Major Events in the Evolution of Life on Earth: Fossils, Extinctions, and Adaptive Radiations
1/277
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
278 Terms
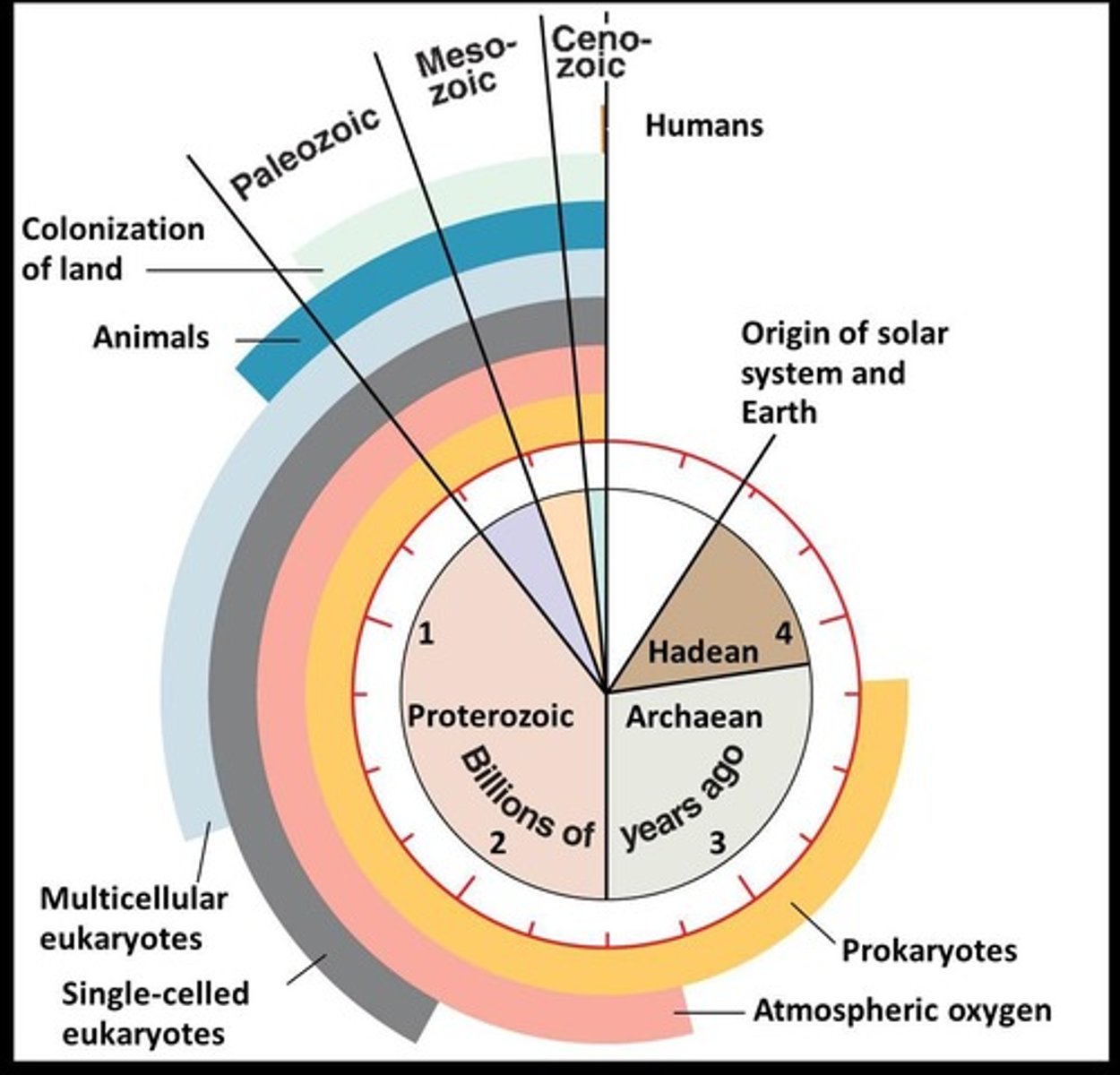
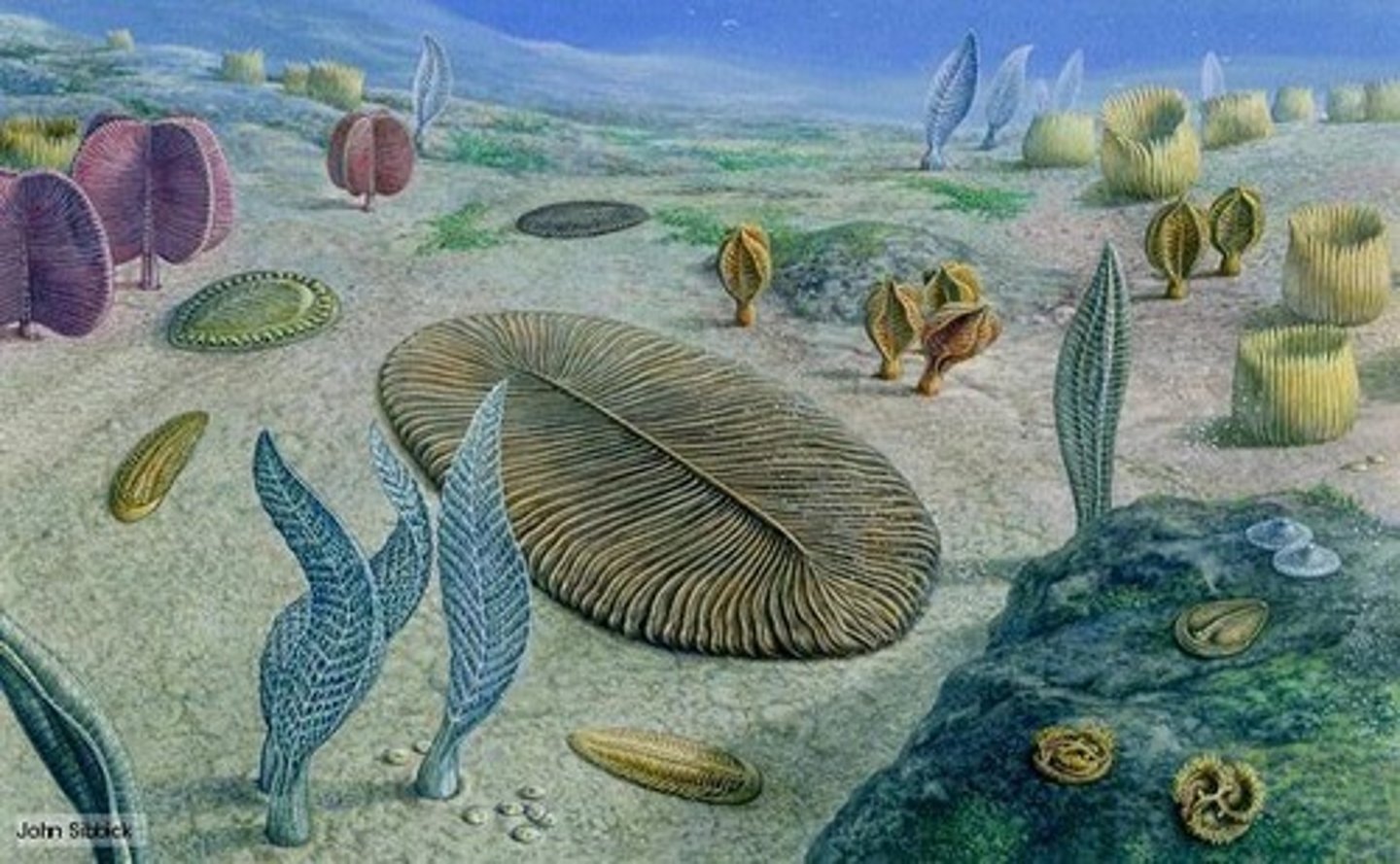
When did the first multicellular fossils evolve?
