Animals - 326
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/240
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
241 Terms
1
New cards
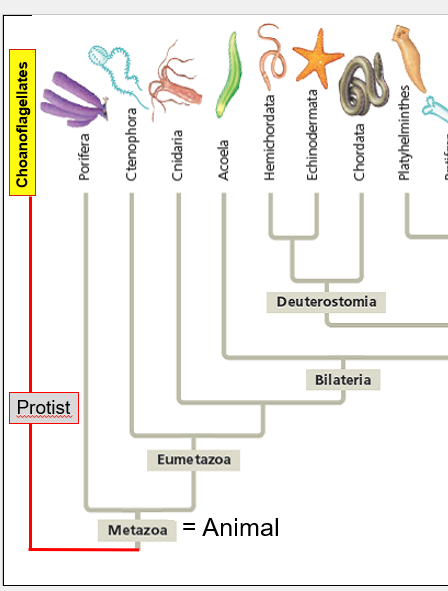
Phylum Porifera - Metazoa
Sponges
2
New cards
Phylum Ctenophora
Comb Jellies
3
New cards
Phylum Cnidaria
What are the 4 classes
What are the 4 classes
Hydrozoa - Hydra and Portuguese man of war
Scyphozoa - Jellyfish and Sea nettles
Cubozoa - Box Jellies and Sea Wasps
Anthozoa - Sea anemone, most coral, sea fans
Scyphozoa - Jellyfish and Sea nettles
Cubozoa - Box Jellies and Sea Wasps
Anthozoa - Sea anemone, most coral, sea fans
4
New cards
Phylum Platyhelminthes are...
Flat worms
5
New cards
Phylum Platyhelminthes 4 classes
Turbellaria - free-living flatworm, eg Planaria
Monogenaea - primarily ectoparasites of fish
Trematoda - trematodes or fluke
Cestoda - tapeworms
Monogenaea - primarily ectoparasites of fish
Trematoda - trematodes or fluke
Cestoda - tapeworms
6
New cards
Phylum Ectoprocta are..
Bryozoans or Moss Animals
7
New cards
Phylum Brachiopoda are
Lamp shells
8
New cards
Phylum Nemertea are...
Ribbon worms
9
New cards
Phylum Annelida = Segmented worms
What are the 3 classes
What are the 3 classes
Oligochaeta - earthworms
Polychaeta - Polychaeta
Hirudinea - leeches
Polychaeta - Polychaeta
Hirudinea - leeches
10
New cards
What makes an animal?
-Eukaryotic
-Multicellular (mostly)
-Heterotrophic
-Multicellular (mostly)
-Heterotrophic
11
New cards
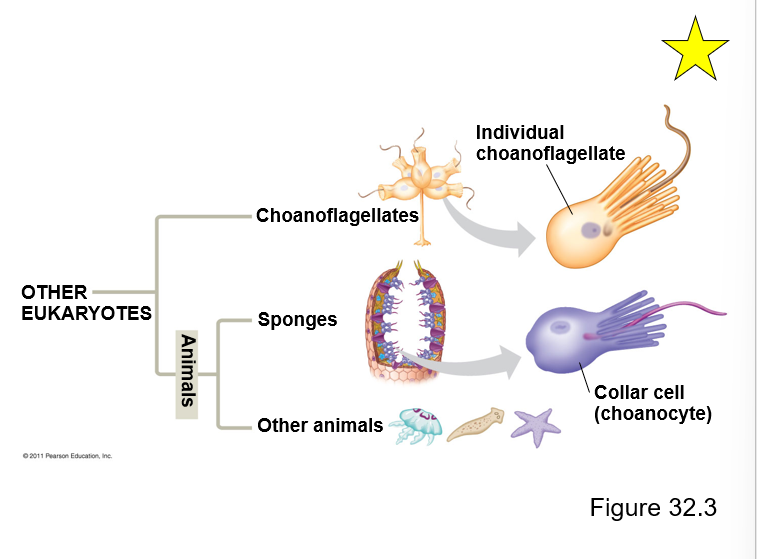
Choanoflagellates are...
Closest living relatives to animals
12
New cards
Choanoflagellates can form colonies through ... meaning...
aggregation of individuals
Two Choanoflagellates merge together to form
-single cell organisms
Two Choanoflagellates merge together to form
-single cell organisms
13
New cards
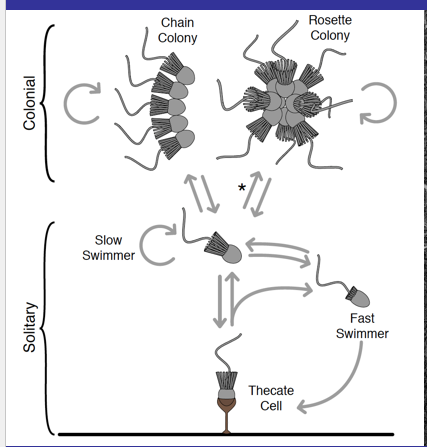
What is the process of Choanoflagellates forming a colony?
solitary - alone
Thecate - recruit bacteria to environmental surfaces surrounding the base of the theca stalk.
Thecate - recruit bacteria to environmental surfaces surrounding the base of the theca stalk.
14
New cards
Some Choanoflagellates form colonies through...
Cell division
15
New cards
Phylum Porifera are ...
Live?
Movement?
Eating?
Live?
Movement?
Eating?
