K103 Chapter 32: The Deuterostomes
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What are the ancestral features of deuterostomes?
Bilateral symmetry, triploblastic tissue layers, and a complete digestive system.
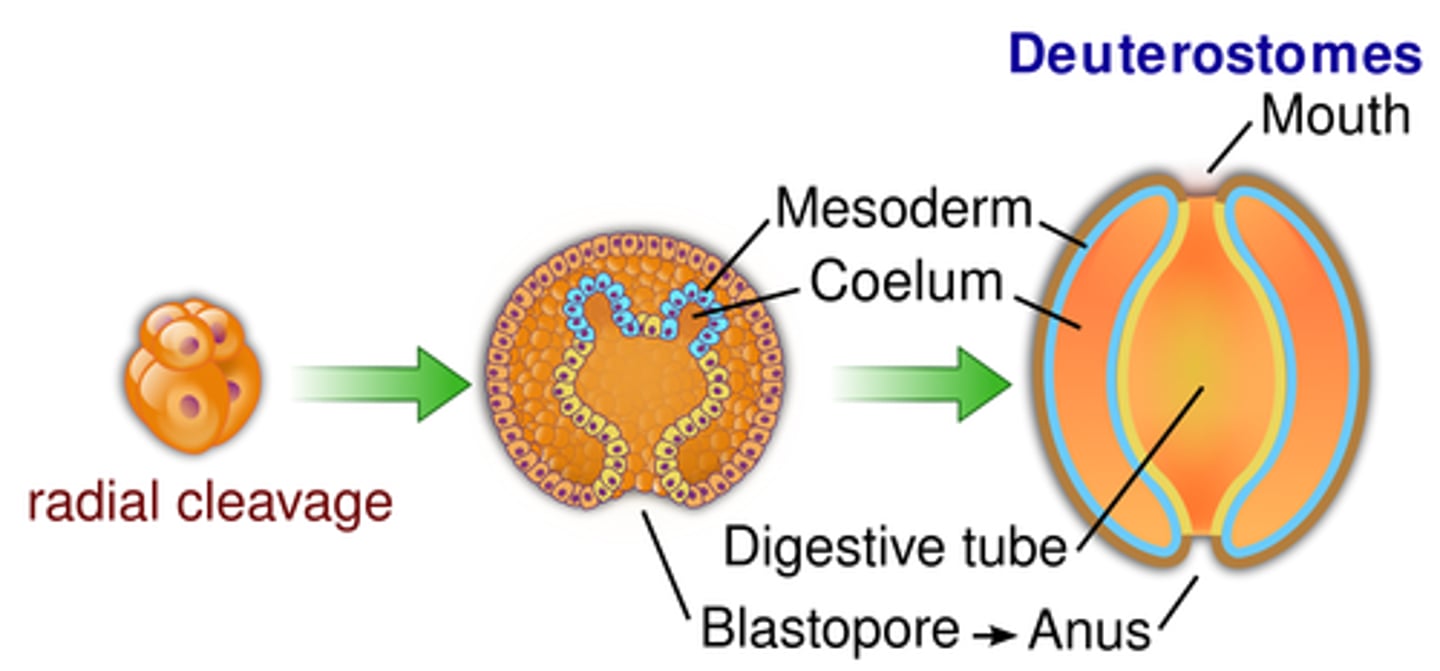
What are the derived features of deuterostomes?
Radial, indeterminate cleavage and formation of the anus from the blastopore.
What are the general characteristics of echinoderms?
Marine organisms
Pentaradial symmetry (in adults)
Calcareous endoskeleton( internal skeleton made of calcium carbonate)
Water vascular system
Regeneration capabilities
What are the main characteristics of class Asteroidea (sea stars)?
Typically five or more arms
Tube feet for movement and feeding
External digestion
What are the main characteristics of class Ophiuroidea (brittle stars)?
Slender, flexible arms
Rapid movement
Tube feet used for feeding, not locomotion
What are the main characteristics of class Echinoidea (sea urchins and sand dollars)?
No arms, rigid body
Movable spines
Flattened or globular body shape
What are the main characteristics of class Crinoidea (feather stars and sea lilies)?
Feather-like arms
Filter-feeding
Sessile or slow-moving organisms
What are the main characteristics of class Holothuroidea (sea cucumbers)?
Elongated, soft body: A long and flexible body that isn't hard.
Reduced skeleton: A smaller or less developed internal skeleton.
Evisceration as a defense mechanism: The ability to expel internal organs to escape danger, often as a way to confuse or distract predators.
What are the four shared derived traits of chordates?
Notochord
Dorsal hollow nerve cord
Pharyngeal slits
Post-anal tail
What are the additional features of vertebrates?
