AQA A level Chemistry 3.1.12 Acids and bases
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
What is the formula of sulfuric acid? (1)
H₂SO₄
What is the formula of sodium hydroxide? (1)
NaOH
What is the formula of phosphoric acid? (1)
H₃PO₄
What is the formula of sodium carbonate? (1)
Na₂CO₃
What is the formula of nitric acid? (1)
HNO₃
What is the formula of potassium oxide? (1)
K₂O
What is the formula of ethanoic acid? (1)
CH₃COOH
What is the formula of barium hydroxide? (1)
Ba(OH)₂
What is the formula of hydrochloric acid? (1)
HCl
What is the formula of ammonia? (1)
NH₃
What is the product of Metal + Acid? (1)
Salt + Hydrogen
What is the product of Metal Oxide + Acid? (1)
Salt + Water
What is the product of Metal Carbonate + Acid? (1)
Salt + Carbon Dioxide + Water
What is the product of Alkaline (Hydroxide) + Acid? (1)
Salt + Water
What is a Brønsted-Lowry acid? (1)
Substance that donates protons in a reaction; it is a proton donor
What is the general reaction of an acid HA(aq) with water? (2)
HA(aq) + H2O(l) -> A-(aq) + H3O+(aq).
What is the reaction of H2SO4 with HNO3? (2)
H2SO4 + HNO3 -> HSO4- + H2NO3+
What is a Bronsted-Lowry base? (1)
A Bronsted-Lowry base is a substance that accepts protons in a reaction; it is a proton acceptor
What is the general reaction of a base B(aq) with water? (2)
B(aq) + H2O(l) -> BH+(aq) + OH-(aq)
What are strong acids and bases? (1)
Acids / bases that completely dissociate into ions in aqueous solution
What is an example of a monoprotic strong acid and its dissociation? (2)
HCl → H+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
What is an example of a diprotic strong acid and its dissociation? (2)
H2SO4 → 2H+(aq) + SO4^2-(aq)
What are weak acids and bases? (1)
Acids / bases that only slightly dissociate into ions in an aqueous soloution
The weaker the acid / bases ...
- The less it dissociates
- The more the equilibrium lies on the left
In terms of reactions, what is the difference between strong vs weak acids / bases? (1)
Weak substances = have an equilibrium reaction (strong do not have an equilibrium reaction - only foward)
What is amphoteric and an example? (2)
- Substance that can act as both an acid (proton donor) and as a base (proton acceptor)
- E.g. water
What is the definition of pH? (1)
[H+] = The concentration of hydrogen ions in soloution (moldm-3)
![<p>[H+] = The concentration of hydrogen ions in soloution (moldm-3)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/12ed7816-2d8b-4998-b9c7-630e0c99bd4c.png)
What is formula for calculating [H] from pH? (1)
10^-ph
As the concentration of [H+] increases...
pH decreases
How can pH be measured? (2)
- Indicator paper / soloution e.g. universal indicator
- pH meter (much more accurate pH reading)

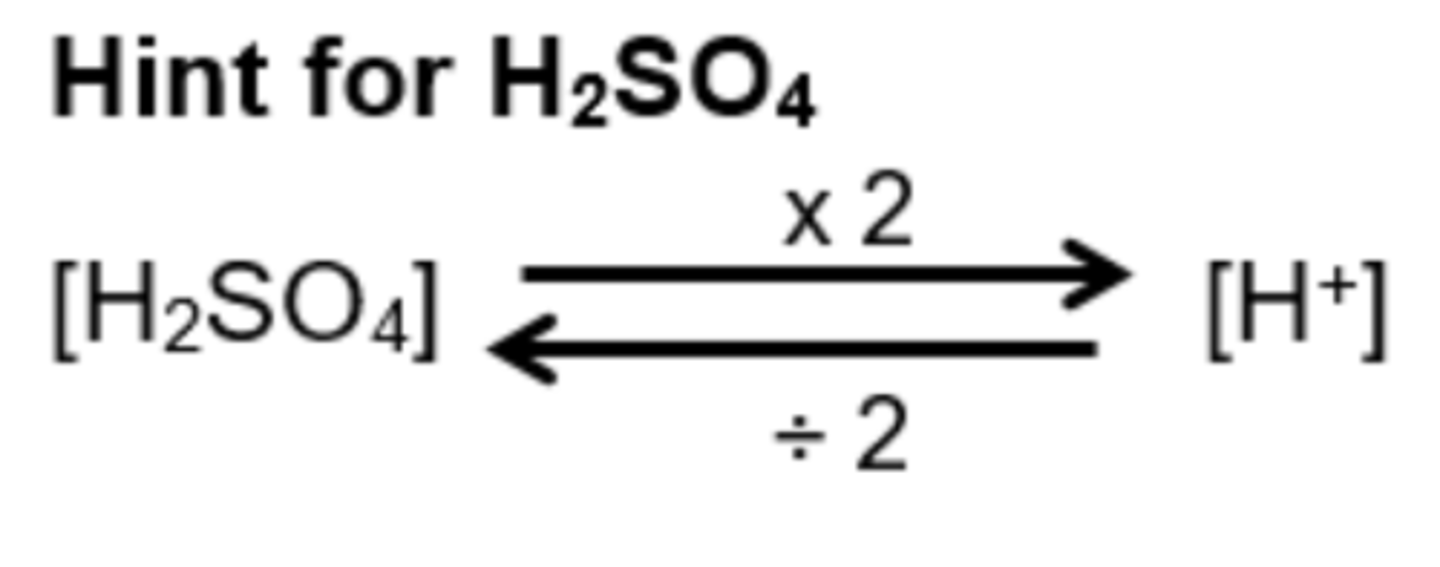
How do you calculate concentration of acid using [H+] e.g. H2SO4?
