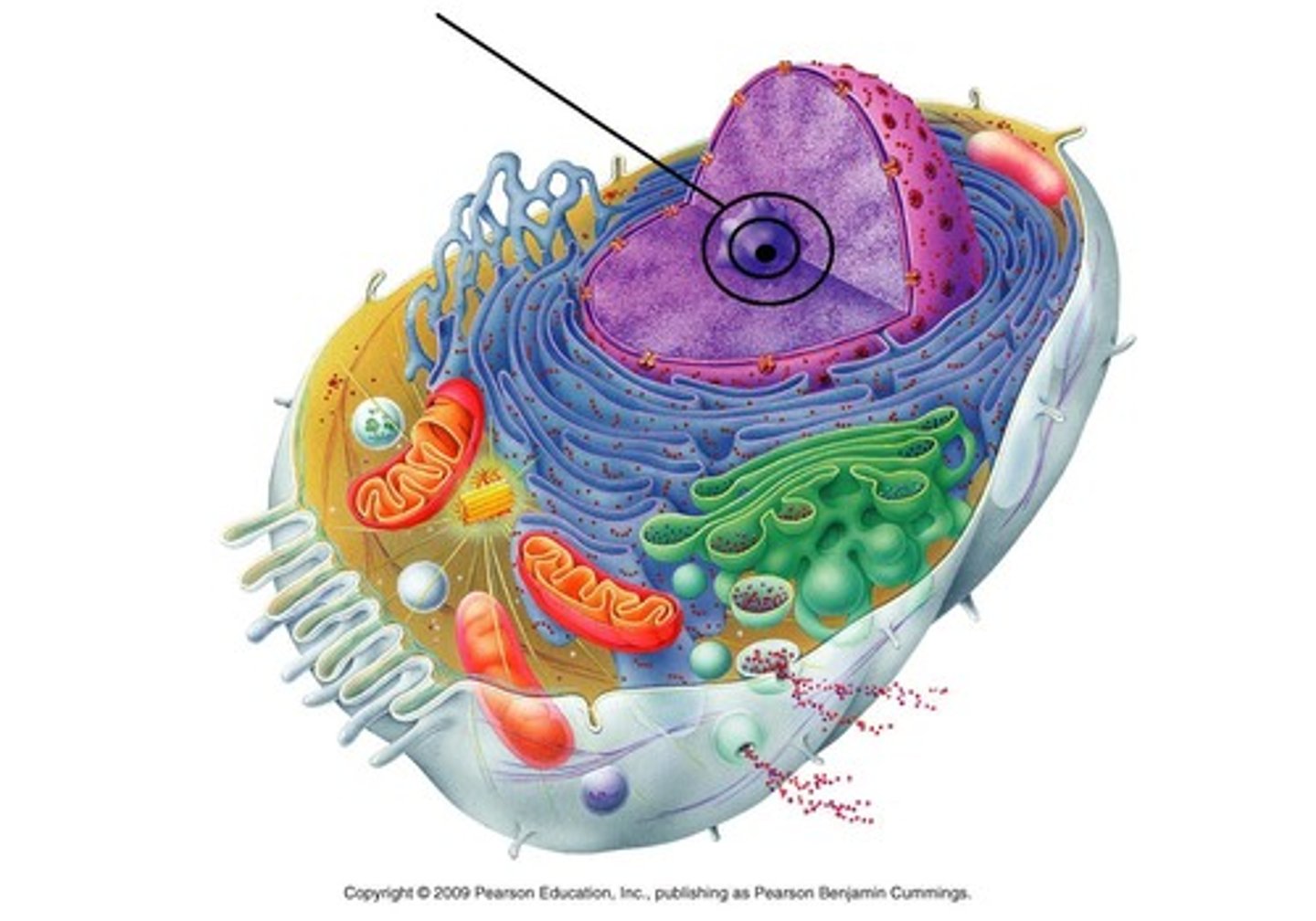
Nucleus
Contains chromosomes; surrounded by selectively permeable membrane that contains nuclear pores for the passage of molecules like mRNA
Glucosidic Linkages
the bond that bonds polysaccharides
Starch
During photosynthesis: glucose is a biproduct that is stored in plastids and chloroplasts
Nucleolus
Where ribosome components are synthesized and assembled
Cellulose
Made up cell walls of plants, using beta rings
Ribosomes
Site of protein synthesis
Found free in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum
Glycogen
An animal polysaccharide. Human produces excess sugar, highly branched. Humans and vertebrates store this in the liver and muscles
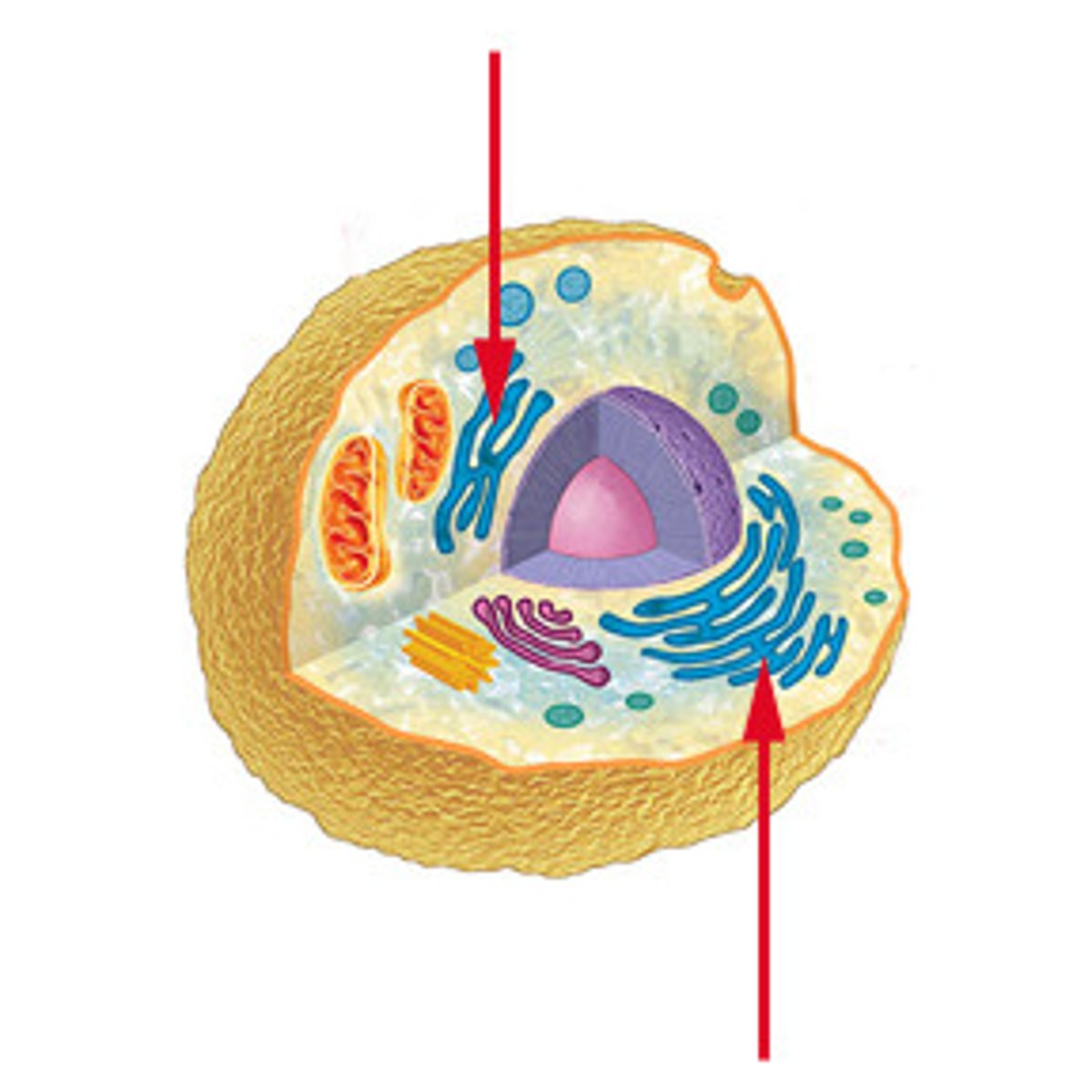
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Membranous system of channels and flattened sacs that transverses the cytoplasm
Rough - site of protein synthesis
Smooth - synthesizes steroid hormones and other lipids; connects rough to Golgi
Chitin
Makes up the exoskeleton of pill bugs; extremely strong, contains nitrogen-containing appendage on each glucose. Structural support for the cell walls of many fungi.