Approximately 1.2 billion years ago (BYA).
When did animals first arise?
Around 650 million years ago (MYA).
What period is known as the Carboniferous Period?
360 to 290 million years ago (MYA).
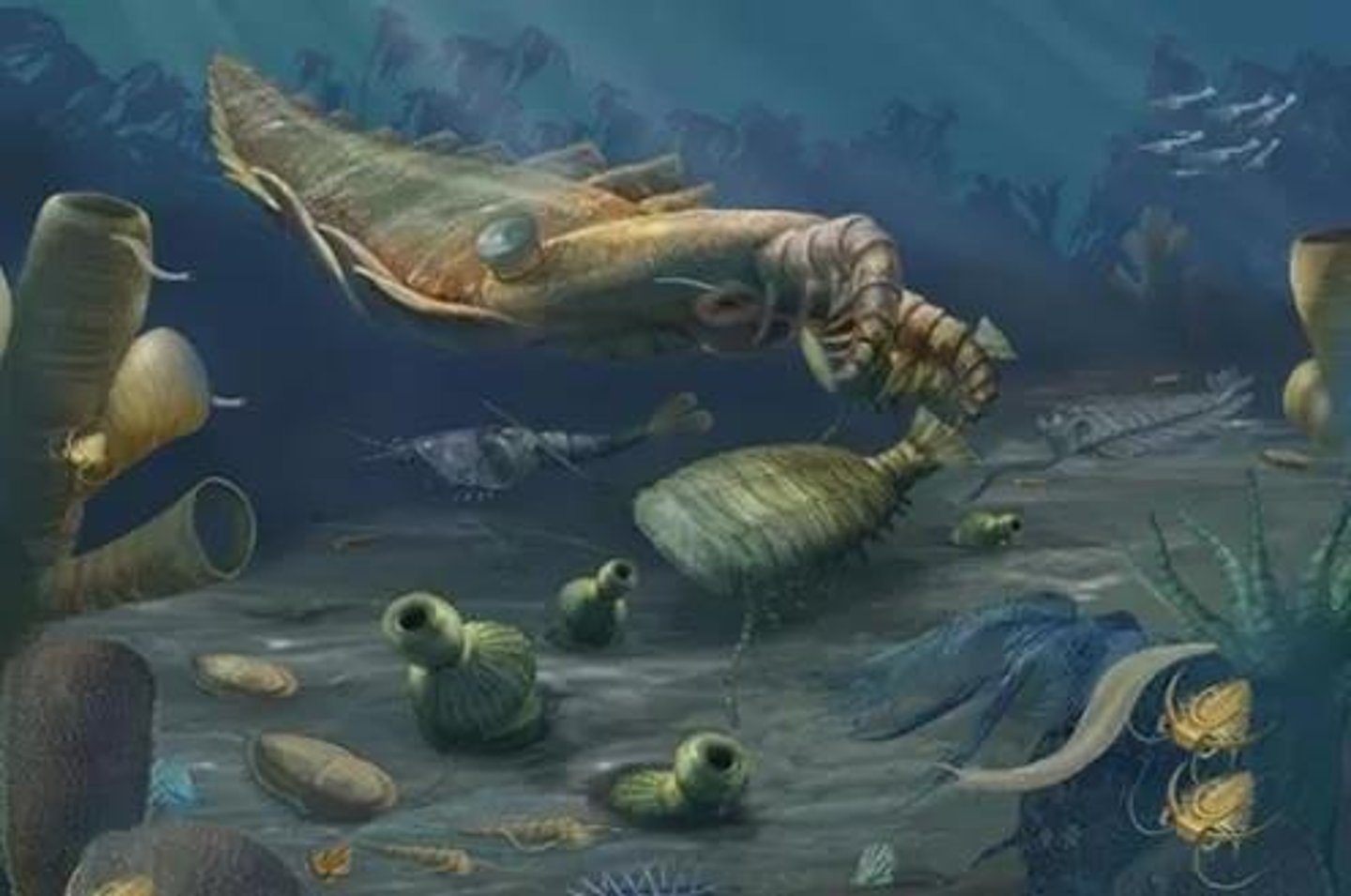
What are the first animals believed to be?
