Cyto-Mendelian Part 1
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Who is the proponent of Classical Genetics?
Johann Gregor Mendel

What is the other name of Classical Genetics?
Transmission Genetics
What are the 2 Laws under Classical Genetics?
Law of Segregation
Law of Independent Assortment
Father of Modern Genetics?
Johann Gregor Mendel
What year was Johann Gregor Mendel born?
1822
Where did Gregor Mendel grew up in?
A farm in Austria
Gregor Mendel was ordained as what? (in 1847)
Augustinian Priest
What university did Gregor Mendel attend?
University of Vienna
Gregor Mendel started studying what? (In 1856)
Pea Plants or Pisum sativum
What did Gregor Mendel publish in 1866?
“Experiments on Plant Hybridization”
What were the reasons why Gregor Mendel’s works were not initially recognized by the scientific community?

When 2 different classes are experimented with each other what is it called?
Hybridization
What is the offspring referred in Hybridization
Hybrid
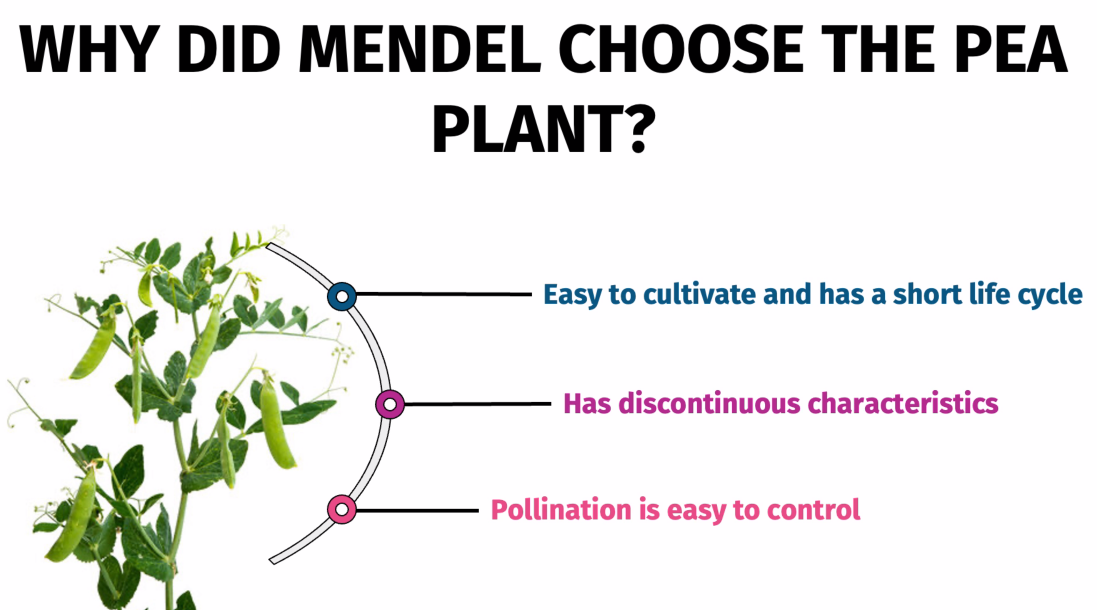
Why did Mendel choose the Pea Plants?
What are the 3 important parts of the Pea Flower?
Anther (Pollen is formed, contains Male Gametes)
Ovules (Contains Egg Cells, Female Gametes)
Stigma (Stimulates the growth of a Pollen Tube)
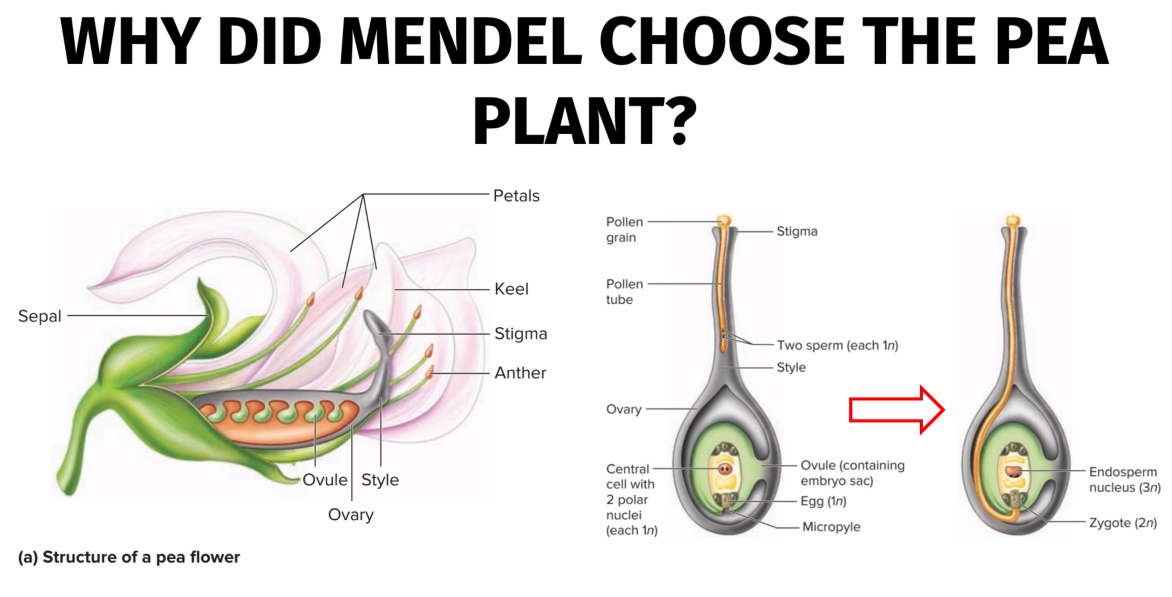
The fusion of 1 sperm and the egg results into?
A Zygote
True or False?
The 2nd sperm fuses with the Eccentric Cell to form the Endosperm?
False. (It fuses with the Central Cell)
Provides nutrition for the zygote
Endosperm
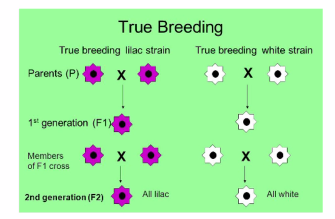