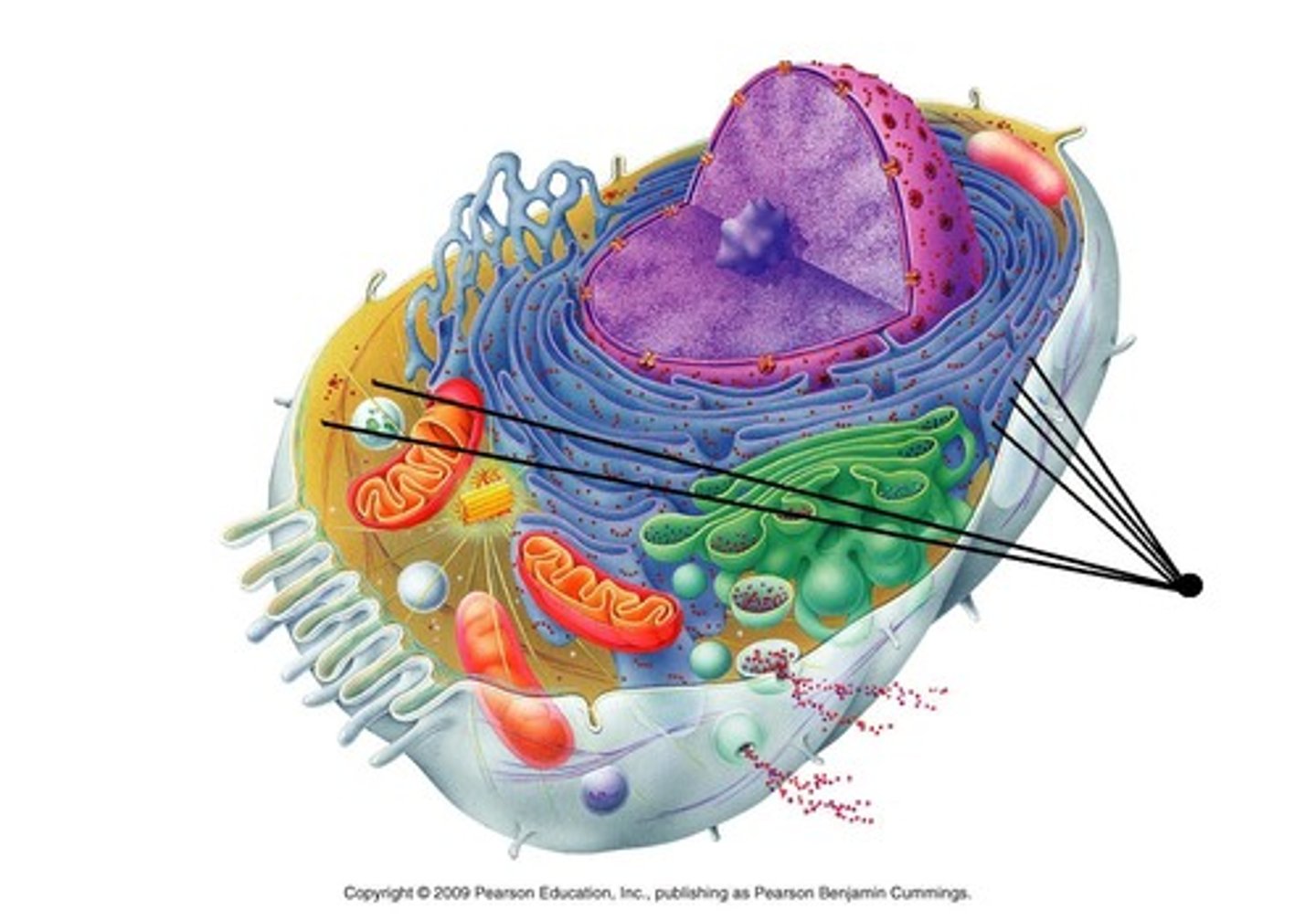
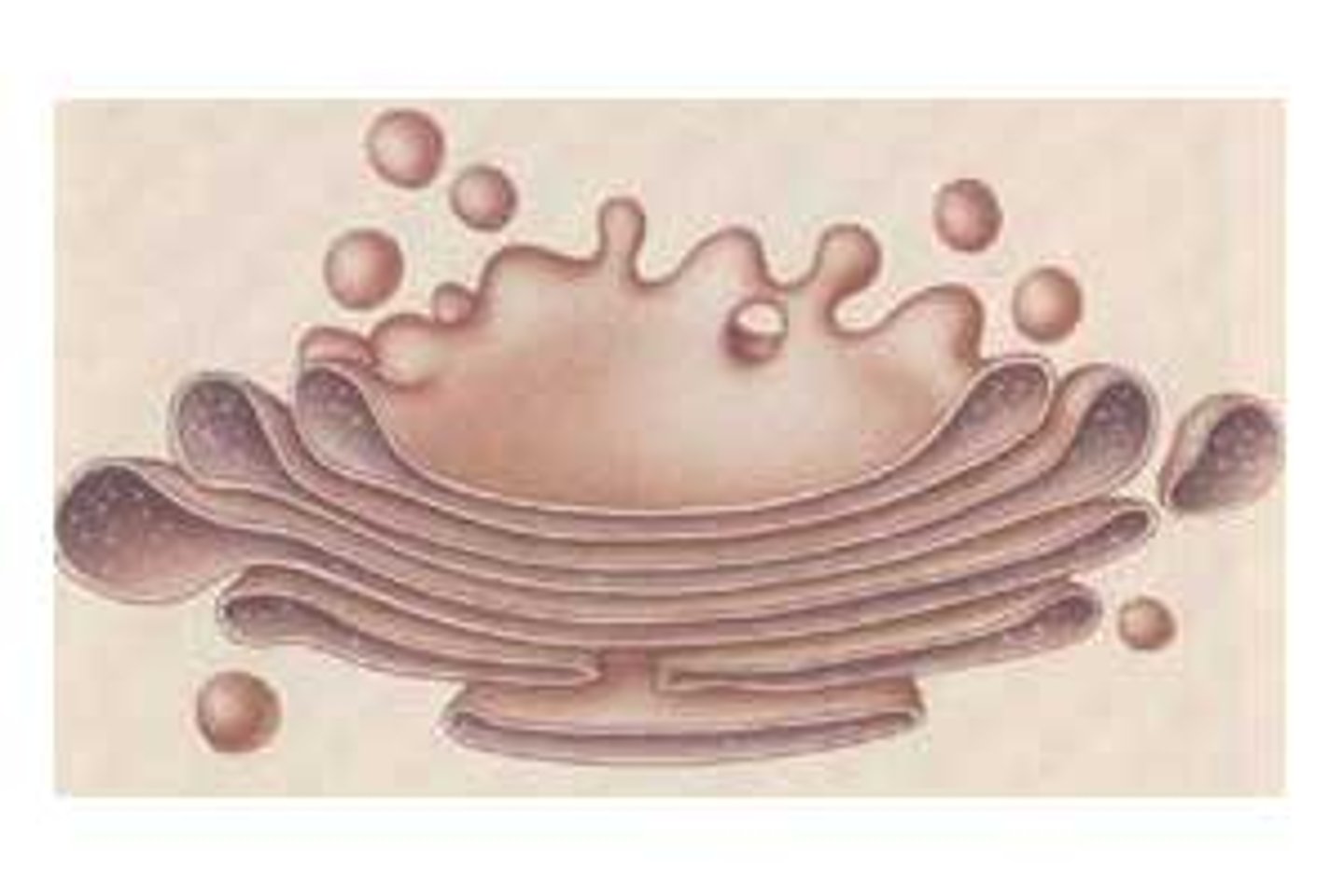
Golgi Apparatus
Packages and secretes substances produced in the ER; lies near nucleus; consists of flattened membranous sacs
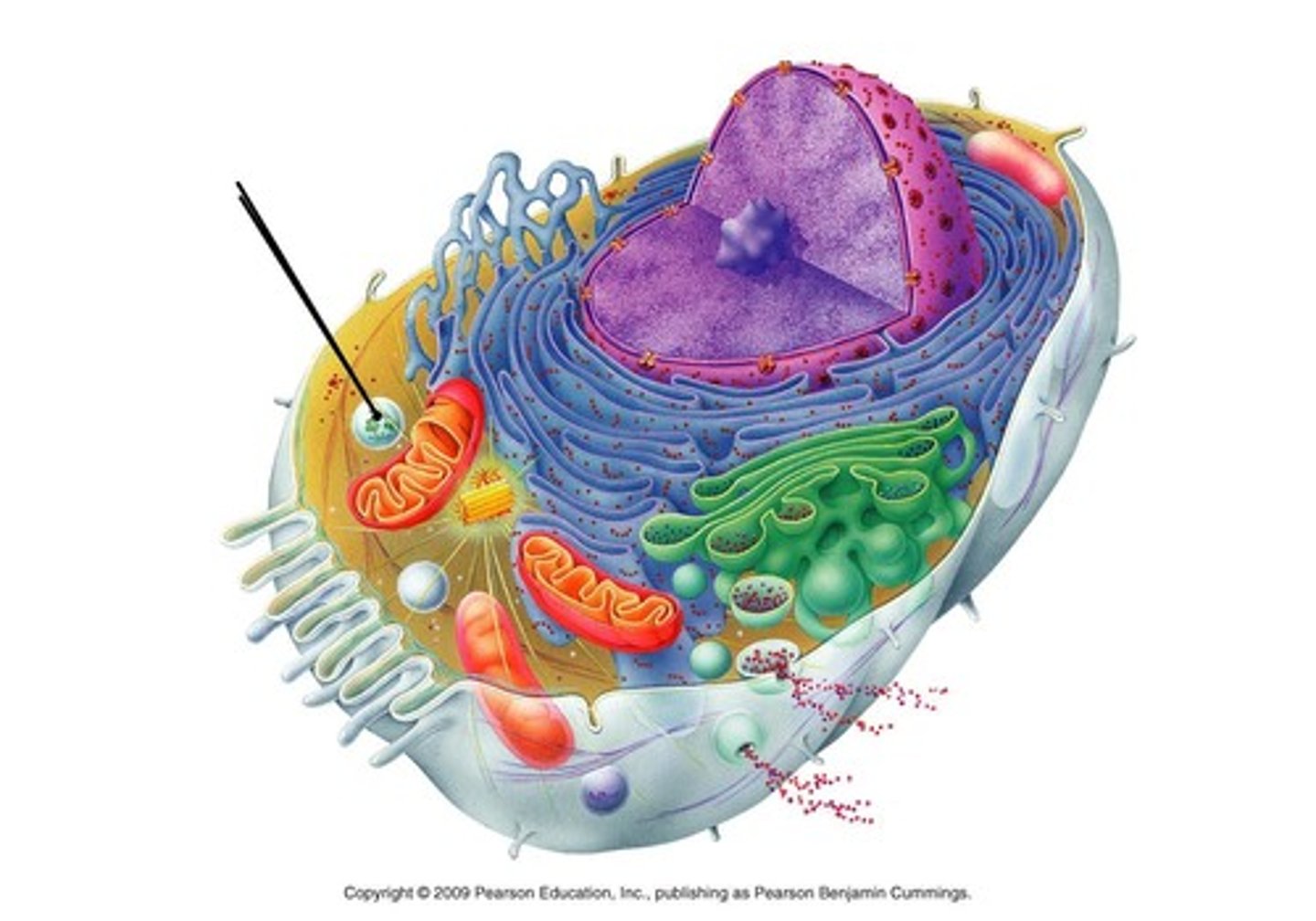
Lysosomes
Sacs of hydrolytic enzymes that digest macromolecules; Also carries of apoptosis
Absent from plant cells
Found in large numbers in white blood cells
Lipids
Literally no affinity for water (hydrophobic), nonpolar molecules. Have C, H and O, but not in a 2:1 ratio.
Triacylglycerols
(Fats): Store large amounts of energy, made up of 1 glycerol + 3 fatty acids -> 1 fat + 3 water molecules. Functions as energy storage, to cushion vital organs, and insulation.