Sponges.

What significant event occurred after the Ediacaran period?
The Cambrian explosion.
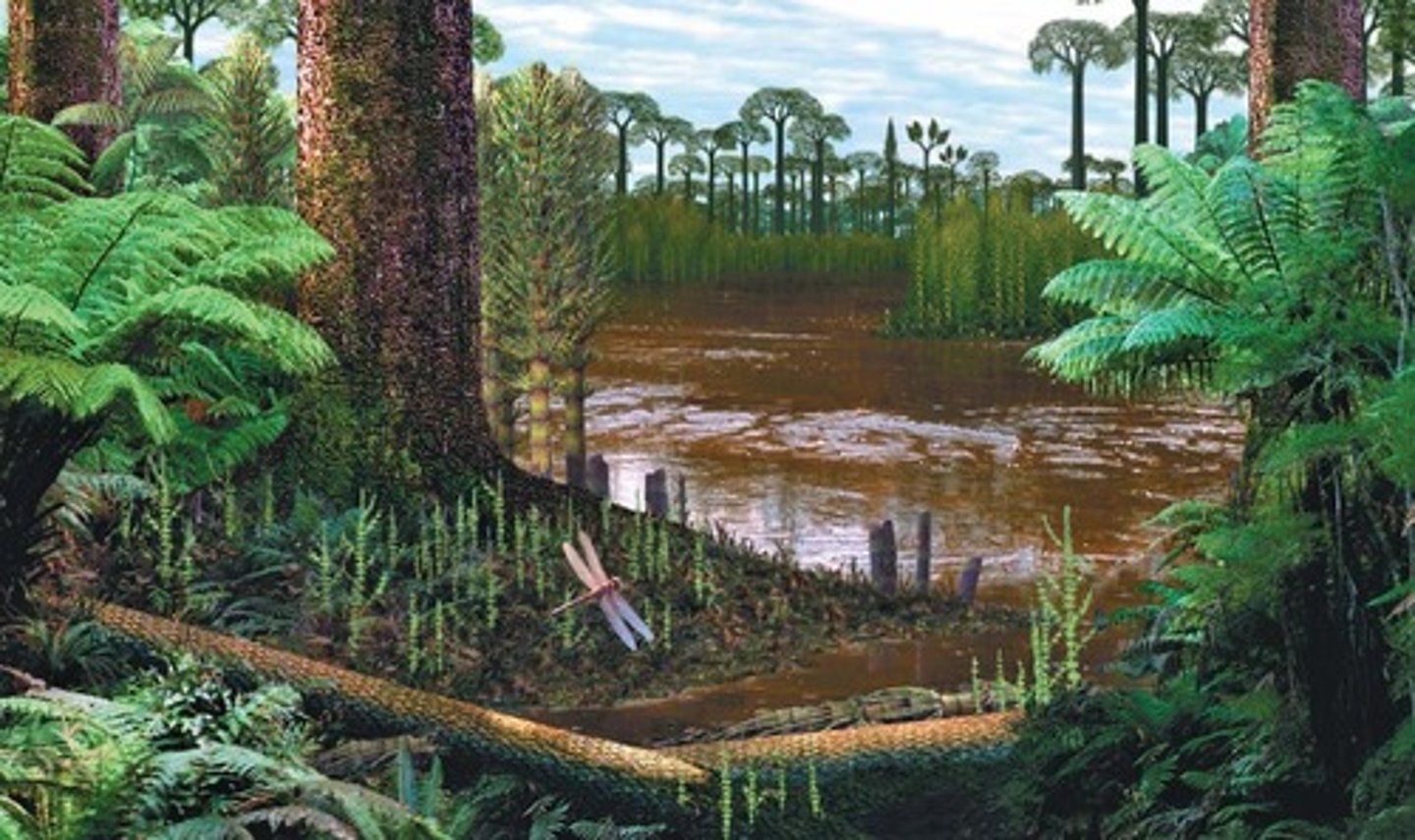
What major transition did plants make around 475 MYA?
The colonization of land.
