Anatomy Unit 5 : intro, heart, fetal circulation, respiratory system
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
183 Terms
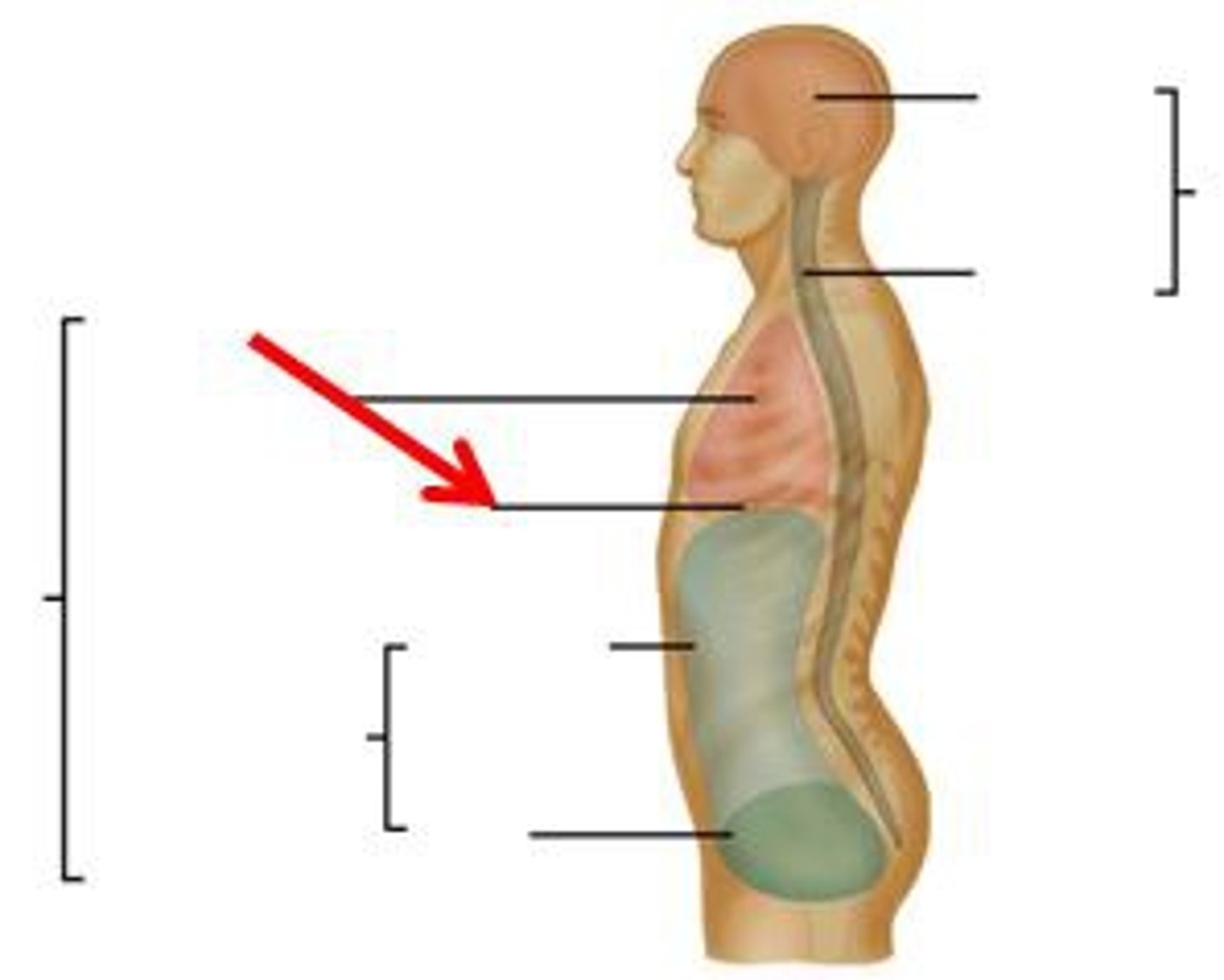
Thoracic cavity
contains heart and lungs
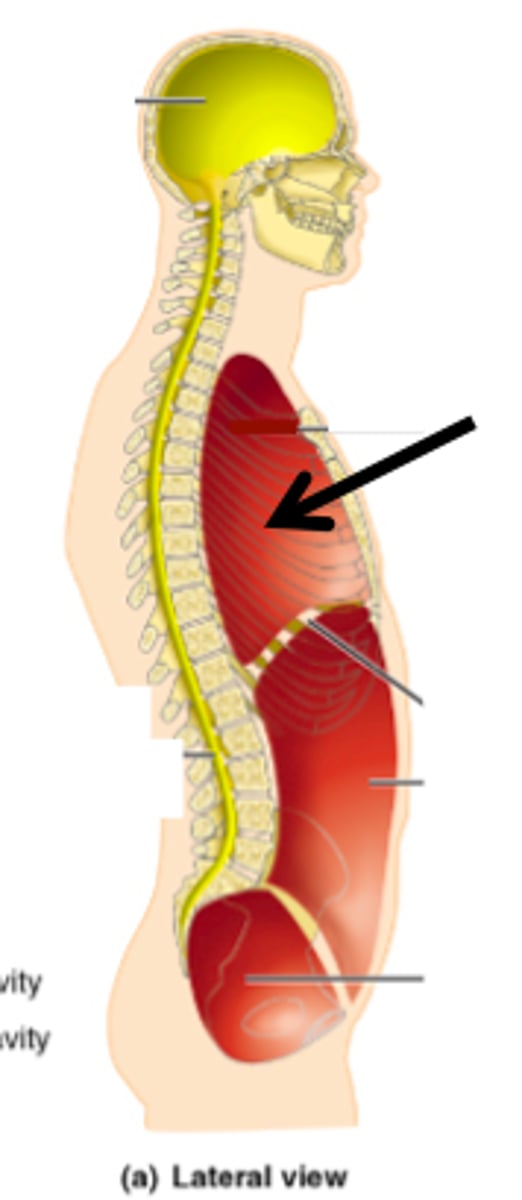
Pleural cavities (of thoracic cavity)
surround lungs
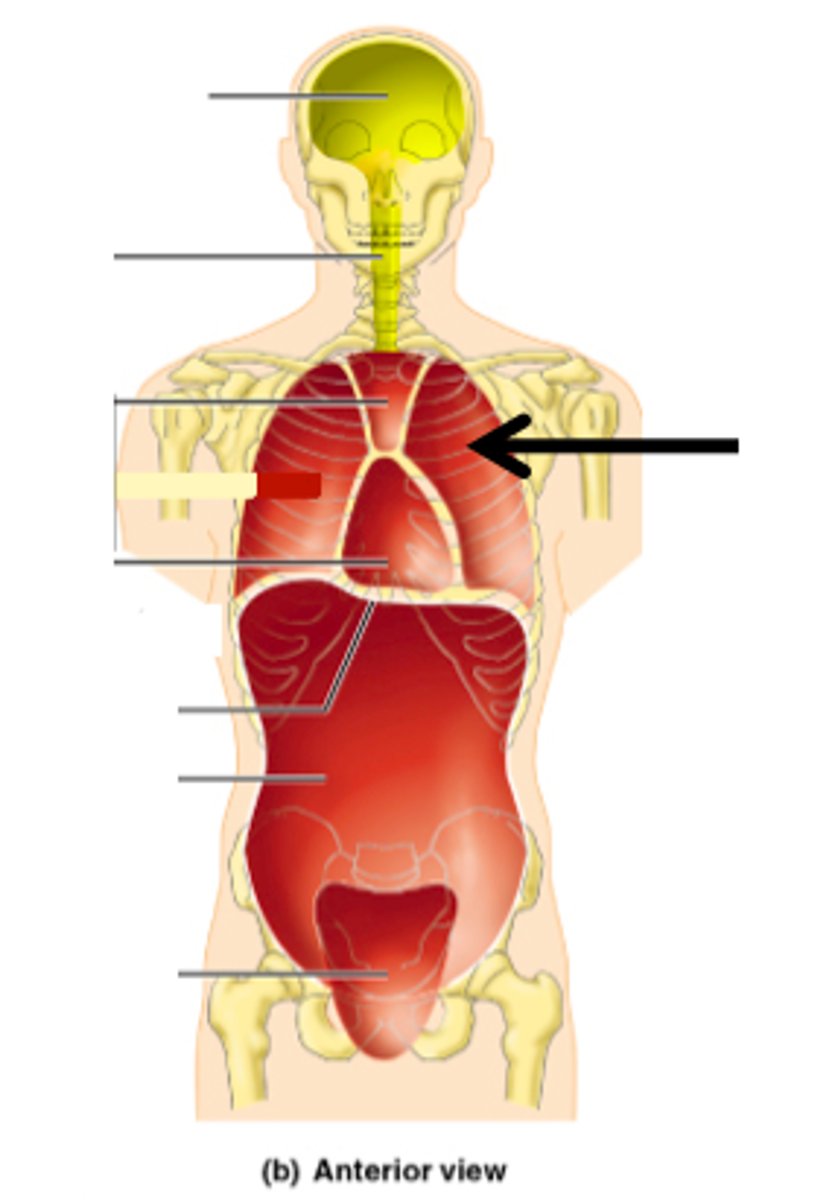
Mediastinum (of thoracic cavity)
contains heart, esophagus, trachea, blood vessels, etc
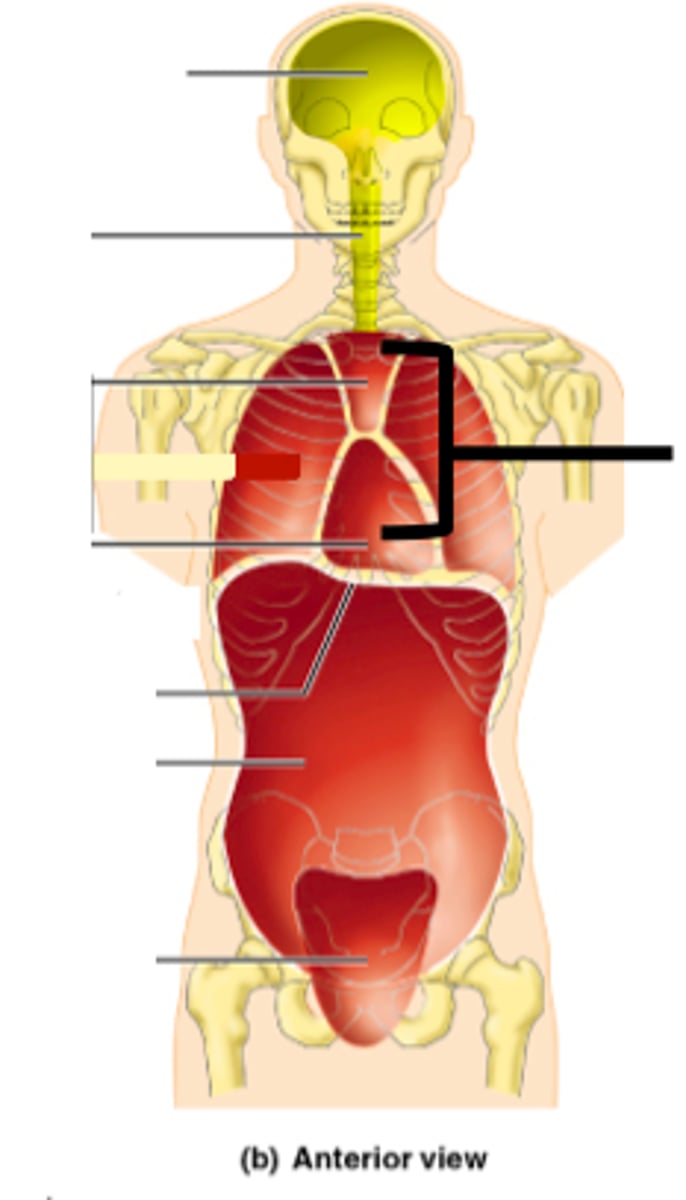
Pericardial cavity (within mediastinum)
surrounding the heart
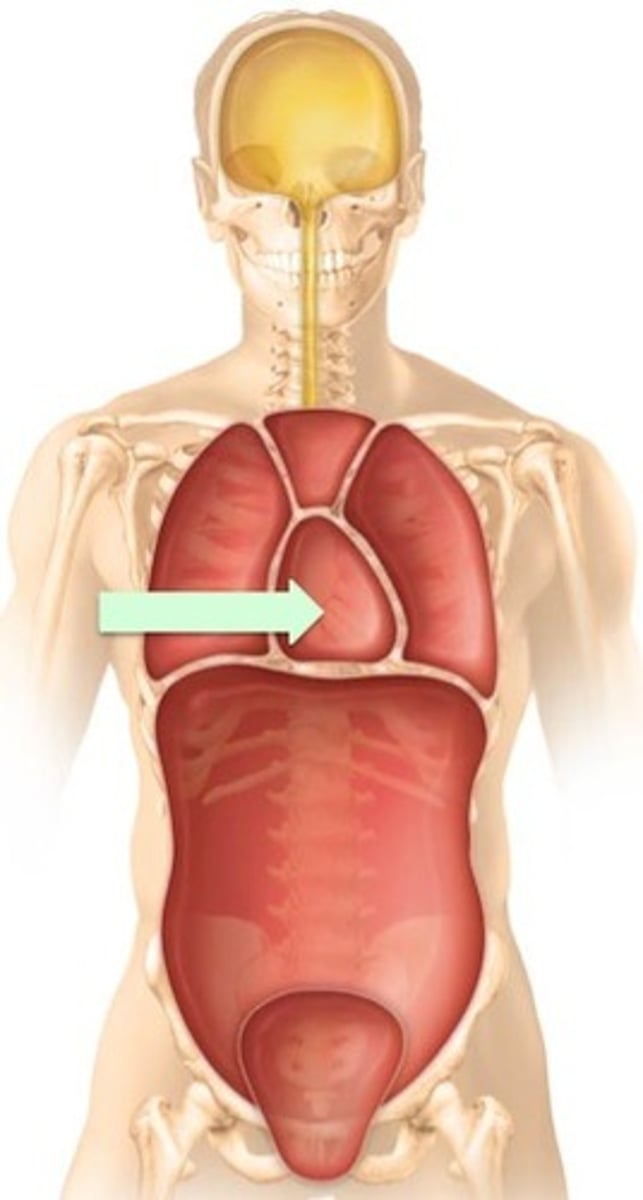
Abdominopelvic cavity
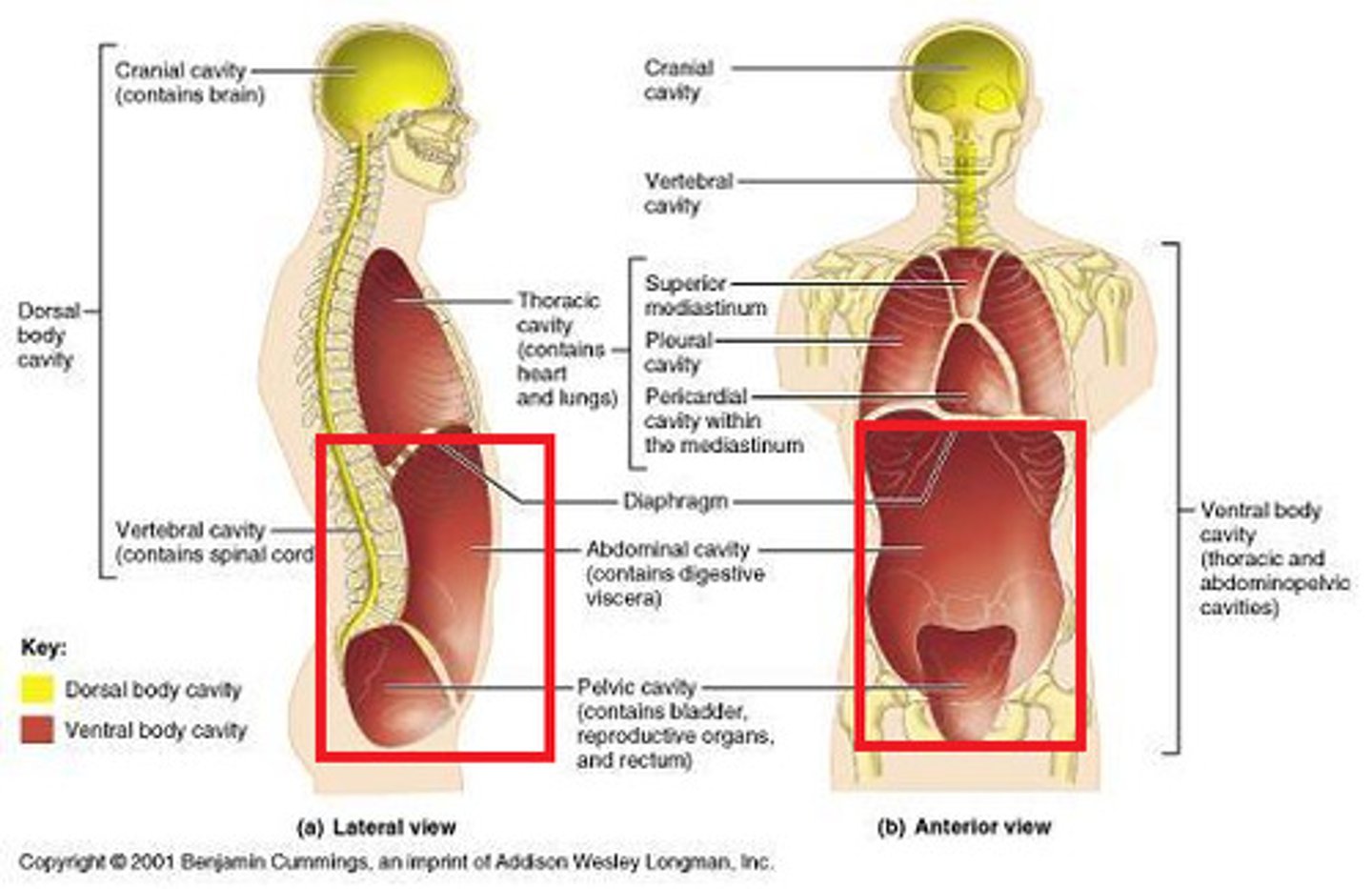
Abdominal (of abdominopelvic) cavity
gastrointestinal structures
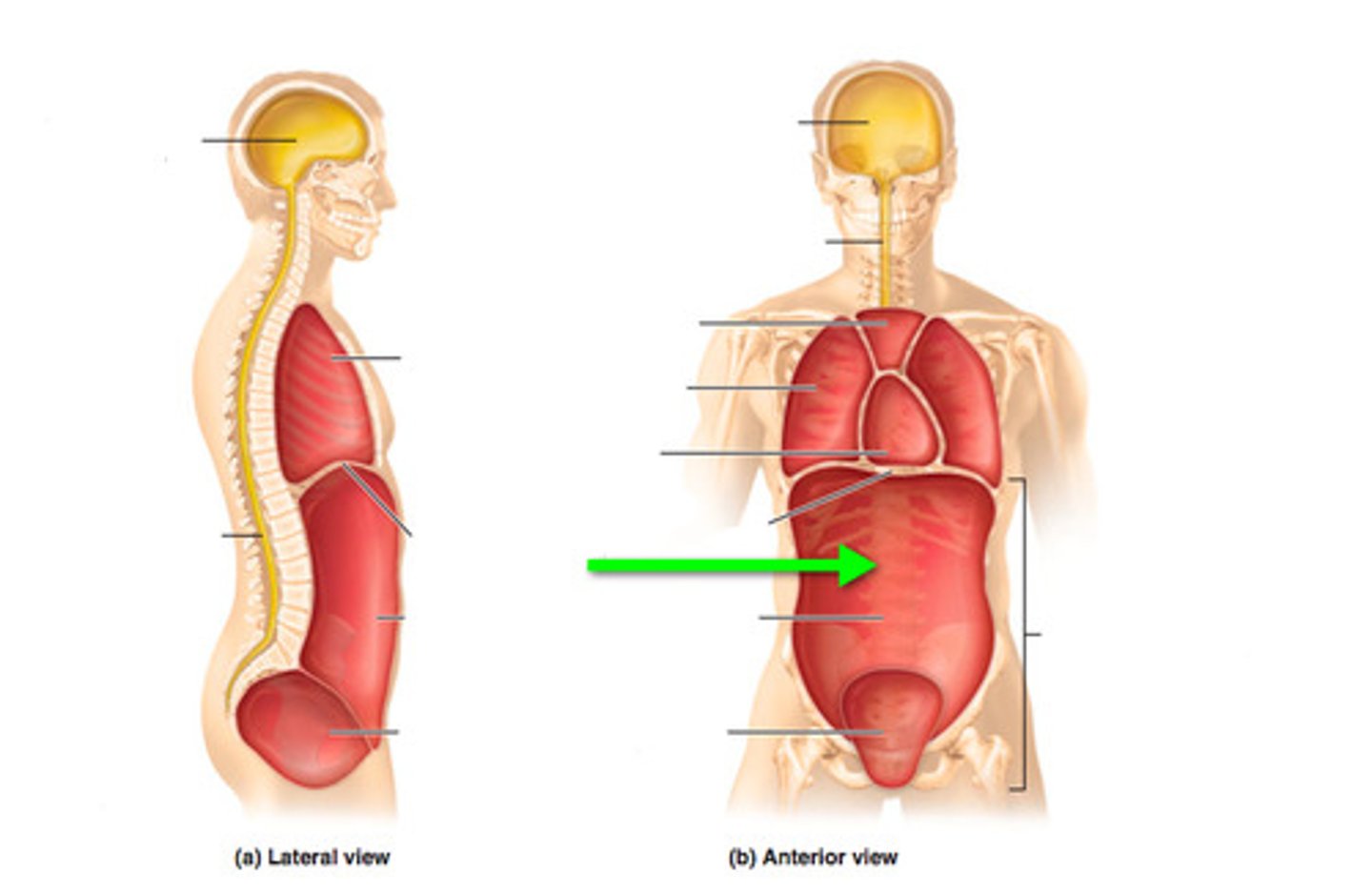
Pelvic (of abdominopelvic) cavity
urinary bladder, reproductive organs, last part of digestive tract
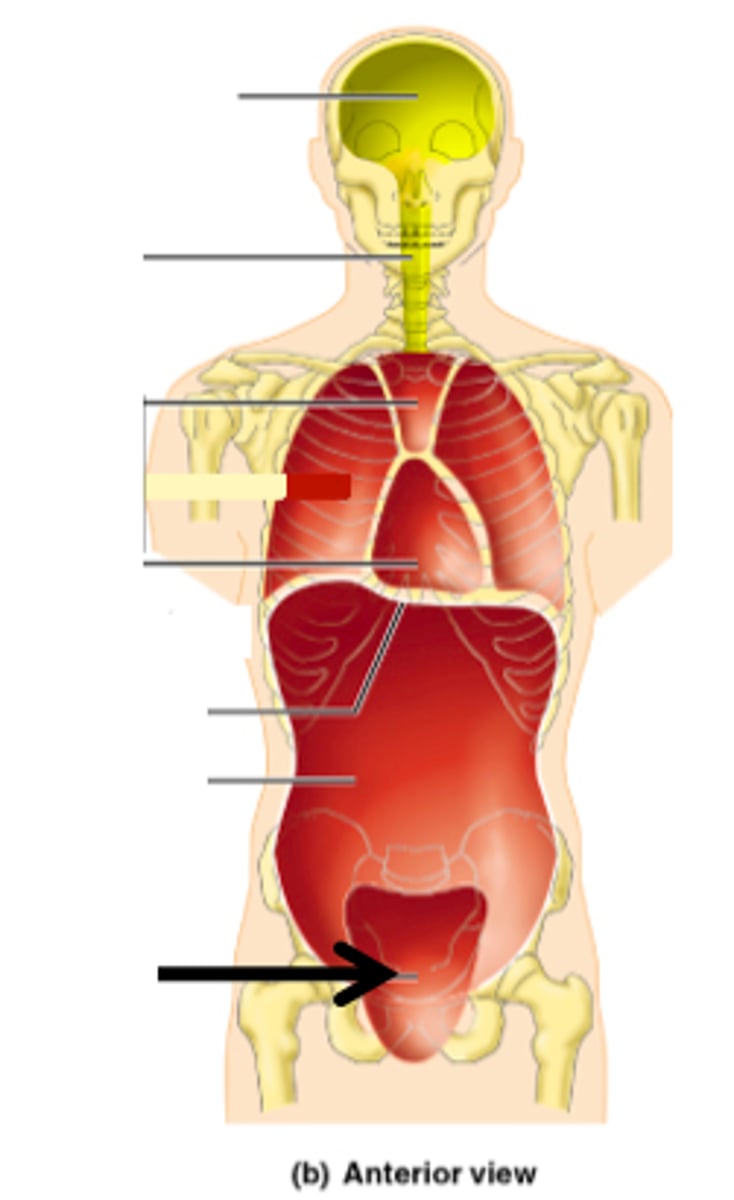
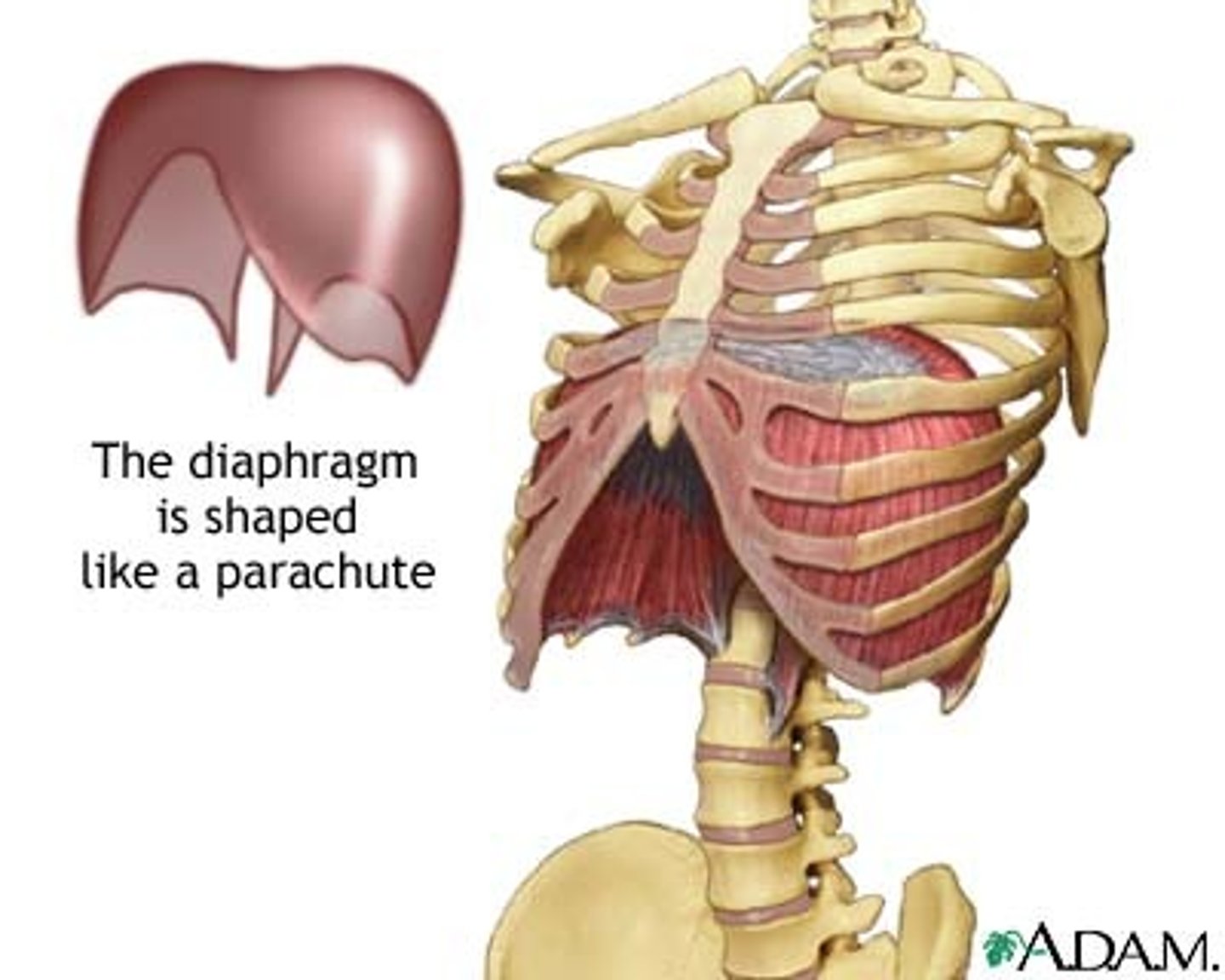
The Thoracic and Abdominopelvic cavity are separated by
the diaphragm
Diaphragm
Large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps with breathing
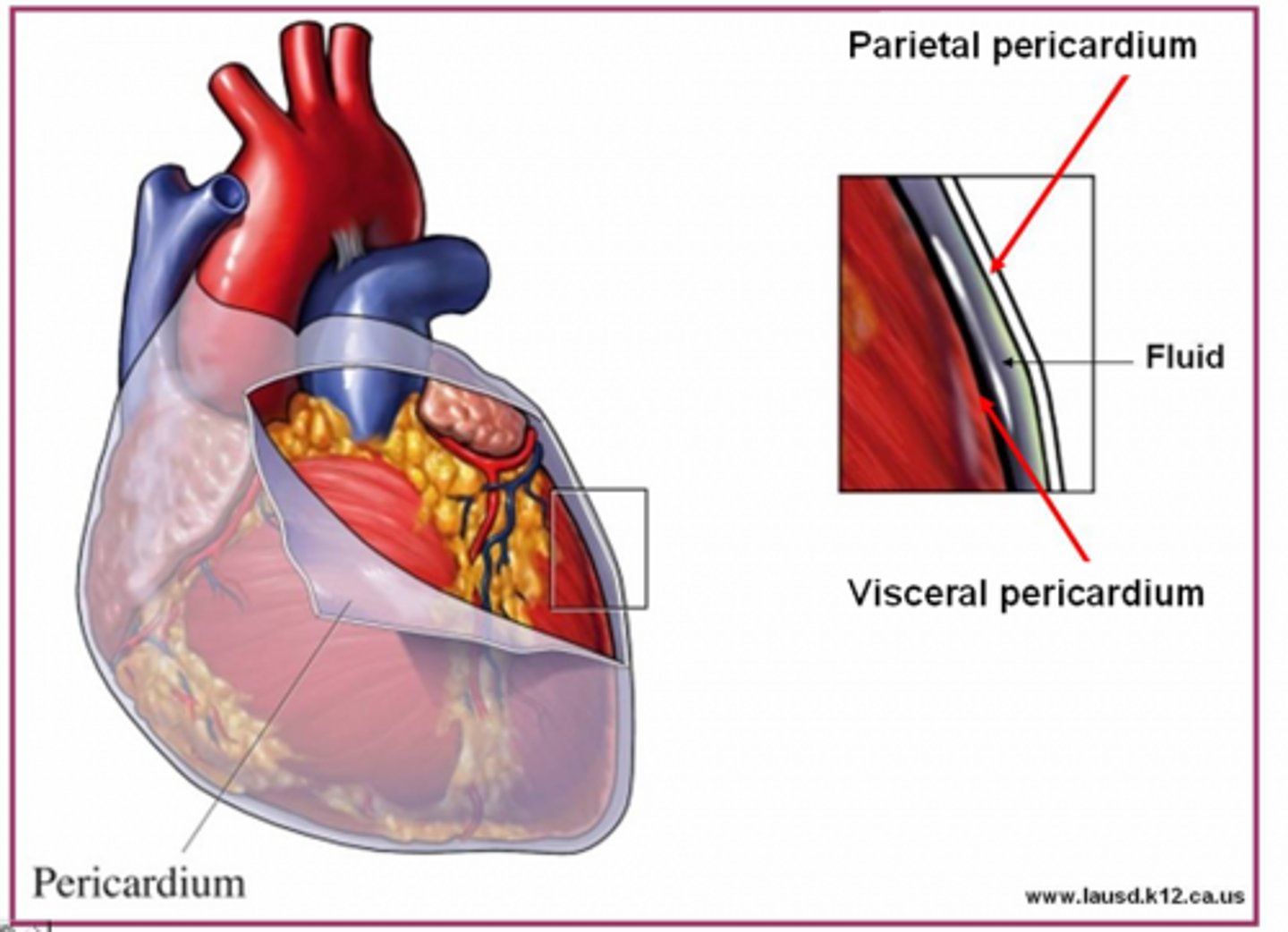
Serous membrane
lines the viscera (organs) and the walls of the ventral body cavity
Parietal layer of serous membrane
lines cavity walls
Visceral layer of serous membrane
adheres to surface of organ
Serous membrane produces...
serous fluid
Serous fluid function
reduce friction between organs and walls
Serous fluids are named for
the cavity that it's in
Parietal/visceral pericardium
pericardial cavity and heart surface
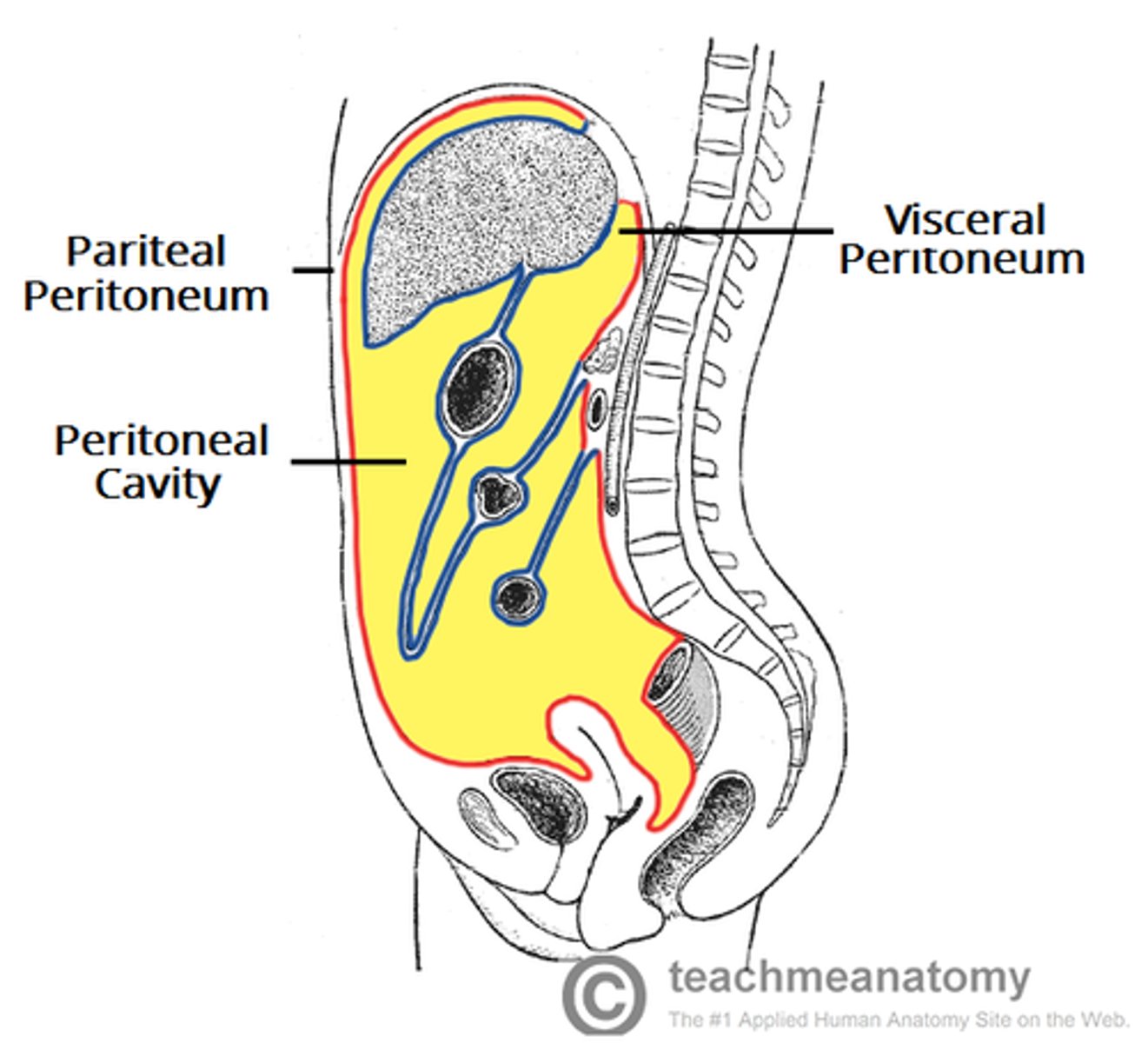
Parietal/visceral peritoneum
abdominopelvic cavity and viscera inside it
Parietal/visceral pleura
pleural cavity and lung surface
2 divisions of nervous system
CNS (brain and spinal cord)
PNS (divided into 2 parts)
2 divisions of PNS
Somatic (sensory/afferent) and Autonomic (motor/efferent)
Somatic nervous system