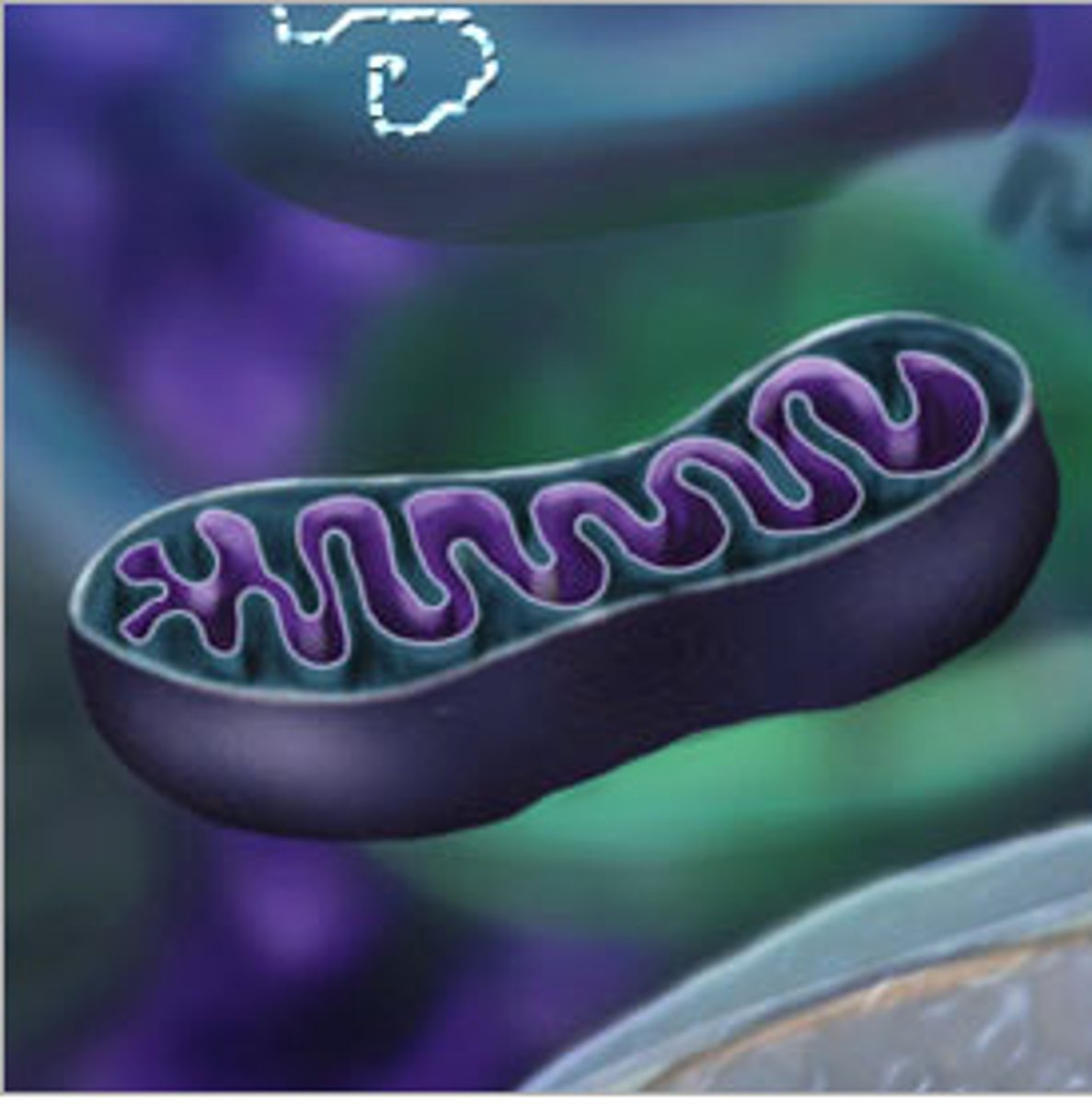
Mitochondria
Site of aerobic cellular respiration, the process that generates ATP
(Tied to theory of endosymbiosis)
Ester Linkage
Joins 3 fatty acids to a glycerol, creating a triacylglycerol
Cytoskeleton
Complex network of protein filaments that extends through cytoplasm and gives cell its shape and ability to moves (e.g., microtubules, microfilaments)
Saturated fatty acids
Fatty acids with single bonds, hydrogen at every possible position, a straight shape, from an animal source. Solid at room temperature.
