Unit 1 MGT of Hearing Disorders
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
The National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (2021) reported that ____ of adults have some degree of hearing loss by age 75.
half
Sine Waves or sinusoids represent ____ _____. Common stimulus for audiometry is pure tones
pure tones
the reference for dB is
normal human thresholds (softest sound the average human can hear)
0 dB means no sound True or False
false
Hearing sensitivity (threshold) measured in dB Hl is _____
equal across all frequencies
It is possible to hear a sound that is negative dB HL ( true or false)
true but your hearing is better than average
Supra-aural earphones
worn over ear
insert earphones
disposable foam tip is inserted into the ear canal
avoids potential for collapsing ear canal
Bone conduction vibrator
placed on mastoid or forehead
vibrations transferred to the skull, where they are then picked up by the cochlea
Circumoral earphones
used for obtaining extended high frequency thresholds (above 8000 Hz
soundfiled testing
using speakers in the test room to deliver the test signal (no transducer worn by patient) threshold obtained are not ear specific (response will always be from the better ear)
How to reads an audiogram
x-axis frequency
y-axis dB HL
Pure tone stimulus selection
steady tone- pulsed tone (preferred choice) - Warble tone typically used with children or testing low frequencies in sound field
Match?
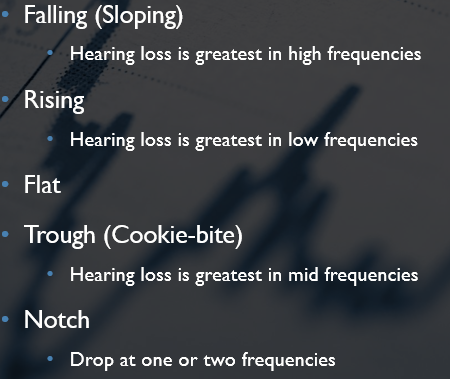
Falling, Notch, Flat, Rising, Trough(cookie-bite)
Hearing loss is greatest in mid frequencies
Drop at one or two frequencies
Hearing loss is greatest low frequencies
Hearing loss is greatest in high frequencies
Hearing loss is greatest in mid frequencies
unilateral vs bilateral hearing loss
unilateral - hearing loss is present in only one ear, other ear is normal
bilateral- hearing loss is present in both ears
is pulsed or steady tone preferred
pulsed tone, helps with tinnitus identify the tone from the “ringing” they perceive”
warble tone is typically used with
children or testing low frequencies in sound field
Narrow band noise
speech noise
Narrow band noise - used for masking or sound field testing
speech noise - used for masking during speech testing
What can an audiogram tell us
Degree (severity) of hearing loss, type of hearing loss, configuration, unilateral/bilateral, symmetrical/asymmetrical ( are both ears equally affected)
Audiometry is used to determine a patients threshold
softest sound a person can hear at different frequencies
Air conduction testing
sounds presented through the normal hearing mechanism
standard earphones, inserts earphones, or soundfield
easier infection control
collapsing ear canal
AC threshold can tell us the ____ of hearing loss, but alone cannot tell us the type of hearing loss.
ac threshold can tell us the degree of hearing loss, but alone cannot tell us the type of hearing loss.
Bone conduction testing
vibrator headband is places on the mastoid or on the forehead.
must be flat on patients head with correct amount of drove.
Signal sent directly to inner ear bypassing out and middle ear
air conduction threshold first, then bone conduction (BC) threshold testing
Stimulus initially presented at ___
30 dBHL, no response, increase to 50 dBHL, If not heard at 50 dB, sound is increased by 10 dBHL
after sound is initially heard it is down, ___ up.
10 down, 5 up
If patient responds sound is decreased ___
when there is no response sound is increased __
10 dB steps
5 dB steps
AC frequencies
250, 500, 1k, 2k, 3k, 4k, 6k, 8k Hz
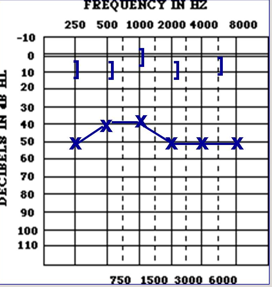
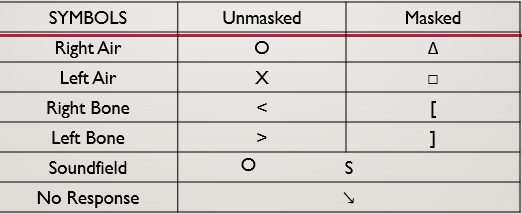
what kind of hearing loss is this
AC:
BC:
Air bone gap
Conductive hearing loss
AC abnormal
BC: normal
Air bone gap greater than or equal to 15
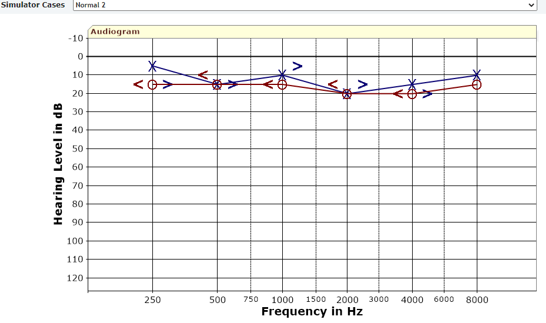
What does this audiogram show ?