voluntary/things we control
motor: skeletal system
sensory: touch, temperature, pain (outside world)
Somatic: efferent pathway
one neuron system (1 motor neuron travels out to a muscle to tell it to contract)
Somatic: neurotransmitter & response of target organ
acetylcholine (excitatory)
Autonomic nervous system
involuntary
motor: smooth muscle (digestive tract)
cardiac muscle
glands
sensory: organs (inside world)
Autonomic: efferent pathway
two neuron system: presynaptic and postsynaptic
(neuron travels out and synapses with another neuron --> where they meet is called a ganglion)
Autonomic: neurotransmitter & response of target organ
Presynaptic: acetylcholine (excitatory)
Postsynaptic: varies between sympathetic (norepinephrine and epinephrine) & parasympathetic (acetylcholine) --> excitatory or inhibitory
2 divisions of Autonomic nervous system
parasympathetic (rest & digest --> slows things down)
sympathetic (fight or flight --> speeds things up)
Parasympathetic
routine maintenance "rest & digest" ; inhibits/slows down body functions (except digestion)
Parasympathetic only innervates
internal organs
Parasympathetic location/origin
in the brainstem (CN 3, 7, 9, 10)
sacral region (S2-S4)
Parasympathetic fiber length
Presynaptic: long
Postsynaptic: short
Parasympathetic location of ganglia
In/near visceral effector organs (terminal ganglia) -->
named ganglia in the head
intramural ganglia in the thorax and abdomen (within the wall of the effector organ)
Parasympathetic (Cranial Outflow): Presynaptic fibers run via
Oculomotor n. (CN III) smooth muscle in the eye
Facial n. (CN VII)
lacrimal, submandibular, sublingual glands
Glossopharyngeal n. (CN IX)
parotid gland
Vagus n. (CN X)
organs in thorax & GI tract through 2/3 of transverse colon
Parasympathetic (Sacral Outflow): Presynaptic neurons travel...
through ventral root --> spinal n. --> ventral rami
exit ventral rami as pelvic splanchnic nn.