For triprotic (E.g. H3PO4 - you would use 3 instead of 2)
What is the equilibrium reaction for water as a amphoteric substance? (1)
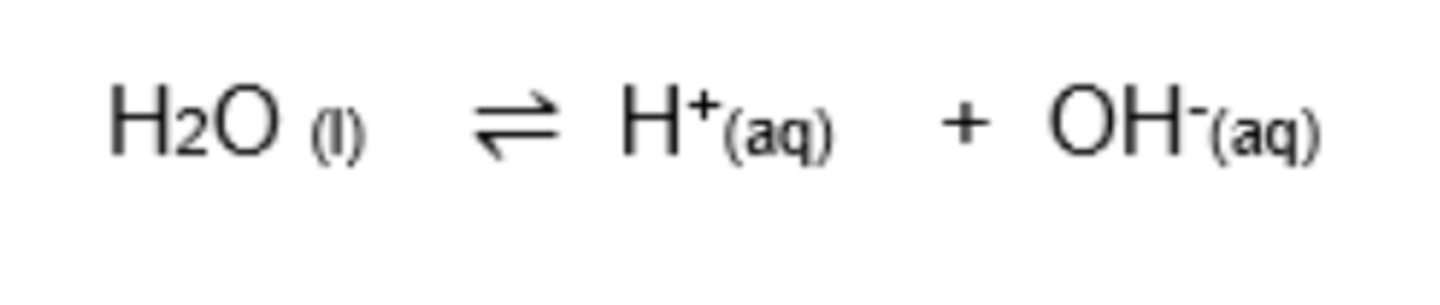
Why is [H2O] treated as constant in the Kc expression?
Because water is weakly dissociated, its equilibrium position lies far to the left, making [H2O] effectively constant
What is kw? (2)
- Ionic product of water
- Kw = [H+][OH-]
What is the value and units of Kw at 298 K?
(1.00 x 10^-14) mol^2dm^-6
Why is pH of water considered neutral? (1)
The hydrogen ion concentration is equal to the hydroxide ion concentration
What is the pH of pure water at 298K? (1)
7
How does Kw vary with temperature? (4)
- As temperature increases, the equilibrium shifts to the right to oppose the change.
- The degree of dissociation increases.
- Kw increases
- pH decreases (but the solution remains neutral
What is a monoprotic base? (1)
Base that can accept one proton, e.g., NaOH, KOH.
What is a diprotic base? (1)
Base that can accept two protons, e.g., Ba(OH)₂, Ca(OH)₂
What is the method for working out the pH of strong acids after they have been diluted? (3)

What is the method for working out the pH of strong bases after they have been diluted? (3)

How do you work out the pH of a soloution for a strong acid-strong base titration? (6)

State the acid dissociation constant, Ka and units (3)
Units = mol dm-3

As strength of acid decreases...
The value of Ka also decreases
What are acids with Ka less than 1? (1)
Weak acids
What are acids with Ka more than 1? (1)
Strong acids
What is the logarithmic expression for pKa? (1)
pKa = -log10(Ka)
What is the relationship between Ka and pKa? (1)
Ka = 10^-pKa
How does the value of Ka relate to pKa? (1)
A low value of Ka matches a high value of pKa, and a high value of Ka matches a low value of pKa
How do you use Ka expression to calculate pH of weak acids? (3)
Use the following formulas - for a weak acid assume [H+] = [A-]
![<p>Use the following formulas - for a weak acid assume [H+] = [A-]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b8d234de-e3a5-48fa-95e3-8eacbd7040aa.png)
What is a pH meter? (1)
Digital device that determines the pH of a solution by placing the probe into the solution and can be clamped in position to track pH during a titration
Why must a pH meter be calibrated before use? (1)
A pH meter must be calibrated because it does not give accurate readings over time
How do you calibrate a pH meter? (4)
E.g.
1. Rinse the probe with deionized water, dry the probe with a paper towel, and place it in a pH 4 buffer solution.
2. Wait for the reading to remain steady, then set the pH meter to pH 4.
3. Take the probe out of the buffer solution, rinse it with deionised water, dry it, and place it in a pH 10 buffer solution.