All thresholds are in the normal range
less than 25 dB HL
Audiogram- shows threshold (softest sound a person can hear) at different frequencies
x-axis: frequency
Y-axis - dB HL
Audiogram symbols
Right air- Unmasked vs masked
left air - unmasked vs masked
right bone- unmasked - masked
left bone - unmasked - masked
soundfield
no response
Masking is important
needed to esnure that the patient is responsing by hearing the tone on the side we are testing
Configuration, unilateral, symmetrical/asymmetrical hearing
air bone gap
reflects how much sound energy is lost as the sound travels through he outer and middle ear

Sensorineural hearing loss is not just attenuation of ____
sound. there is a distortion and makes things sound less clear
Sensorineural hearing loss
caused by dysfunction in the inner ear and or auditory nerve
Problem not just attenuation of the sound
damage to cochlear hair cells
structural or functional problem
distortion
threshold obtained by air and bone conduction will be about the same
Both AC and BC thresholds are poorer than normal and they are within 10 dB of each other
Conductive hearing loss
caused by problems anywhere in outer or middle ear
BC thresholds are within nomral limits, because there is no problem with cochlea or auditory nerve
AC threqhols are poorer than monral because there is a problem getting sound to the cochlea through the outer or middle ear.
only considered a conductive hearing loss if there is an air-bone gap of greater than or equal to 15 dB
sounds are getting to the cochlea but they are not loud enough
what hearinng loss is this . what is SC, BC, air bone gpa
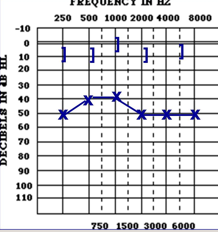
Mixed hearing loss
combination of sensorineural loss and conductive loss in the same ear
bone air and bone conduction will show a loss
air conduction will show a greater degree of hearing loss
both AC thresholds and BC thresholds are poorer than normal AND there is an air bone gap greater than or equal to 15 dB
Speech Audiometry
Pure tone audiograms do not provide direct information about an individual’s ability to understand speech
Speech Audiometry
Process of determing speech understanding speech understandign using speech stimuli
2 possible modes of presentation what are they ? Recorded speech material
played through a CD player, or computer
What is MLV
Monitored live voice ( Clinician speaks into a microphone of the tester side of the sound booth)
Recroded stimulu ensure a ____ and _____ _____.
Recroded stimuli ensure a valid and reliable score.
Difficult to maintain a consistent volume level when performing MLV
Children are more engaged by MLV
Common tests for speech audiometry
Speech detection/awareness threshold (SDT/SAT)
speech recognition threshold (SRT)
word recognition score ( WRS)
Speech in Noise testing
Speech detection threshold
lowest level at whcih speech sound can be detected
typiclaly measures for infants or others who cannot provide an SRT
Speech recogniction threshold (SRT)
lowest level at which familiar words can be correctly repeated
uses spondaic words (baseball, cupcake airplane)
The SRT should ____ with pure-tone average (
3-frequency PTA = average ( 500, 1000, 2000 HZ)
2- frequency PTA (less common)= average (500, 1000 HZ)
Word Recognition score (WRS) Word recognition (in quiet)
percentage of CNC words correctly repeated at a suprathreshold stimulus level (typicllay, 40 dB greater SRT)
Fixed level, that does not change
Calculated as a percentage correct, not a dB value
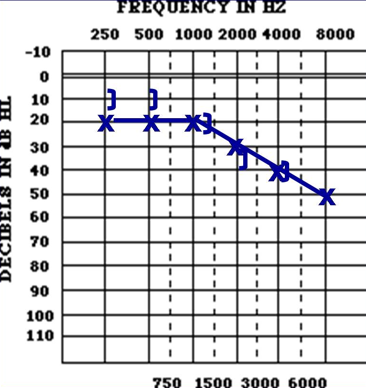
what kind of hearing loss is this
AC:
BC:
air bone gap?
