11 & 12 - Adrenergic Agonists and Antagonists
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
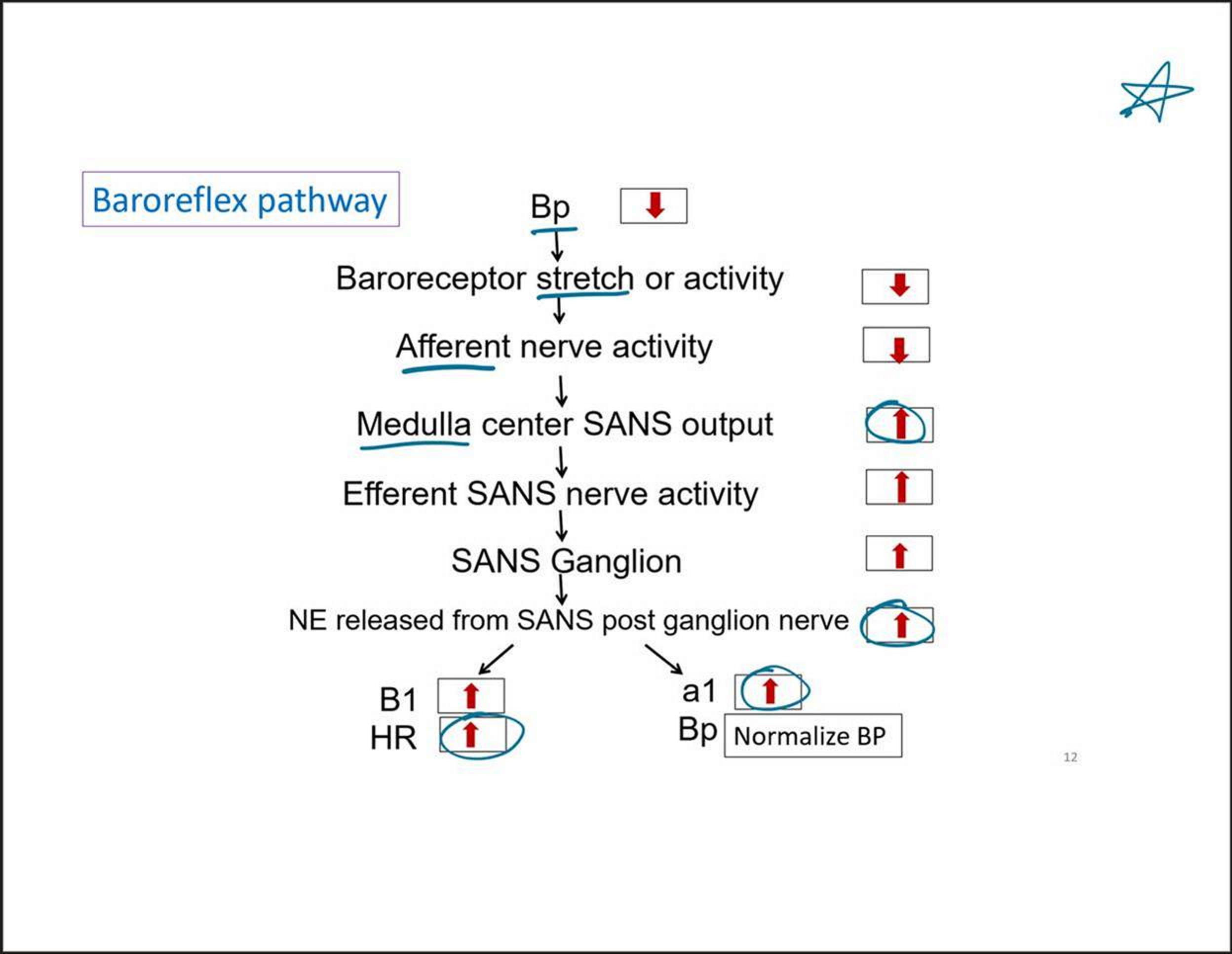
Baroreflex Pathway
Decreased BP → decreases stretch
Decreasing afferent nerve activity
Medulla increases sympathetic output (to increase BP)
Increasing symp. Nerve activity
NE is released from sympathetic post-ganglionic nerve
B1 increased, so HR increases
Alpha 1 increased, BP normalized
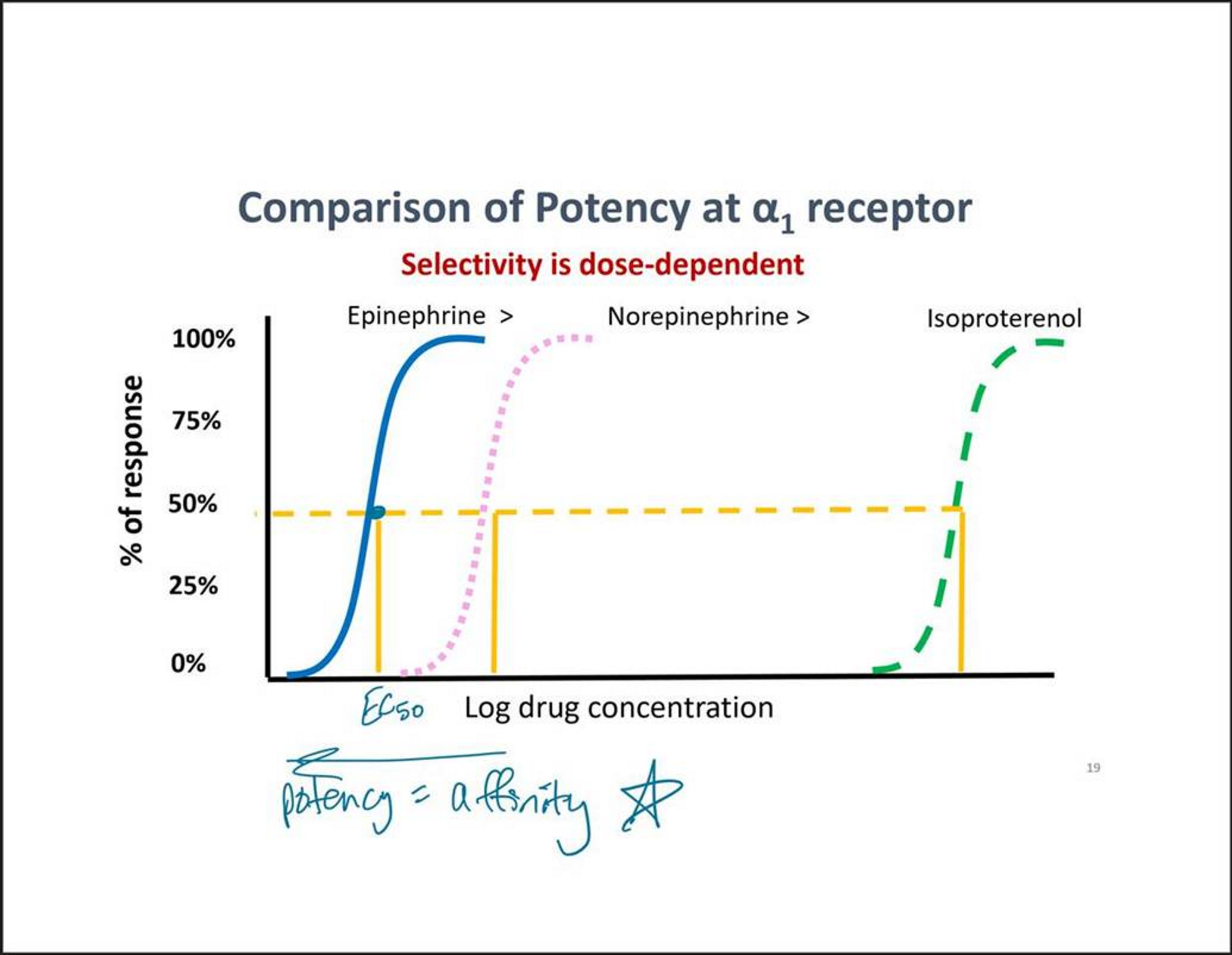
Selectivity of adrenergic agonists
Is dose dependent