Sponges
Marine, freshwater
Sessile
Benthic suspension feeders
Marine, freshwater
Sessile
Benthic suspension feeders

16
New cards
Choanoflagellate are the closest relative to animals
17
New cards
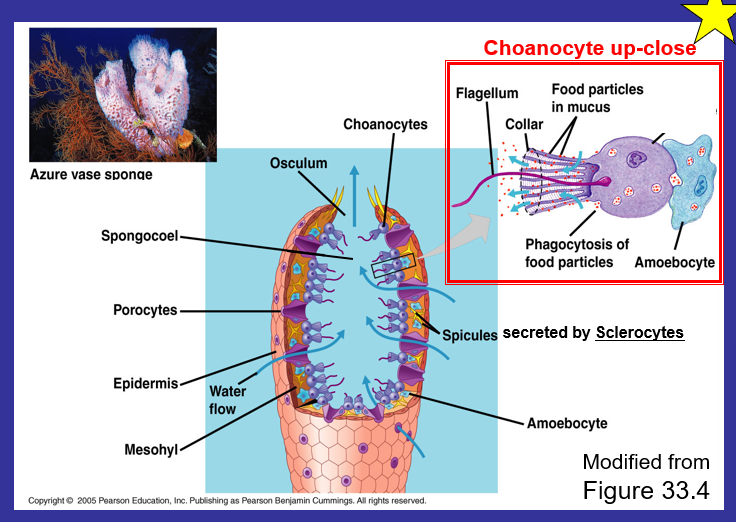
What is the process in sponges? What is it made up of and function?
Osculum - a large aperture in a sponge through which water is expelled.
Spongeocoal - large, central cavity of sponges
Porocytes - control the amount of water that enters pores
Amoebocyte - delivering nutrients from choanocytes to other cells within the sponge, giving rise to eggs for sexual reproduction
Phagocytosis - the ingestion of bacteria
Mesophyll - had Amoebocyte
Sclerocytes are the hard parts that make up the sponges - specialized cells that secrete the mineralized structures in the body wall of some invertebrates.
Spicule - the structural components of a sponge, or the bricks - made of calcium carbonate or silica
Spongeocoal - large, central cavity of sponges
Porocytes - control the amount of water that enters pores
Amoebocyte - delivering nutrients from choanocytes to other cells within the sponge, giving rise to eggs for sexual reproduction
Phagocytosis - the ingestion of bacteria
Mesophyll - had Amoebocyte
Sclerocytes are the hard parts that make up the sponges - specialized cells that secrete the mineralized structures in the body wall of some invertebrates.
Spicule - the structural components of a sponge, or the bricks - made of calcium carbonate or silica
18
New cards
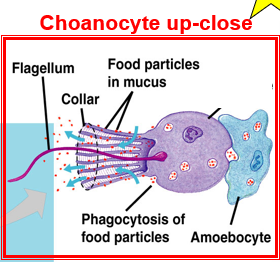
Choanocyte
create the active pumping of water through the sponge
Collar - nutrients are absorbed into the sponge
Collar - nutrients are absorbed into the sponge
19
New cards
Spicules secreted by ...
sclerocytes

20
New cards
Spongocytes make... which are...
Spongin - fibrous substance found in the skeleton of many sponges

21
New cards
What are sponges vulnerable to? 2
Sponge Grazers - Angelfishes, Filefishes, Parrotfishes
- Eukaryotes, bacteria, and viruses
- Eukaryotes, bacteria, and viruses
22
New cards
How do sponges defends themselves?... and..
Secondary metabolites (secrets particles)
Trade-offs
Trade-offs
23
New cards
Secondary Metabolites
secrets particles
in sponges:
Antimicrobial
Antiviral
Antifungal
Antiprotozoal
Anticancer
in sponges:
Antimicrobial
Antiviral
Antifungal
Antiprotozoal
Anticancer
24
New cards
Trade-offs
arise when you have limitations
-a condition in which an increase in the performance of one trait causes a decrease in the performance of another, given the limited amount of available resource
-a condition in which an increase in the performance of one trait causes a decrease in the performance of another, given the limited amount of available resource
25
New cards
Eumetazoa - Animal with "true tissues"
Ctenophora
26
New cards
What is Ctenophora phylum
Comb jellies
27
New cards
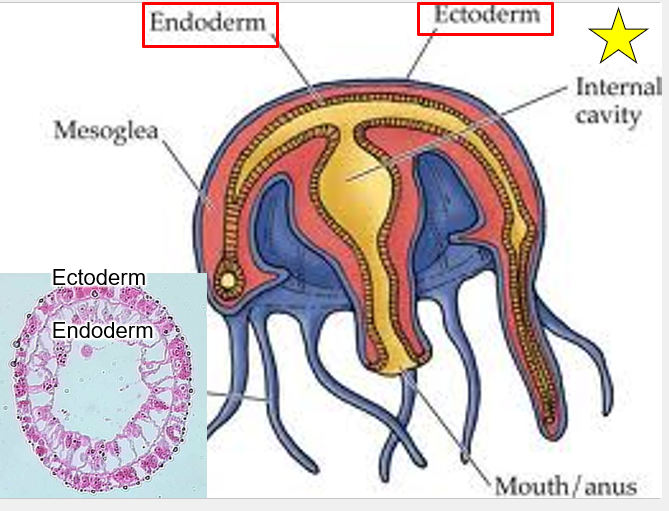
What is the diagram of Comb jellies (5)
Mesoglea
Endoderm
Ectoderm
Internal cavity
Mouth/anus
Endoderm
Ectoderm
Internal cavity
Mouth/anus
28
New cards
Ctenophora (Comb Jellies) are...
All... and mostly....
Has eight combs of ... that ...the animal
All... and mostly....