Pelvic splanchnic nn. innervate 1/3 of large intestine & its components
Sympathetic
mobilization & increased metabolism; "fight, flight, or fright"; speeds up or stimulates body functions (except digestion)
Sympathetic location/origin
thoracolumbar region (T1-L2)
lateral horn (where cell bodies are)
Sympathetic fiber length
Presynaptic: short
Postsynaptic: long
Sympathetic location of ganglia
close to spinal cord;
Paravertebral ganglia: sympathetic chain (located on both sides of vertebral column; extend from cranial base to coccyx)
Prevertebral ganglia:
on abdominal aorta (celiac ganglion; superior mesenteric ganglion; inferior mesenteric ganglion)
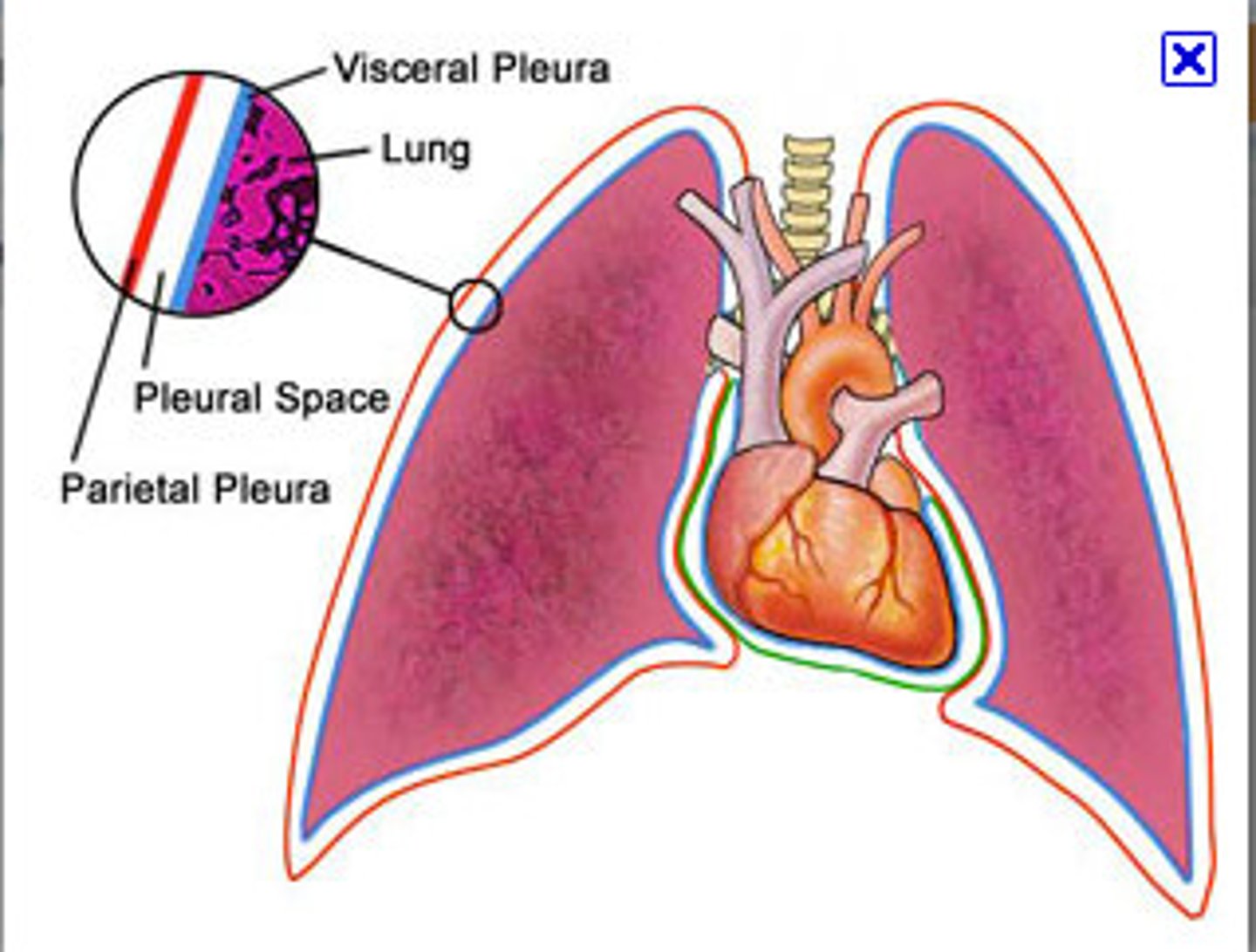
Sympathetic Outflow (3 options)
1. synapse at paravertebral ganglia at same level
2. synapse at paravertebral ganglia at a different level
3. does not synapse on chain --> splanchnic nerve (will synapse at a prevertebral ganglia on abdominal aorta)
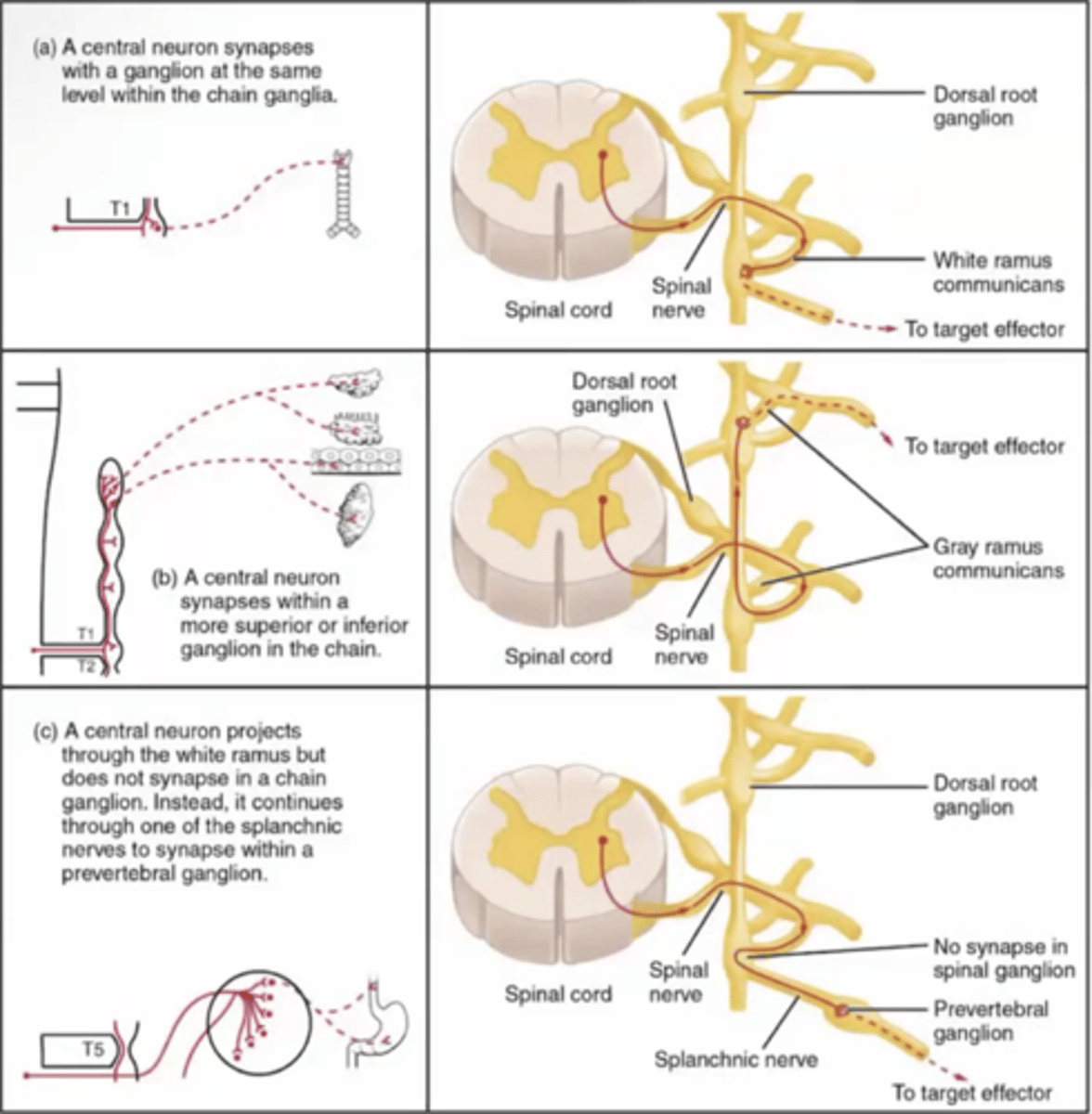
Adrenal medulla
modified sympathetic ganglion; a gland sitting above kidney; produces neuro-horomones that travel through the whole body (sends signal into blood stream)
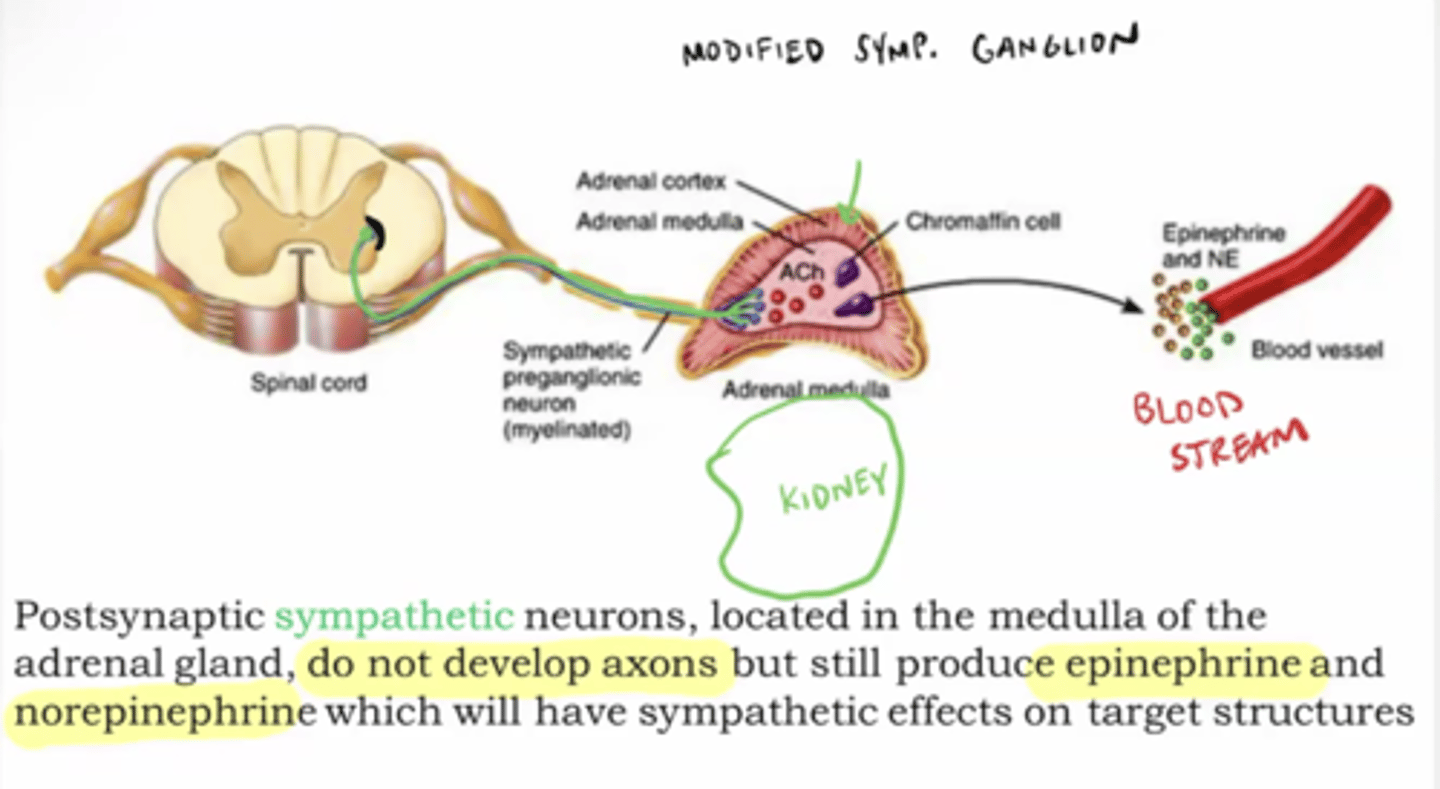
Parasympathetic vs sympathetic effects on organs
Cardiovascular system major components
heart, blood vessels, blood
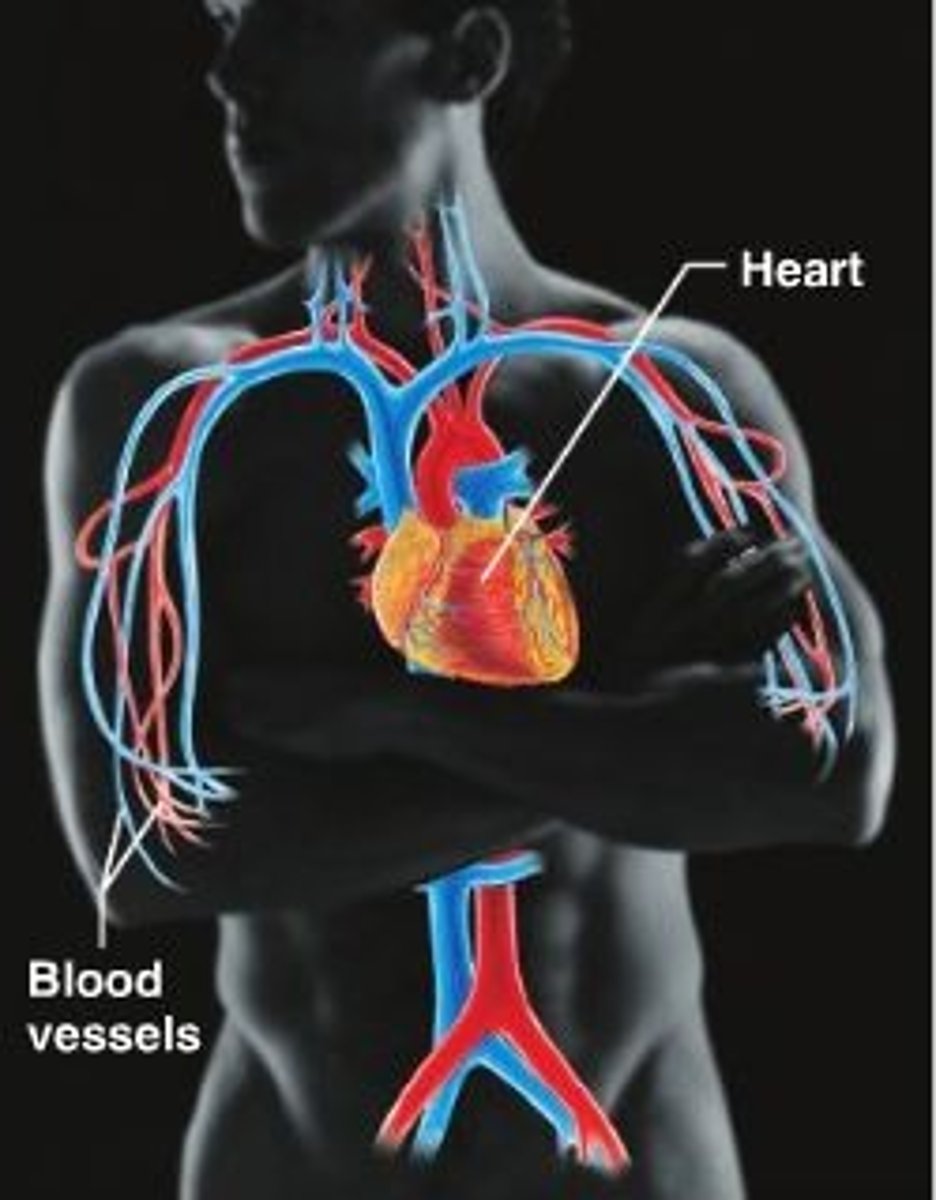
Cardiovascular system major function
transportation of nutrients and oxygen, waste products, and hormones
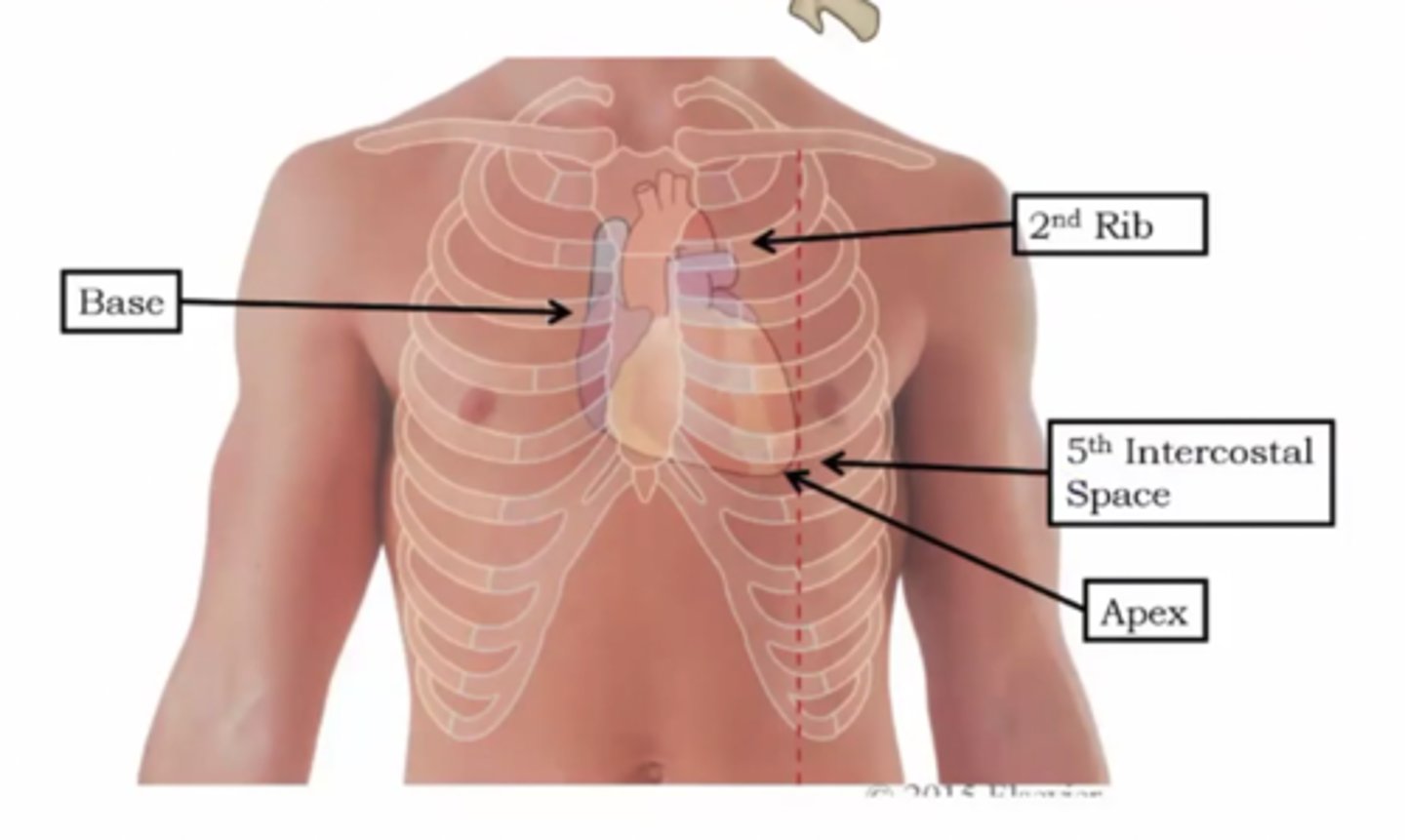
The heart is located ...