Sensorineural hearing loss
AC: abnormal
BC: abnormal
No air-bone gap
Word recognition in noise
signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) at which 50% of words can be correctly identified
words are presented at fixed, suprathreshold stimulus level
Purpose of WRS
Provides an estimate of a patients ability to recognize single words at a suprathreshold levels
used as an estimate of potential benefit from hearing aids
Can assist in the differential diagnosis of some auditory disorder
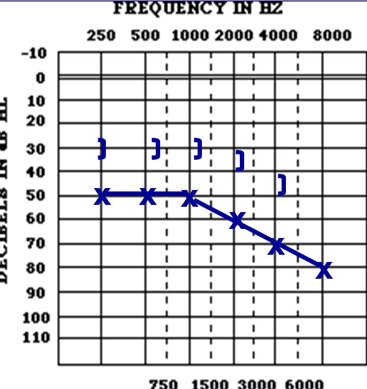
What kind of hearing loss is shown?
AC:
BC:
Air bone gap?
Mixed hearing loss
AC: Abnormal
BC: Abnormal
Air bone Gap greater than 15 dB
BOA Behavioral Observation Audiometry
used for babies that are 0-4 months old
Observe the baby’s response to a sudden sounds in sound field
BOA
reflexive responses
VRA (Visual Reinforcement Audiometry
at 4-7 months a child is able to turn to look at sounds
at 5-6 months children are good enough at turning their heads
(CPA) Conditioned Play Audiometry
Child is trained to make a certain motor response when a sound is heard (like a game)
Parents should not be in test room
two audiologist
Acoustic Immittance
measure of how well energy moves through the hearing system.
Acoustic Impedance
opposition (resistance) to the flow of sound energy through the system
Acoustic Admittance:
ease of energy flow through the system
Admittance
some vibration passes through (admitted) to the middle ear and go to cochlea
Impedance
some vibration reflected (impeded) into ear canal
Immittance testing allows clinicians to infer the status of the ___ ___ system
middle ear
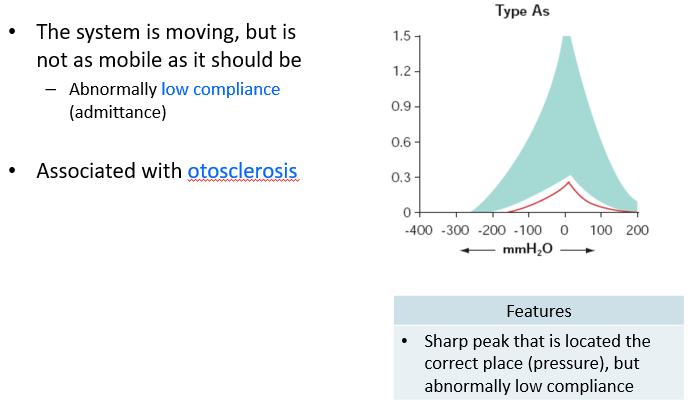
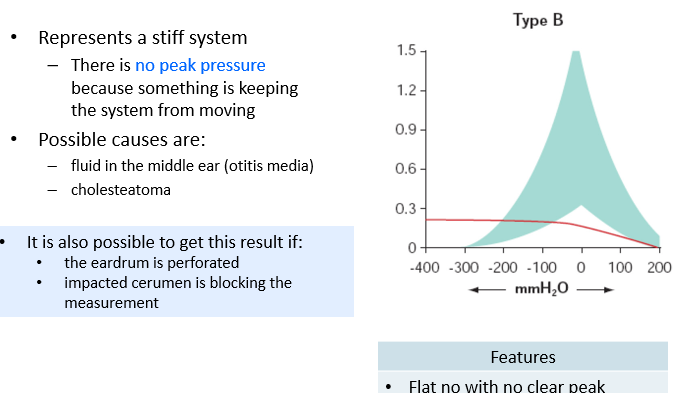
Pathologies that increase stiffness
otitis media
otosclerosis
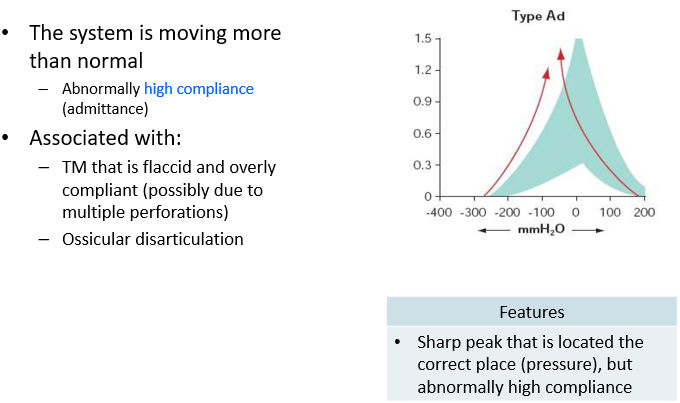
Pathology that decreases stiffness
disarticulated ossicular chain
For all immittance testing, a probe is inserted into the ear canal to create a ___ seal.