Has eight combs of ... that ...the animal
All marine and pelagic
Pelagic - occurring in the open sea
Has eight combs of cilia that propel the animal
Pelagic - occurring in the open sea
Has eight combs of cilia that propel the animal
29
New cards
Phylum Cnidaria have...4
Jellies, corals, hydras, anemones
30
New cards
Cnidaria live in...
Marine and Freshwater
31
New cards
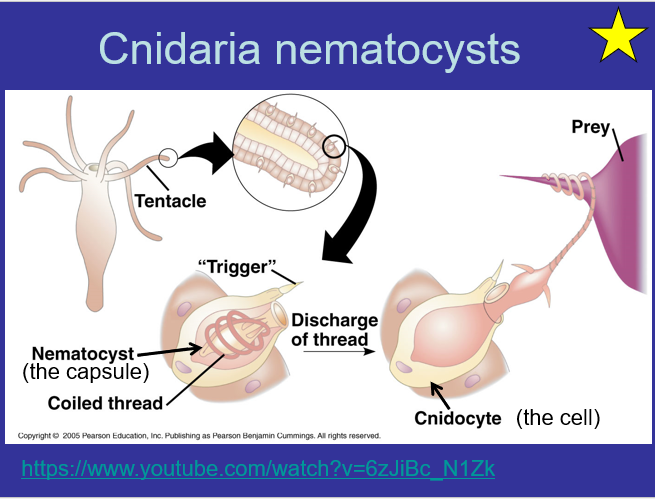
Cnidaria have nematocyst which are...
a specialized cell in the tentacles of a jellyfish containing a venomous coiled thread that can be projected in self-defense or to capture prey.
32
New cards
What are the parts of Cnidaria nematocysts
-Tentacle
-Trigger
-Nematocyst (The Capsule)
-Coiled thread
-Cnidocyte (stinging cells)
-Trigger
-Nematocyst (The Capsule)
-Coiled thread
-Cnidocyte (stinging cells)
33
New cards
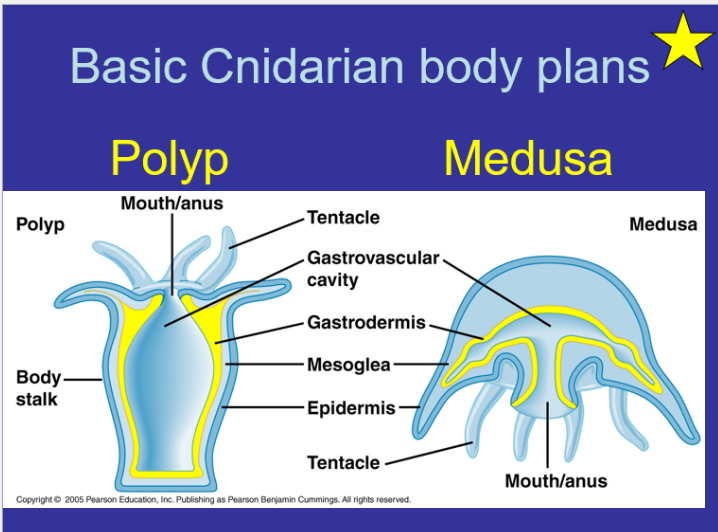
What are the Basic Cnidarian body plans for Polyp and Medusa
Gastrovascular - primary organ of digestion and circulation
Gastrodermis - the inner layer of cells that serves as a lining membrane of the gastrovascular cavity
Gastrodermis - the inner layer of cells that serves as a lining membrane of the gastrovascular cavity
34
New cards
What are the 4 classes of Cnidarians?
Anthozoans
Hydrozoans
Scyphozoans
Cubozoans
Hydrozoans
Scyphozoans
Cubozoans
35
New cards
Anthozoas are (2)
Sea anemones, corals
36
New cards
Anthozoas
Live in?
what stage?
Sexual or asexual or both?
most...
Live in?
what stage?
Sexual or asexual or both?
most...
All marine
Polyp stage only (medusa absent)
Most Sessile and Colonial
Asexual or sexual polyp
Polyp stage only (medusa absent)
Most Sessile and Colonial
Asexual or sexual polyp
37
New cards
Anthozoans have exoskeletons made up of what?
Calcium Carbonate
38
New cards
What is Coral Bleaching?
changes in ph, killing corals, leaving behind the exoskeleton of anthozoans
39
New cards
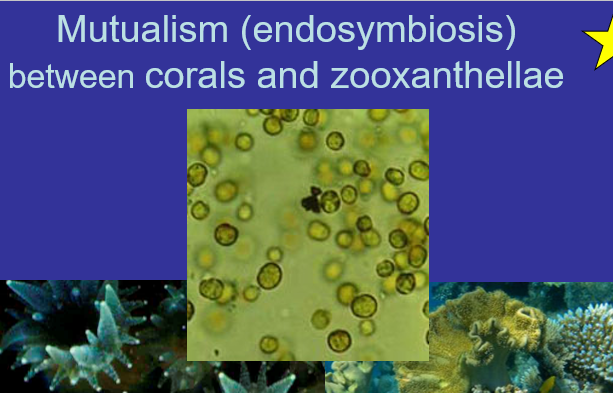
Mutualism endosymbiosis
Between corals and zooxanthellae (protist) has an endosymbiosis relationship from corals.
40
New cards
What are the 4 classes of Cnidarians
Anthozoans
Hydrozoans
Scyphozoans
Cubozoans
Hydrozoans
Scyphozoans
Cubozoans
41
New cards
What is the Cnidarian Life Cycle?