encased in pericardial sac in the middle mediastinum; apex of the heart points down towards our left hip
2 circuits of blood from the heart
Pulmonary & Systemic circuits
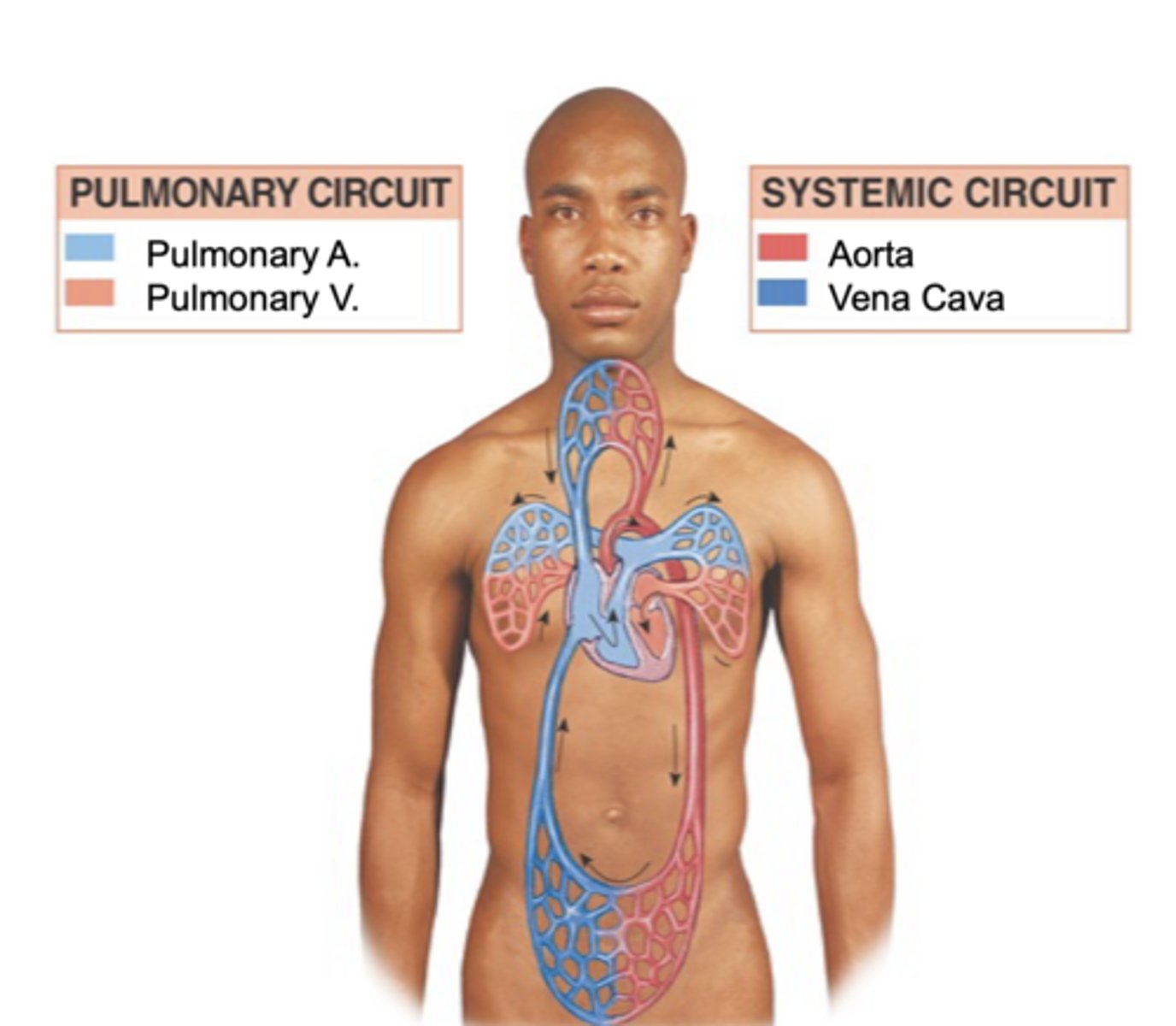
Pulmonary circuit path
Right side of heart pumps (unoxygenated) blood to lungs, then it goes back (oxygenated) to left side of heart
"Pulmonary"
heart and lungs
Why does blood travel to the lungs
to become oxygenated
Systemic circuit path
Left side of heart pumps (oxygenated) blood to the body, then it goes back to right side of heart (deoxygenated)
Right side circulation
Deoxygenated blood FROM body enters right side of heart & gets pumped TO lungs
Left side circulation
Oxygenated blood FROM lungs enters left side of heart & gets pumped TO body
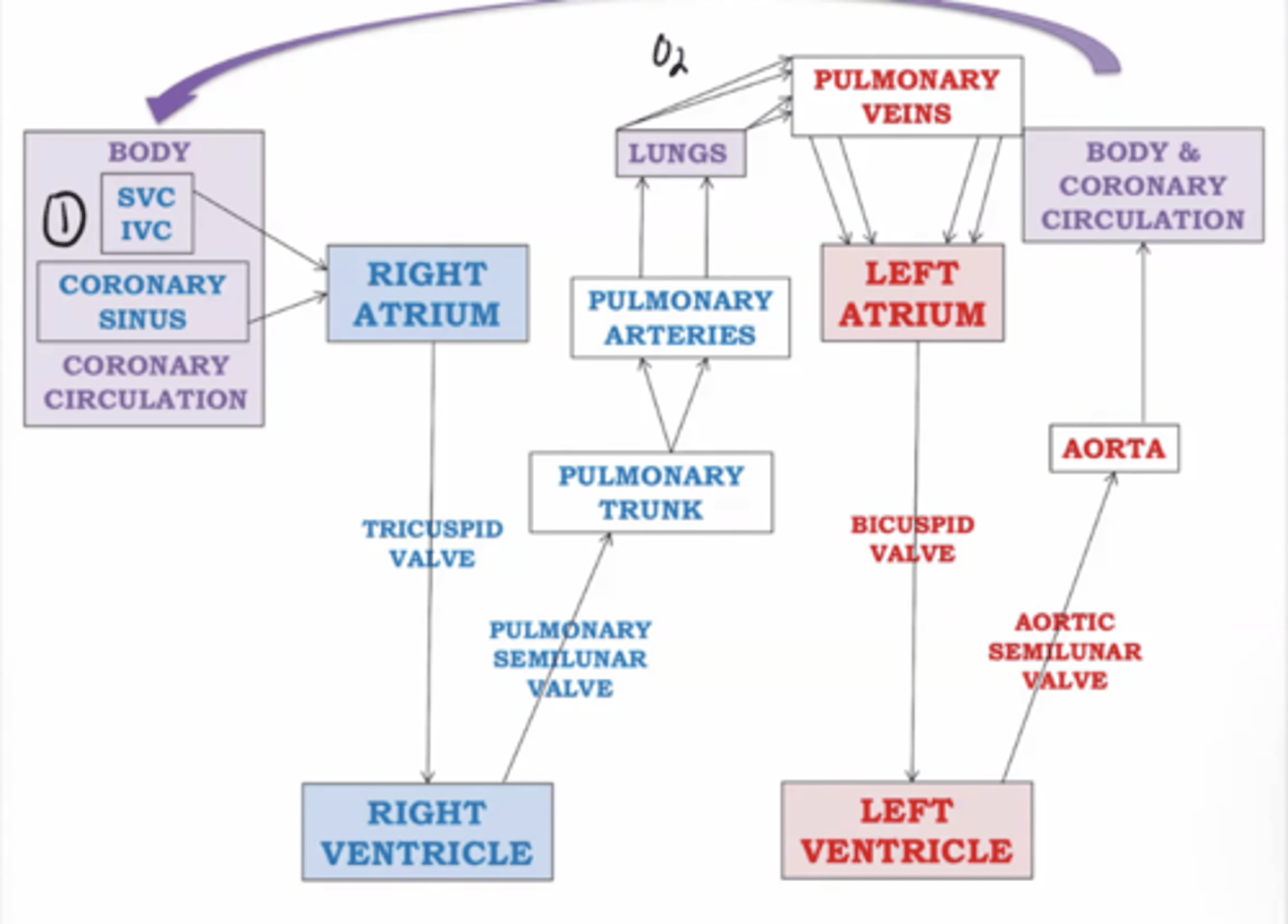
Right atrium
Receives deoxygenated blood from the body
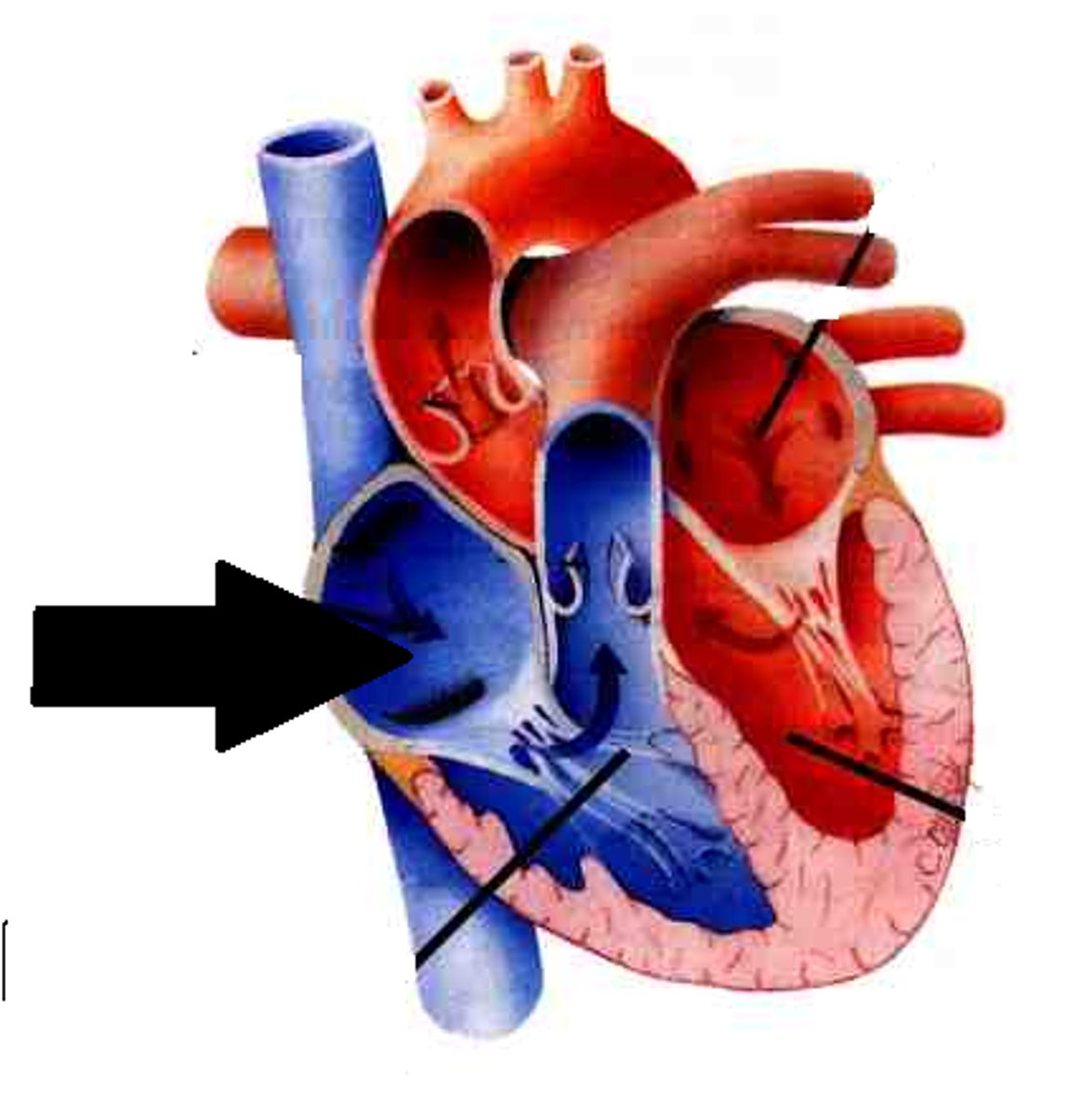
Right ventricle
pumps deoxygenated blood received from right atrium to the lungs
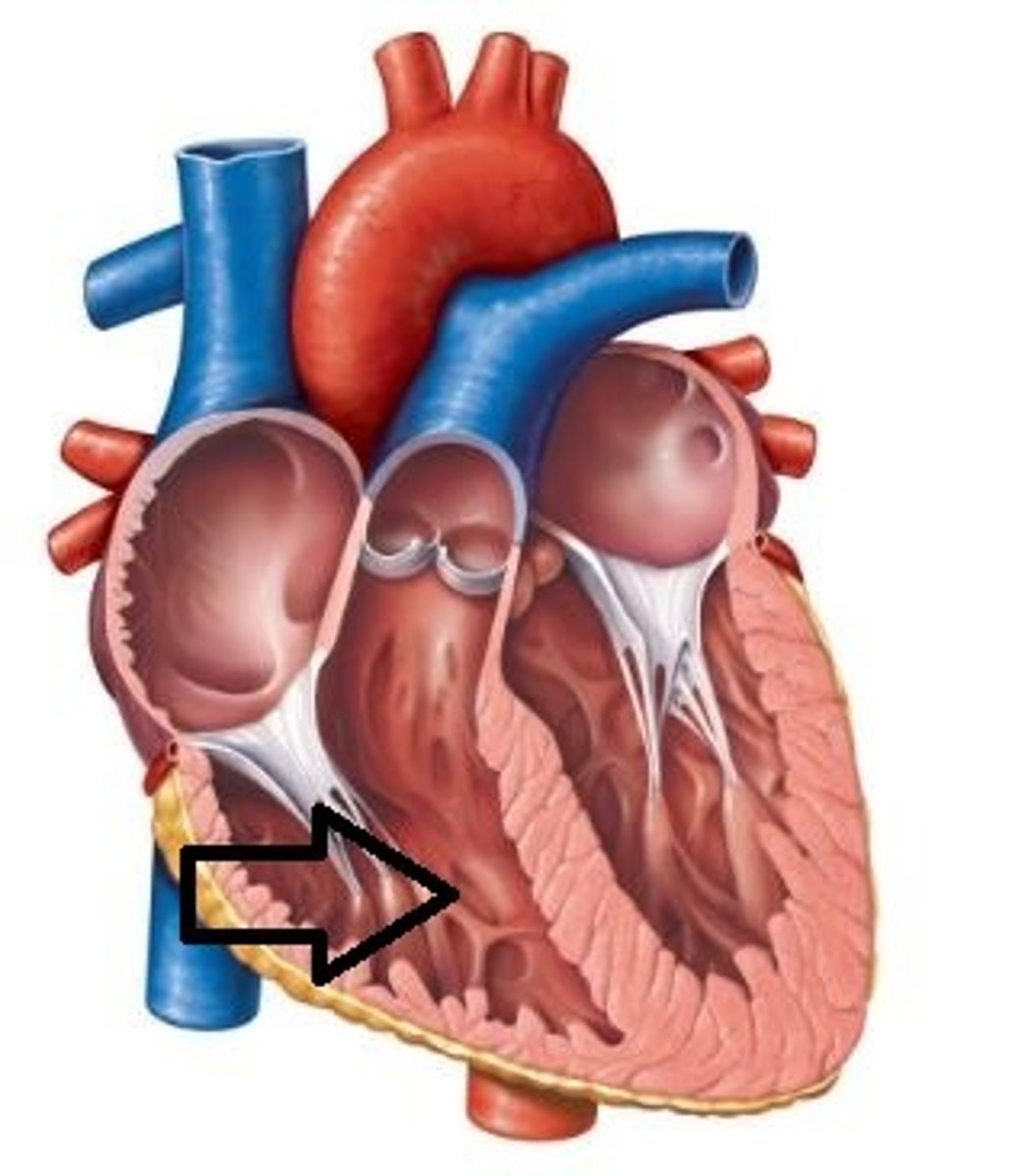
Left atrium