Vertebral column (backbone)
Skull
Well-developed brain
Specialized sensory organs
What are the characteristics of Urochordata (tunicates)?
Sessile marine filter feeders
Chordate traits present only in the larval stage
What are the characteristics of Cephalochordata (lancelets)?
Retain chordate features throughout life: Keep the main characteristics of chordates, like a notochord (a flexible rod), even as adults.
Burrow and filter feed in marine environments: Live by digging into the ground and feeding on tiny organisms in the water by filtering them out.
What are the major vertebrate groups in the cladogram?
Craniates
Vertebrates
Tetrapods
Amniotes
What are Craniates?
Animals that possess a skull (e.g., hagfish)
What are Vertebrates?
Animals with a vertebral column (e.g., fish, amphibians)
What are Tetrapods?
Four-limbed vertebrates (e.g., amphibians, mammals)
What are Amniotes?
Tetrapods that lay amniotic eggs (e.g., reptiles, birds, mammals)
What are the major vertebrate classes?
Agnatha: Jawless fish (e.g., hagfish, lampreys).
Chondrichthyes: Cartilaginous fish (e.g., sharks, rays).
Osteichthyes: Bony fish (ray-finned and lobe-finned).
Amphibia: Frogs, salamanders.
Reptilia: Turtles, snakes, lizards.
Aves: Birds.
Mammalia: Monotremes, marsupials, placentals.
What is oviparous reproduction?
Egg-laying, where fertilization occurs outside the body (e.g., birds, amphibians, reptiles)
What is viviparous reproduction?
Live birth with the embryo developing inside the mother's body, connected by a placenta (e.g., most mammals)
What is ovoviviparous reproduction?
Eggs develop inside the mother's body and hatch internally, but there is no placenta (e.g., some sharks, snakes)
Ray Finned Fish
Thin, flexible fins supported by bony rays (e.g., trout).
Lobe Finned
Fleshy, limb-like fins with internal bones (e.g., coelacanths, ancestors of tetrapods)
How did land-dwelling tetrapods evolve from lobe-finned fish?
Stronger bones
Limb-like fins for movement in shallow waters
Adaptation of lungs for breathing air, leading to amphibians
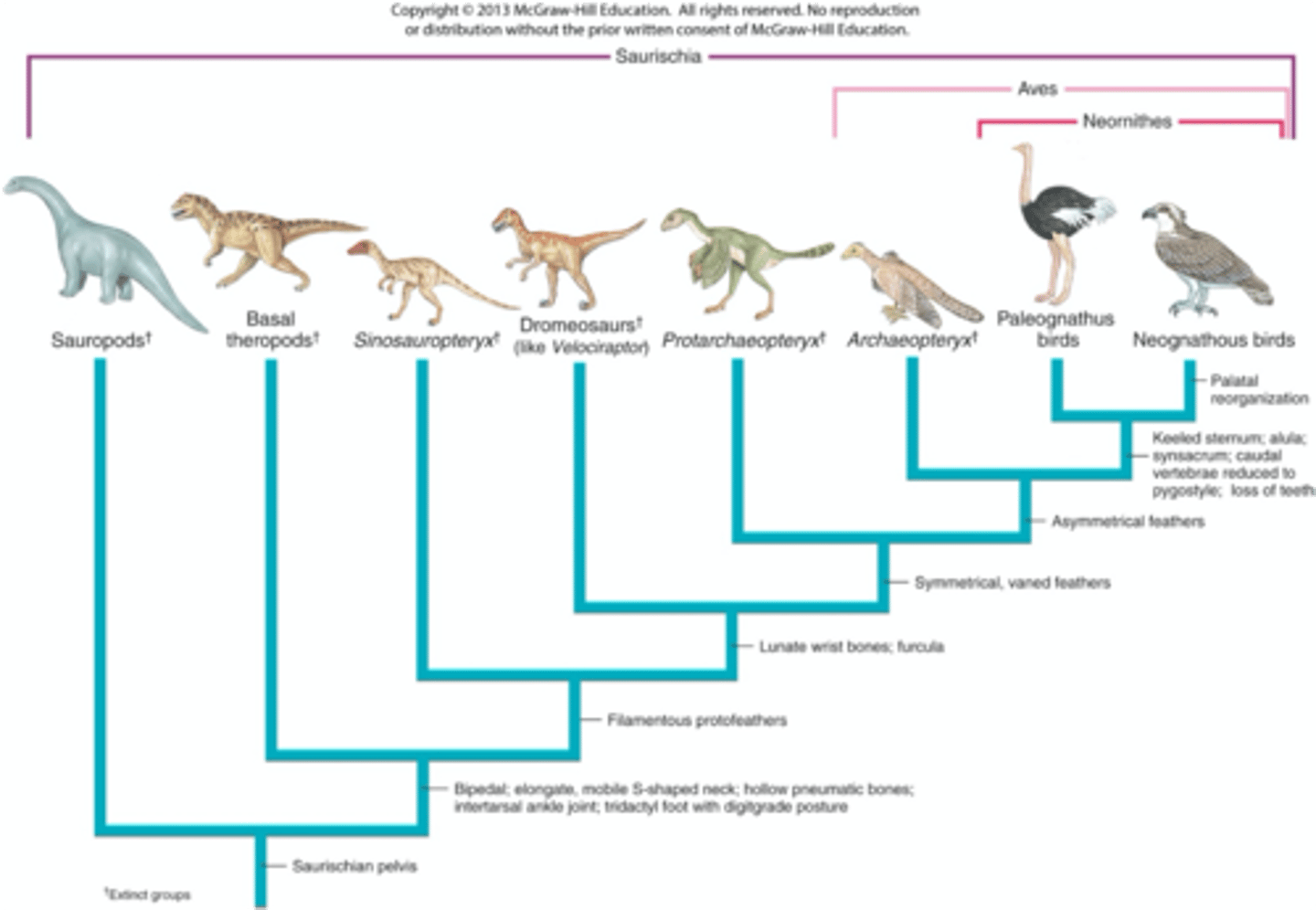
What are the two clades of modern birds?