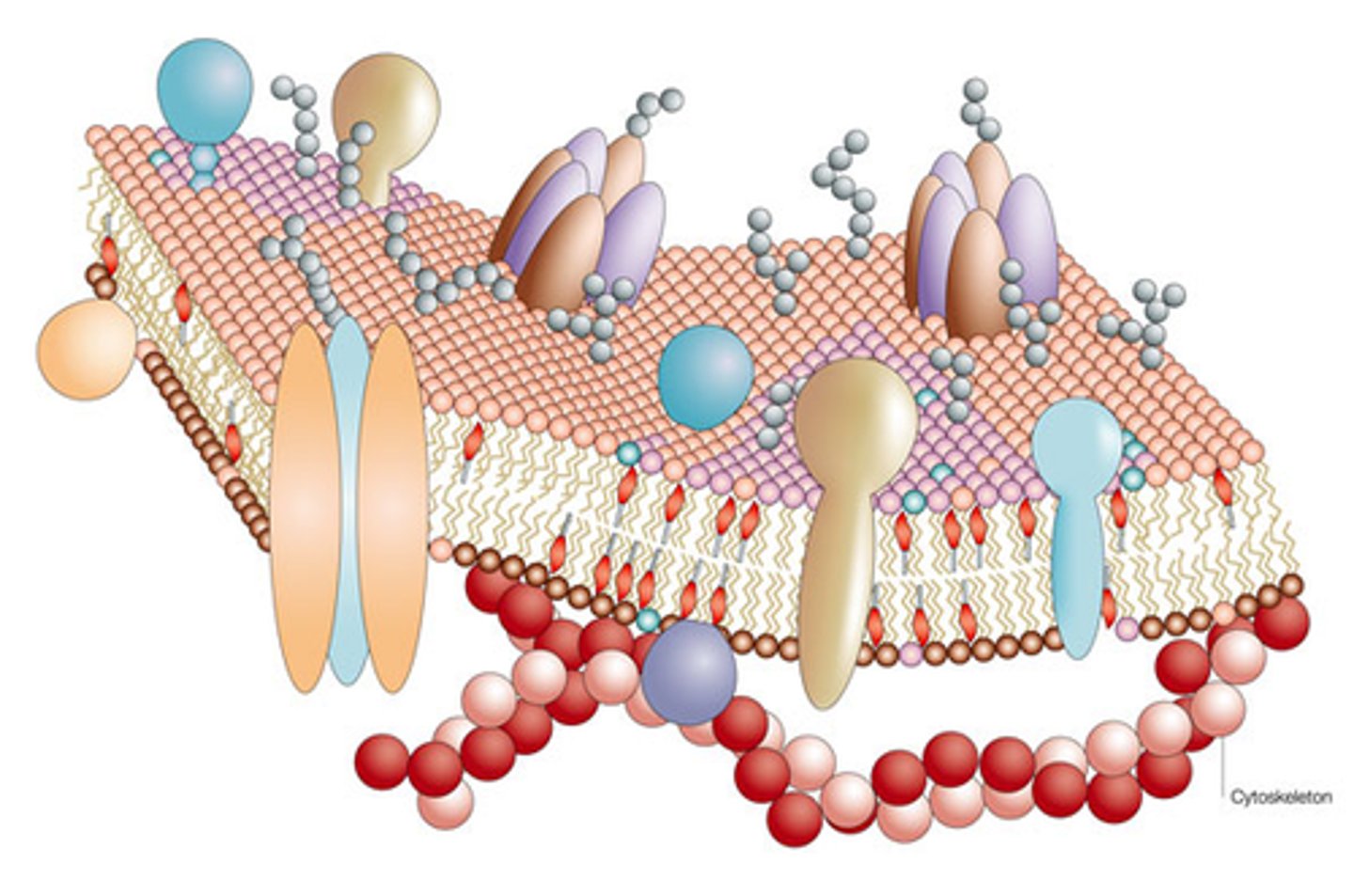
Plasma membrane
Selectively permeable outer layer of cells; made of a phospholipid bilayer with proteins dispersed throughout
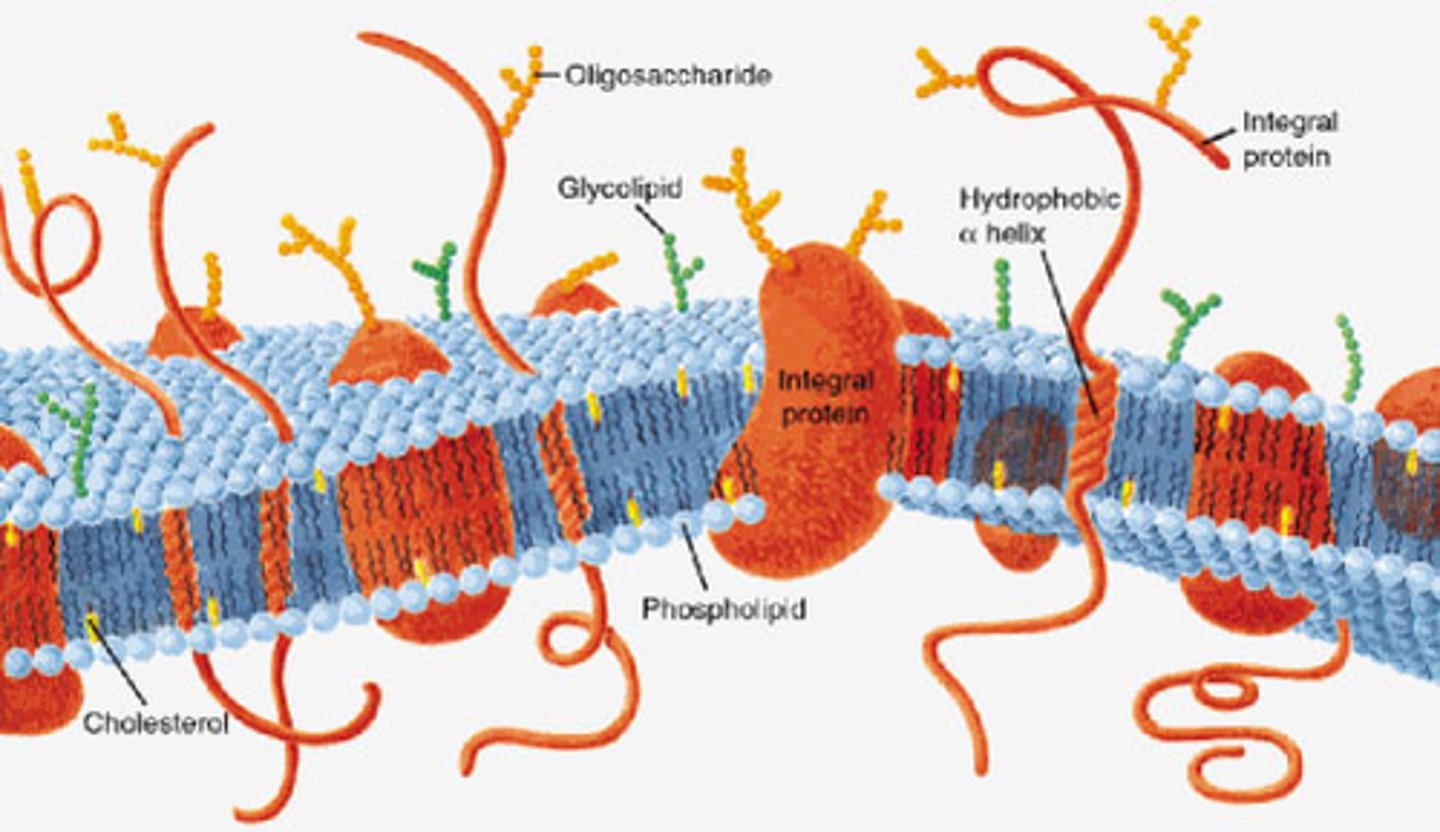
Fluid mosaic model
Model for plasma membrane that includes
-glycolipids: cell-to-cell recognition
-phospholipids: hydrophobic tails, hydrophilic heads
-cholesterol: for stability
-transmembrane proteins (e.g., pumps, enzymes, channels): for movement of large polar molecules and active transport
Unsaturated fatty acids
Fatty acids with double and single bonds, without hydrogens at every possible position, a kinked/bent shape, from a plant source. Liquid at room temperature.