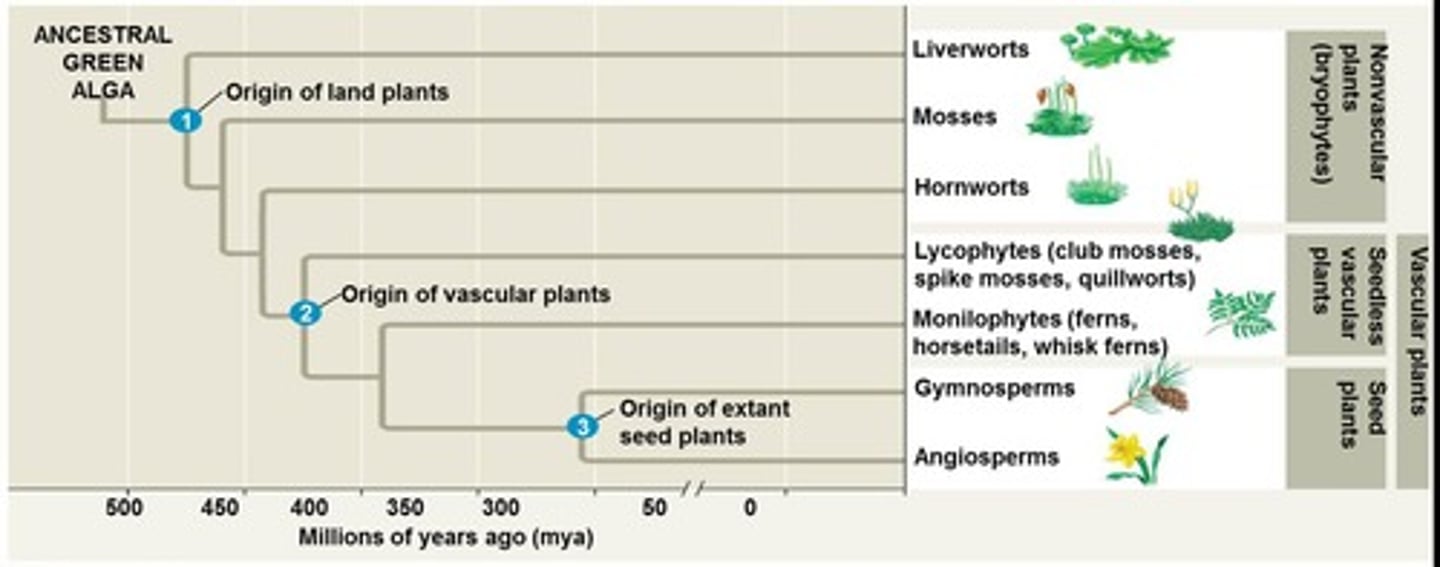
What allowed plants to grow tall during their evolution?
The development of vascular tissues.
What was the atmospheric oxygen concentration during the Carboniferous period?
Increased from 2% to 30%.
What role do fungi play in ecosystems?
Fungi are decomposers that break down dead organic matter.
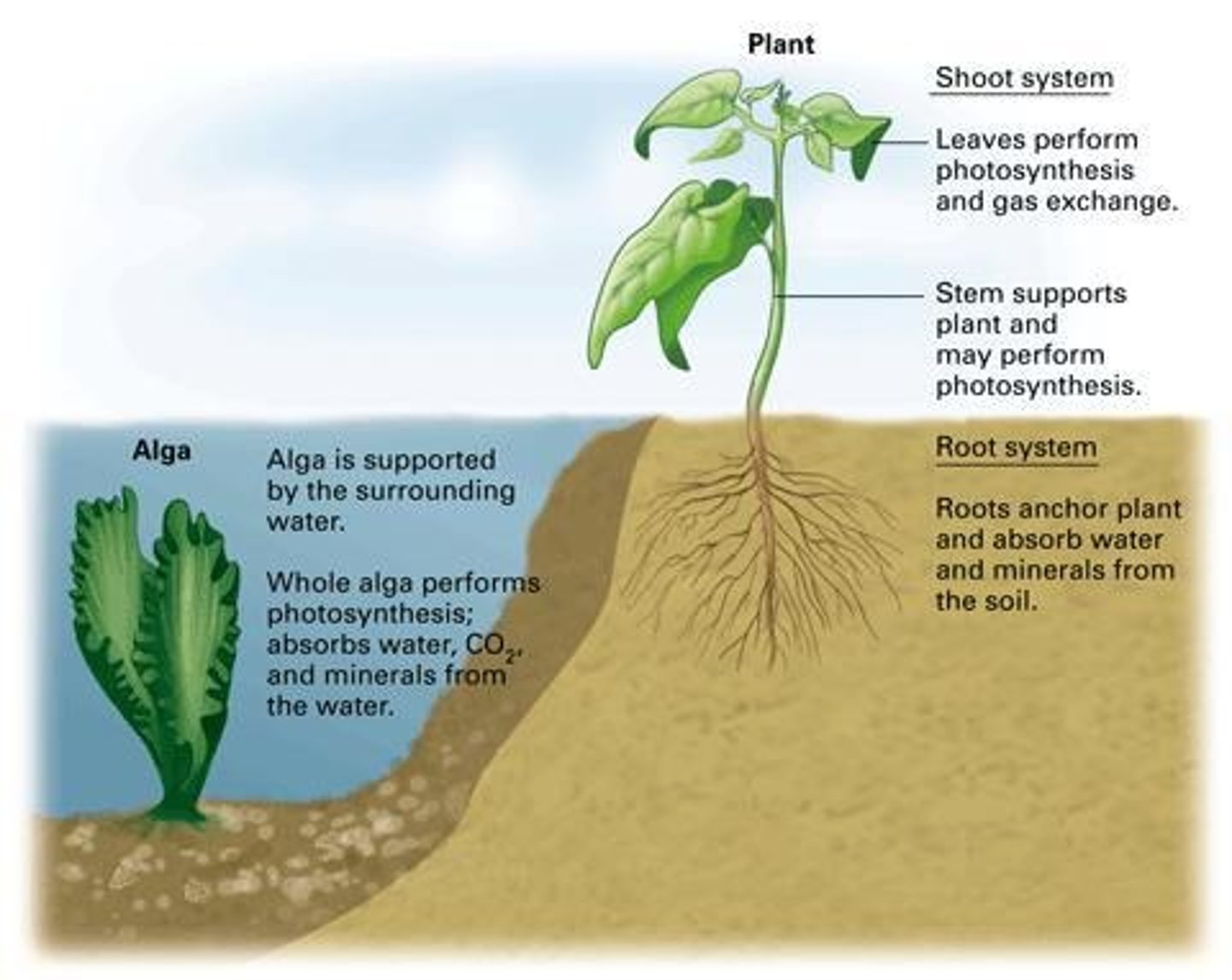
What are the closest relatives of land plants?