4. Wait for the reading to remain steady, then set the pH meter to pH 10.
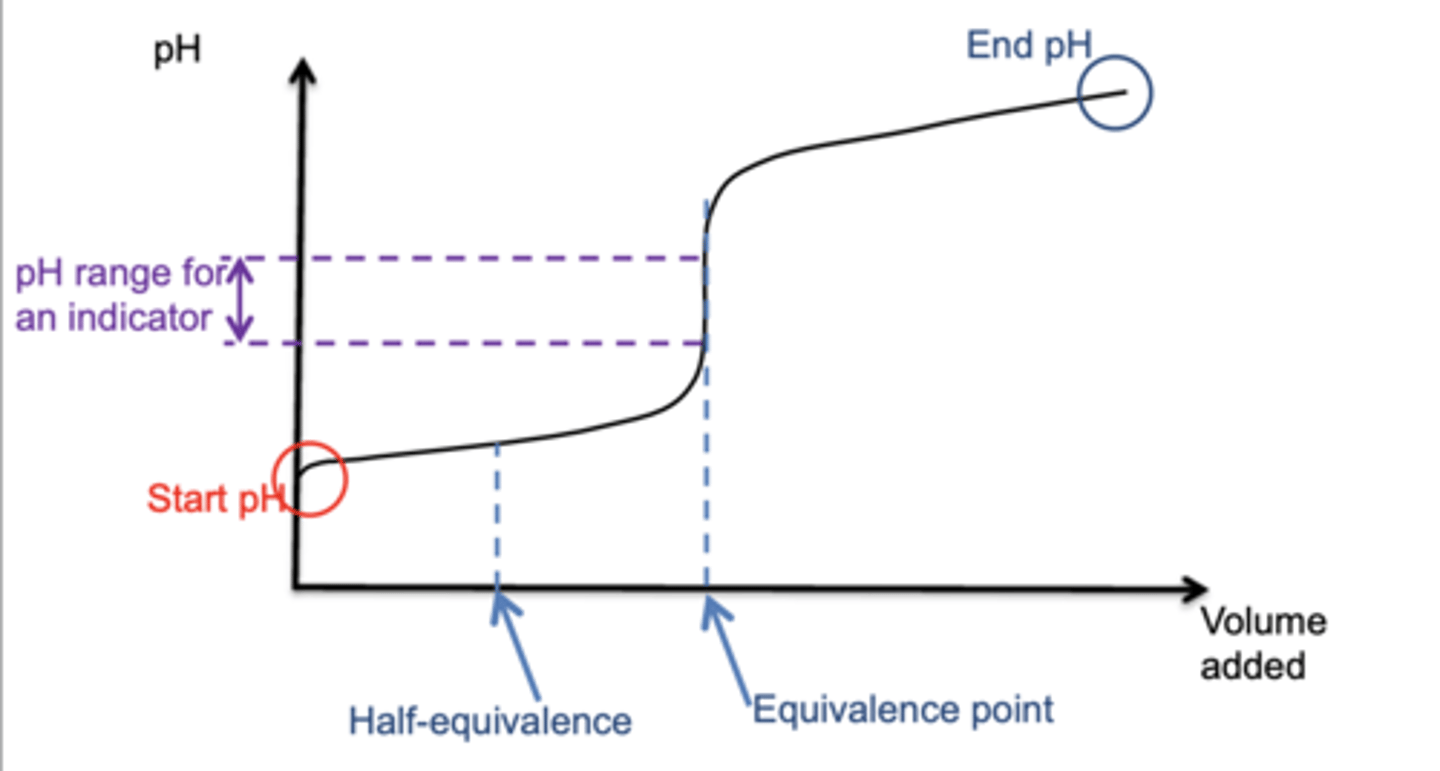
Draw a basic structure of a pH curve showing the key features (5)
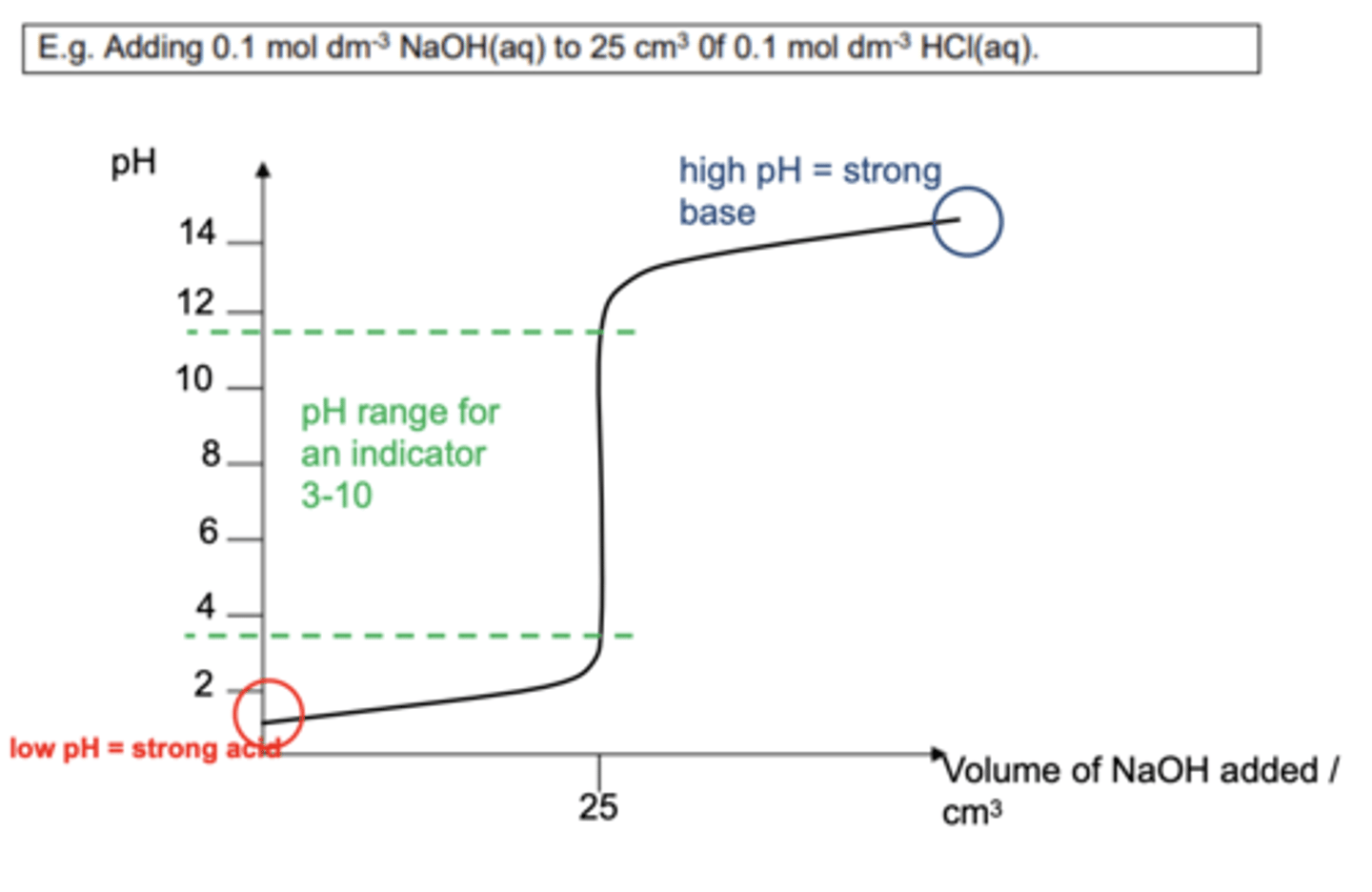
Draw a pH curve for a strong acid / strong base titration (4)
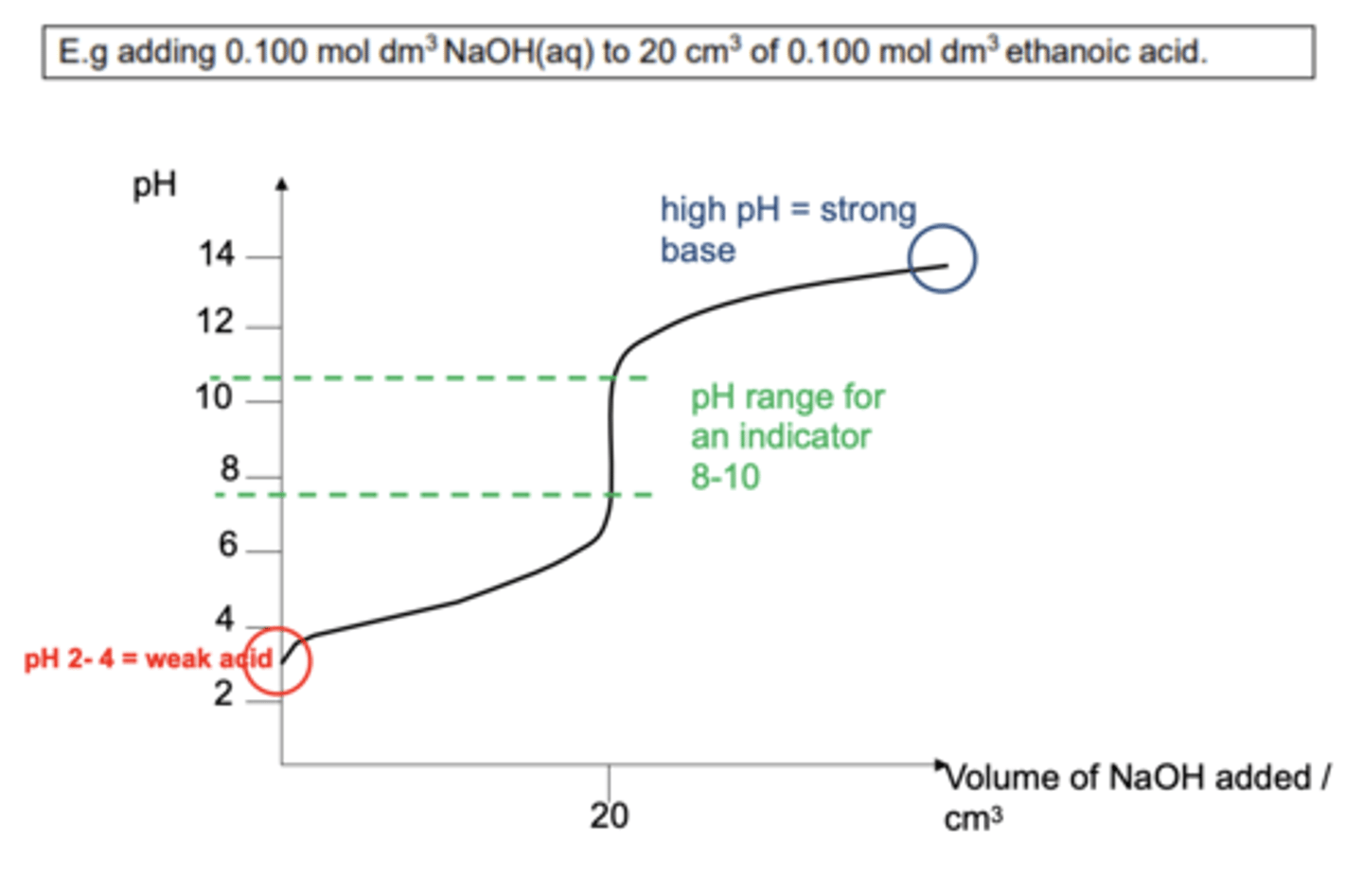
Draw a pH curve for a weak acid / strong base titration (4)
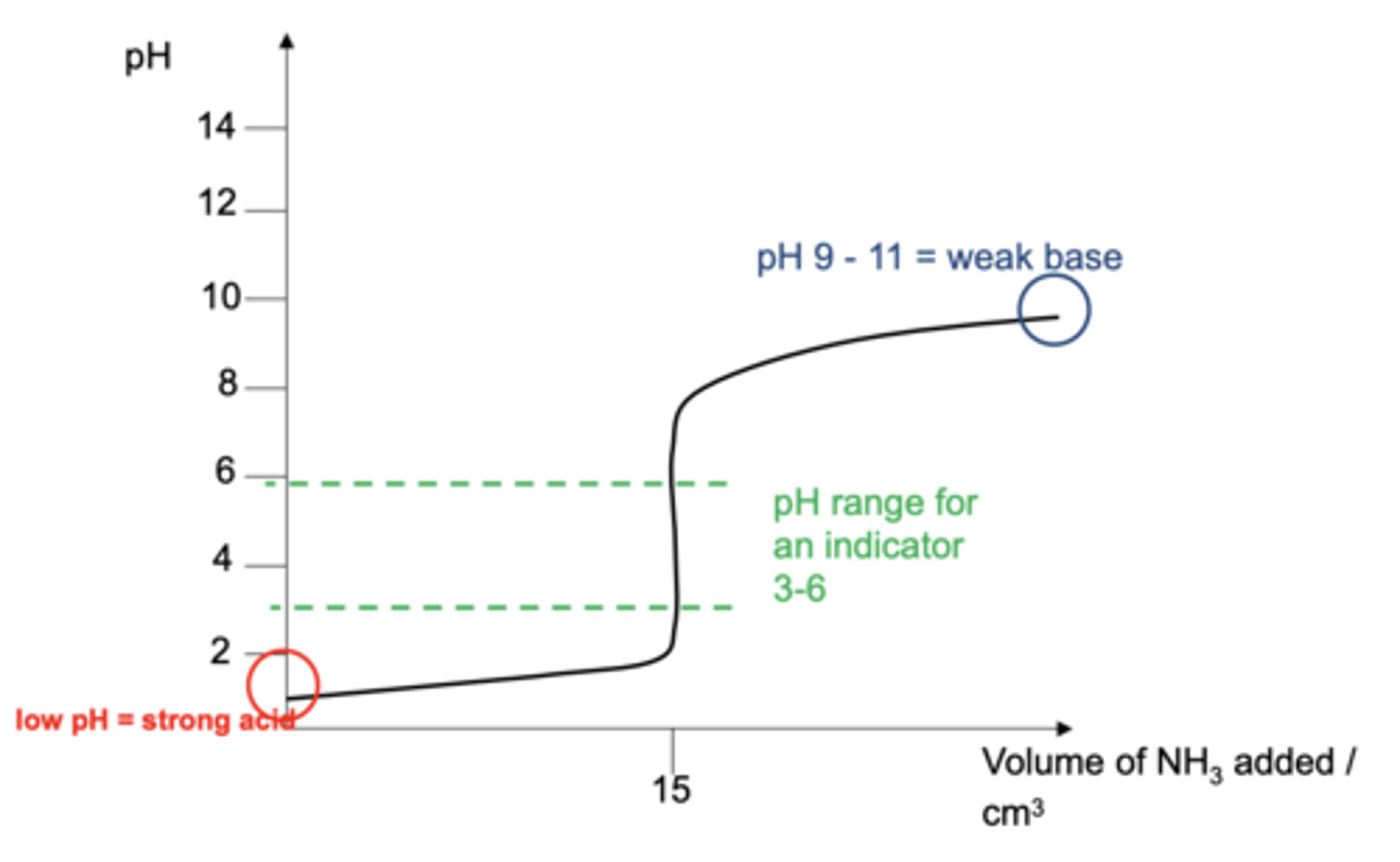
Draw a pH curve for a strong acid / weak base titration (4)
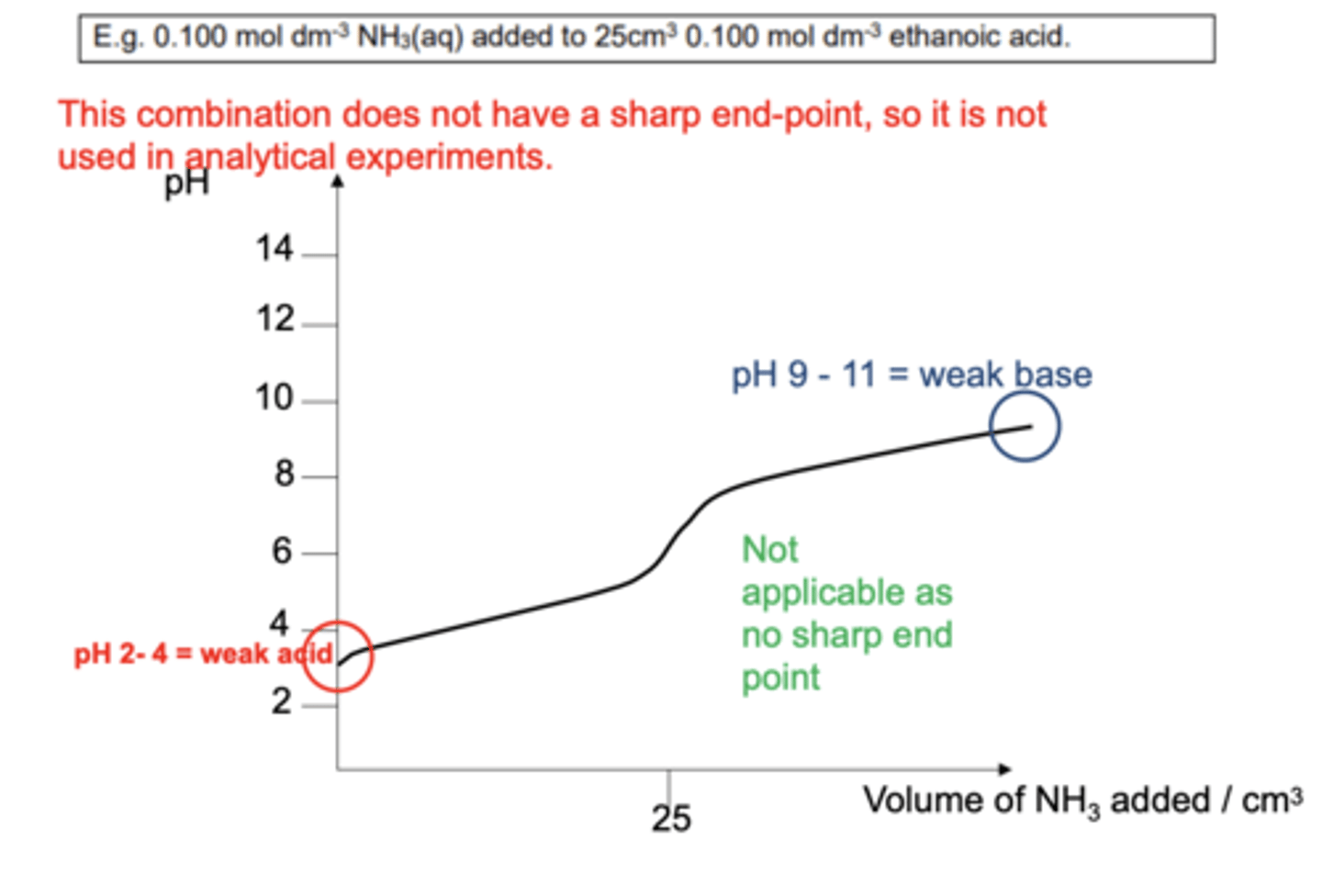
Draw a pH curve for a weak acid / weak base titration (4)