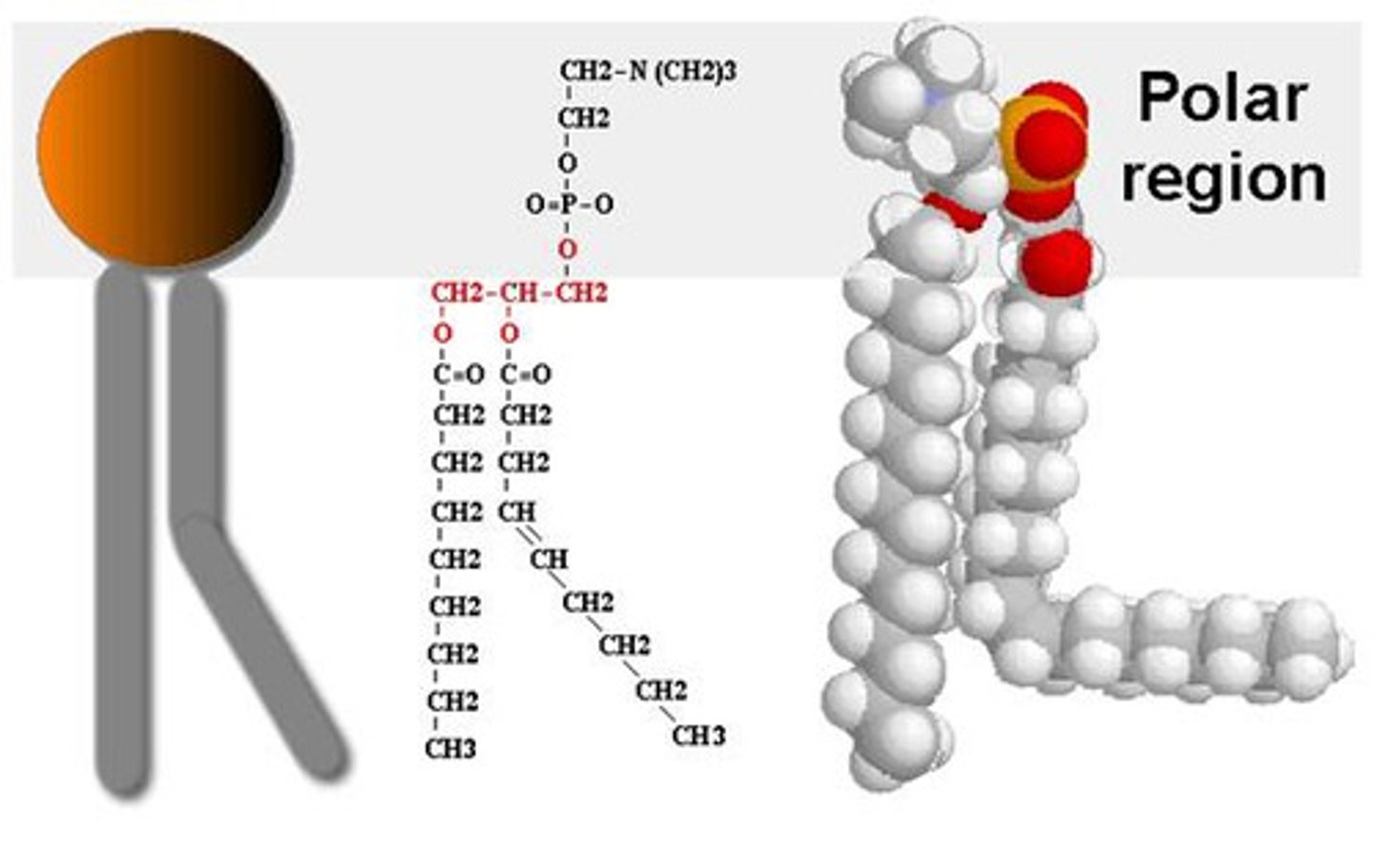
Phospholipid
2 fatty acids attached to a glycerol, with a phosphate group in the 3rd position. Have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic bonds
Passive transport
Movement of molecules down a gradient from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration; no energy required
Steroid
A type of phospholipid: A carbon skeleton with 4 fused carbon rings, which are closely interlocked. ex., cholesterol
Facilitated diffusion
Diffusion that requires membrane channels; larger, polar molecules
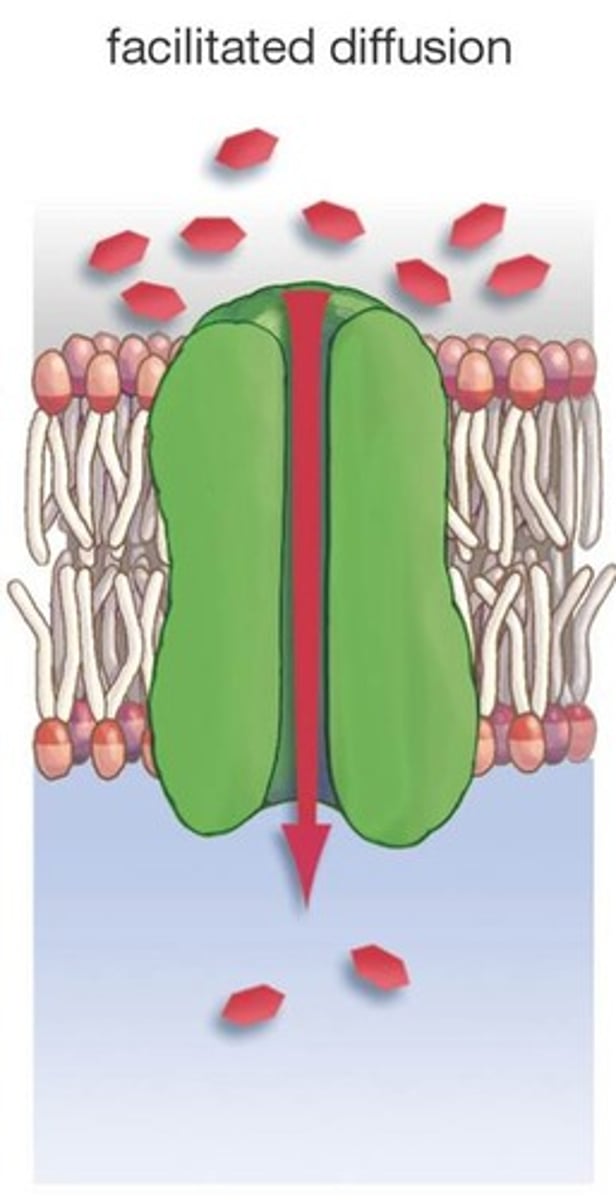
Proteins
Built up of 20 types of amino acids, which can unravel or denature in response to changes in pH, salt concentration, and temperature because they disrupt the bonds between parts of the protein
Osmosis
Type of diffusion where water diffuses across a membrane
Primary Structure
The unique sequence of amino acids, determined by DNA. Changing this affects a protein's conformation and ability to function.
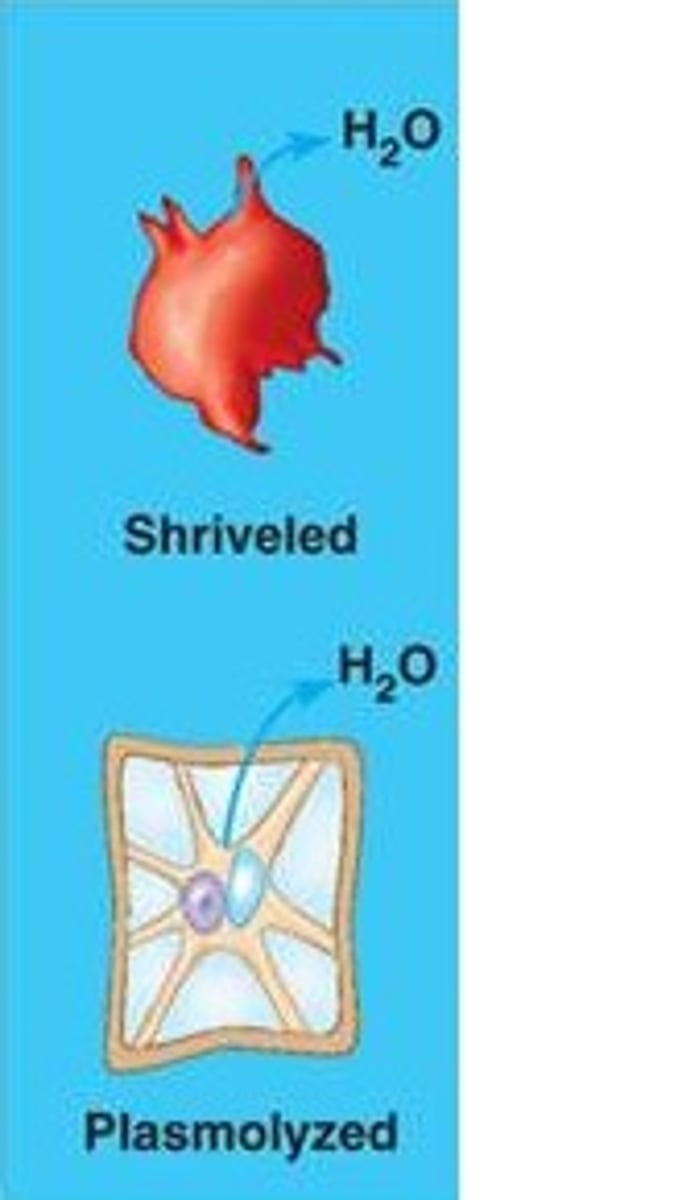
Hypertonic
Cell shrinks because water flows from higher water potential to lower water potential out of the cell; solution has higher concentration of solute
Secondary Structure
Results from hydrogen bonds at regular intervals doing the polypeptide backbone, typically developed as an alpha helix or a beta pleated sheet.