receives oxygenated blood from the lungs
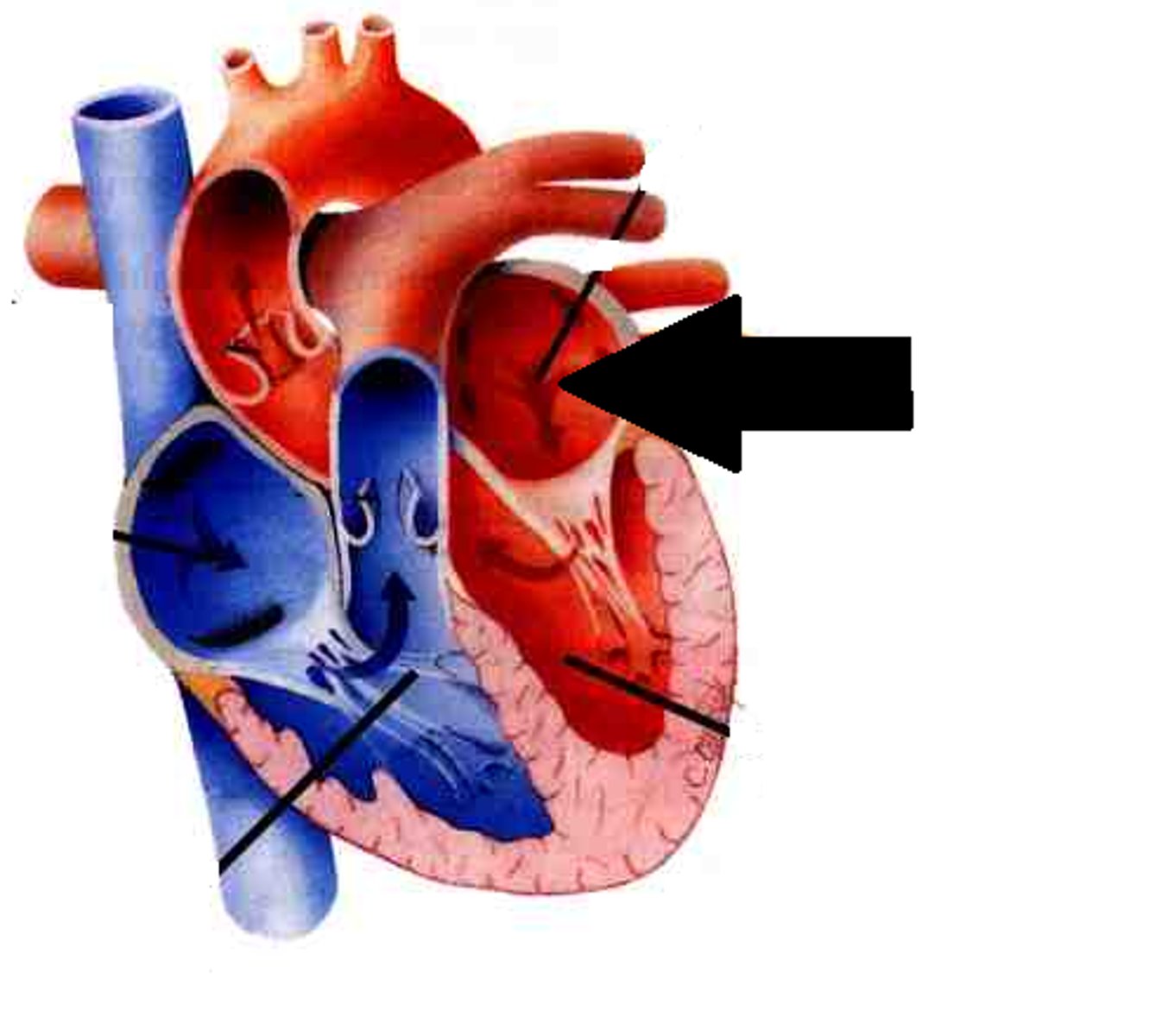
Left ventricle
received oxygenated blood from left atrium and pumps it to the body
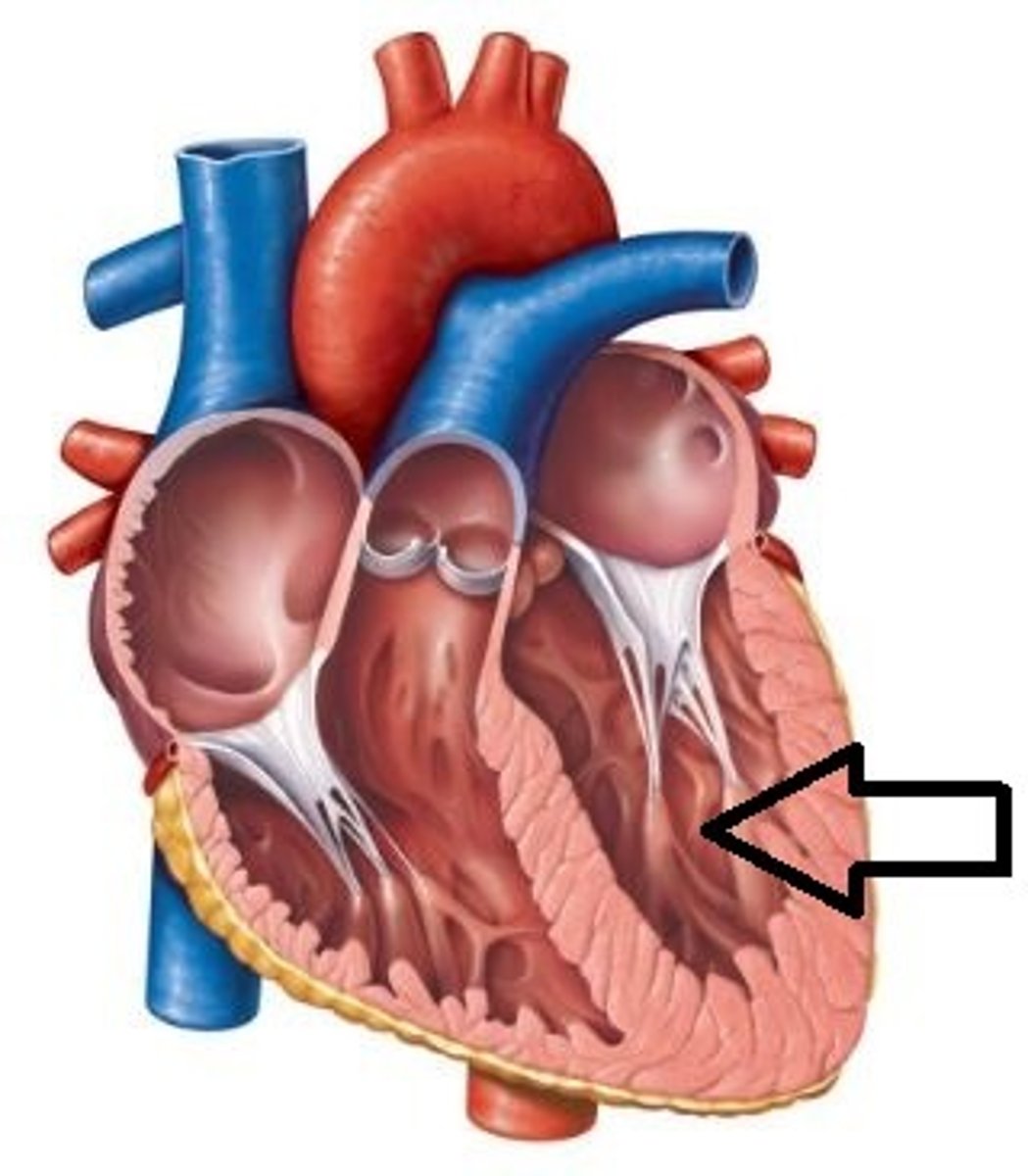
Veins
take blood towards the heart
Arteries
take blood away from the heart
Right auricle
increases holding capacity of right atrium
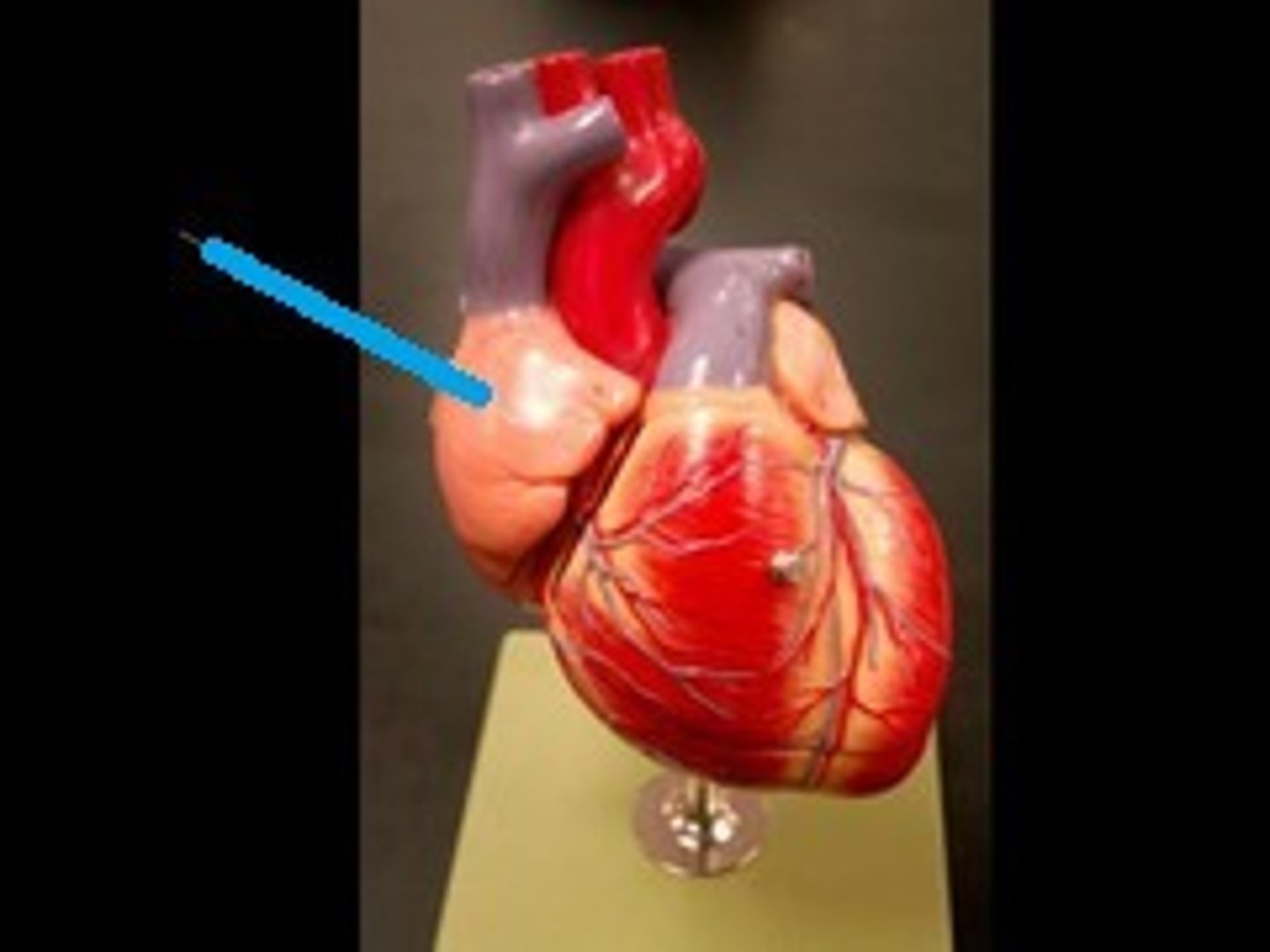
Left auricle
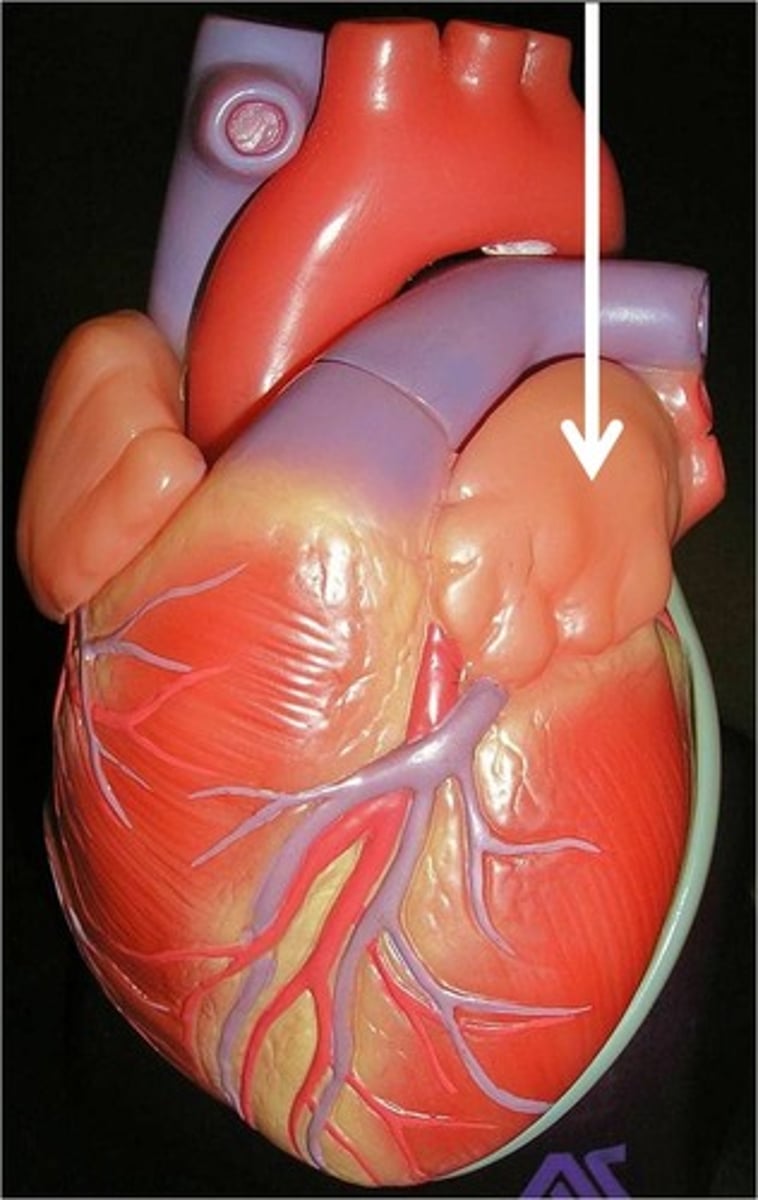
Great vessels of the heart
veins: superior vena cava
inferior vena cava
pulmonary veins
arteries: pulmonary trunk and arteries
aorta
Superior vena cava
sits superiorly to right atrium; returns blood from thoracic wall, upper limb, head, and neck
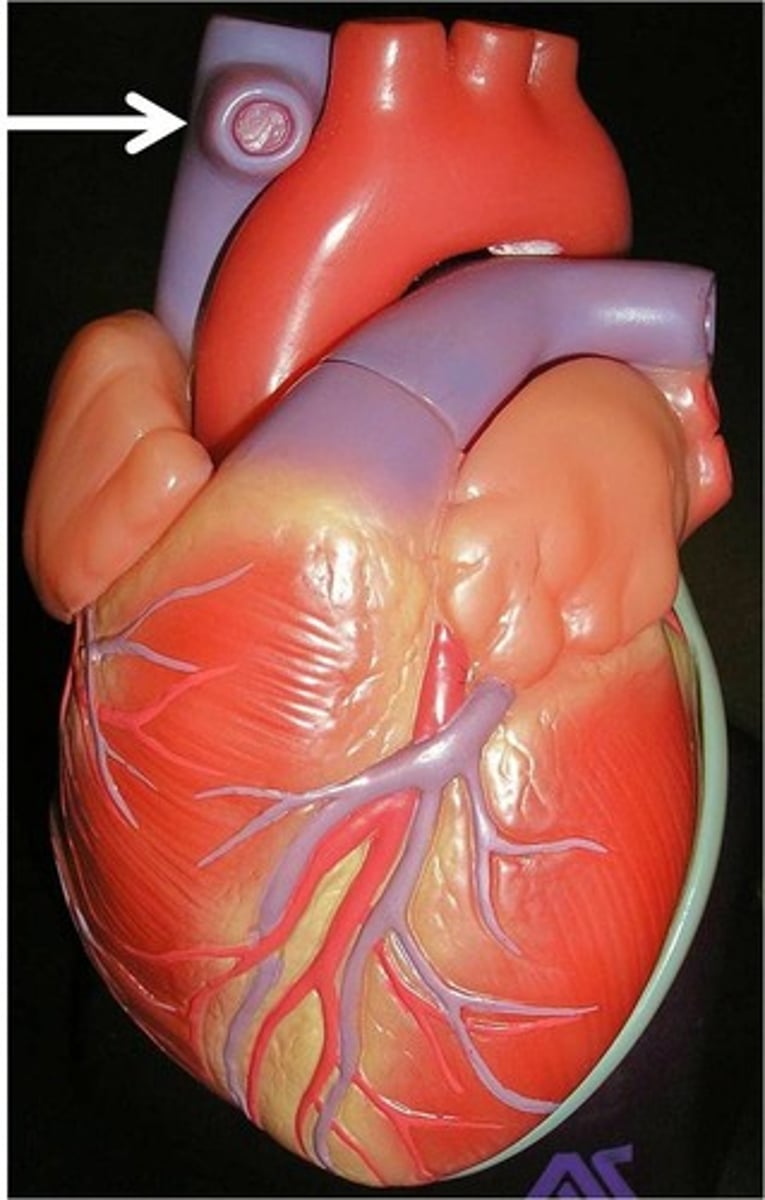
What drains into the superior vena cava
right and left brachiocephalic veins
Inferior vena cava
sits inferiorly to right atrium; returns blood from the abdomen, pelvis, and lower limb
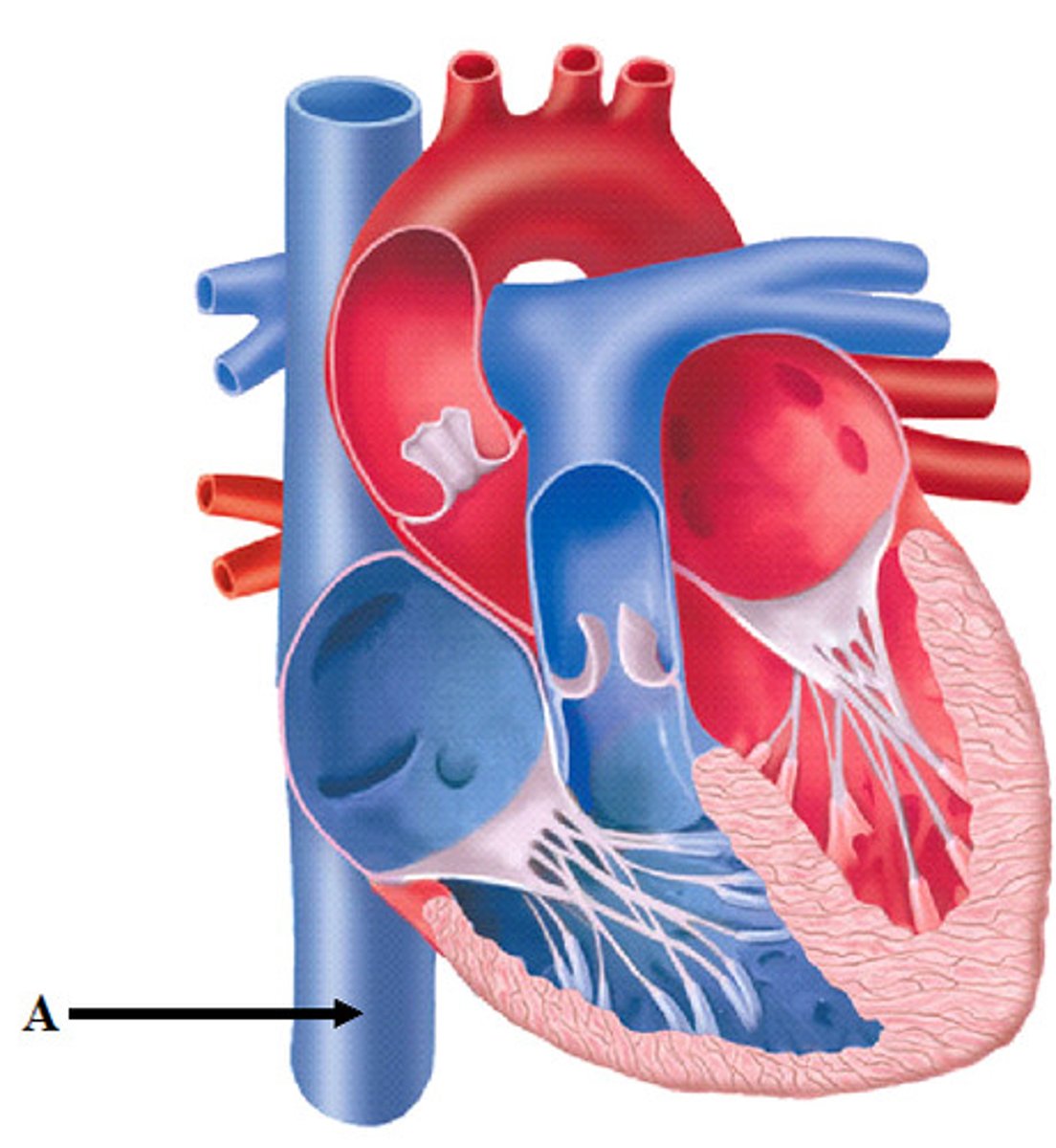
What drains into the inferior vena cava
right and left common iliac veins
Pulmonary veins
