Topic 4 Computational Thinking
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
4.1 and 4.2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Decision Making Process
Identification
Development
Selection
Implementation
Ways to express an algorithm
Simple English (Not very common bc it is verbose and ambiguous)
A flow chart (avoids issues of ambiguity)
Pseudo code (combines programming language and written language)
Programming Language (ways to communicate with a computer system)
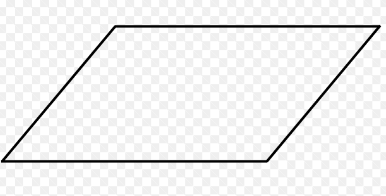
What does this symbol mean in flowcharts?
Input/Output
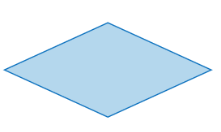
What does this symbol mean in flowcharts?
If/While/For

What does this symbol mean in flowcharts?
Start/end

What does this symbol mean in flowcharts?
Declaration/Assignment

What does this symbol mean in flowcharts?
Call a method/function
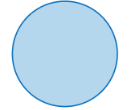
What does this symbol mean in flowcharts?
Connector
Psuedocode
Meant to help programmers develop computer programs. The syntax used is not as strict as the one used in computer languages.
Top down design or stepwise refinement
breaking up the problem into smaller sub problems, very effective and efficient.
Iteration
Process of repeating a series of instructions. It is extremely useful in programming and is used to repeat a statement or a block of statements within an algorithm.
Conditional Statement
Performs different instructions depending on a Boolean test.
If - then - else conditional statement
When an If is used, the boolean condition must be evaluated before executing the statements. Otherwise it will continue to the else statement, if there is no else then it will move to the end if.
Logical rules or Rules of Inferenece
Programming and algorithmic thinking involves the translation of these rules into algorithms.
Input
Something that is put into a program
Output
Something that is produced by the program after a process
Pre-Planning
the process of planning something in advance
Prefetching
broad terms means getting data or instructions from memory into the cache before they are actually needed. When a program requests data that was previously pre-fetched, it can use the pre-fetched data and continue with execution.
Gantt Chart
type of bar chart. It is widely used for project schedule and project management, as a way of showing activities, tasks, and events against time. On the left of the chart is a list of the tasks, activities, and events. Along the top is an appropriate time scale.
Exception
an act or event that disrupts the anticipated flow of the program’s execution. The exception take place during the execution of the program and can be effectively handled by specific mechanisms that most modern programming languages provide.
Concurrent Processing
The execution of different instructions simultaneously by multiple processors so as to achieve the best performance.
Simplified explanation
programs are broken down into procedures and procedures are broken down to sub-procedures.
Abstract Thinking
reflecting on events, ideas, attributes and relationships in a general manner that hides all unnecessary details of specific objects. All information that is not necessary to accomplish a goal is removed and ignored and a generalization technique is implemented.
Object - Oriented Programming
Uses abstraction and is based on the principle that everyday tasks can be considered as entities.
Collection
A data structure that consists of the data and the predefined methods which operate on the data. Some collections allow custom specification of the collection item elements.
Abstract Data Type (ADT)
Group of operations and data.
Mathematical Modeling
Process where a system is understood well enough and scientists describe it using mathematical language. A set of mathematical rules is used to describe the function of the particular system. It is clear that the mathematical model is an abstraction of the real system.
Array
can hold multiple data elements of the same type. An array has a name, a static size, and a data type. 1-D arrays are linear.
Parallel Arrays
Data organized as a table. Each row represents a particular student and all columns are of the same data type.
Array of Objects
Array of reference variables. Each reference variable is an element of the array and it’s a reference to an object.
Binary Search
Searching method used only in sorted arrays. Relies on divide and conquer strategy to accomplish its purpose.
It works by comparing the target value to the middle
If they aren’t equal, the lower of upper half of the array is eliminated depending on the results and the search is repeated in the remaining sub-array until it is is successful
Sequential or Linear Search algorithm
Very simple method to find a particular element in an array. Considered to be the simplest search algorithm. Does not require the use of a sorted arrays and it relies on brute force strategy to accomplish its purpose.
Starts with the first element and compares each element to the one it’s looking for, until it is found
Advantages of Concurrent Processing
Increase computation speed
Increases complexity of programming language and hardware (machine communication)
Reduces complexity of working with array operations within loops, conducting parallel searches in data based, sorting files, etc.
Reasons for Gantt Charts
Efficient organization; helps establish timeframe
Highly visual, easy to stick to
Reasons Against Gantt Charts
Potentially over complex
Needs to be constantly updated if project requirements change
Doesn’t show whole picture; details of task
Batch processing
Large amount of input happens over time, then whole set of input is processed in one go
Online Processing
Input processed almost immediately
Real-time processing
Input processed immediately and continuously; generally without any user input, of which comes from system sensors
Types of Flowcharts
Algorithm Flowchart: each process represented by a flowchart symbol, started in detail