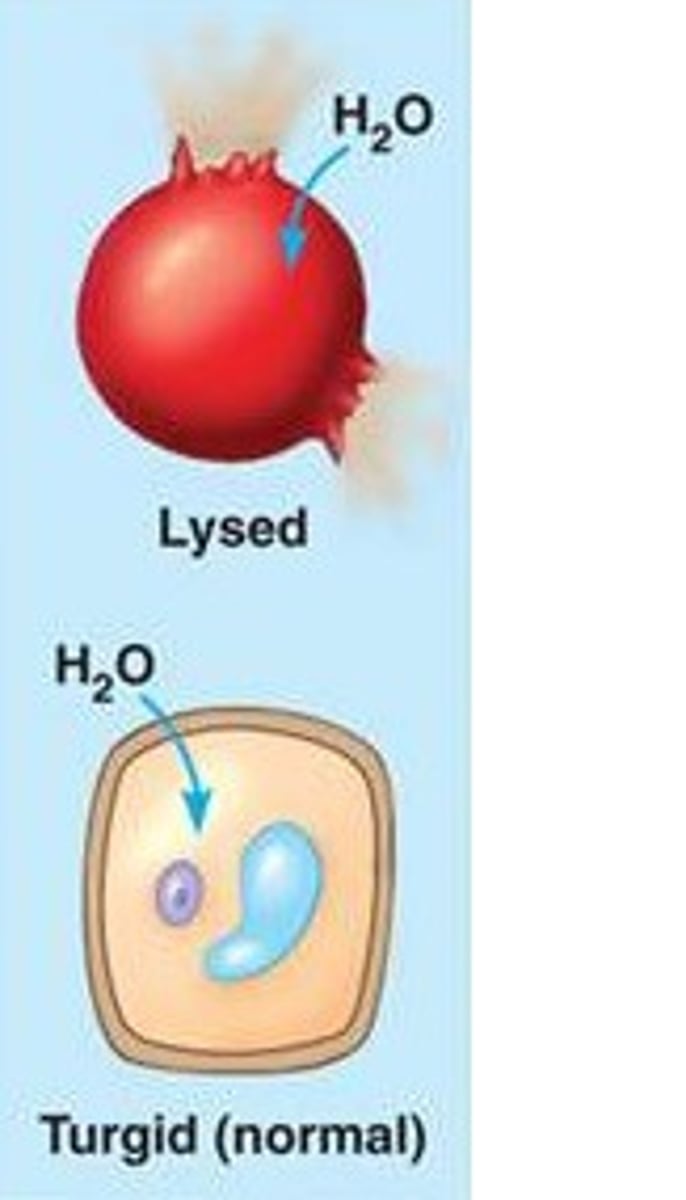
Hypotonic
Cell swells or bursts because water moves from higher water potential to lower water potential into the cell; solution has lower concentration of solute
(Plant cells do not burst, they become turgid)
Tertiary Structure
The protein has folded up upon itself, held together by hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, Van der Waals reactions, or disulfide bridges
Isotonic
Nothing happens to the cell because the concentrations of the solutions outside and inside the cell are equal
Quarternary structure
Union of 2+ polypeptide subunits
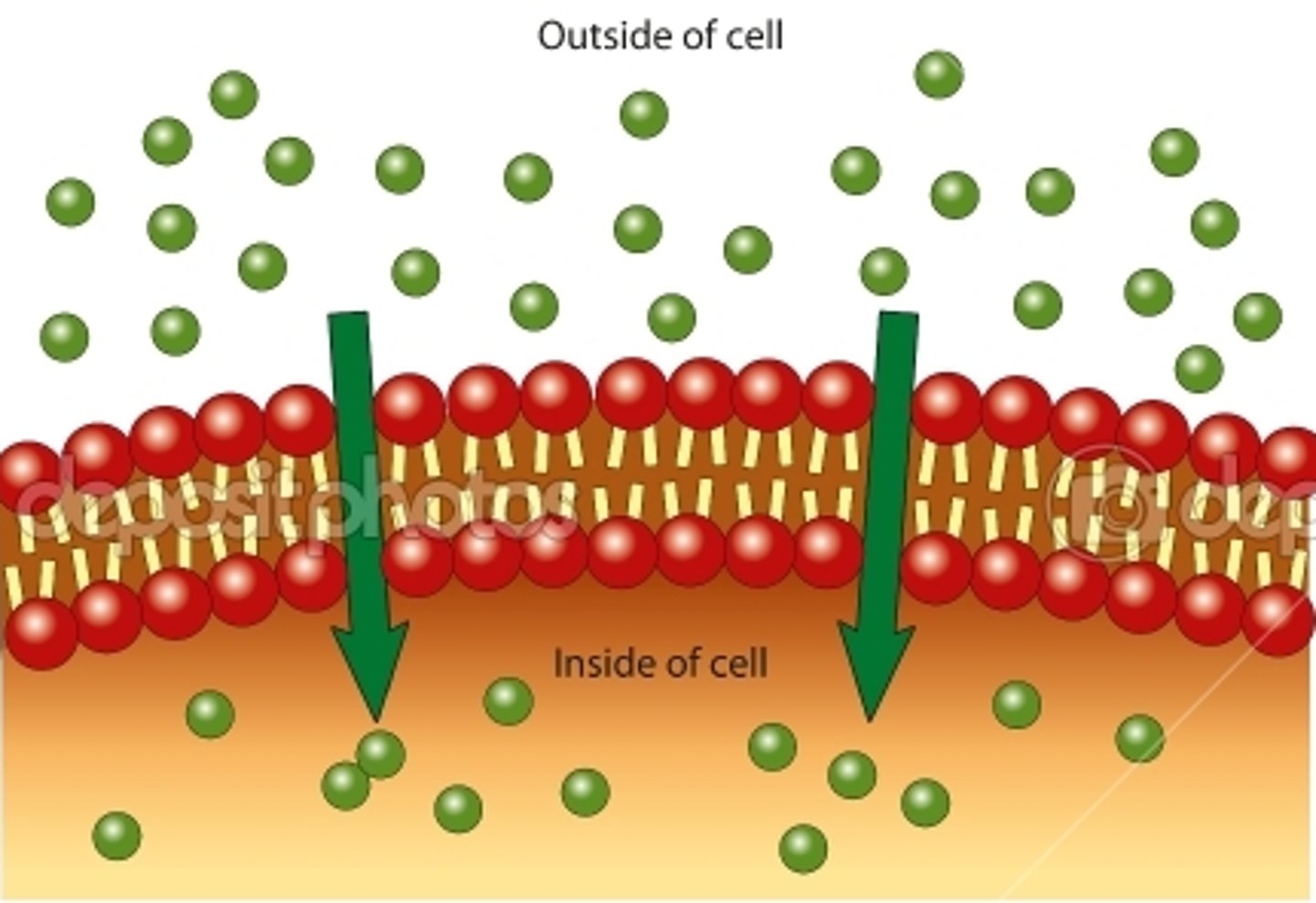
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Enzymes
Speeds up the rate of reactions, but are not consumed by the reaction. Lowers the activation energy of a reaction, and makes it easier to perform these reactions.
Endocytosis
A cell engulfs material from the environment by folding its plasma membrane inward
Exocytosis
a process by which the contents of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior through fusion of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane.
Substrate
A reactant that binds to an enzyme
Active Site
A pocket/groove on the surface of a protein on the surface of the protein into which the substrate fits. The substrate is held to this area through weak interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or Van der Waals.
Phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which a cell engulfs large particles or whole cells
Induced Fit Hypothesis
As the substrate binds, the enzyme changes shape leading to a tighter induced fit, bringing chemical groups into position to catalyze the reaction.
Pinocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which the cell ingests extracellular fluid and its dissolved solutes.
Cofactors
Non-protein factors, helping the enzyme fit substrates. ex: zinc, iron, copper
Receptor Mediated endocytosis
The movement of specific molecules into a cell by the inward budding of membranous vesicles containing proteins with receptor sites specific to the molecules being taken in; enables a cell to acquire bulk quantities of specific substances.
Competitive Inhibitors
Blocks the active site from having a substrate meet. Acts as a feedback mechanism
Selective Permeability
A property of a plasma membrane that allows some substances to cross more easily than others.
Noncompetitive inhibitors
Blocks the substrates at a place away from the active site.