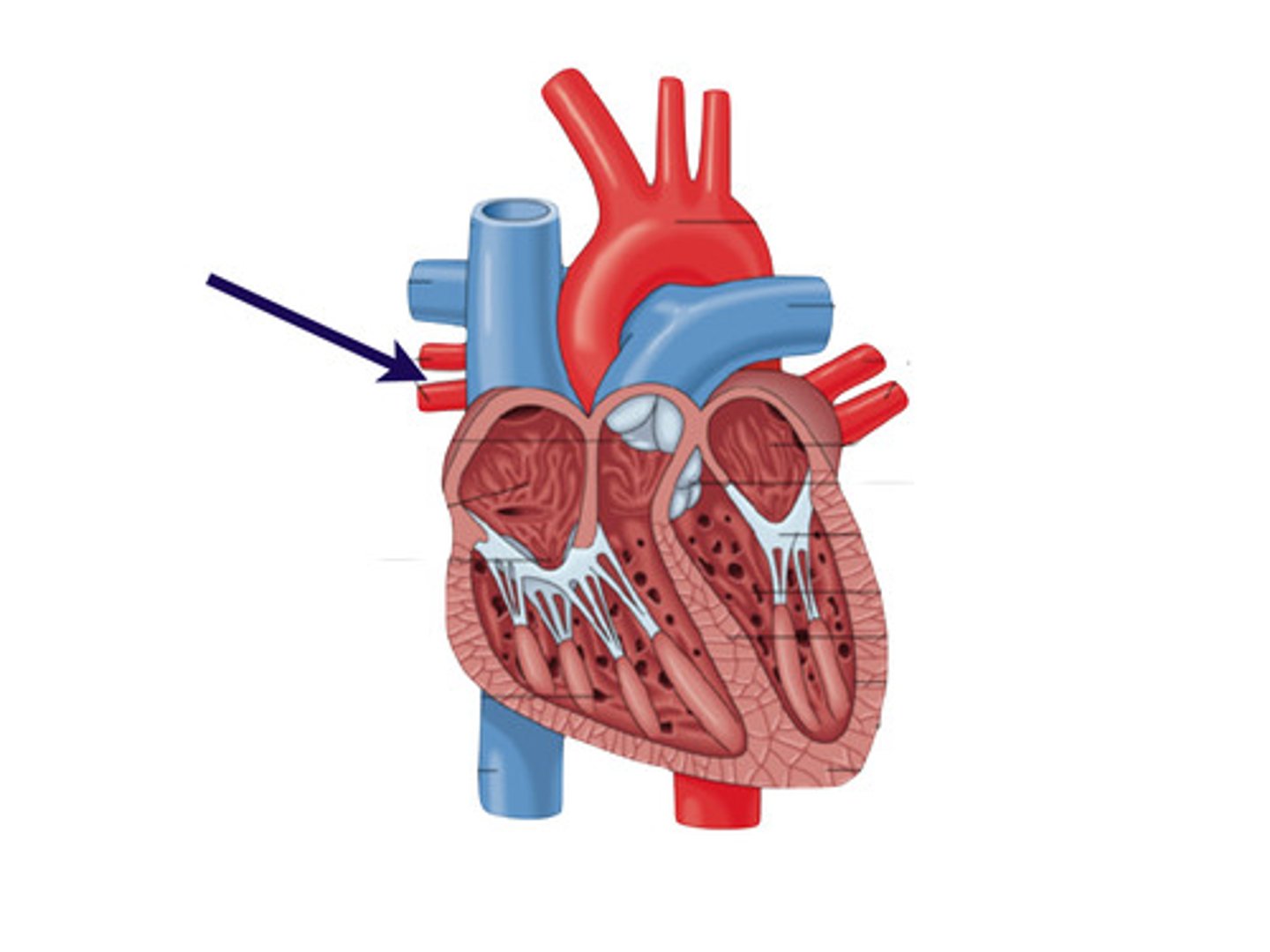
Pulmonary trunk
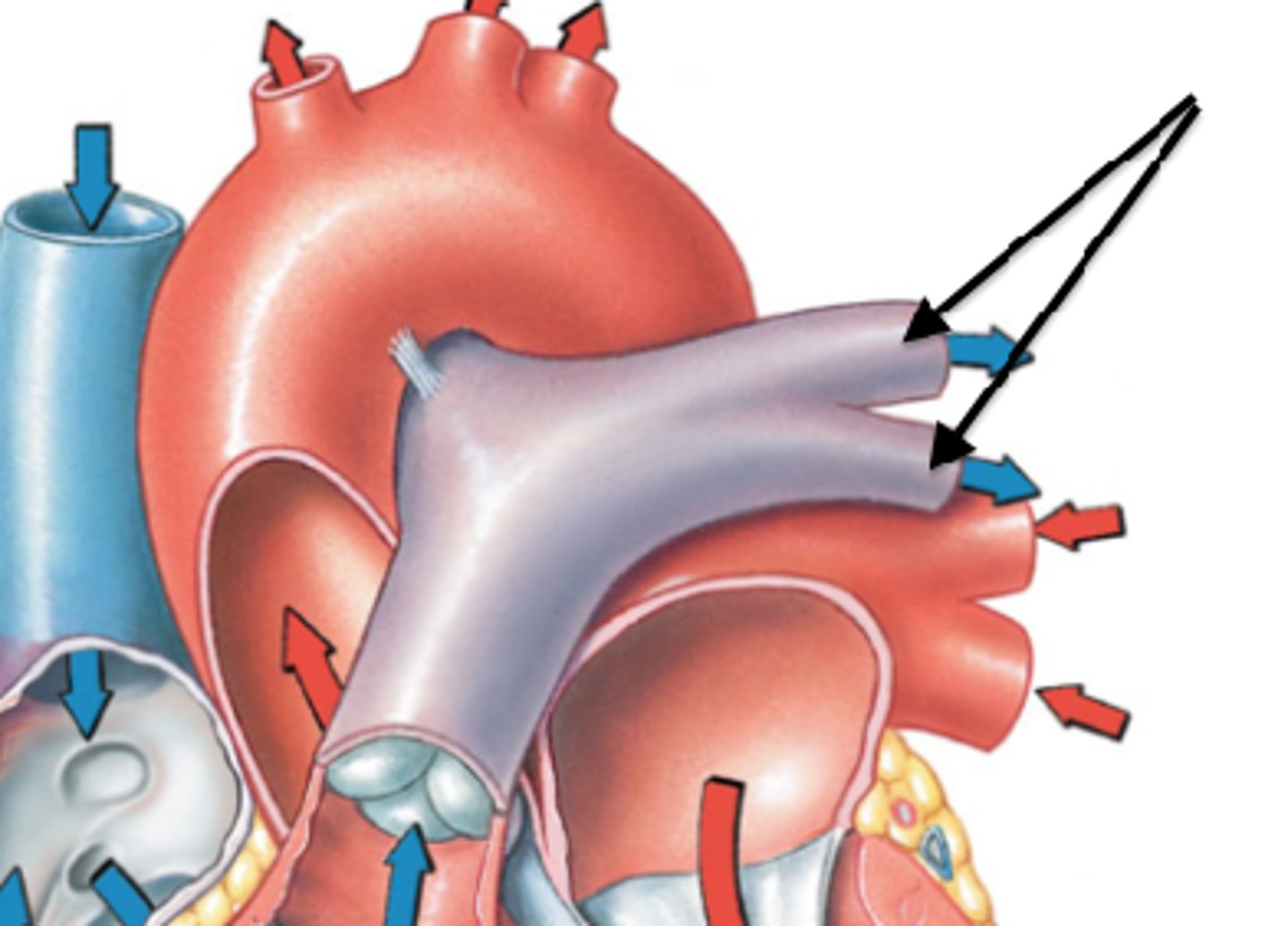
Pulmonary arteries
branches of pulmonary trunk
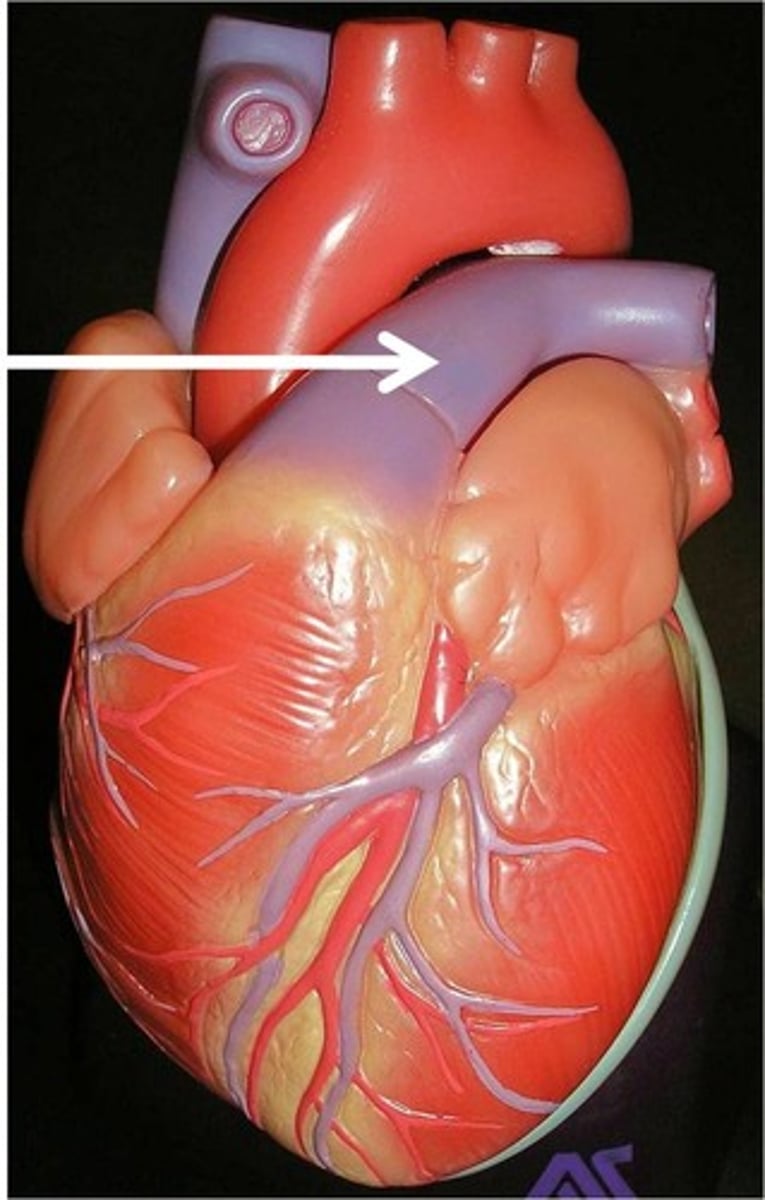
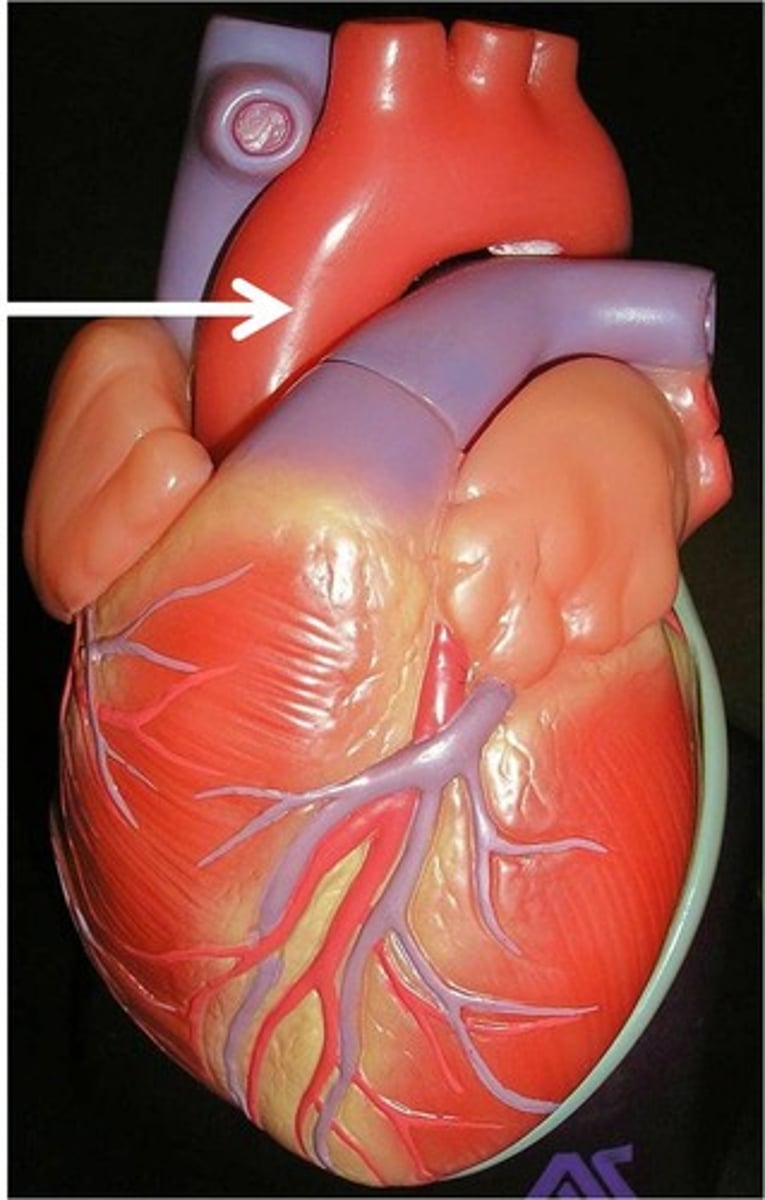
Aorta
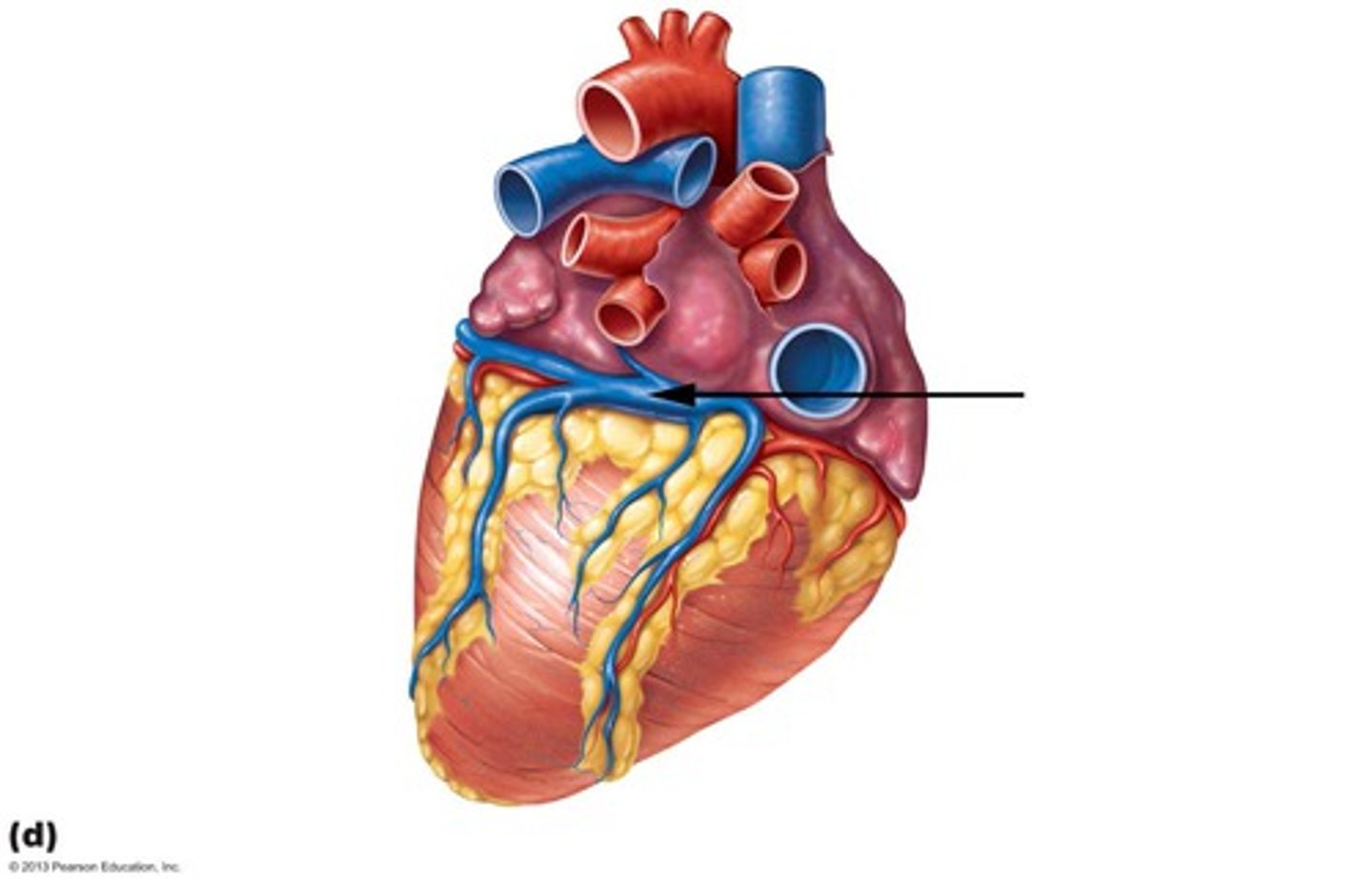
Right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from
superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, coronary sinus
Coronary sinus
drains deoxygenated blood from the heart into the right atrium
Right ventricle discharges deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary circuit via the
pulmonary trunk (splits into pulmonary arteries)
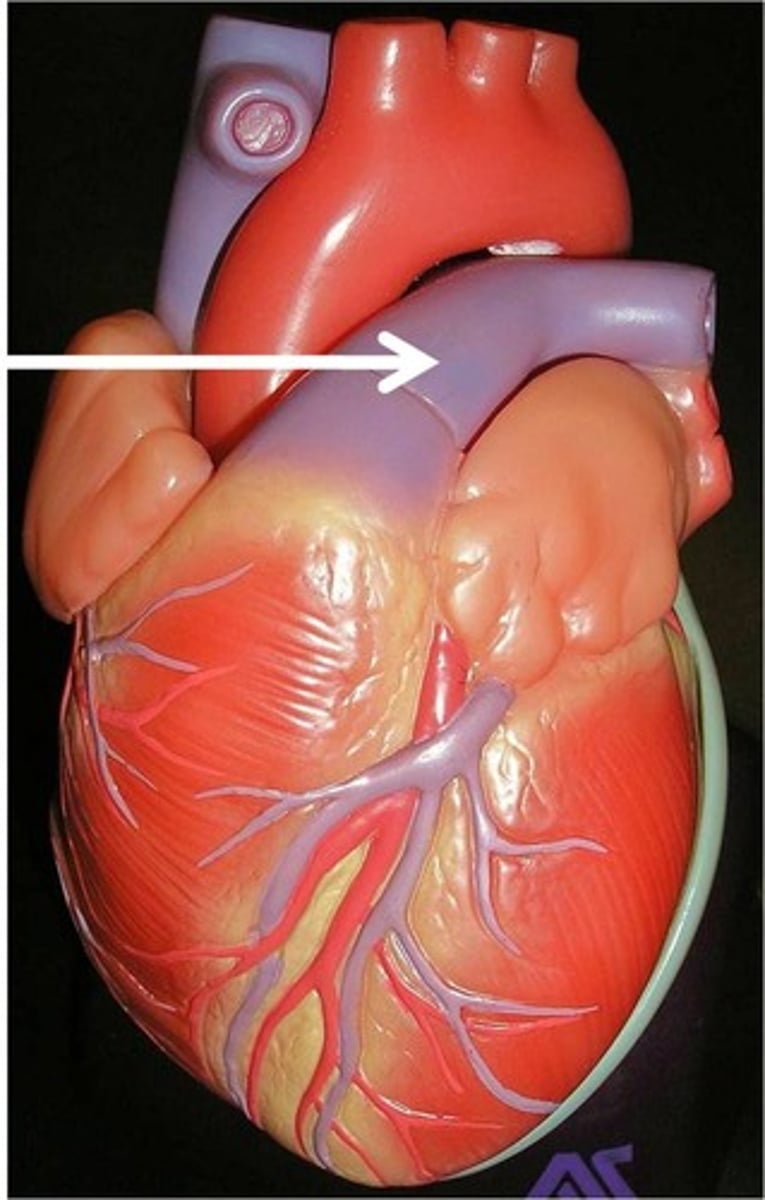
Left atrium receives oxygenated blood from
4 pulmonary veins; 2 right veins and 2 left veins
Left ventricle discharges oxygenated blood into the systemic circuit via the
aorta: ascending aorta, arch of aorta, descending aorta
Oxygenated blood travels in
both arteries and veins
What prevents backflow in chambers/keeps blood going in one direction?