What is a polyp - non-motile with cylindircal body and long stalk (Polyps generally reproduce asexually (by budding))
Medusas are free swimming, umbrella-shaped and have a reduced stalk
Gonad - organ that produces gametes; a testis or ovary
Planula - free-swimming coelenterate larva with a flattened, ciliated, solid body.
Medusas are free swimming, umbrella-shaped and have a reduced stalk
Gonad - organ that produces gametes; a testis or ovary
Planula - free-swimming coelenterate larva with a flattened, ciliated, solid body.
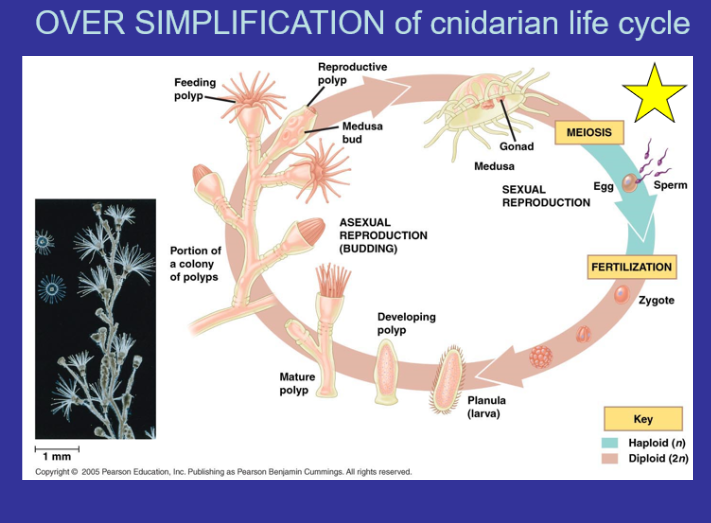
42
New cards
Hydrozoans are...
Hydras, Portuguese man of war
43
New cards
Hydrozoans
Lives in?
has what stage?
Lives in?
has what stage?
Most marine, few freshwater
Polyp and medusa stage in most species
Polyp and medusa stage in most species
44
New cards
Scyphozoans:
Medusa Jellies
45
New cards
Scyphozoans
live in..
live in..
All marine
Mostly medusa with Polyp reduced
Mostly medusa with Polyp reduced
46
New cards
Cubozoans:
Sea wasps (box Jelly)
47
New cards
Cubozoans are ...
mostly medusa with polyp reduced
Box shaped medusa
Box shaped medusa
48
New cards
lecture 2
49
New cards
Cnidarian phylogeny and life cycle summary
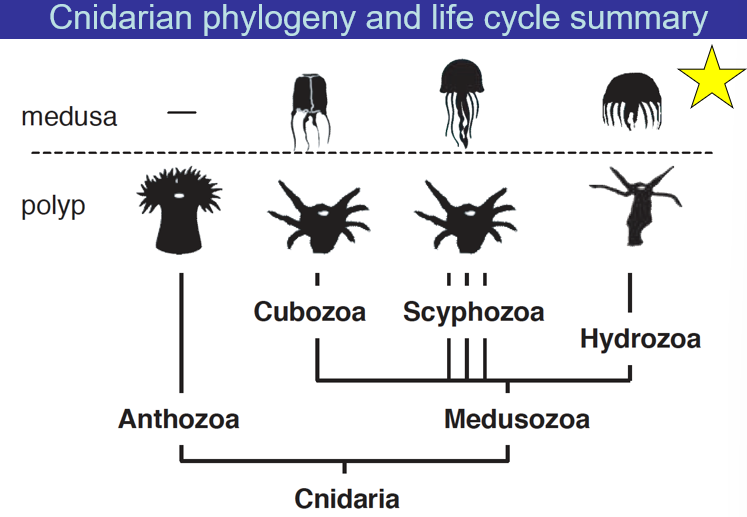
50
New cards
Animal Symmetry
51
New cards
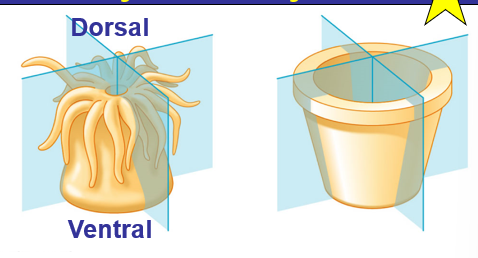
Radiata mean...
Radial symmetry
52
New cards
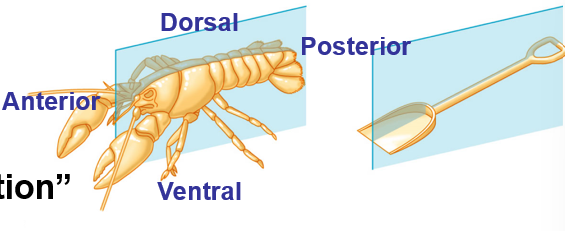
Bilateria
Bilateral Symmetry
53
New cards
Cephalization
anterior end of the body, forming a head and brain, both during evolution and in the course of an embryo's development.