Drugs will only activate certain receptors at a low dose or others at a high does
Affinity
Equal to potency of a drug
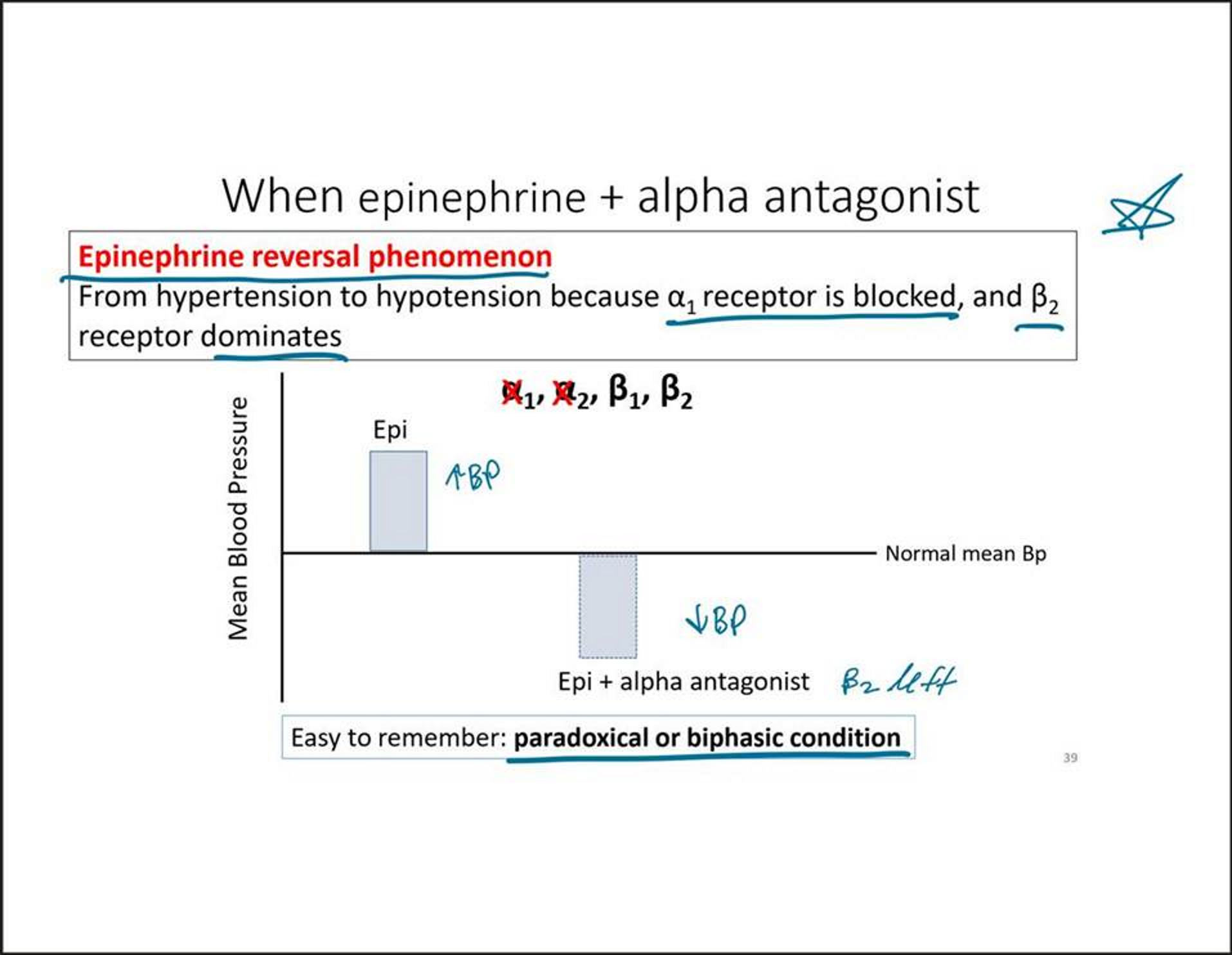
Epinephrine reversal phenomenon
Hypertension to hypotension
Due to alpha 1 receptors being blocked, so now B2 receptors dominate
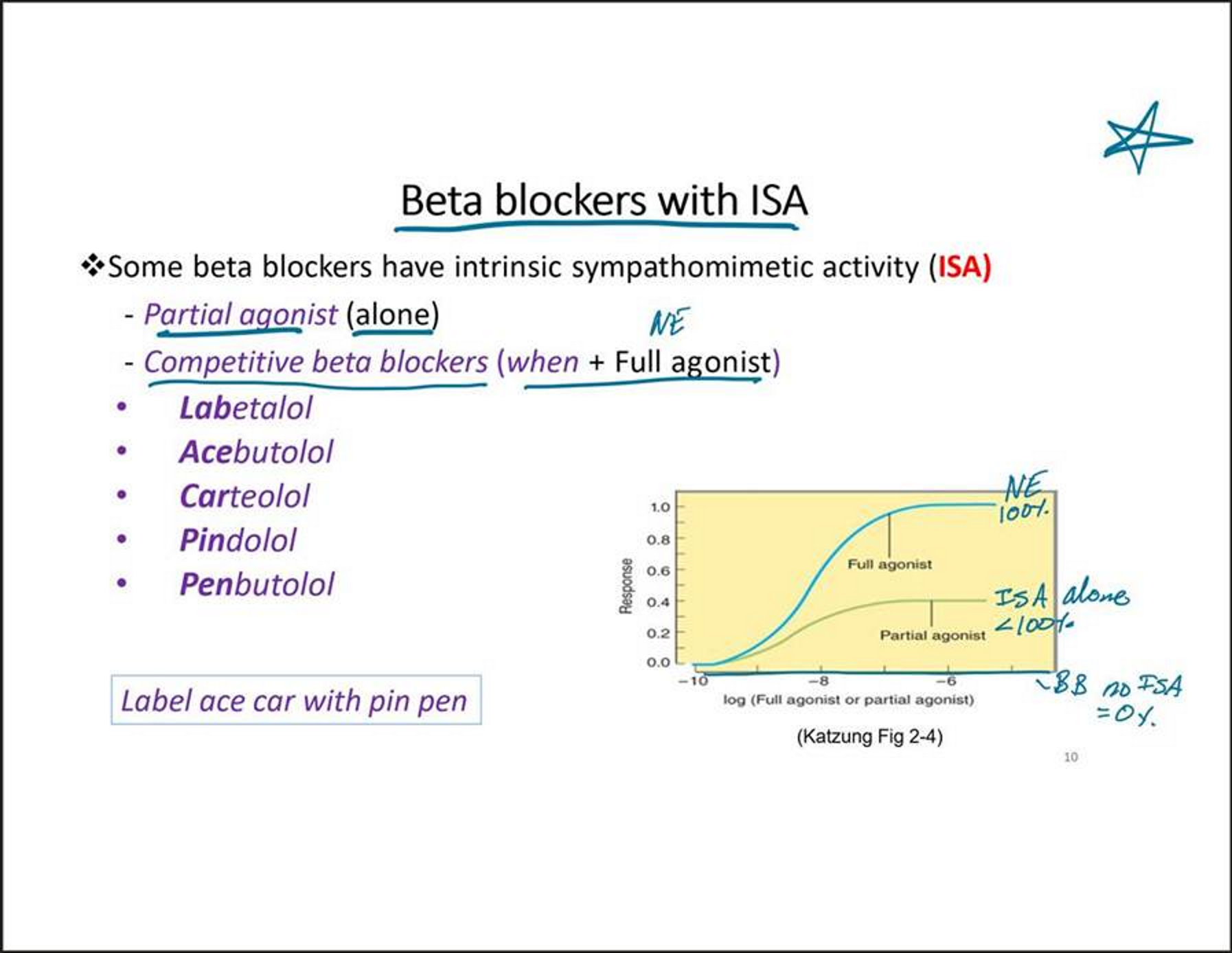
Beta blockers with ISA
Act as partial agonists alone
Act as competitive antagonists/blockers when combined with full agonist
Intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA)
Uses of beta blockers:
HTN
Angina
Arrhythmia
Post-MI
Chronic CHF
Glaucoma
Hyperthyroidism
Side effects of beta blockers:
Bronchospasm
Hyperlipidemia (VLDL)
Hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia (masks symptoms of hypo-dangerous)
Contraindications of beta blockers with ISA:
Hyperthyroidism
Angina (MI within past 1mo)
Non-selective beta blocker contraindications:
Asthma
Diabetes
Beta blocker overdose treatment:
Use glucagon! Binds to Gs to activate adenylyl cyclase (increasing cAMP)
Rebound hypertension (from beta blocker withdrawal)
Made too many receptors on drug
Suddenly stopping drug causes more NE to be attached, leading to tachycardia and HTN
BPH (benign prostate hypertrophy)
Activation of alpha 1a receptors increases smooth muscle tone (bladder, prostate)
Blocking these receptors via Tamsulosin relaxes them, increasing emptying (symptomatic relief)
Side effects of alpha blockers:
Orthostatic hypertension
Decreased venous tone → lower baroreceptor stretch → blood accumulates → less venous return → less cardiac output (CO) → lower BP→ sympathetic output increased in response
Alpha 1 decreases BP
Favorable effect on blood glucose!