Paleognathae: Flightless birds with a primitive palate (e.g., ostriches, emus).
Neognathae: Birds with strong flight adaptations (e.g., songbirds, hawks).
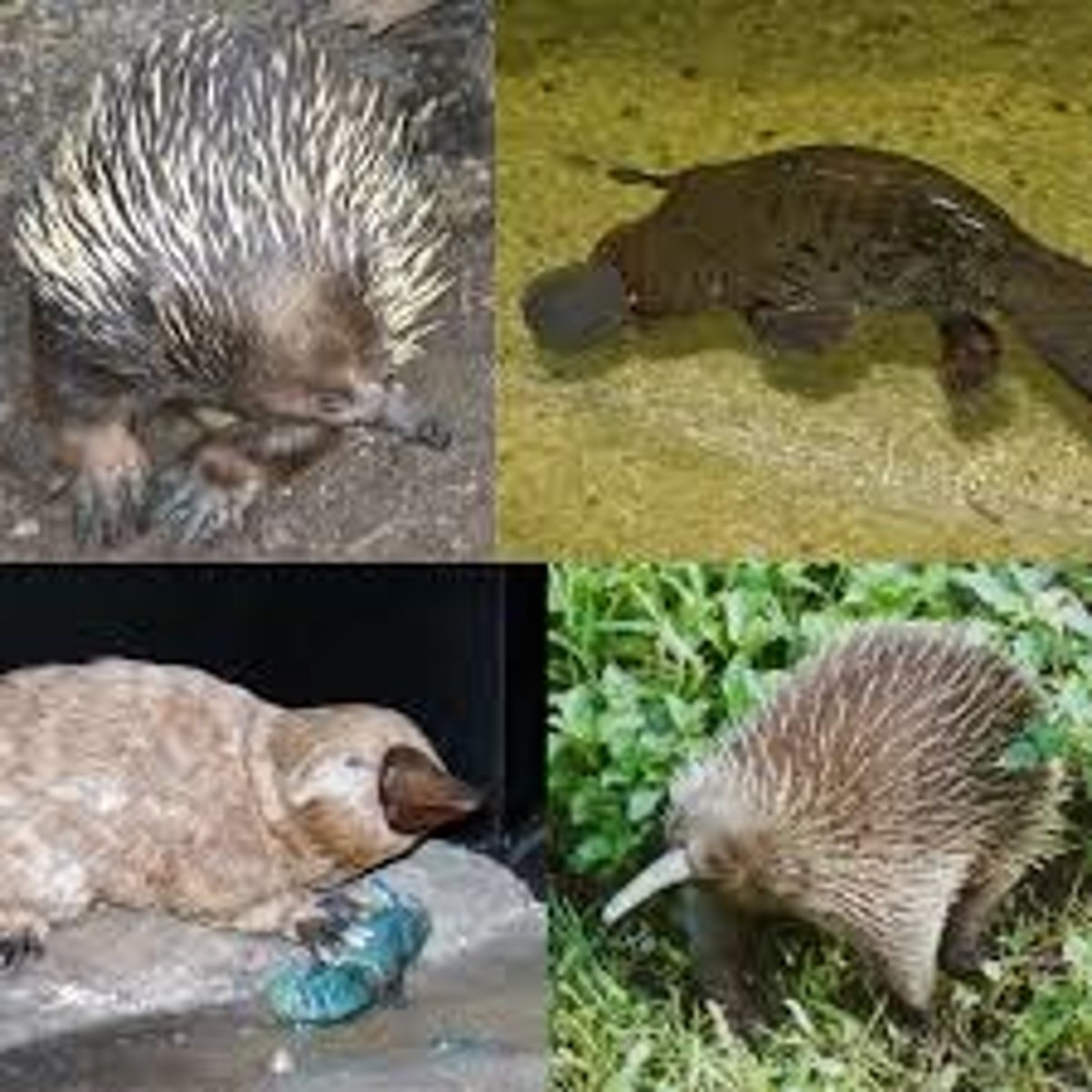
What are Monotremes (Prototheria)?
