2.2 People of the Planet
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
What is Development?
The progress of a country as it becomes more economically/technologically advanced
What is Social Development?
An improvement in people’s quality of life - e.g, education, health, life expectancy
What is Economic Development?
An improvement in wealth e.g, GNI and GDP
What is Environmental Development?
An improvement in the quality of the natural world - e.g, air pollution and water quality
What is Sustainable Development?
An improvement in meeting the need’s of the present whilst protecting the need’s of those in the future - e.g, renewable energy
What are AC’s?
Advanced Country
Well-developed finanical market, diversified economic structure, rapidly growing service sector - e.g, UK, USA, Japan and Australia
What are EDC’s?
Emerging Developing Country
Not eligible for Poverty Reduction and Growth Trust (supported by the IMF) - e.g, South Africa, India, China and Brazil
What are LIDC’s?
Low-Income Developing Country
Eligible for Poverty Reduction and Growth Trust - e.g, Nigeria, Bangladesh and Afghanistan
How can Development be measured?
Economically OR Socially
What is Gross National Income?
Total income divided by the number of people per capita - 1000
What is Gross Domestic Product?
Total value of the good’s and service’s produced in a country
What is the Human Development Index?
Composite measure (combining multiple data) using data on income, life expectancy and education, to calculate an index from 0-1
What are the advantages of using Gross National Income per Capita?
It can show a clear pattern or variation between each country
It prioritises AID payment
It can be calculated easily using the government’s data
What are the disadvantages of using Gross National Income per Capita?
Average figure is misleading. disparities not shown as wealthy people can distort the data
Many people working in an informal sector will not have their income taken by the official GNI
Many data about income is personal, sensitive
What are the advantages of using the Human Development Index?
It can show a clear pattern or variation between each country
It will provide a composite measure, including social aspects as well as wealth
It can be used as a measure of improvement, following government initiatives
What are the disadvantages of using the Human Development Index?
It only considers a selection of measures and doesn’t consider of other important indicators
It can hide the disparities that exist with countries
Data from some countries may be unreliable
What are the advantages of using Internet User’s?
It is useful as it relies upon other infrastructural improvement, so it is an accurate measure for electricity, satellite access and disposable income
What are the disadvantages of using Internet User’s?
Doesn’t consider the variation in countries
It can hide the disparities that exist in countries
Internet access may not be central to the infrastructure or functioning of the community
How do indicators illustrate the ‘development gap’ between countries?
Half of the world’s wealth is owned by 1% of the population
Last 50 years, 16 countries have moved from their LIDC status to the EDC status
How do indicators illustrate the health between countries?
LIDC’s have a lower level of investment in health and nutrition, accounting for high infant mortality and birth rate
How do indicators illustrate the education between countries?
Primary education is almost globally avaliable
European-style secondary education is unavaliable in LIDC’s - some vocational training may be present
How do indicators illustrate the standard’s of living between countries?
LIDC’s have to endure a lack of clean water and poor sanitation, leading to disease and reducing the life expectancy rate
Where are most AC’s?
Most of North America, Europe and Australasia
Where are most EDC’s?
Most of South America, Asia and some of Africa
Where are most LIDC’s?
Most of Africa, a few in the Middle East, Asia
How can weather and climate cause uneven development?
Heavy rainfall, droughts, extreme heat/cold and vulnerability to tropical storms will hinder economic development
E.g, influencing agricultural productivity, infrastructure damage
Name an example of how climate can cause uneven development?
In 2016, over 1000 people in Haiti were killed by Hurricane ‘Matthew’ just 6 years after 230,000 people were killed by a Earthquake
How can relief cause uneven development?
A mountaineous region will tend to be remote and have a poor infrastructure, dealing with extreme weather
How can land-locked countries cause uneven development?
8/15 of the lowest ranking countries according to the HDI are land-locked
Those LIDC’s don’t have a coast, lacking the benefit of sea trade, which has led to the development of the world’s most developed nation’s
How can a tropical environment cause uneven development?
Tropical environment is prone to pest and disease, which can spread rapidly, devastating communities and affecting people’s abilities to work
E.g, Malaria and Cholera
How can a water shortage hinder development?
Water is essential for life and development, and a serious shortage can lead to dehydration and a lack of sanitisation
Name a place of where water shortage did cause uneven development?
Africa and the Middle East
How can poverty cause uneven development?
Lack of money will prevent refining to living conditions, infrastructure and sanitation, education and training
Development in agriculture and industry will be extremely slow, economy will not succeed
How can trade cause uneven development?
Most of the world’s powerful international countries (TNC’s) are based in the AC’s, so LIDC’s have limited access to the trade market
LIDC’s trade raw material which have a low-cost, and their value has fluctuated, causing uncertainty and instability to LIDC’s
Which continent’s are most involved in global trade?
Europe, Asia and North America
How can history cause uneven development?
AC’s have experienced a long history of development, based upon agricultural, industrial growth and international trading - highly developed and rapidly wealthy
Rapid industrialisation has taken place in EDC’s, but not yet in LIDC’s
Which EDC’s has rapid industrialisation taken place?
China, Malaysia and South Korea
What is the impact of colonialism on trade?
Many LIDC’s were colonialised - exploited for their raw material, population was enslaved, labour being exploited for profit
Global development became uneven - most colonised countries became independent in the mid-twentieth century, facing huge challenges such as poor infrastructure and political instability
Which powerful trading nations’ were the main colonist’s?
UK, France, Spain and Portugal
Name an example of how colonialism can cause uneven development?