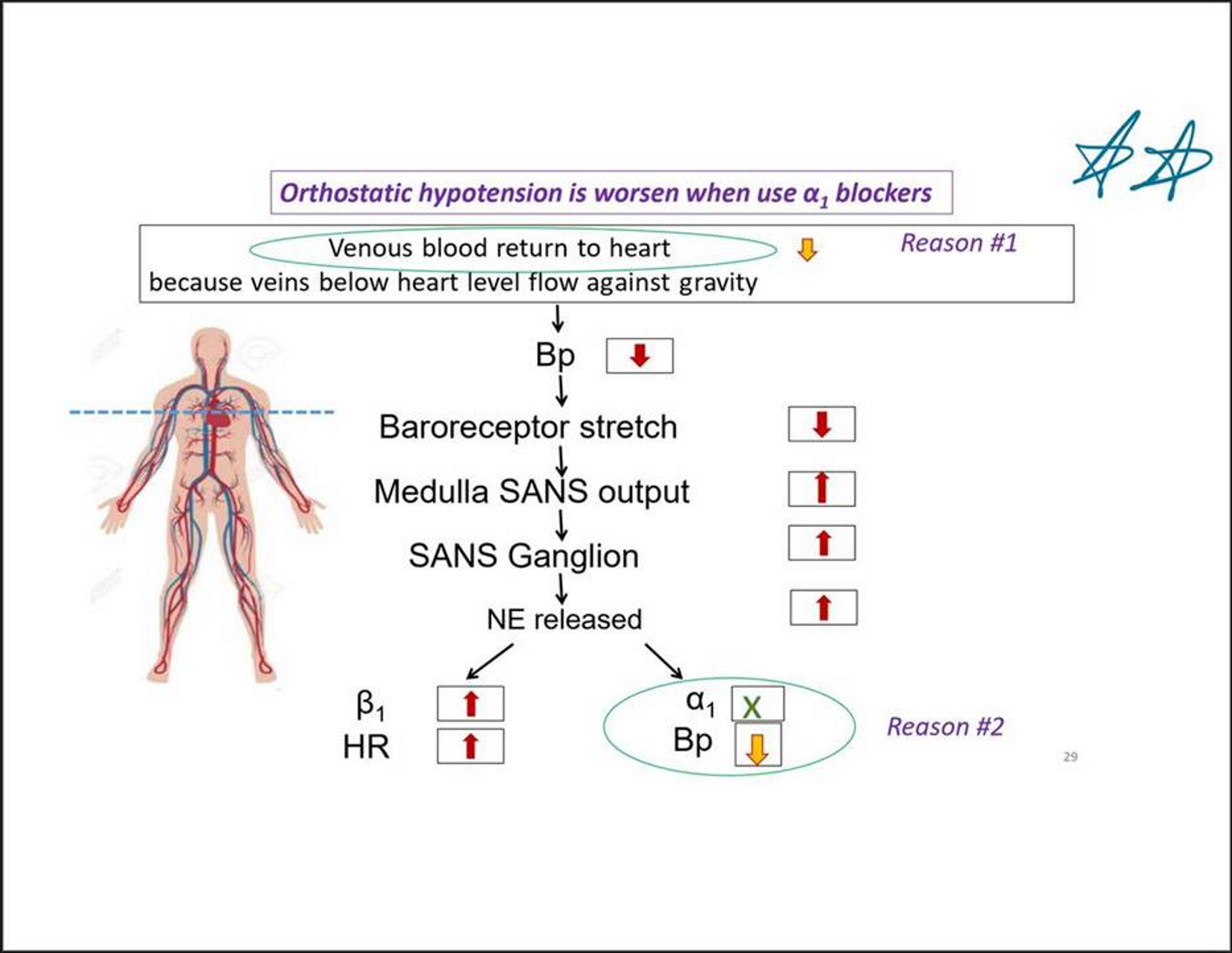
First dose effect of alpha 1 blockers Prazosin:
Postural hypotension after receiving first dose
Give lower initial dose to avoid this
Competitive Antagonists
All M blockers and beta blockers are THIS.
With ISA, beta blockers are partial agonists acting as competitive antagonists with full agonists present.
Epinephrine
THIS reverses alpha-blockers!
Alpha Blockers
THESE have first dose effect because of vein dilation
Rebound Tachycardia and HTN
Avoid THESE by tapering off beta-blockers
MAO inhibitors
Pts on THESE should avoid red wine (cheese)
Mixed Direct & Indirect
THESE agonists deplete faster
Example is ephedrine
Asthma
With THIS, you avoid beta blockers, the only one that is safe to use are Beta 1 blockers
Contraindications of BB+ISA
Hyperthyroidism
Angina within 1 month of MI
Beta blockers (especially B1)
THESE can mask the symptoms of hypoglycemia
The other one can prevent recovery from hypoglycemia
D1
Increases kidney perfusion and natriuresis (urine)
Dopamine and Fenoldopam
THESE increase kidney perfusion (thanks to D1 agonist activity)