hermetic (air tight)
Changes in pressure result in changes in the _____ component of the middle ear system
stiffness
Intensity of probe tone in the ear canal is measured while the pressure is _____ ____
being changed
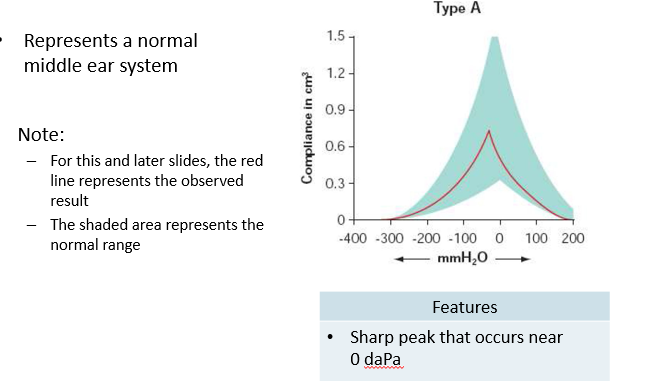
Type A Tympanogram
Type As Tympanogram
Type Ad Tympanogram
Type B Tympanogram
Type B with an abnormally large volume
Tm is perforated or a P.E tube is present
Type B with normal volume
Conductive component in the middle ear space
such as otitis media
Type B with an abnormally small volume
Impacted cerumen or foreign object in the ear canal
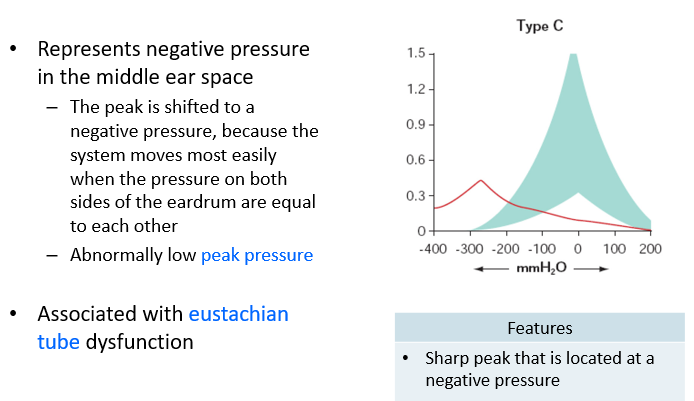
Type C Tympanogram
Pure Tone Audiogram
Measures hearing sensitivity at different frequencies
Speech detection Threshold (SDT)
Lowest level at which speech sounds can be detected (heard)
Speech recognition threshold (SRT)
measures the lowest level at which a word can be correctly identified
Word Recognition score
percentage of words correctly identifies by the patient at a level well above threshold
OAEs
Reflect outer hair cell health movement
ABR
used to asses the integrity of the auditory nerve. Normal results indicate that a synchronous signal is being sent by the auditory system
Immittance
Tympanometry: measures the mobility of the middle ear system
Acoustic Reflex threshold: measures the lowest intensity that triggers the acoustic reflex
Test Reliability
Refers to whether or not test results obtained are valid. One way we check for this is the relationship between speech recognition thresholds (SRT) and the pure tone average (PTA)
cross checking
looking across multiple tests to ensure the accuracy of all results
Unilateral Conductive Hearing Loss
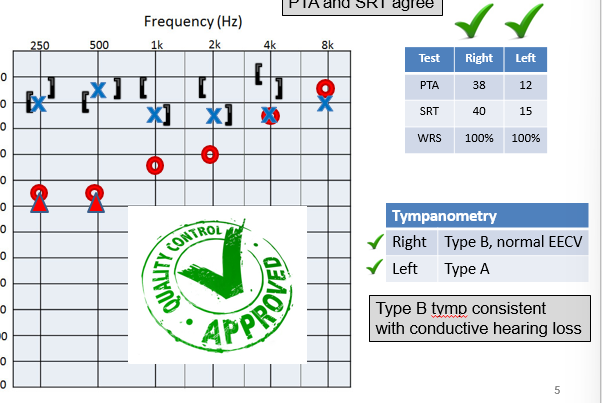
Good test reliability
Means that the test results are in agreement and are valid
Poor test reliability
test result may not be completely valid
We usually say this because tests results are not in agreement
Functional Hearing Loss
Term used to describe people exhibiting a hearing loss that is not due to an “organic” cause
Many terms exist to describe patients who exhibit unreliable/inconsistent test result.
If person is deliberately exaggerating HL
non-organic Hearing loss
Malingering
Pseudohpacusis
Functional Hearing Loss
Problem is at unconscious level
hysterical
psychogenic
Should refrain from describing the patient as ____ or ____ hearing loss
malingering or feigning
Words such as ____ are ___ ____ preferred instead
Words such as inconsistent are poor reliability preferred instead
Why would patients want to be diagnosed with a hearing loss
Financial gain, veteran benefits
Patients attempting to fake a hearing loss tend to lack false responses because the sound is actually always easy for them to hear.