Green algae called charophytes.
What challenges did plants face when transitioning to land?
Scarcity of water and lack of structural support.
What is the significance of the plant transition to land?
It allowed life to spread from water to terrestrial environments.
What are the five mass global extinctions identified?
1) Ordovician-Silurian, 2) Late Devonian, 3) Permian, 4) Triassic-Jurassic, 5) Cretaceous.
What was the most devastating mass extinction event?
The Permian extinction, which occurred about 252 million years ago.
What are two hypothesized causes of past mass extinctions?
Increased volcanism and asteroids hitting the planet.
What evidence indicates climate change over the last 15 years?
Not significant changes in temperature and CO2 data.
What proof do we have of climate change?
Melting glaciers and ice caps.
What are the first life forms on Earth believed to be?
Unicellular prokaryotic microorganisms.
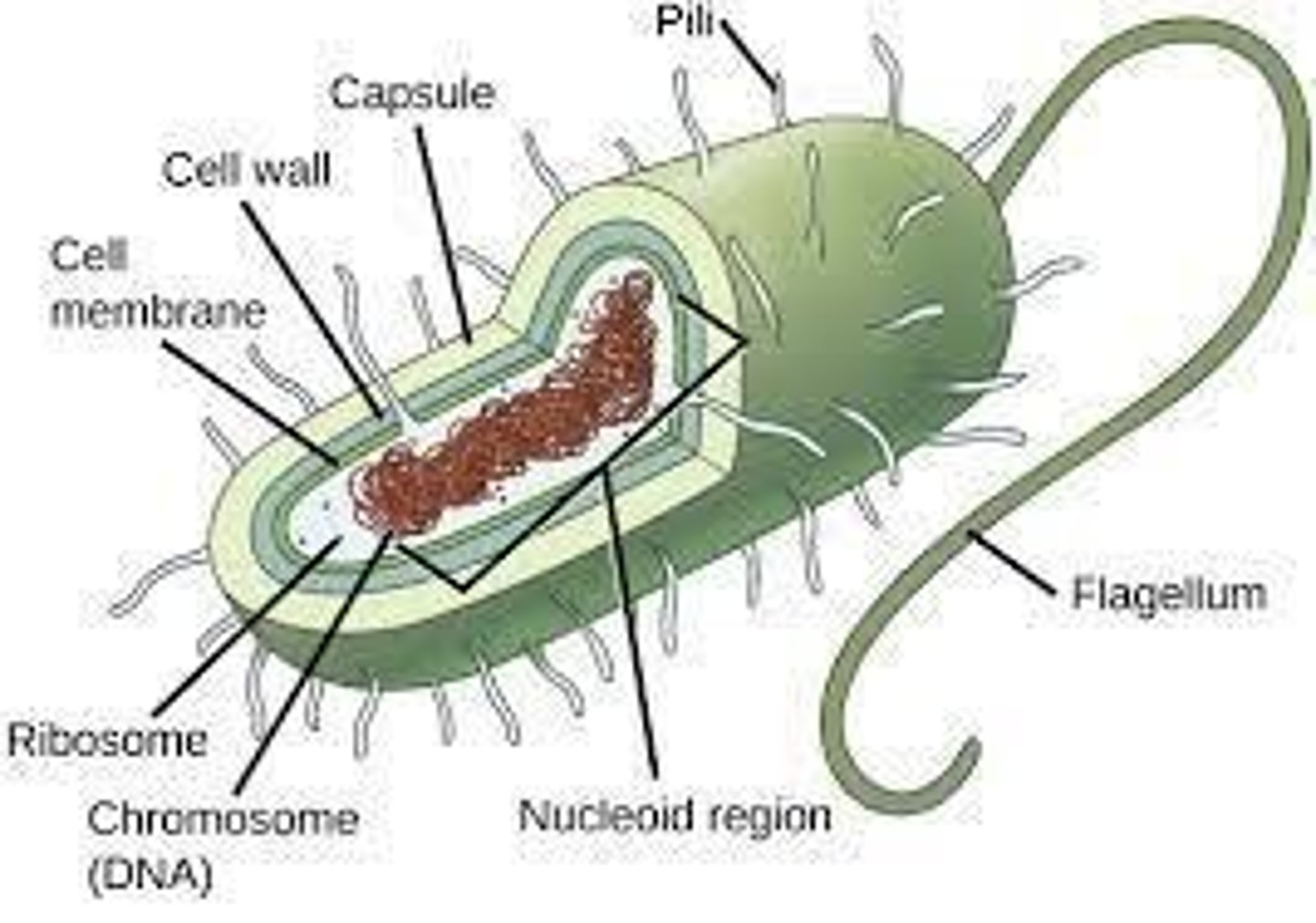
What is the role of decomposers in ecosystems?