India - independent from the UK in 1945
Nigeria - independent from the UK in 1960
How can exploitation of natural resources cause uneven development?
Raw material were exploited by colonial power and exported to AC’s to further their industrial development
LIDC’s were paid lower for the resources with most of the value being added in the AC’s
What is aid?
Aid is when a country, organisation or individual give resources to an other country
What is short-term aid?
Emergency aid following a disaster, involving the provision of water, food, medical help and shelter
What is long-term aid?
Sustainable development, involving improvement to infrastructure, education, agriculture or health-care
What is government aid?
Aid which is given from one government to an other government directly
What is voluntary aid?
Aid which is given by individuals to NGO’s or charities to direct it to the right place
What is bi-lateral aid?
Aid that has to be given back in return
What is multi-lateral aid?
Aid which is provided by many countries and organised by an organisation
How can the provision of basic resources promote development?
It can lead to a healthier lifestyle, enabling people to work more effectively and earn money to improve their living condition
How can education promote development?
Improved knowledge and access to loans can increase food productivity and wealth in farming
Improved literacy rate
How can health-care promote development?
It will reduce child mortality rate, lower birth rate due to contraception and increase the life expectancy
How can inappropriate aid hinder development?
Inappropriate aid e.g, machinery can increase dependency on AC’s, e.g, for spare equipment/energy
How can the provision of emergency aid hinder development?
It could threaten local farmer’s, forcing them out of business
How can the lack of co-ordination hinder development?
It could result in an imbalance of support between aid donor’s
How can animal aid hinder development?
Some animal-gift schemes have been criticised for increasing livestock in place’s already suffering from water shortage and desertification
What is urbanisation?
The process of a town or city developing as the population increases
What is a settle-ment hierarchy?
The ranking of a settle-ment based on it’s services and functions
What are the ranking of the settle-ment hierarchy?
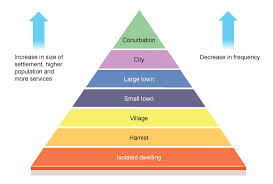
What is a city?
A human settlement of a substanial size
What is a mega-city?
A large city that has a population of over 10 million people
What is a world city?
A large city that has a major influence on the global economy
What does a world-city have?
Global businesses
Cultural opportunity
Major transportation
Where are most mega-cities distributed?
Most mega-cities are distributed in developing regions (Asia, Africa)
How has the distribution of mega-cities changed over time?
Shift from AC’s (West of Europe) to mainly EDC’s (Asia and Africa)
What is a problem faced by mega-cities?
Rapid urbanisation, placing pressure on infrastructure and housing
How do AC’s vary in growth rate?
Cities in Europe and North America has reached the peak of their growth in the 1950s or earlier
When were the AC’s most sustained period of growth?
Industrial Revolution in the late 1700s to 1800s.
What event has lead to the growth of cities in AC’s?
The ‘baby boom’ after the World War 2 and the building of new housing
Which two AC’s were the first ‘millionare’ cities?
London and Paris (1 million)
What percentage of AC’s live in an urban area?
70%
How do EDC’s/LIDC’s vary in growth rate?
Cities in Asia and Africa have now overtaken Europe and North America
How did the economic development affect EDC’s/LIDC’s?
Economic development has driven the rural to urban migration, causing younger people in a rural area to move to a urban area in search of a job
How did Natural Growth affect EDC’s/LIDC’s?
Many people from a rural area then have children in the city, leading to a high rate of natural growth
How many people have moved to an urban area in EDC’s/LIDC’s?
Almost 200 million people between 2000-2010
Which EDC’s/LIDC’s are facing the highest level of growth in a city?
Dhaka - 7%
Lagos - 5.6%
Delhi - 4.6%
What is the main cause of rapid urbanisation in LIDC’s?
Rural to urban migration, internal growth
What is rural to urban migration?
People moving from a rural area to live in a city
What is internal growth?
People who have moved in the city have a lot of children
What is a push factor?
A negative factor causing the movement of people away from an area
What is a pull factor?
A positive factor causing the attraction of people to go to an area
What are 4 push factors in migration?
Lack of job opportunities
Lack of education/health-care
Poorer infrastructure
Lack of clean water
What are 4 pull factors in migration?
More of job opportunities
More of education/health-care
More of housing
More of transport
What is natural growth?
The population growth once people have settled in the city
What is the natural growth trend in LIDC’s?
Natural growth is increased, as there is a large, youthful population
What is the natural growth trend in AC’s?
Natural growth is decreased, as there is a ageing population
Why is the natural growth increasing in LIDC’s?
Less access to contraception will lead to a higher birth rate
Why is the natural growth decreasing in AC’s?
More access to contraception will lead to a lower birth rate
What is the informal sector?
A job which doesn’t offer any features of formal employment
Why is a job in the informal sector easy to set up?
They require little capital to set up, require a few skills, are labour intensive and small scale, so those who are desperate can work
What are the advantages of the informal sector?
People working in this sector do not pay taxes, so they do not contribute directly to the country’s gross national product
What are the disadvantages of the informal sector?
People working in this sector do not have any legal rights and would not recieve holiday and sick pay, remaining in poverty
What is an informal housing?
Housing which are built on land belonging to the government
What are some examples of an informal housing?
Favela, shantytown, squatter settle-ment
What location is used when building informal housing?
River-bed, vulnerable to heavy flood after rain
Industrial, vulnerable to air quality and pollution
Steep slope, vulnerable to flood and landslide
What are the disadvantages of an informal housing?
Infrastructure is poor, cannot rely on electricity and water supply
High population density, disease can spread, crime is common