System Flowchart: most basic, general overview of the system itself, with no detail
Bubble Sort (“Swap to Sort”)
Repeatedly steps through the array to be sorted. It compares adjacent items and exchanges them if they are not in the correct order (ascending or descending). The algorithm makes multiple passes until no swaps are necessary and the elements of the array are sorted.
Selection Sort (Sublist to Sort)
Very simple and inefficient sorting algorithm that divides the input array into two sub arrays: the first array are already sorted elements and the second sub-array contains the unsorted elements and occupies the rest of the array.
Generic Collections
Can only hold data of the same elements
Non Generic Collections
can hold elements of different data types.
Advantage of Collections
They can hold different data types and can act like a resizable array
addItem(data)
Used to add an item in the collection
getNext()
return the first item in the collection when it is called
resetNext()
starts at the beginning
hasNext()
tells whether there is another item the list
isEmpty()
check whether collection is empty
What are the predefined sub-programs (Collection Methods)
addItem()
getNext()
resetNext()
hasNext()
isEmpty()
Efficiency
The amount of the computer resources required to perform its functions. Minimizing the use of various resources such as the CPU and computer’s memory is very important
Correctness
the extent to which the algorithm satisfies its specification, free from faults, and fulfills all objectives set during the design and implementation phase
Reliability
the capability of the algorithm to maintain a predefined level of performance and perform all required functions under stated conditions, having a long mean time between failures
Flexibility
the effort required to modify the algorithm for other purposes than those for which it was initially developed
Big O notation
measure of the efficiency of an algorithm. O(n), where n is the number of times am algorithm was executed.
flag
a variable used to indicate a condition. when the condition is changed the value of the flag is changed. Usually a Boolean variable and is used to terminate a loop.
Lists
used to store a sequence of values under s single name. Allow duplicated to act as containers and to be typically implemented either as linked lists or as arrays.
Fundamental Operations
Add
Compare
Retrieve
Store
Compound Operations
Combining fundamental computer operations. Example: find max.
Semantics
The meaning of every construction that is possible in the language
Syntax
Structure of a programming language
Assembler
used to convert the assembly language mnemonics to machine code
High Level Programming Language
Programming language that uses elements of natural language, is easy to use, facilitates abstraction by hiding significant areas of computing systems, and makes the program development simpler, faster, and more understandable.
Compiler
When a high-level language is translated into lower-level language. Translation into machine code for final execution.
Interpreter
When a high-level language is translated into an intermediate code which will be immediately executed by the CPU (done line by line). Warns syntax error, shows outputs for tested processes.
Variable
a storage location for data in a program. They are a way of naming a memory location for later usage. Each variable has a name and a data type that is determined at its creation and cannot be changed
Constant
an identifier with an associate's value which cannot be altered by the program during execution. Opposite of a variable (putting “final”)
Operator
A set of characters which represents an action. Types:
Boolean: (And/Or && ||)
Arithmetic Operators: (± div mod)
Assignment Operator: =
Relational Operators: (>, ==, !=, .equals())
Object
comprised of data and actions. Actions refer to the operations that can be performed by the object. Object data may include a number of data members, while actions may also be referred to as methods.
=
is equal to. Used to assign a value to a variable. Min = 6.
≠
not equal to. Min ≠ Max
>
is greater than
>=
is greater than or equal to
<
less than
<=
less than or equal to
div
“integer part of quotient”
mod
modulo operation. Calculates the remainder of division of one number by another.
Scope
the visibility of that variable. It defines which parts of the algorithm can store, access, and retrieve the data of the variable.
Global variable is visible to all parts of your program
Local Variable has limited scope.
Container/Collection
Consisted of 0 or more elements such as objects and values. It is equipped with the necessary operations to handle data. Collections allow duplicate elements and may contain ordered and unordered data elements.
Sub-Program
unit that contains a sequence of computer instructions that perform a specific and pre-defined task
Code reuse
allows programmers to take advantage of existing code and solutions developed by other programmers to speed up their tasks. Code reuse saves time and resources and allows for the completion of demanding projects in the shortest period of time
Software LIbraries
Contain sub-programs that can be used by different types of programs
Advantages of Breaking Program into Sub-Programs
Breaking down a complex programming job into simpler jobs
Distributing a very large programming problem among various programmers all over the world
Enabling code reuse across multiple programs
Facilitation of abstraction by hiding implementation details from uses of the subprogram
Improving maintainability and traceability
Reducing programming code duplication within the same program
Advantages of Using Collections
The methods of collections are predefined algorithms that the programmer can immediately use
Performance is increased by the data management capabilities provided by the collection
Software reuse is facilitated because the use of methods is based on a common language and standard interface.