54
New cards
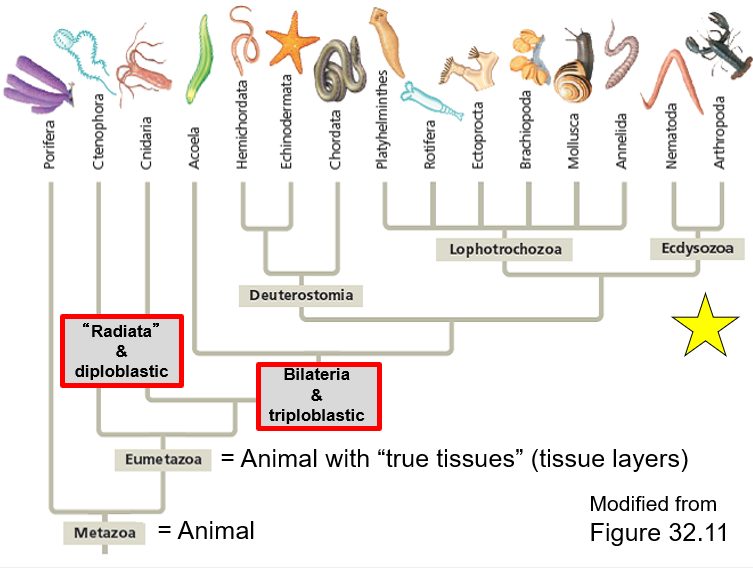
What class is Radiata and Diploblastic
What class is Bilateria and Triploblastic
What class is Bilateria and Triploblastic
Ctenophora
Cnidria
Cnidria
55
New cards
What are the two Tissues types?
Diploblastic
Triploblastic
Triploblastic
56
New cards
Diploblastic?
2 layers of living cells: ectoderm, endoderm
57
New cards
Triploblastic?
3 layers of living cells: ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
58
New cards
Endoderm?
Gives rise to liver, pancreas, lungs, and lining of digestive tract
59
New cards
Mesoderm
Gives rise to: notochord, lining of coelom, muscles, skeleton, gonads, kidneys, and most of circulatory system
60
New cards
Notochord?
The notochord is a rod-like embryological structure, which plays a vital role in the development of the vertebrate
61
New cards
Ectoderm
Gives rise to: outer covering, nervous system components in some phyla, inner ear, lens of eye.
62
New cards
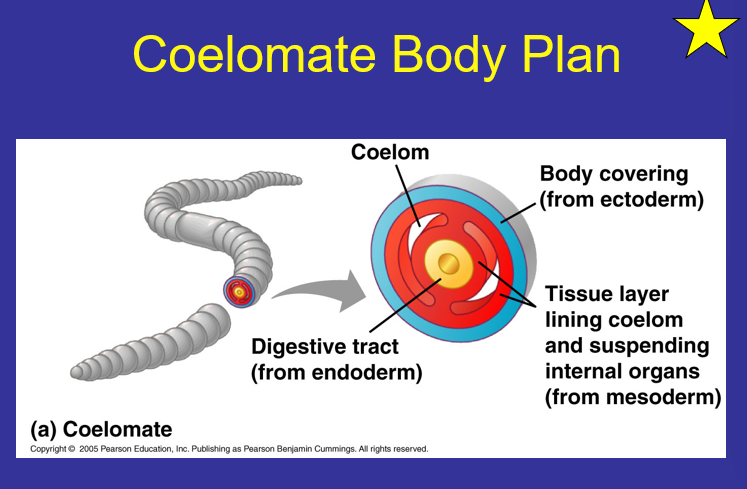
What is the Coelomate Body Plan?
Triploblastic
Coelom
Endoderm
Ectoderm
mesoderm
Coelom
Endoderm
Ectoderm
mesoderm
63
New cards
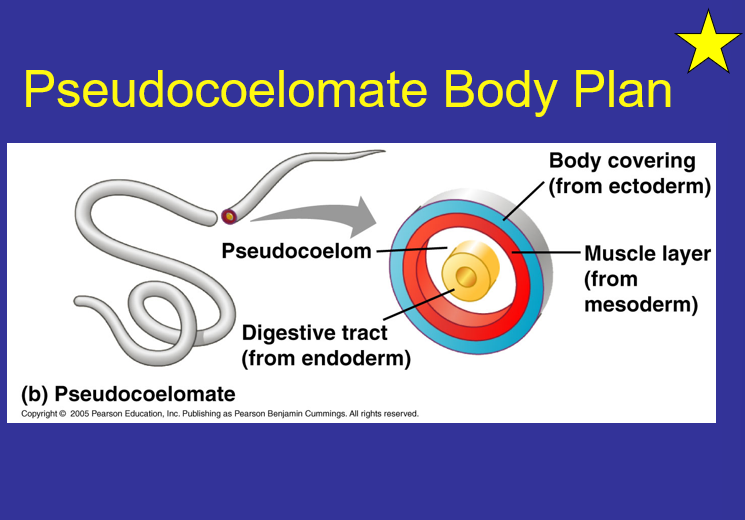
Pseudocoelomate Body plan?
Triploblastic
Pseudocoelom - no body cavity
Endoderm - digestive tract.
Ectoderm - body covering
mesoderm - muscle layer
Pseudocoelom - no body cavity
Endoderm - digestive tract.
Ectoderm - body covering
mesoderm - muscle layer
64
New cards
Acoelomate Body Plan?