valves
Valves of the heart
4 total:
2 atrioventricular
2 semilunar
Atrioventricular valves function
prevent backflow into atria
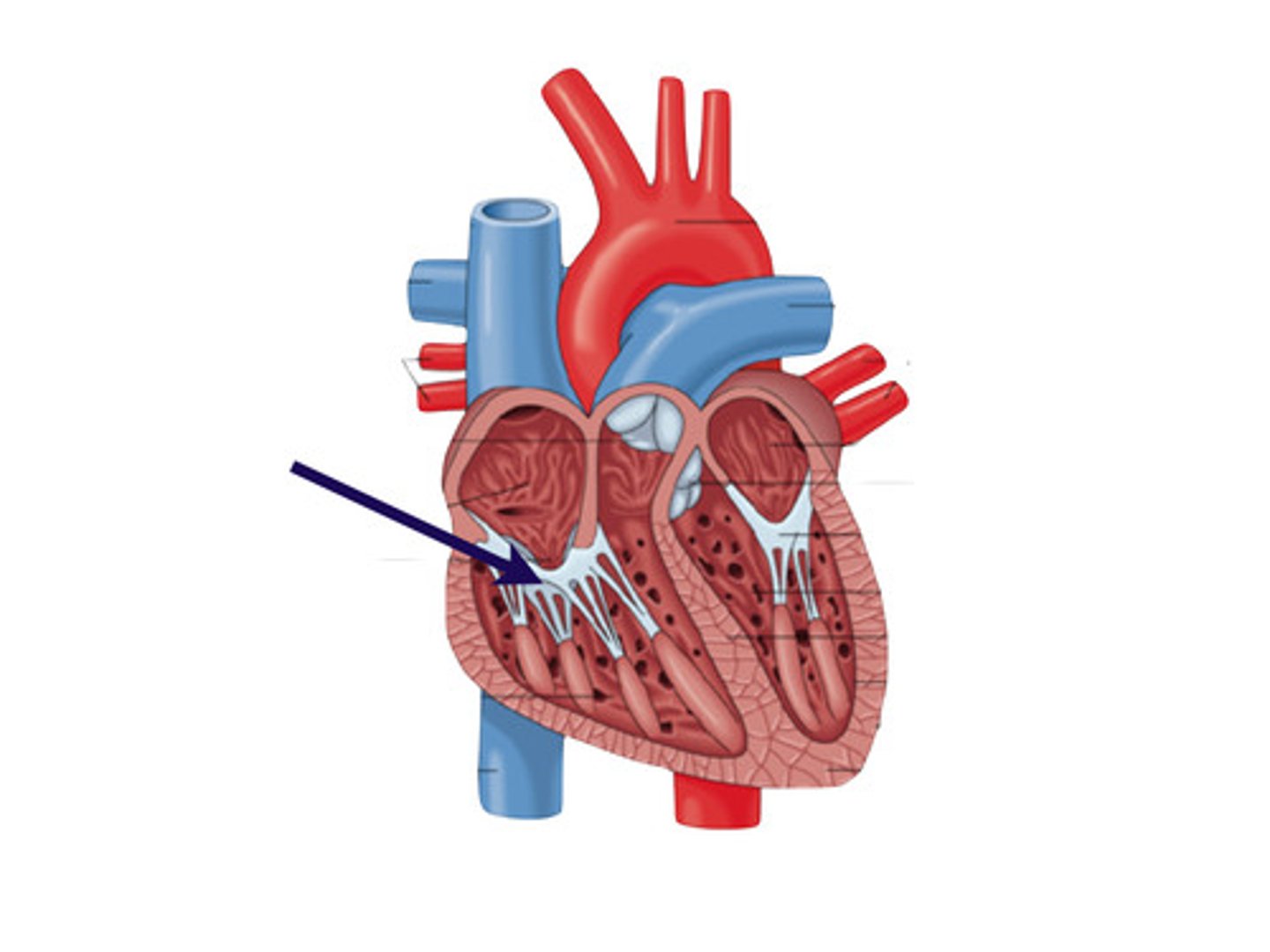
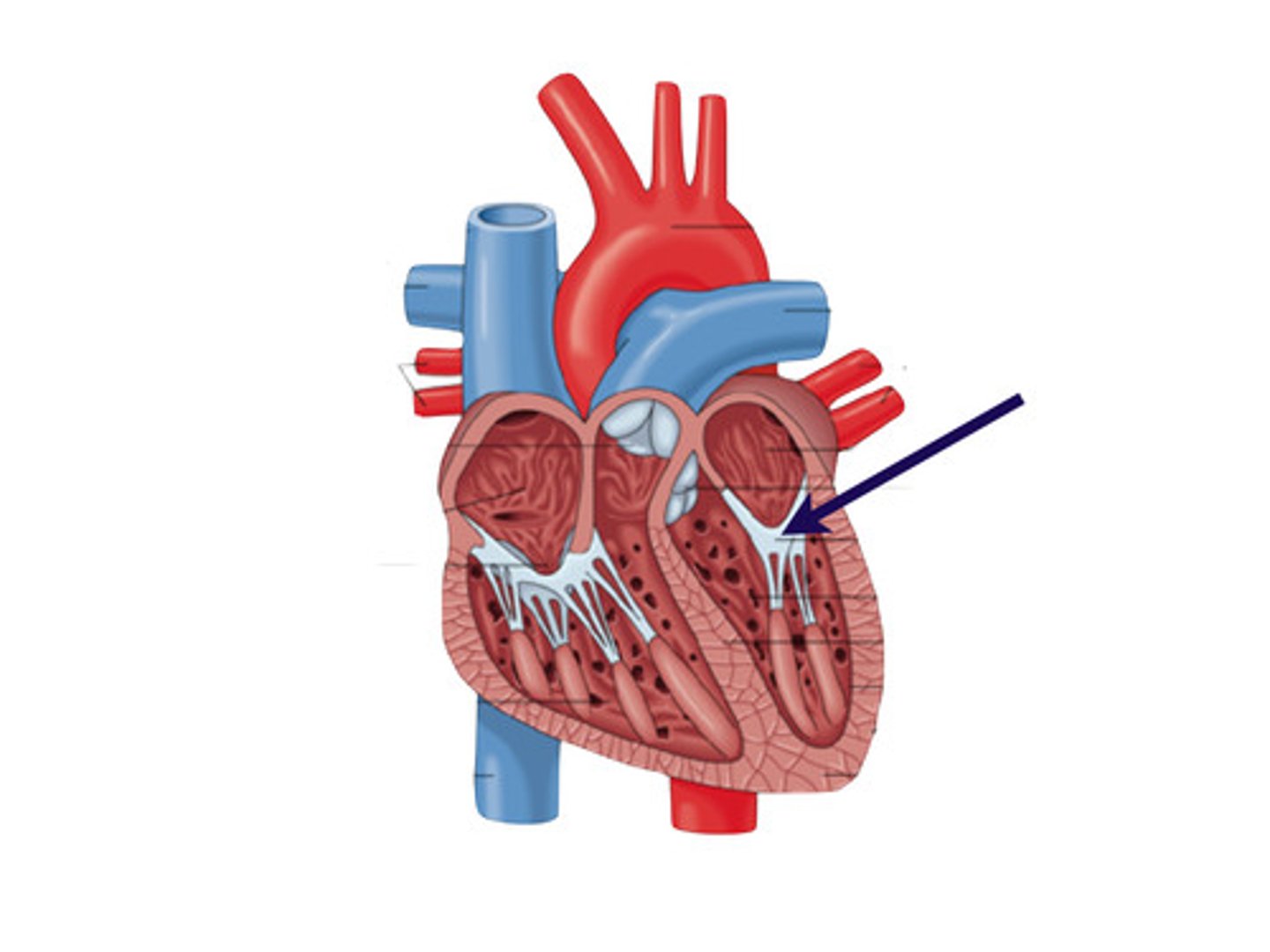
Atrioventricular valves
Tricuspid & Bicuspid/Mitral valves
"Try before you Buy"
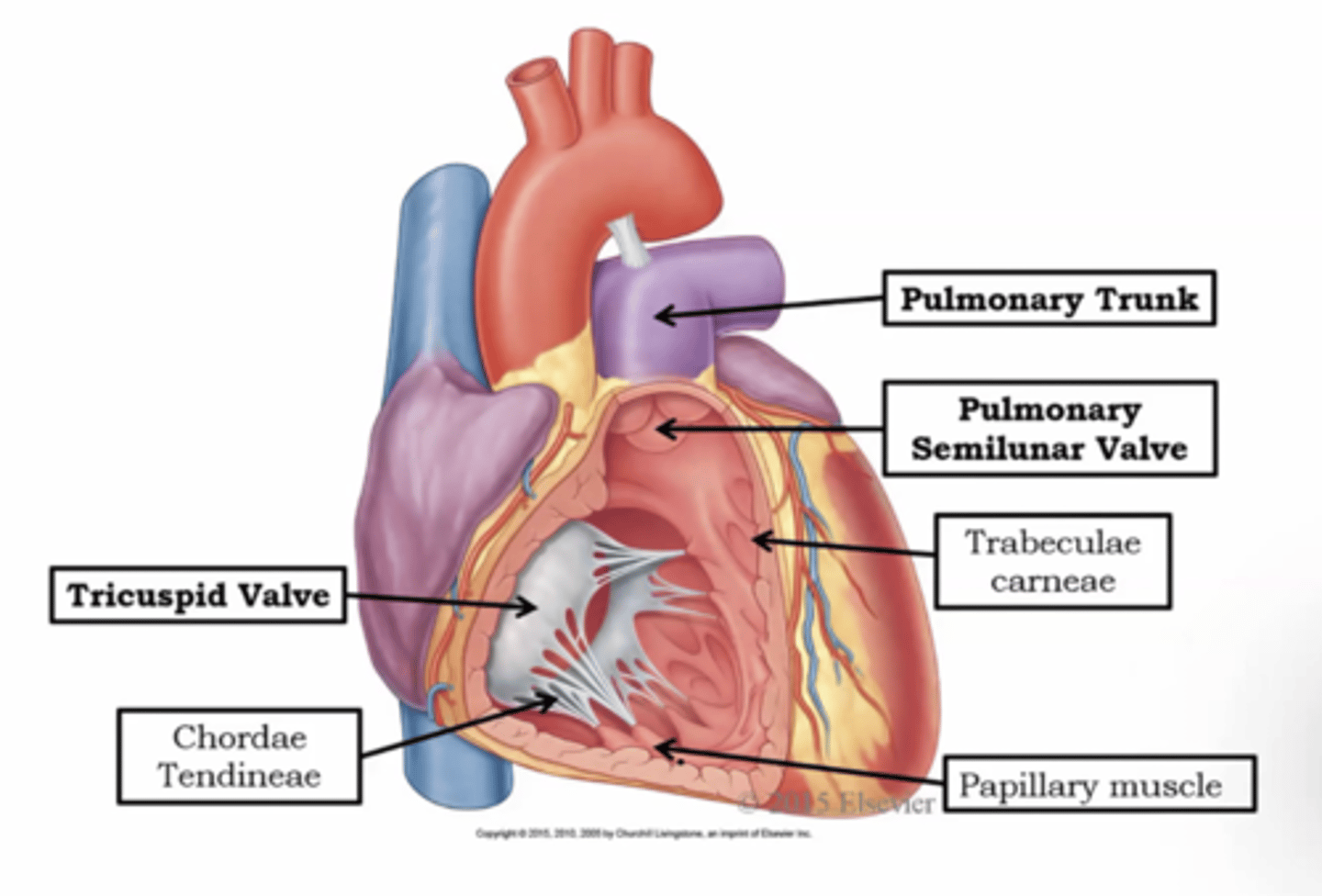
Tricuspid valve
right side; between right atrium and rightt ventricle
Bicuspid or Mitral valve
left side; between left atrium and left ventricle
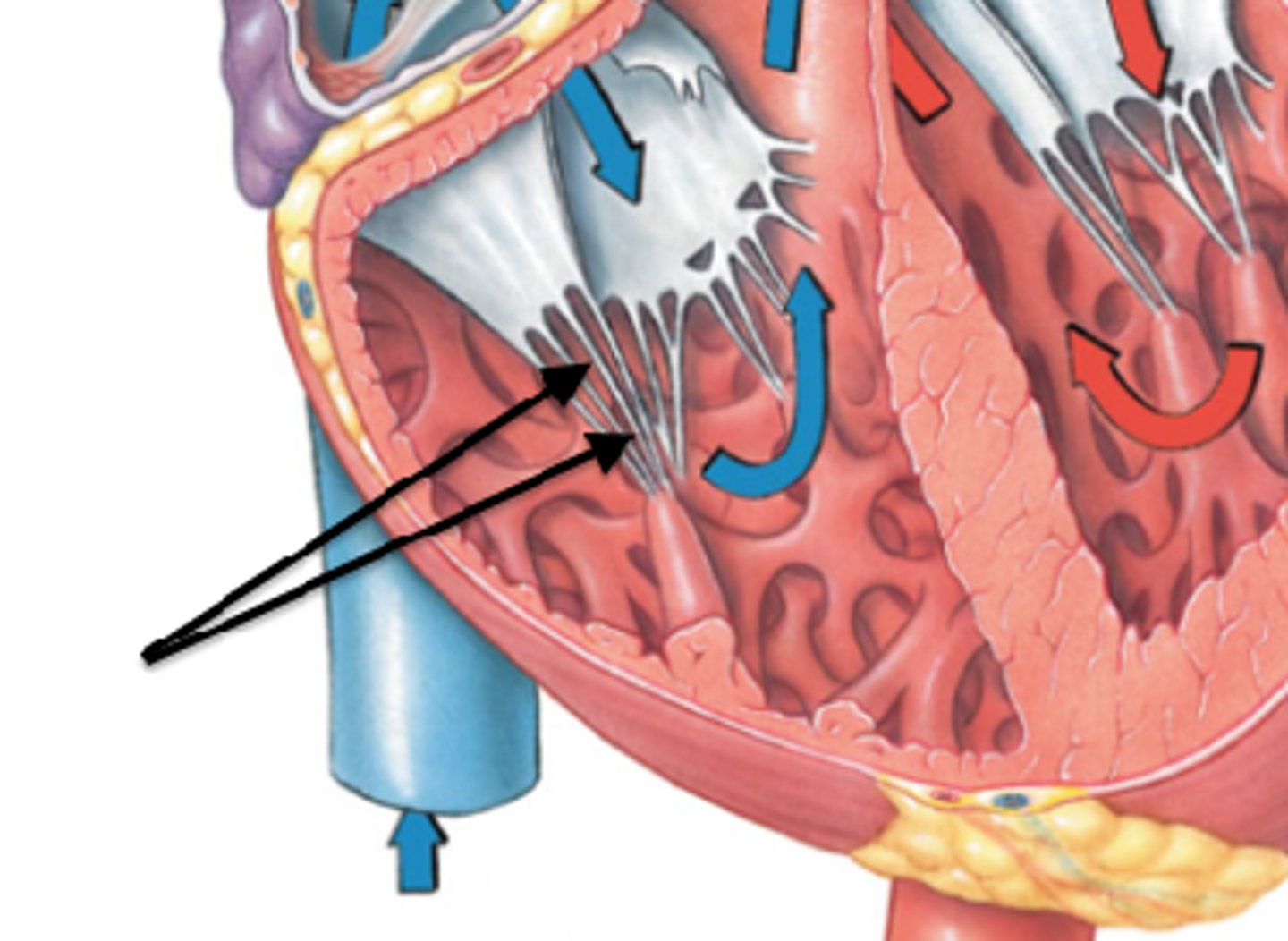
Chordae tendineae
attached to papillary muscles; act as anchor points (holding heart together)
Semilunar valves function
prevent backflow into ventricles
Semilunar valves
Pulmonary Semilunar & Aortic Semilunar
Pulmonary Semilunar valve
between right ventricle and pulmonary trunk
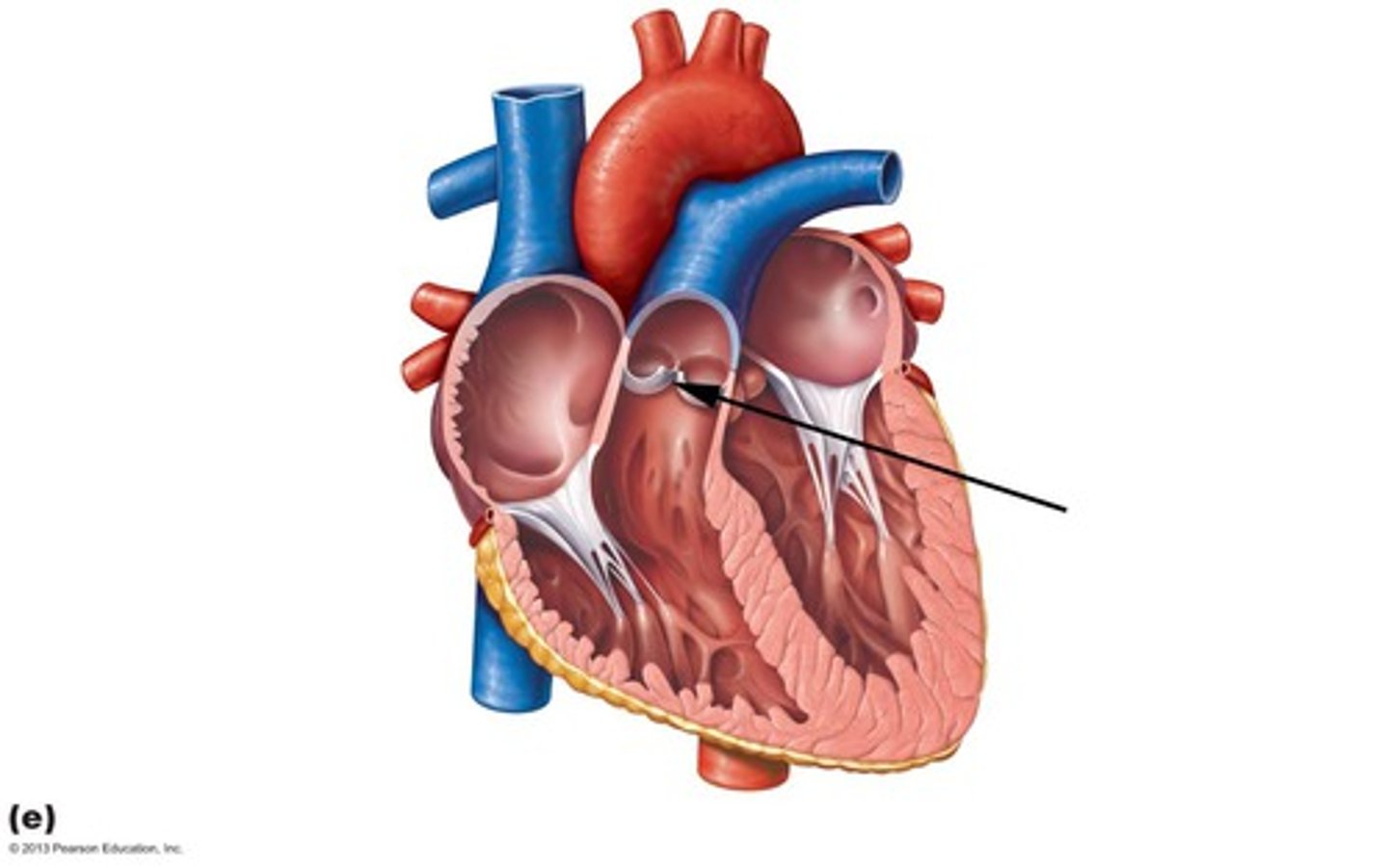
Aortic Semilunar valve
between left ventricle and aorta
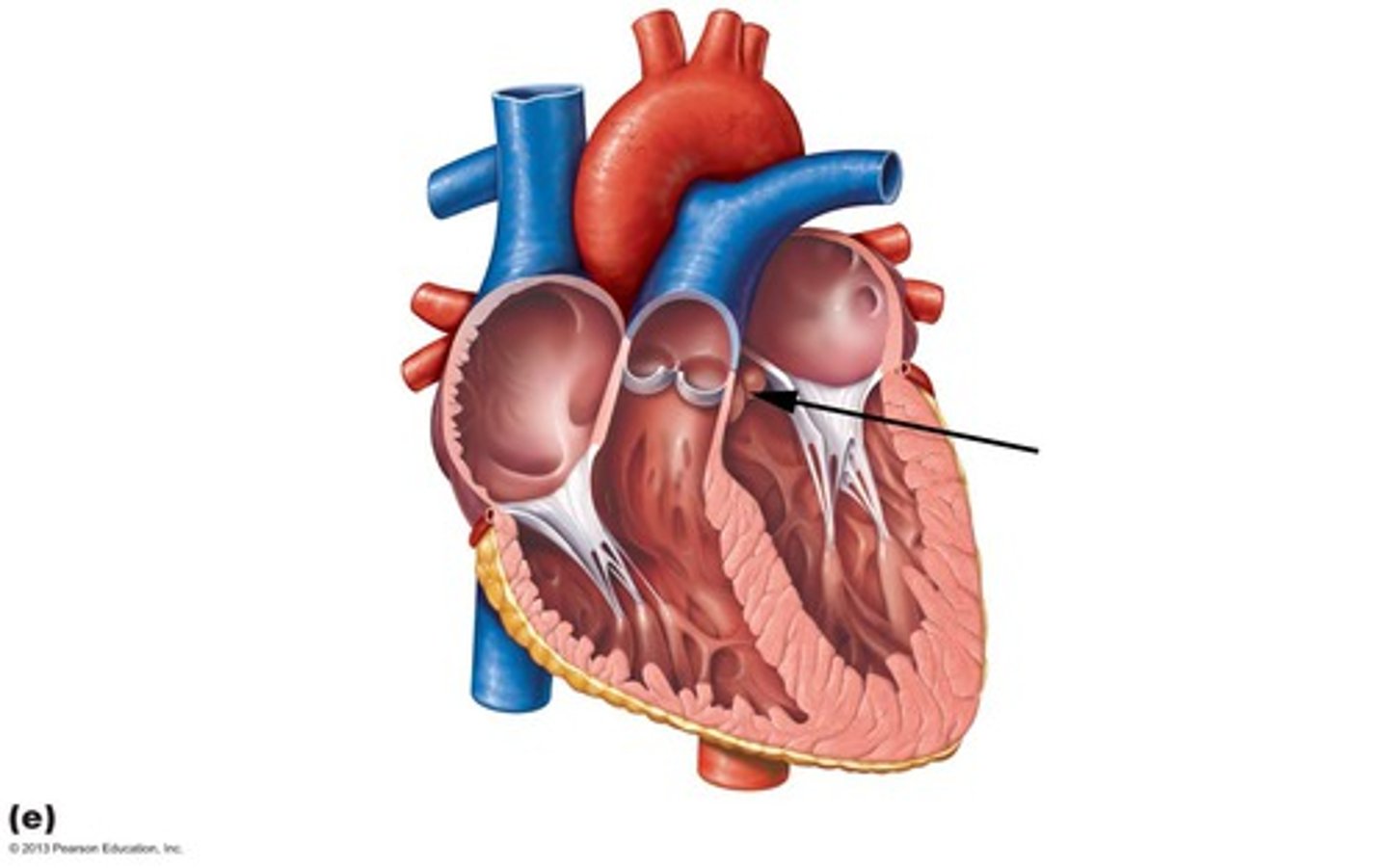
Systole
ventricles contract to pump blood out of the heart
During systole tricuspid & bicuspid valves _________
close (don't want back-flow)
"lub" sound
Diastole
ventricles relax so blood can fill them again
During diastole tricuspid & bicuspid valves ________ and the pulmonary and aortic semilunar valves _________