They break down dead plants, animals, and waste into simpler substances.
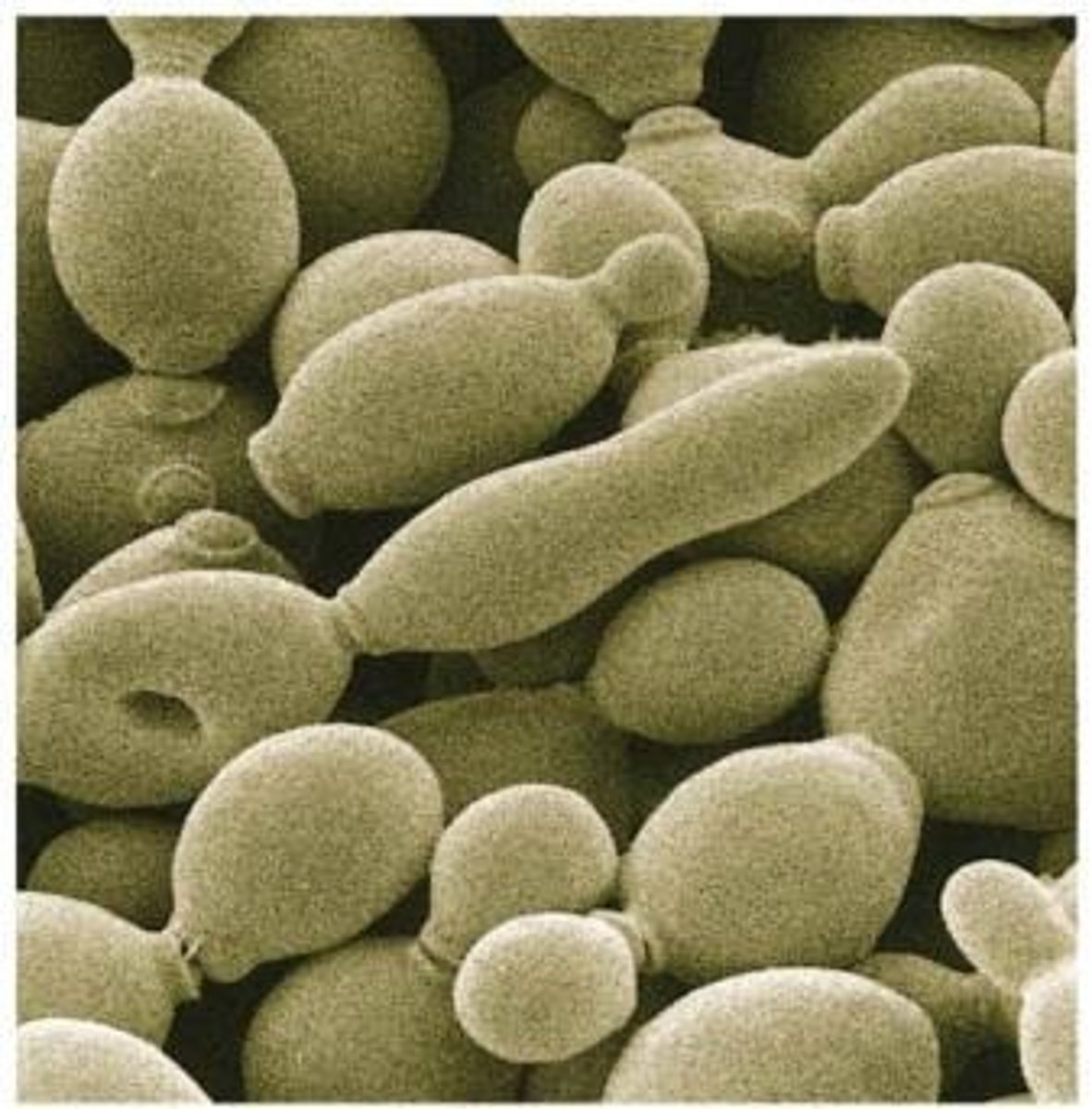
What type of organisms are yeast and mushrooms classified as?
Yeast is unicellular, while mushrooms are multicellular.
What significant change occurred in CO2 levels during the Carboniferous period?
A five-fold decrease in CO2 levels.
What adaptations did early land plants have?
They were adapted to periodic drying and exposure to air.