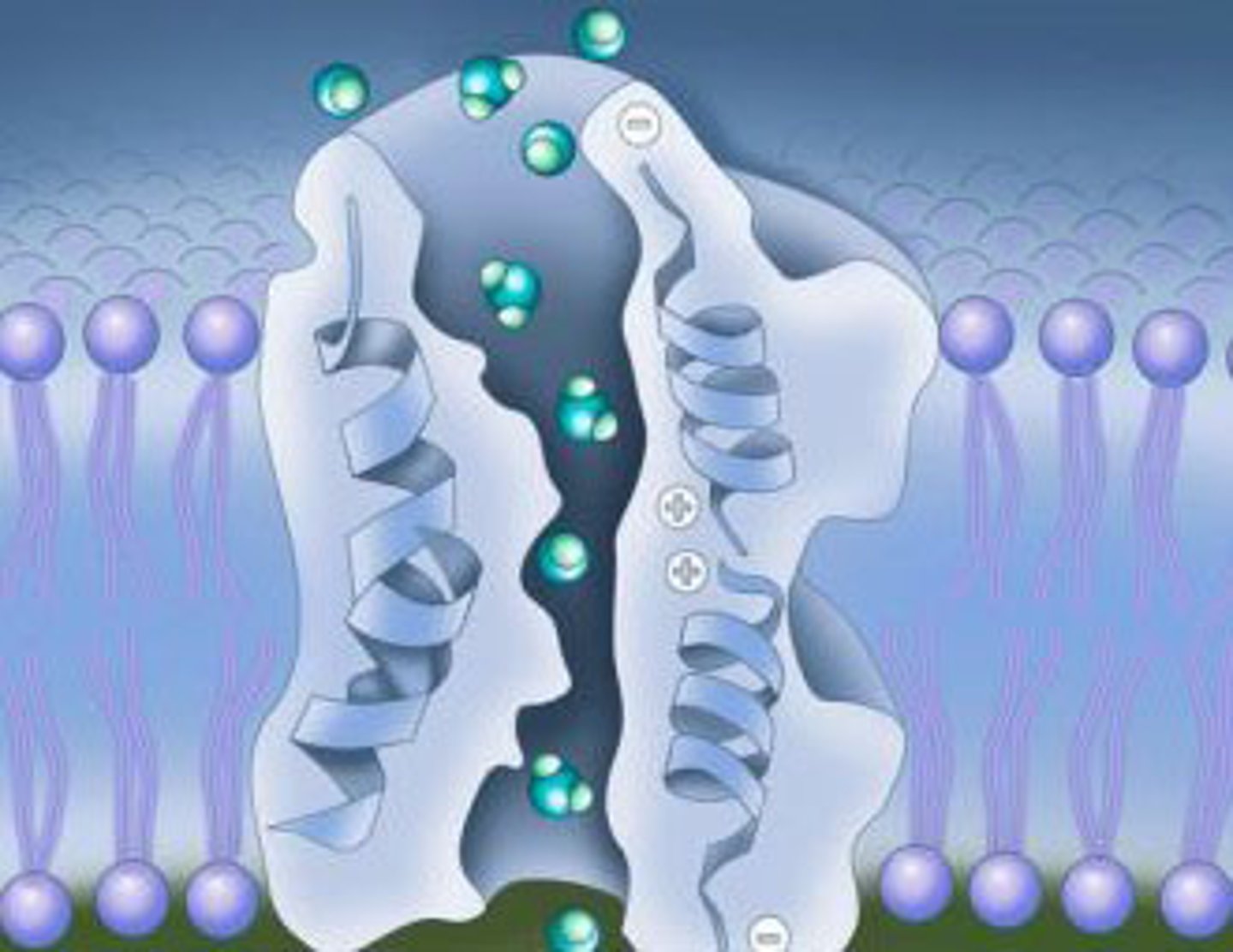
transport protein
A membrane protein that is responsible for moving hydrophilic substances from one side to the other.
Allosteric Enzymes
Enzymes that can change their shape: one shape is active (reaction occurs) and one is inactive (reaction doesn't occur)
Cells
Smallest functional unit of life
Nucleic Acids
An organic compound made up of a pentose sugar, phosphate, and nitrogen base. The three types are DNA, RNA and ATP
Organelles
A membrane-enclosed structure with a specialized function within a cell.
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
Many types of instructional nucleic acid, which is directed by DNA and contributes to protein production
Cell Theory
This says that all living things are made of cells, that cells are the basic unit of structure and function and that cells only come from other cells.
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Provides the genetic coding for organisms and directs RNA synthesis: synthesized through dehydration synthesis, connecting the sugar of one nucleotide to another with a strong phosphodiester.
Nucleotide
The building blocks of nucleic acids
Hydrophilic
water loving
Pentose sugar
Deoxyribose and ribose; a building block of nucleic acids
Hydrophobic
water fearing

Phosphate
Makes DNA and RNA charged; a building block of nucleic acids
Phospholipid
A molecule that is a constituent of the inner bilayer of biological membranes, having a polar, hydrophilic head and a nonpolar, hydrophobic tail.
Nitrogen base
Adenosine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine, Uracil (RNA); building blocks of DNA. A+T are always together, and G+C are always together based on their properties. U is only found in RNA.
Receptor Protein
proteins in the plasma membrane that are sensitive to the presence of specific extracellular molecules called ligands
Purines
Adenosine, Guanine; have a double ring,
Aquaporin
A membrane protein, specifically a transport protein, that facilitates the passage of water through channel proteins.
Pyrimidines
Thymine, Cytosine, Uracil; Single ring
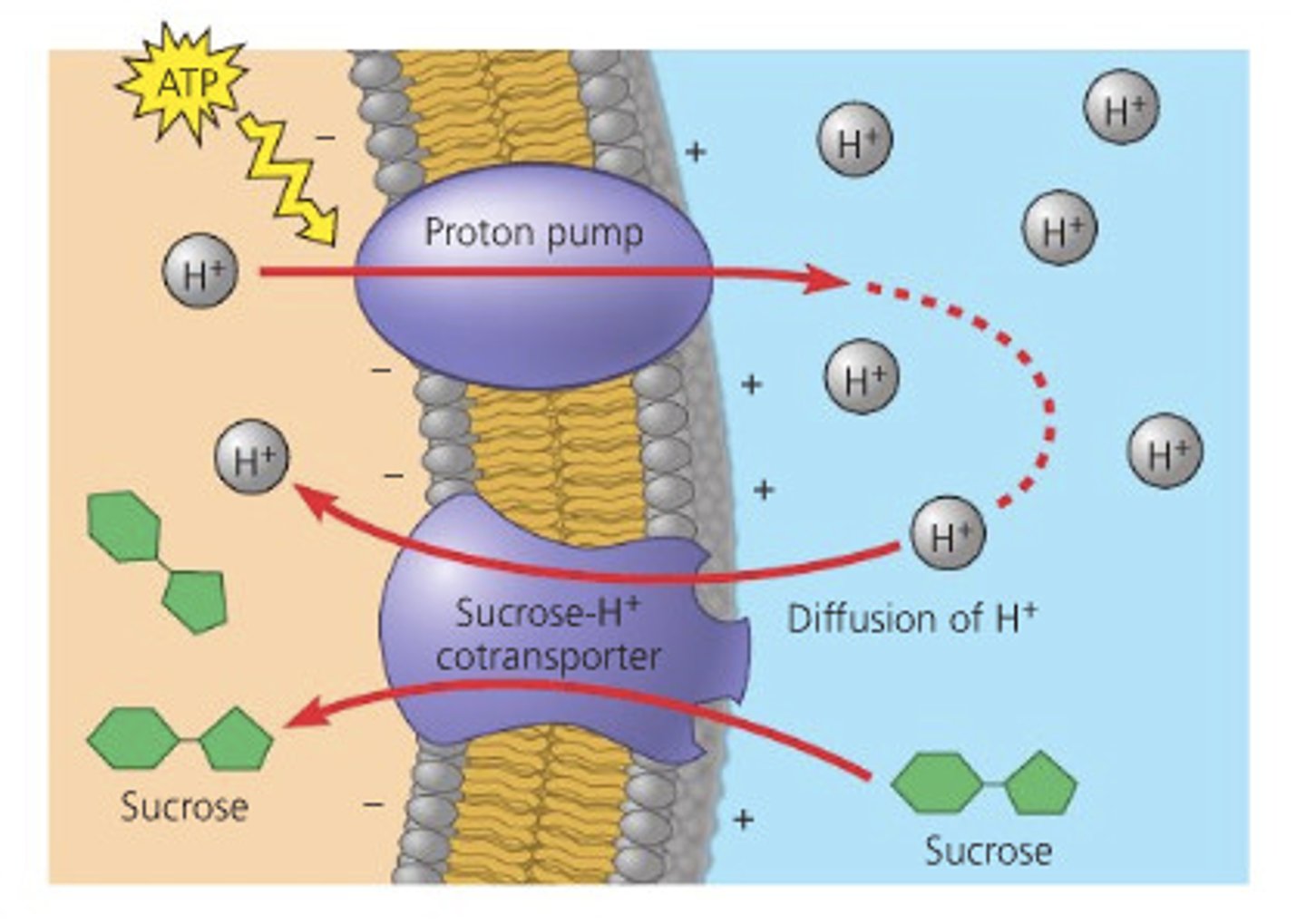
Cotransport
The coupling of the "downhill" diffusion of one substance to the "uphill" transport of another against its own concentration gradient.