Variety that produces the same trait after several generations of fertilization
"Breeding True"
In Mendel’s experiment on Pea Plants what were the Characters/ Characteristics involved?
Height, Flower Color, Flower Position, Seed Color, Seed Shape, Pod Color, Pod Shape
What were the Variants of Each Characteristic?
Height -
Flower Color -
Flower Position -
Seed Color -
Seed Shape -
Pod Color -
Pod Shape -
Height - Tall, Dwarf
Flower Color - Purple, White
Flower Position - Axial, Terminal
Seed Color - Yellow, Green
Seed Shape - Round, Wrinkled
Pod Color - Green, Yellow
Pod Shape - Smooth, Constricted
This means that an experimenter observes a Single Character.
Monohybrid/ Single-factor Cross
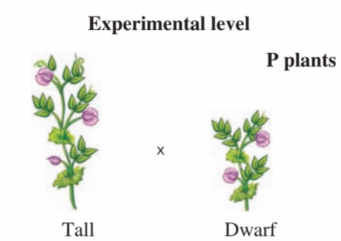
A generation in which both parents are Homozygous for different traits.
P Generation (Parental Generation) or (P Cross)
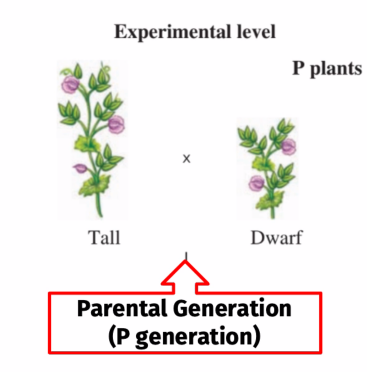
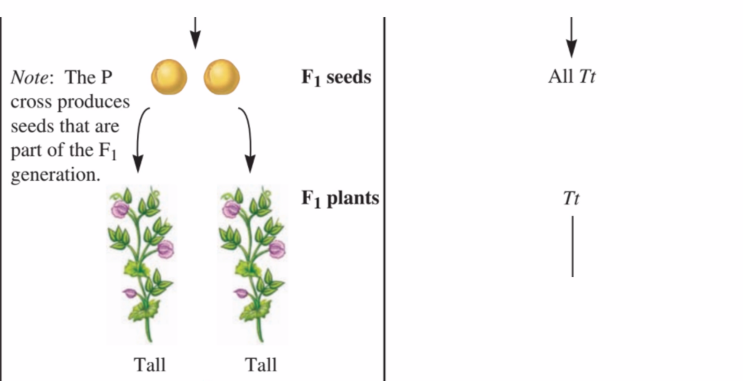
This generation is the result of the P Cross?
First Filial Generation (F1 Generation)
True or False?
The F1 Generation contains both Heterozygous Parents.
True.
Is able to silence or retest the recessive allele.
Dominant Allele
Starting what generation can recessive traits be observed
Second Filial Generation (F2 Generation)
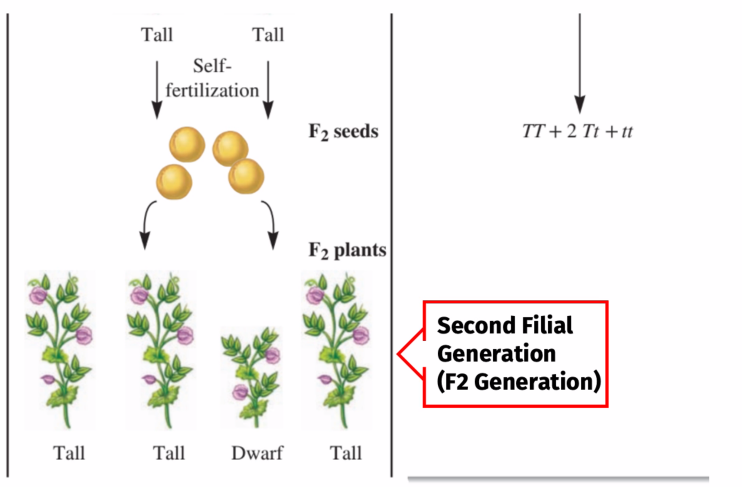
Genetic Determinant of Traits are passed along as?
Unit Factors
What are the 3 Main Observations that Mendel found throughout the Monohybrid Crosses?

True or False?
The F1 Generation only shows Dominant Phenotypes.
True.