Triploblastic
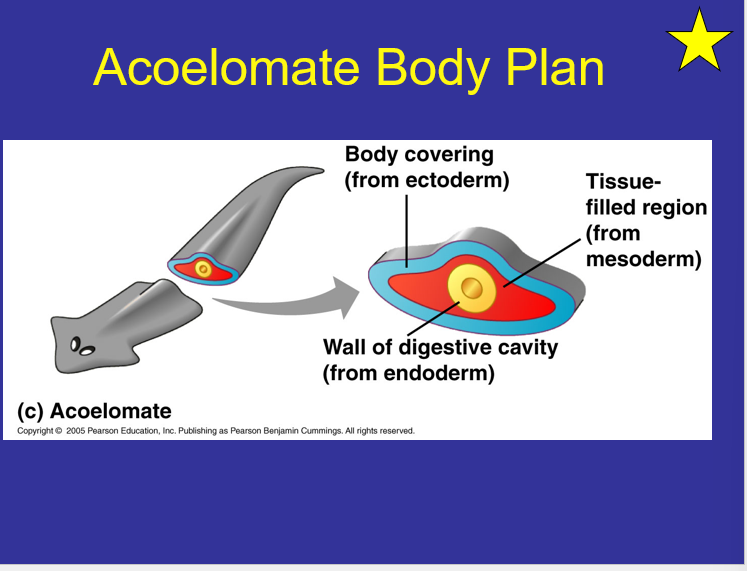
65
New cards
Who is in the Lophotrochozoa?
Platyhelminthes
Rotifera
Ectoprocta
Brachiopoda
Mollusua
Annelida
Rotifera
Ectoprocta
Brachiopoda
Mollusua
Annelida
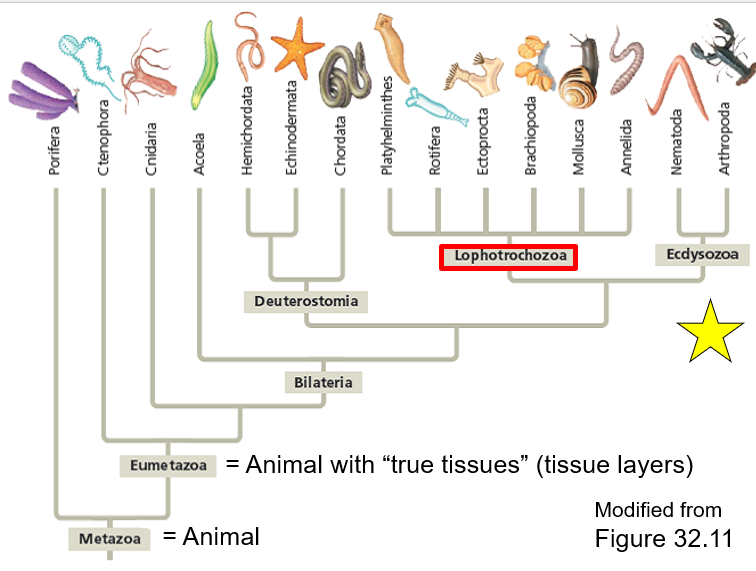
66
New cards
Lophotrochozoa
67
New cards
Platyhelminthes are..
Flatworms
68
New cards
Ectoprocta
Bryozoans
69
New cards
Brachiopoda
Brachiopods or lamp shells
70
New cards
Annelida
Segmented worms
71
New cards
Nemertea
Ribbon worms
72
New cards
Mollusca
Snails, clams, squid octopus
73
New cards
What are the 4 classes of Platyhelminthes
turbellaria
Monogenea
Trematoda
Cestoda
Monogenea
Trematoda
Cestoda
74
New cards
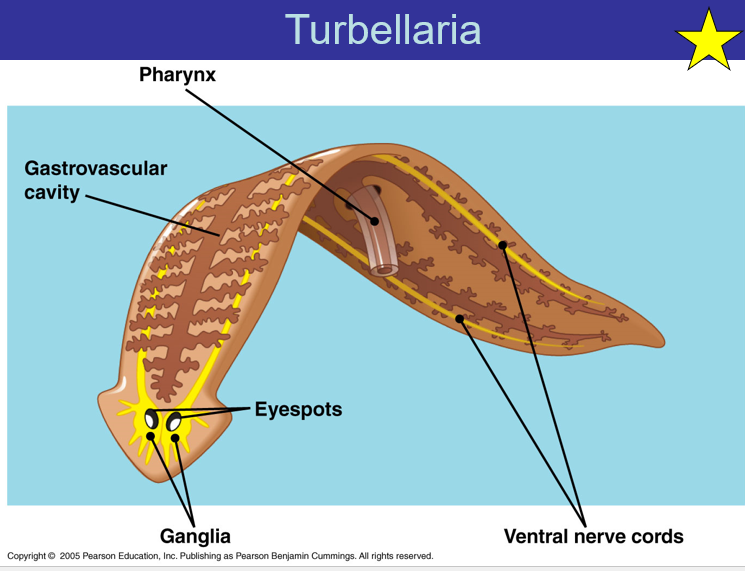
Turbellaria
Gastrovascular cavity - two-way digestive tract with a single opening that serves as both the mouth and the anus for the animal.
Pharynx
Ganglia - clusters of nerve cells
Eyespots
Ventral nerve cord - a chain of connected segmental ganglia
Pharynx
Ganglia - clusters of nerve cells
Eyespots
Ventral nerve cord - a chain of connected segmental ganglia
75
New cards
Turbellaria (dugesia)
Reproduce.... and...
Models for...
Can completely regenerate with as little as ... of the animal
Turbellaria are ... and ...
Reproduce.... and...
Models for...
Can completely regenerate with as little as ... of the animal
Turbellaria are ... and ...
Reproduce sexually and asexually
Models for regeneration
1/279
Terrestrial and Marine
Models for regeneration
1/279
Terrestrial and Marine

76
New cards
Monogenea are what?
Are the free-living?
Are the free-living?