Phosphodiester Link
The bond between a sugar and a phosphate.
integral protein
Transmembrane proteins with hydrophobic regions that completely span the hydrophobic interior of the membrane.

Element
a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions
Peripheral Protein
Protein appendages loosely bound to the surface of the membrane and not embedded in the lipid bilayer.
Pressure Potential
This measurement has a minimum value of 0 (when the solution is open to the environment); it increases as pressure increases.
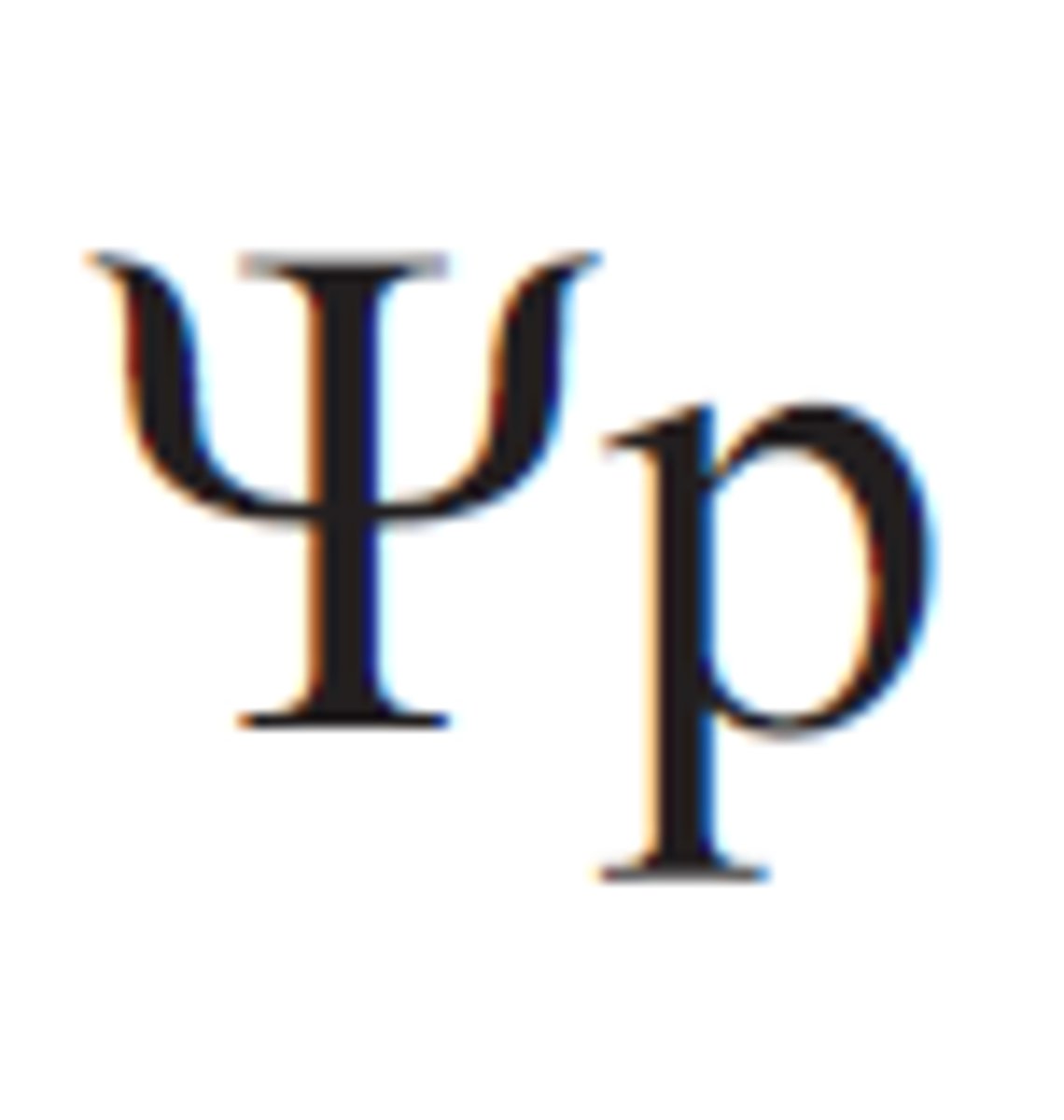
Atom
smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of an element
Atomic number
number of protons, which is unique to that element
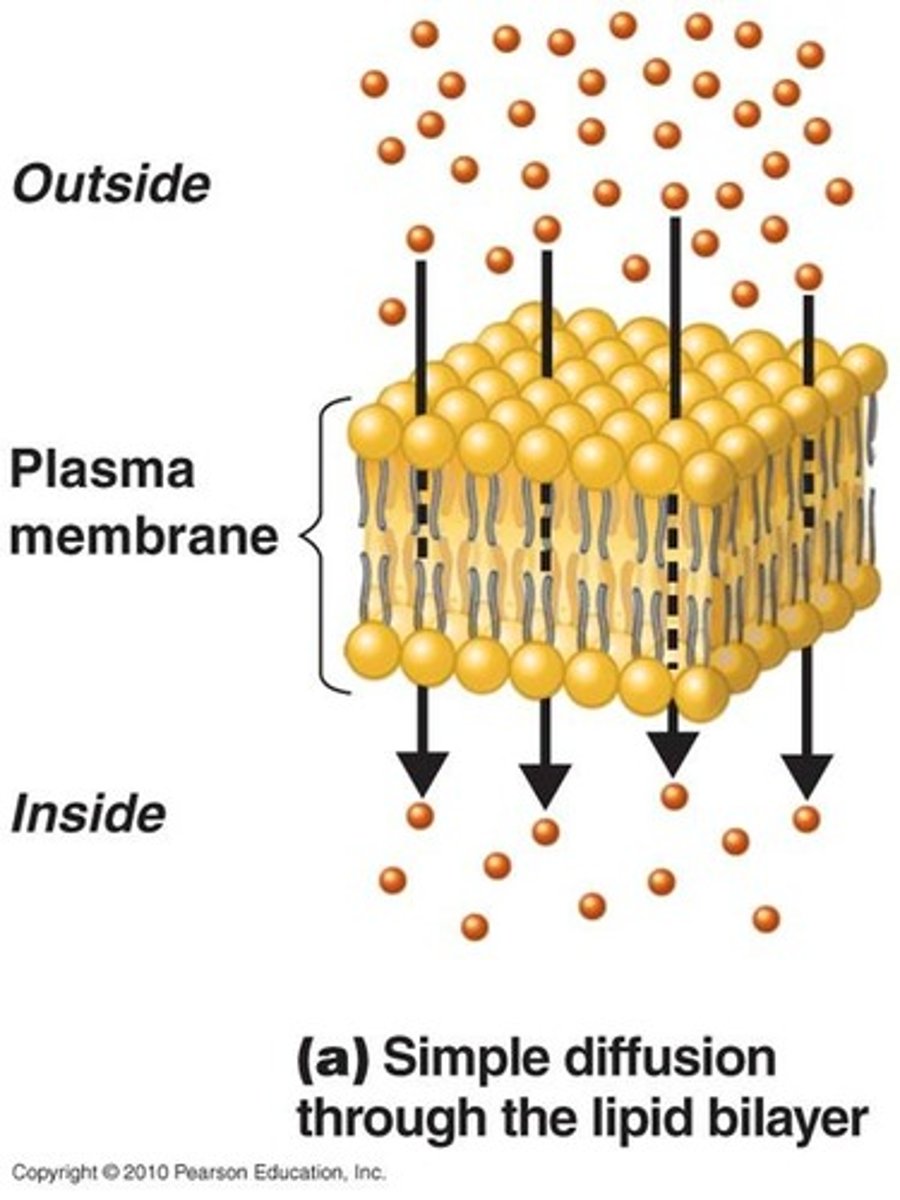
Simple Diffusion
Net movement of dissolved particles from higher concentration to a region of lower concentration