Egg-laying mammals that are the most primitive group of living mammals (e.g., platypus, echidna).

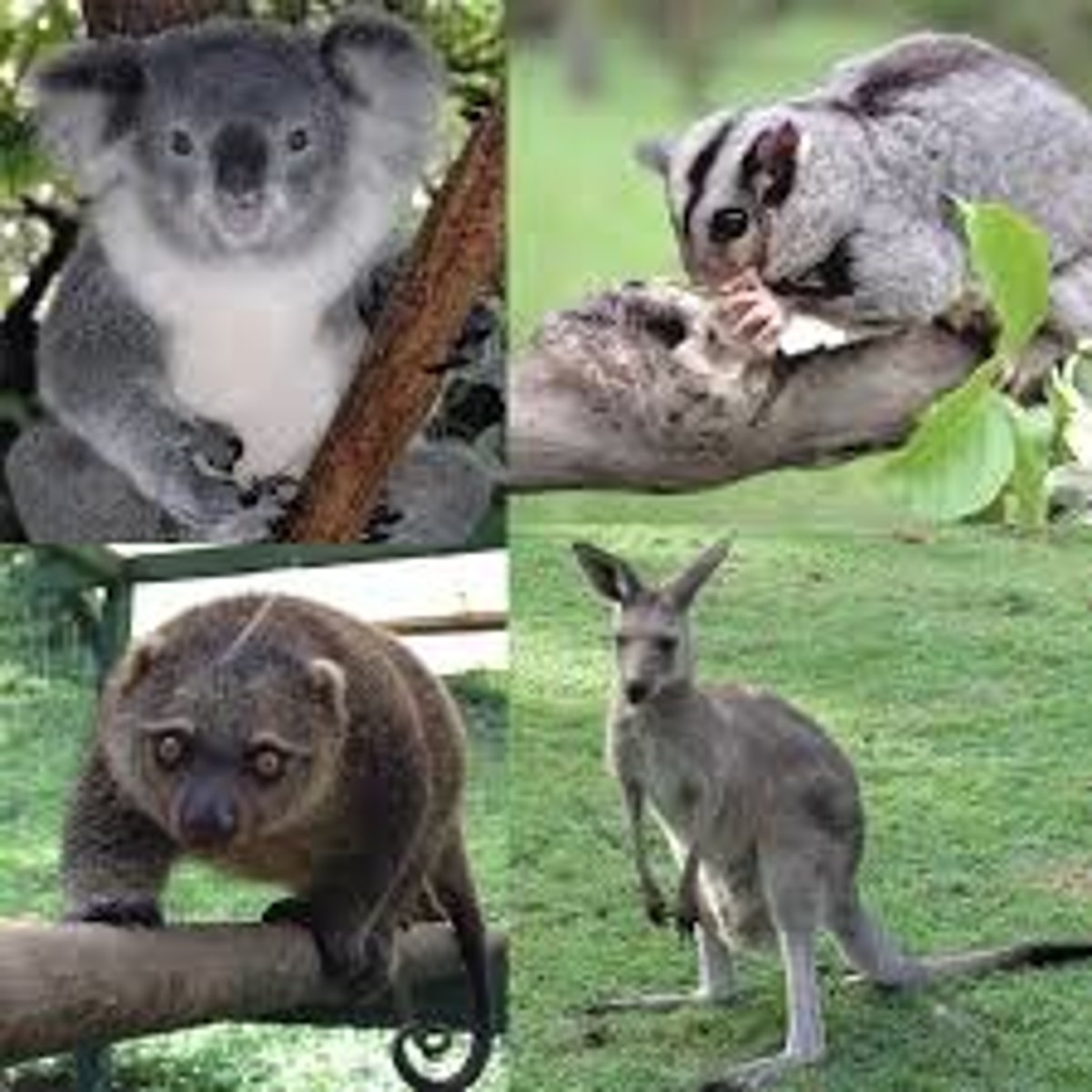
What are Marsupials (Metatheria)?
Mammals with a pouch where young develop after birth (e.g., kangaroos, koalas)

What are Placental Mammals (Eutheria)?
Mammals that give live birth with a placenta to nourish the developing fetus (e.g., humans, whales, elephants).