Parasites that hook on to fish gills
Free-living and ectoparasitic
Free-living and ectoparasitic
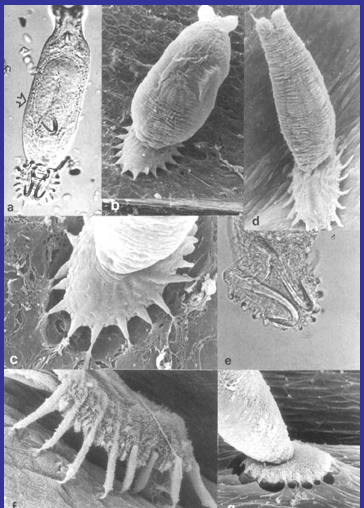
77
New cards
Ectoparasitic
parasite lives outside the body of the host.
78
New cards
What are Trematoda?
Endoparasites or ectoparasitic
... life cycle
... host?
Endoparasites or ectoparasitic
... life cycle
... host?
Endoparasites
Complex life cycle
Multiple host?
Complex life cycle
Multiple host?
79
New cards
Ribeiroia life cycle?
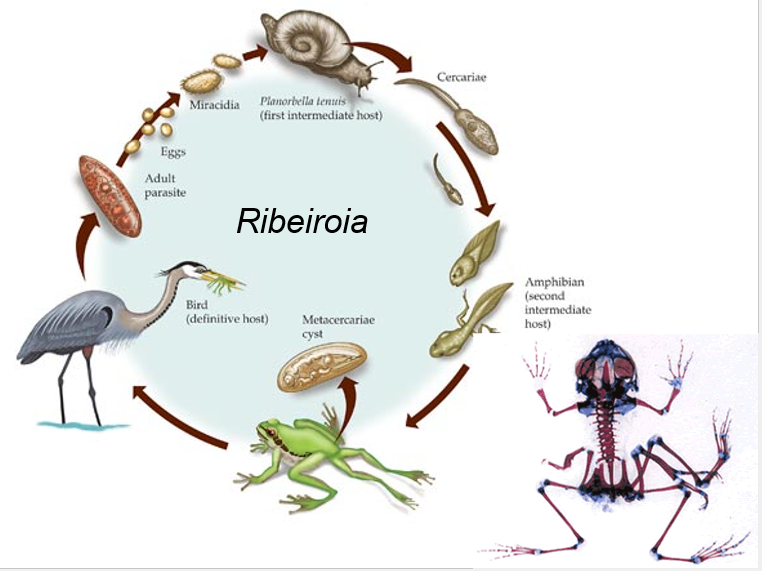
80
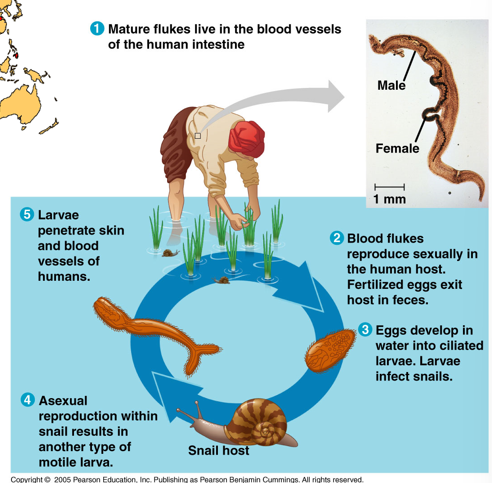
New cards
Blood Fluke Schistosoma?
1. Mature flukes live in the blood vessels of the human intestine
2. Blood flukes reproduce sexually in the human host. Fertilized eggs exit host in feces
3. Eggs develop in water into ciliated larvae. Larvae infect snails
4. Asexual reproduction within snail results in another type of motile larva
5. Larvae penetrate skin and blood vessel of human
2. Blood flukes reproduce sexually in the human host. Fertilized eggs exit host in feces
3. Eggs develop in water into ciliated larvae. Larvae infect snails
4. Asexual reproduction within snail results in another type of motile larva
5. Larvae penetrate skin and blood vessel of human
81
New cards
cestoda
Are endoparasites or ectoparasites
...life cycle
can use ... host
Are endoparasites or ectoparasites
...life cycle
can use ... host
Endoparasite
Complex life cycle
Can use multiple host
Complex life cycle
Can use multiple host
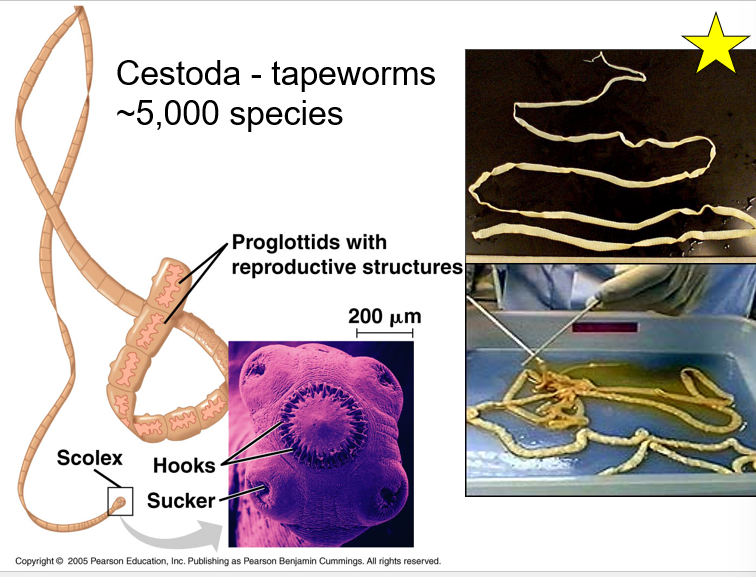
82
New cards
Cestoda are...