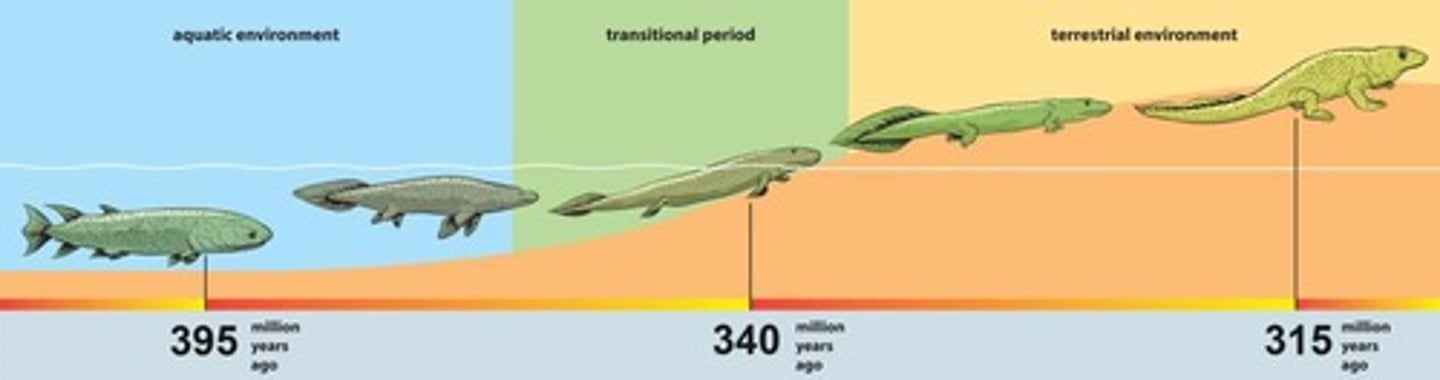
What is the significance of the Cambrian explosion?
It marked a rapid diversification of life forms.

What are the three groups to categorize personal choices to reduce climate change impact?
1) Low impact, 2) Moderate impact, 3) High impact.
What phenomenon explains how the evolution of a new species can lead to the evolution of subsequent species?
New species present new habitats or resources for additional species to specialize.
What is the fundamental niche?
The potential niche of a species.
What is the realized niche?
The actual niche that a species occupies.
What is adaptive radiation?
The evolution of one species into many to fill available niches.

What are the three main types of interspecific interactions?
Competition, predation, and symbiosis.

What is competition in ecological terms?
An interaction where two species compete for the same limiting resource, resulting in a negative effect on both (-/-).
What is competitive exclusion?
The principle stating that two species competing for the same resource cannot coexist indefinitely.
What is predation and its effect on species?
An interaction where one species (predator) benefits at the expense of another (prey), resulting in a positive/negative effect (+/-).
What is co-evolution?
The process where two species evolve in response to each other, often seen in specific interactions.
What are the two types of mutualism?
Facultative mutualism, where both species can survive independently, and obligate mutualism, where one cannot survive without the other.
What is commensalism?
A symbiotic relationship where one species benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed (+/0).
What is parasitism?
A symbiotic relationship where one species benefits at the expense of another, typically not killing the host immediately (+/-).
What is an example of co-evolution involving a star orchid and a sphinx moth?
The Madagascar star orchid provides nectar for the moth, which has a long tongue to access it, facilitating pollen dispersal.
What is the difference between a food chain and a food web?
A food chain shows a linear sequence of who eats whom, while a food web illustrates the complex interconnections between multiple food chains.

What role do food webs play in ecology?
They help understand biological communities and the interactions among organisms.
What are some defenses prey may use against predators?
Speed, camouflage, mimicry, chemical defenses, alarm calls, and schooling/herding.
What is the significance of resource partitioning?
It provides evidence of competition by showing how species adapt to share resources.
What is the role of mutualism in ecosystems?
It enhances survival and reproduction for both species involved, often leading to increased biodiversity.
What is an example of facultative mutualism?
Pseudomyrmex ants and acacia trees, where both can survive independently.
What is an example of obligate mutualism?
Coral polyps and dinoflagellates, where both depend on each other for survival.
What is a trophic structure?
The feeding relationships between organisms in an ecosystem.
What are producers in an ecosystem?
Autotrophs, usually plants, that produce energy through photosynthesis.
What are consumers in an ecosystem?
Heterotrophs, usually animals, that obtain energy by consuming other organisms.
What are dominant species?
Species that are most abundant or have the highest biomass in a community.
What are the two hypotheses regarding dominant species?
1. They are most competitive in exploiting resources. 2. They are most successful at avoiding predators.
What are keystone species?
Species that control communities without being dominant, often due to their ecological niche.
What is the significance of the starfish in intertidal communities?
Starfish are keystone species that control mussel populations, preventing them from becoming dominant.
What is an energy pyramid?
A model that conceptualizes the flow of energy through different trophic levels in an ecosystem.
What is a biomass pyramid?
A model that represents the total mass of living matter at each trophic level in an ecosystem.
What is the latitudinal diversity gradient?
The increase in species diversity as one moves from the poles to the equator.
What does ESA stand for in ecological theory?
Energy-Stability-Area.
What does the ESA theory imply about biodiversity?
Greater stability, more solar energy, and larger areas lead to greater biodiversity.
What rule of thumb does Wilson use to relate area and diversity?
A tenfold increase in area results in a doubling of the number of species.
What are microplastics?
Small plastic pieces less than five millimeters long that can harm ocean and aquatic life.
What is the impact of invasive species on ecosystems?
Invasive species may become dominant due to a lack of predators or disease.
What is the significance of the Carboniferous Period?
It was characterized by giant trees and significant coal deposits due to the absence of organisms that could digest lignin.
What is plastic recycling?
The reprocessing of plastic waste into new products to reduce landfill use and environmental impact.
What percentage of plastic produced has been recycled?
Less than 10% of the more than 10 billion tons of plastic produced.