What is true at the half neutralisation point of a titration? (2)
- Half the acid has been neutralised by base
- So [HA(aq)] = [A-(aq)]
- Therefore, Ka = [H]
What is the pH at half equivalence of any titration? (1)
The same as pKa value because of the diagram
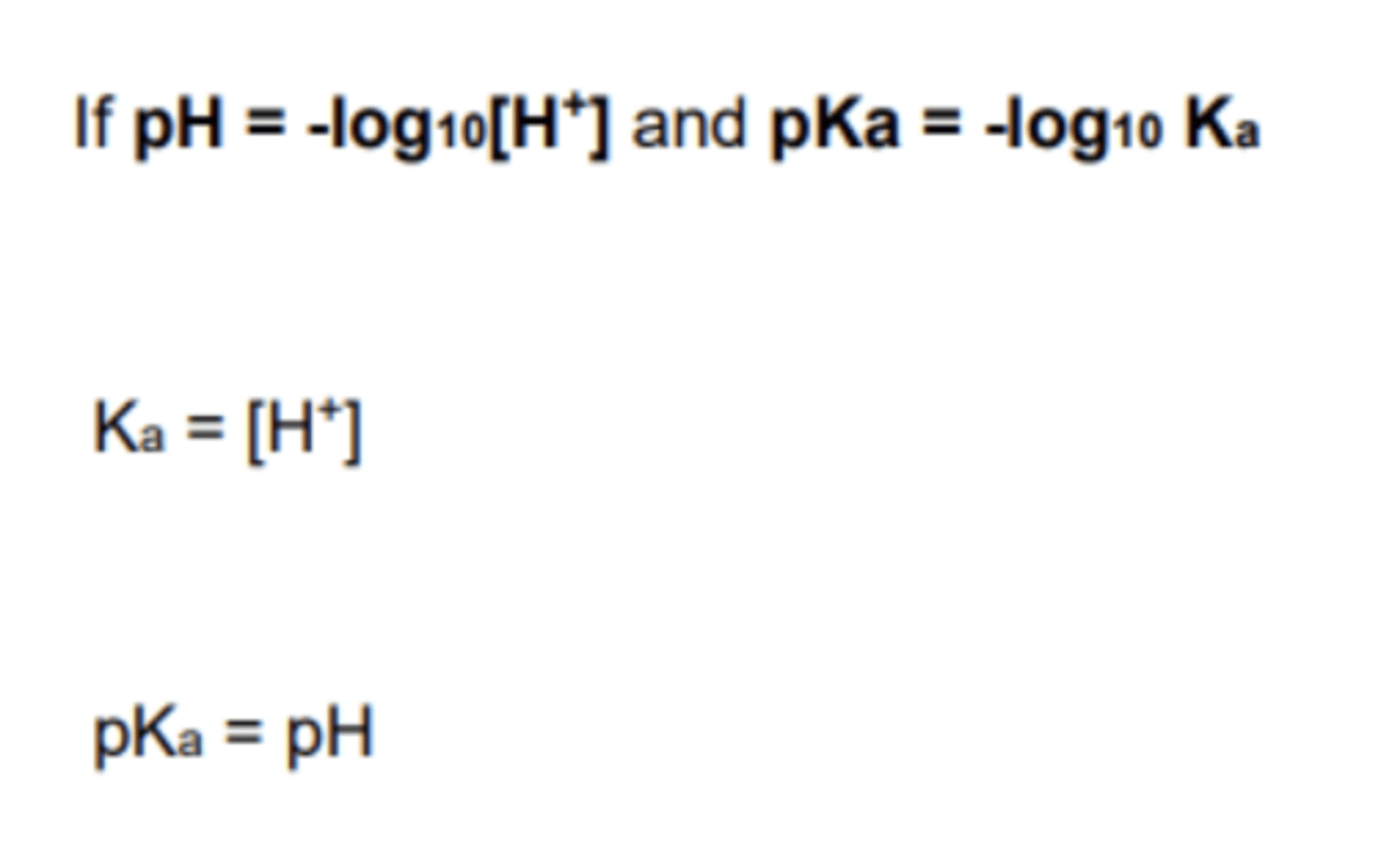
What is a quick practical method for determining pKa of a weak acid? (4)

What are the properties of a suitable indicator for a titration? (3)
1. The colour change must be sharp rather than gradual at the end point, meaning no more than one drop of acid or alkali is needed to give a complete colour change.