Proglottids are...
Scolex are...
Proglottids are...
Scolex are...
Tapeworms
Reproductive structures
Hooks and sucker
Reproductive structures
Hooks and sucker
83
New cards
What is Disease Taeniasis?
Pork tapeworm
Beef tapeworm
Beef tapeworm
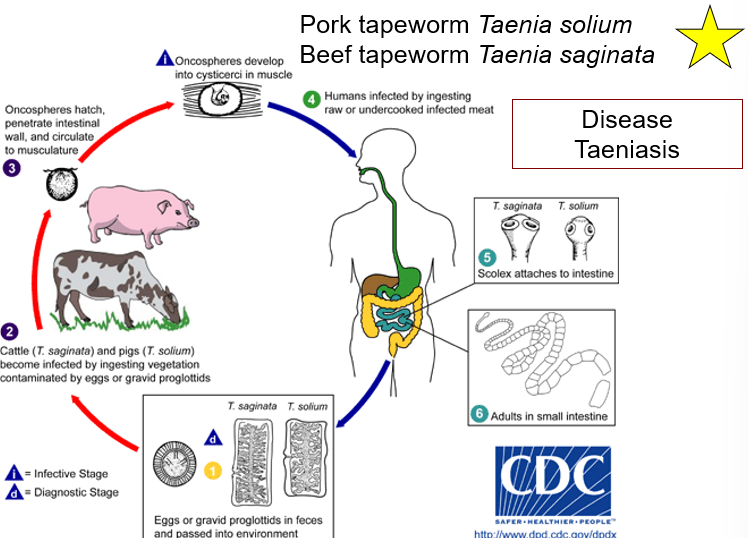
84
New cards
Pork tape worm and Beef tapeworm create what diseases?
Cysticercosis
Neurocysticercosis
Neurocysticercosis
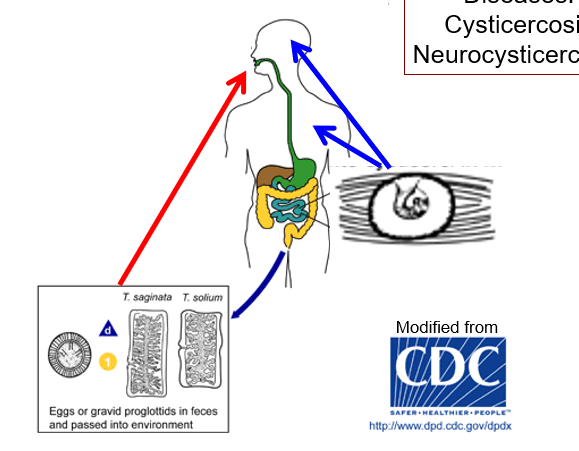
85
New cards

What is this?
bryozoans
86
New cards
lophotrochozoans are...
lophotrochozoans are triploblastic
87
New cards
What is lophophore
ring of tentacles
88
New cards
What are in the Lophotrochozoa
Platyhelminthes
Rotifera
Ectoprocta
Brachiopoda
Mollusca
Annelida
Rotifera
Ectoprocta
Brachiopoda
Mollusca
Annelida
89
New cards
What has lophophore? 2
Ectoprocta
Brachiopoda
Brachiopoda
90
New cards
Ectoprocta: Bryozoans (moss animals) are..
mostly... and some....
Colonies can contain millions of ..
mostly... and some....
Colonies can contain millions of ..
Mostly marine and some freshwater
Colonies can contain millions of zooids
Colonies can contain millions of zooids
91
New cards
What is Ectoprocta?
Individual is a zooid usually
92
New cards
Ectoprocta
lophophore
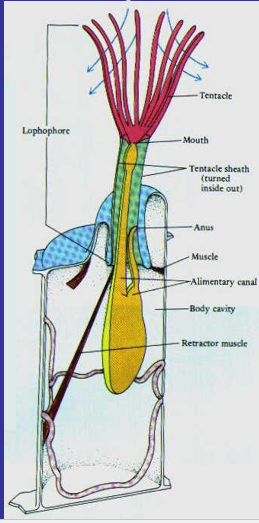
93
New cards

Brachiopoda (lamp shells) are called?
Marine "worm" with dorsal and ventral shell
94
New cards
Brachiopoda shells are made of what?
Part chitin and part Ca+ carbonate or phosphate
95
New cards
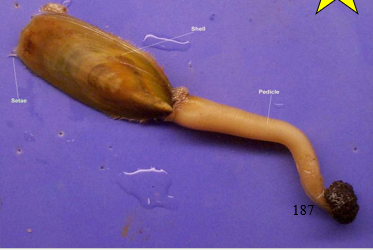
Shells on top of a stalk called a
pedicle
96
New cards
Brachiopoda
live?
s... and... b
live?
s... and... b
Marine
Sessile, and benthic
Sessile, and benthic
97
New cards
Diagram of Brachiopoda
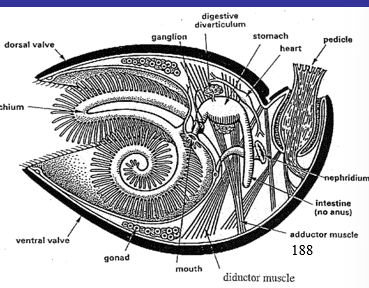
98
New cards
Permian Extinction
Triassic extinction (one of the species extinctions)
There are tens of thousands of species recognized
There are tens of thousands of species recognized
99
New cards
Permian Extinction
Rugose Corals
100
New cards
Extinction of Conulariids
Late Triassic