What happens to plastic in the natural world?
Natural substances decompose, but plastics do not break down easily and can persist in the environment.
What are the two types of recycling mentioned?
Bio-recycling and chemical recycling.
How do interactions between species vary?
They differ in physical proximity, whether they are symbiotic or non-symbiotic, and their effects on survival and reproduction.
What is the role of decomposers in an ecosystem?
Decomposers break down dead organic matter, returning nutrients to the soil.
What are the primary consumers in a food chain?
Herbivores that consume primary producers.
What are secondary consumers in a food chain?
Carnivores that eat primary consumers.
What are tertiary consumers in a food chain?
Carnivores that eat secondary consumers.
What are quaternary consumers in a food chain?
Top carnivores that eat tertiary consumers.
What does fossil evidence reveal about ancient Antarctica?
Fossils show that 500 million years ago, Antarctica had warm ocean waters and was home to tropical invertebrates.
What type of birds and dinosaurs lived in ancient Antarctica?
Ancient Antarctica was home to 3-meter-tall predatory 'terror birds' and giant dinosaurs like Cryolophosaurus.
What is macroevolution?
Macroevolution refers to broad patterns of evolution above the species level, including the emergence of terrestrial vertebrates and the impact of mass extinctions.
What are the four main stages proposed for the origin of life on Earth?
1) Abiotic synthesis of small organic molecules, 2) Joining of small molecules into macromolecules, 3) Packaging of molecules into protocells, 4) Origin of self-replicating molecules.
What evidence supports the abiotic synthesis of organic molecules?
Miller-Urey experiments and findings from meteorites, such as the Murchison meteorite, which contains amino acids and other organic compounds.
What was the composition of Earth's early atmosphere according to some hypotheses?
The early atmosphere may have been thick with water vapor, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, methane, ammonia, and hydrogen.
Who proposed the hypothesis that Earth's early atmosphere was a reducing environment?
A. I. Oparin and J. B. S. Haldane independently proposed this hypothesis in the 1920s.
What did Stanley Miller's 1953 experiment demonstrate?
Miller's experiment demonstrated that organic compounds, including amino acids, could be synthesized under conditions thought to resemble early Earth.
What role did volcanic eruptions play in the synthesis of organic compounds?
Volcanic eruptions could have provided the necessary conditions for the formation of organic compounds, as suggested by experiments simulating these conditions.
What is the significance of the Murchison meteorite in the study of life's origins?
The Murchison meteorite contains over 80 amino acids and other organic molecules, indicating that some organic compounds may have extraterrestrial origins.
What is the 'primitive soup' hypothesis?
The 'primitive soup' hypothesis suggests that early oceans were a solution of organic molecules from which life arose.
What is the importance of the fossil record in understanding the history of life?
The fossil record documents the history of life, including key events like the origins of single-celled and multicelled organisms and land colonization.
How do speciation and extinction rates affect the diversity of life?
Differences in speciation and extinction rates reflect the rise and fall of groups of organisms over time.
What are some major changes in body form attributed to?
Major changes in body form can result from changes in the sequences and regulation of developmental genes.
What is the significance of the 3.5 billion-year-old microorganisms?
They provide direct evidence of life on early Earth.
What factors contributed to the early conditions on Earth that allowed for life?
The cooling of the planet, formation of oceans, and the reduction of bombardment by space debris created conditions suitable for life.
What is the relationship between natural selection and the origin of life?
Natural selection may have aided the chemical and physical processes that led to the formation of simple cells.
What are protocells?
Protocells are droplets with membranes that maintain an internal chemistry different from their surroundings, potentially leading to the first living cells.
What is the role of amino acids in the origin of life?
Amino acids are fundamental building blocks of proteins and were likely among the first organic molecules formed on early Earth.
How did the early atmosphere affect the synthesis of organic molecules?
The composition of the early atmosphere, whether reducing or neutral, influenced the potential for organic molecule synthesis.
What does the term 'self-replicating molecules' refer to?
Self-replicating molecules are those that can reproduce themselves, a key step in the evolution of life.
What is the significance of the 2008 reanalysis of Miller's experiment?
The reanalysis found that more amino acids were produced under conditions simulating volcanic eruptions than in the original experiment.
What is the impact of mass extinctions on life's diversity?
Mass extinctions significantly reduce biodiversity and can lead to the emergence of new species as ecosystems recover.
What is the significance of the term 'abiotic synthesis'?
Abiotic synthesis refers to the formation of organic compounds without biological processes, crucial for understanding the origin of life.
What role does montmorillonite clay play in vesicle self-assembly?
Montmorillonite clay greatly increases the rate of vesicle self-assembly by providing surfaces for organic molecules to concentrate and react.
What is necessary for the emergence of life as we know it?
A vast assortment of macromolecules, including enzymes, proteins, and nucleic acids, is essential for self-replication.
What did a 2009 study demonstrate regarding RNA monomers?
The study showed that RNA monomers can be synthesized spontaneously from simple precursor molecules.
How can amino acids or RNA nucleotides produce polymers?
By dripping solutions of amino acids or RNA nucleotides onto hot sand, clay, or rock, researchers have produced polymers without enzymes or ribosomes.
What are ribozymes?
Ribozymes are RNA catalysts that can carry out enzyme-like functions, including making complementary copies of RNA.
What properties do abiotically produced vesicles exhibit?
They can reproduce, grow, and maintain an internal chemical environment different from their surroundings.