2. The end point of the titration given by the indicator must match the equivalence point; otherwise, the titration will give the wrong answer
3. The indicator should give a distinct colour change
What are buffers? (1
A buffer solution is a solution that maintains the same pH despite the addition of acid, base, or water
What is an acidic buffer? (1)
An acidic buffer is a solution that maintains a pH below 7
What does an acidic buffer typically consist of? (1)
Weak acid and one of its salts
What are the two types of acidic buffers? (2)
1. A weak acid added to one of its salts.
2. A weak acid added to a strong base, where the salt is made as a product of the reaction
What happens when more H+ ions (an acid) are added to an acidic buffer? (2)
1. The H+ ions react with A- ions, shifting the equilibrium to the left to decrease the moles of H+.
2. As a result, [H+] remains unchanged, maintaining the pH
What happens when OH- ions are added to an acidic buffer? (2)
1. The OH- ions react immediately with H+ to form H2O, shifting the equilibrium to the right as more acid dissociates to replace H+.
2. This keeps [H+] constant and maintains the pH
What is an example of an acidic buffer? (1)
A common acidic buffer is an aqueous solution containing a mixture of ethanoic acid, CH3COOH, and the ethanoate ion, CH3COO-
What does ethanoic acid act as in an acidic buffer? (1)
Ethanoic acid acts as the weak acid, CH3COOH
What does sodium ethanoate act as in an acidic buffer? (1)
Sodium ethanoate, CH3COONa, acts as a source of the conjugate base, CH3COO-
What is a basic buffer? (1)
A basic buffer is a solution that maintains a pH above 7 and typically consists of a weak base and one of its salts.