open ; close (don't want back-flow from outflow vessels)
"dub" sound
Flow of blood through heart
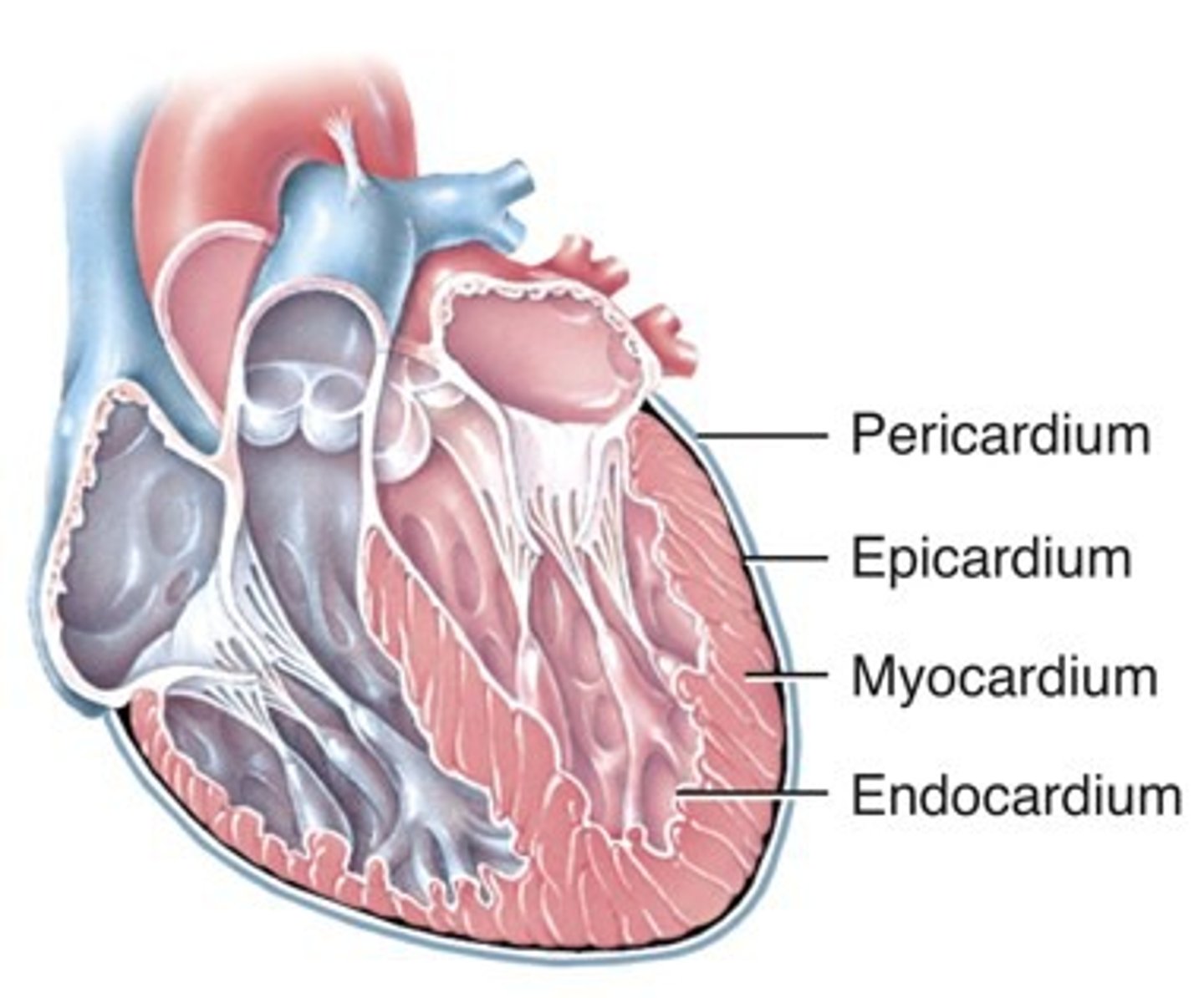
Layers of the heart
epicardium (superficial)
myocardium endocardium (deep)
Pectinate muscle
reduces stress within right atrium
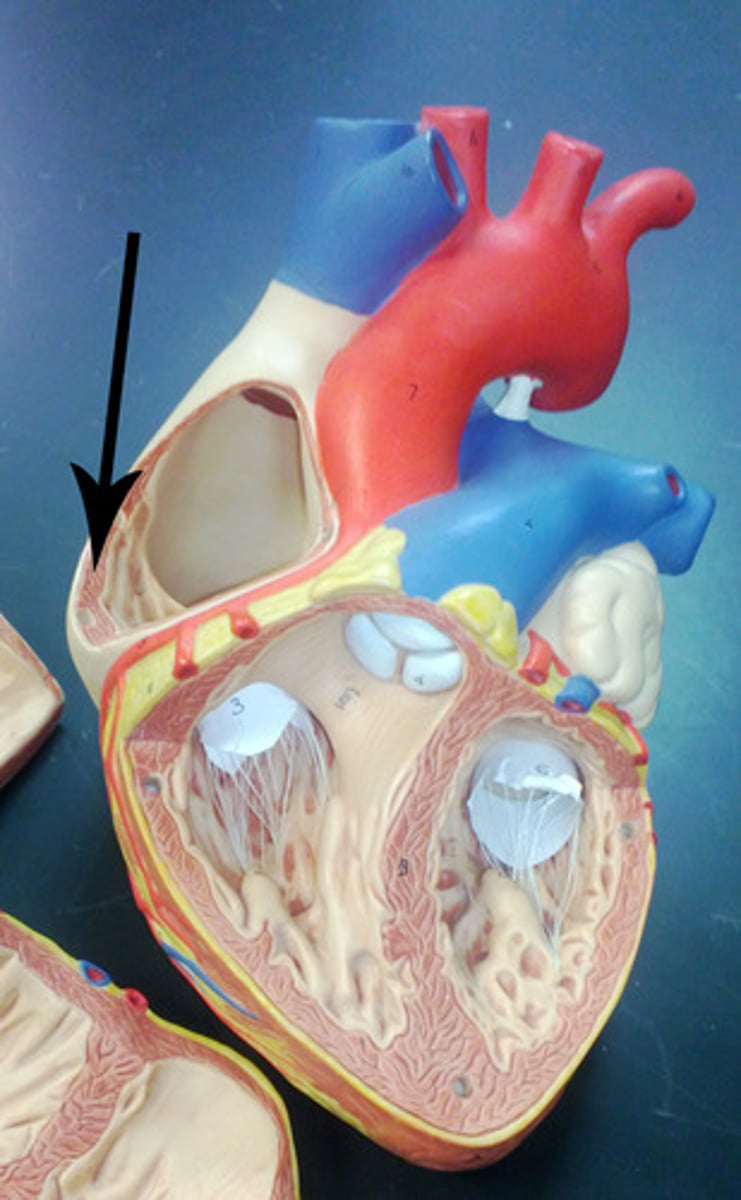
Opening of coronary sinus
within right atrium; drains deoxygenated blood
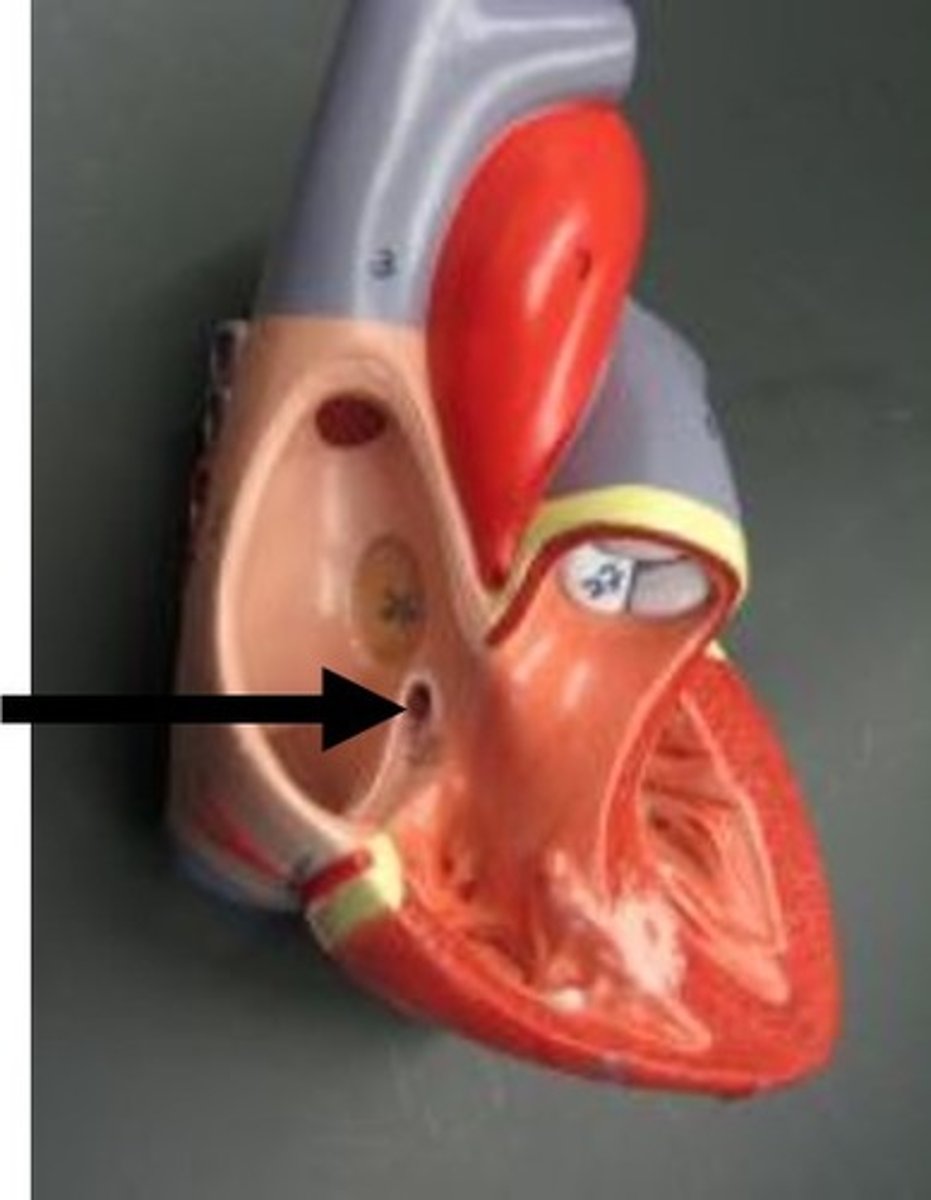
Fossa ovalis
within right atrium; opening in utero that closed after birth
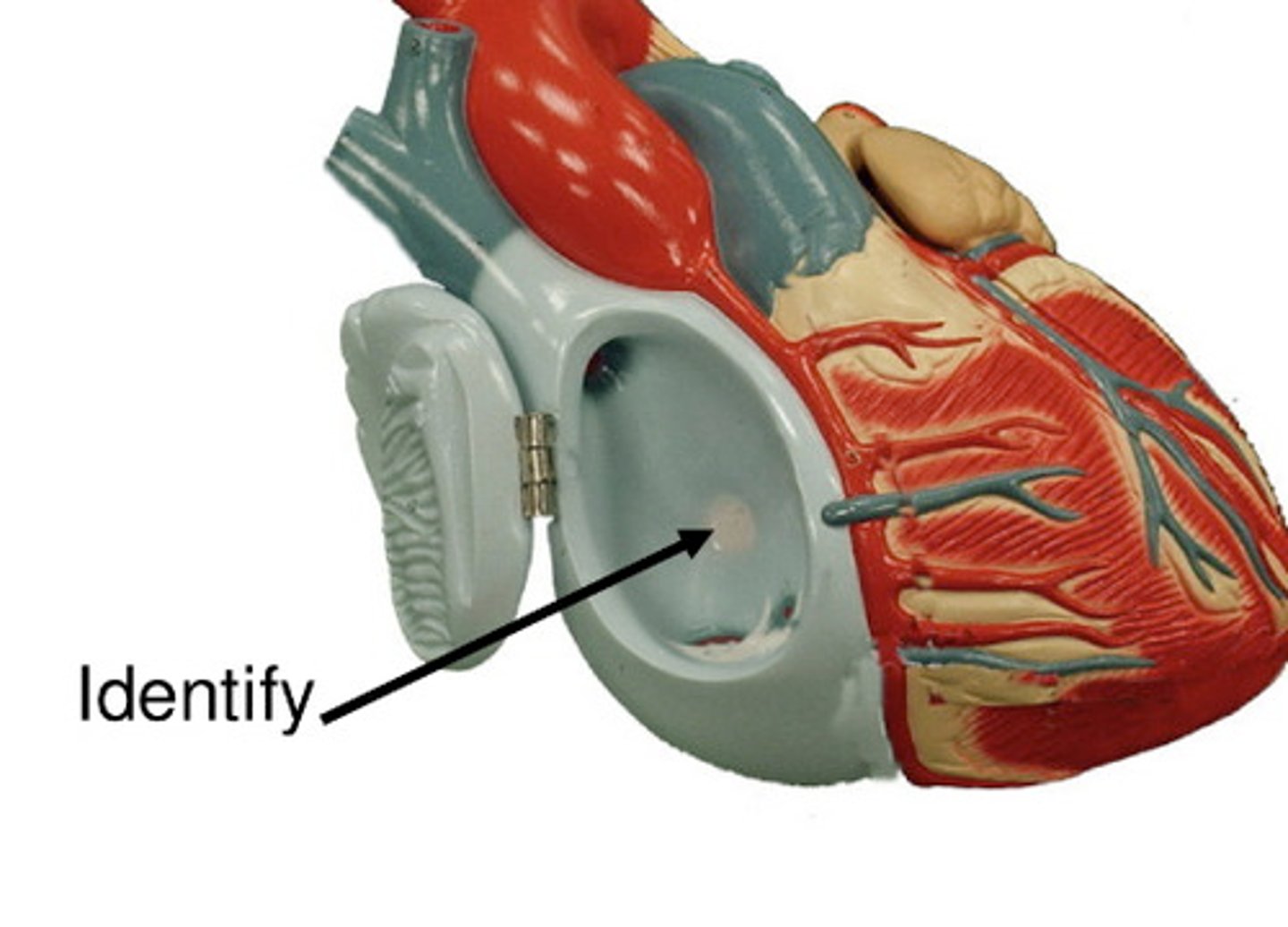
Trabeculae carneae
papillary muscles attach here; muscle that makes up wall between right and left ventricle
Maximal blood flow to the myocardium occurs when the heart is __________
diastole (relaxed)
There is little blood flow through the coronary circulation when the heart is ____________
systole (contracting)
Contraction of myocardium compresses __________
coronary arteries
Entrances into the coronary circulation are partially blocked by the ____________
cusps of the open aortic semilunar valve
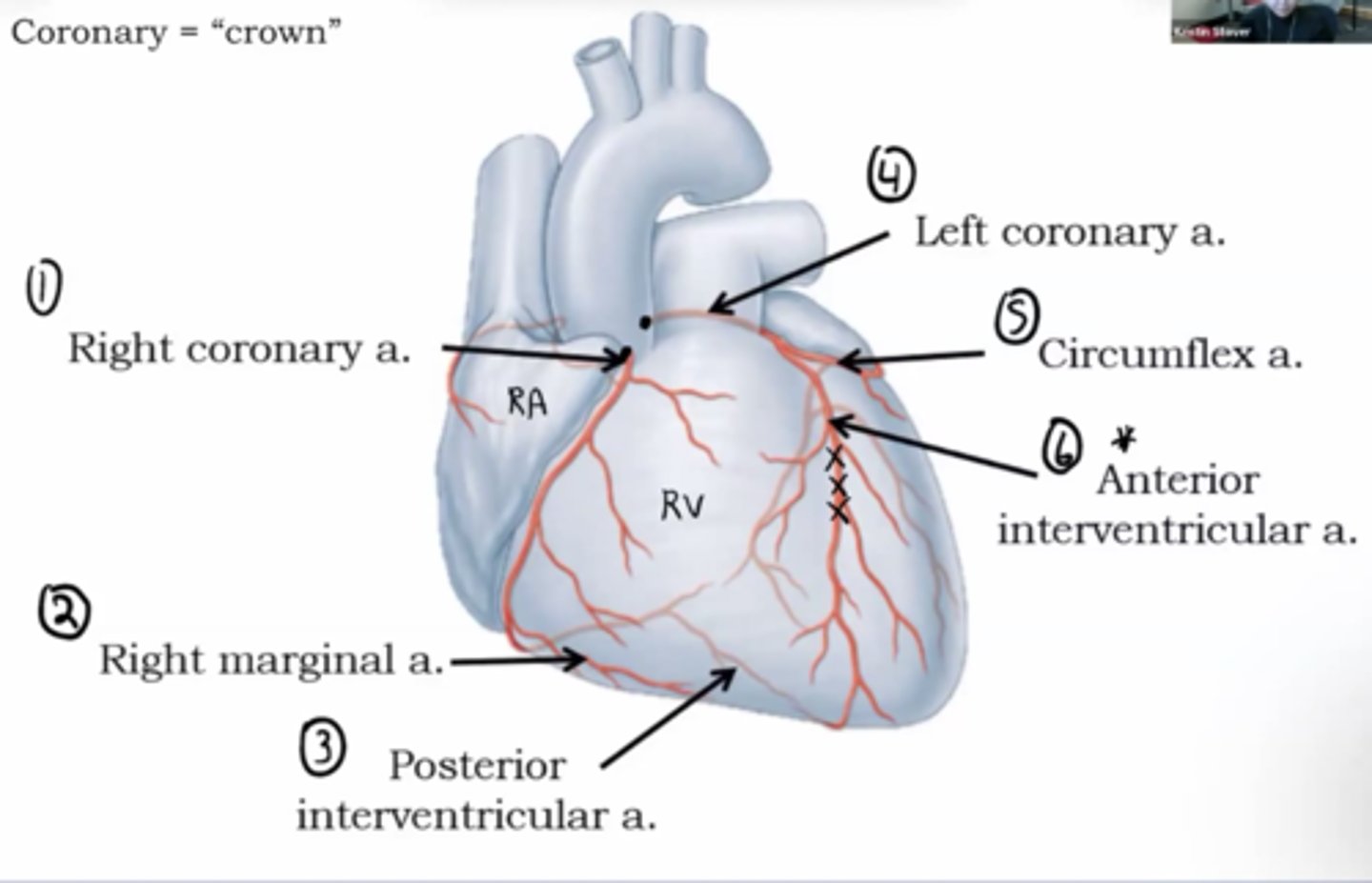
Right coronary artery
exits from aorta and travels between right atrium and right ventricle