What is an example of a basic buffer? (1)
A solution containing ammonium chloride and ammonia
How does a basic buffer respond when H+ ions are added? (2)
- The H+ ions react immediately with the OH- ions, forming water.
- The equilibrium moves to the right to replace the OH- ions, keeping [H+] and pH unchanged.
How does a basic buffer respond when OH- ions are added? (2)
- The OH- ions react immediately with NH4+ ions, forming NH3.
- The equilibrium moves to the left to decrease the moles of OH-, keeping [H+] and pH unchanged
What is an example of a buffer system in the human body, and why is it important? (2)
- Blood
- It maintains a pH of approximately 7.4, which is crucial because even a small pH change of 0.5 units can be fatal
How does the blood buffer system respond to changes in H+ and OH- concentrations? (2)
- When H+ ions are added, the equilibrium shifts to the right, removing excess H+ ions.
- When OH- ions are added, they react to form water, and the equilibrium shifts to the left, releasing more H+ ions.
What are some examples of buffers in everyday products? (1)
Buffers are used in detergents and shampoos to prevent damage to fabrics, skin, or hair caused by overly acidic or alkaline conditions
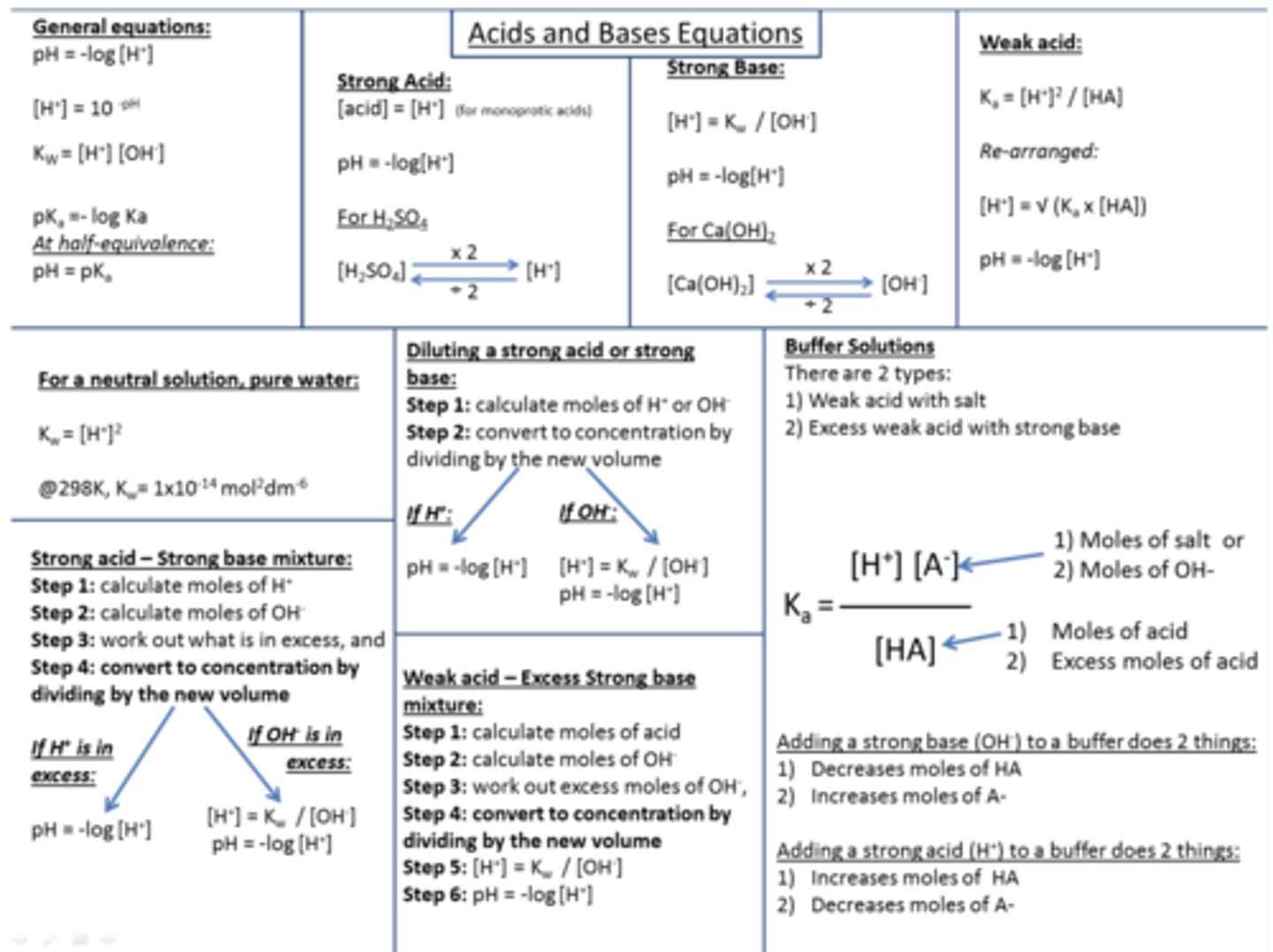
Summary diagram of ALL acids and bases formulas and maths you need to know for your exams! (20)